9-13 Enzyme kinetics
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
K
Represents the equilibrium constant in enzyme kinetics, reflecting the ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium.
k
The rate constant in the equation that describes the speed of an enzymatic reaction, related to the concentrations of reactants and products.
Km
The Michaelis constant in enzyme kinetics, representing the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of its maximum value.
Enzymes
proteins that lower the Ea of a rxn by providing an alternative reaction pathway, increasing the reaction rate without being consumed.
An enzyme speeds up
both the forward and reverse reactions, decreasing time to reach equilibrium
ΔG+
activation energy
ΔG
difference in energy from reactants to products
ΔGo’
standard free energy
change at pH 7
Exergonic rxn
spontaneous reactions that give off energy
Endergonic rxn
non-spontaneous reactions that require energy input to proceed.
At equilibrium ΔG
is equal to zero, meaning no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products.
The ΔG of a reaction provides no information about the
rate of the reaction.
in a living cell, reactions which appear unfavorable
can be made to proceed by
removing products rapidly, or by coupling an unfavorable reaction to a
favorable one
Catalase
is an enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, by lowering Ea 3-fold and increasing rate by 108
Carbonic Anhydrase role
catalyze and increase the rate of
conversion of carbon dioxide to carbonic acid
and back again
Carbonic Anhydrase makes a fast reaction
even faster by 106
Cofactors
small
molecules required by
some enzymes for activity, can be coenzymes or inorganic ions and metal
Coenzymes
cofactors that are often organic molecules derived from vitamins
holoenzyme
an enzyme that contains its cofactor and is fully active.
Apoenzyme
the protein part of an enzyme, inactive without its cofactor.
Discovery of enzymes that are not proteins
led to the identification of ribozymes, which are RNA molecules that can catalyze biochemical reactions. Tom Cech
How do enzymes differ from chemical catalysts
Enzymes work under mild conditions
often regulated
stereospecific
Active sites of enzymes create
unique microenvironments
Lock and key model
substrate binds to
that portion of the
enzyme with a
complementary shape
Induced fit model
binding of the
substrate induces a
change in the
conformation of the
enzyme that results in
a complementary fit
Example of induced fit
glucose must be bound to hexokinase before the enzyme alters its shape to initiate the phosphorylation process.
Prevents non-productive ATP hydrolysis
How do enzymes decrease the activation
energy and accelerate reactions?
Transition State (TS) Stabilization
Enzymes can also catayze by bringing reactive groups into
proximity and orientation, facilitating interactions that lower the activation energy needed for reactions.
Acid-Base Catalysis
creating a strong nucleophile reactant by donating or accepting protons, thus stabilizing the transition state.
Nucleophilic Substitutions
Electron rich nucleophile attacks e- poor electrophile
Metal Ion Catalysis
involves metal ions facilitating reactions
Ex carbonic anhydrase
Mechanism of carbonic anhydrase
The zinc ion in the active site promotes the ionization of a bound water molecule
Losing electrons
the process of oxidation, which increases the positive charge of an atom or molecule.
Gaining electrons
is known as reduction, which increases negative charge
Covalent Catalysis
Involves a transient covalent bond between the enzyme and a substrate
examples of covalent catalysis
protein kinase and chymotrypsin
Oxidoreductases
catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions.
(e.g., alcohol dehydrogenase)
Hydro-lyases
cleave bonds with the addition of water.
(e.g., proteases)
Ligases
join two molecules using energy, such as ATP.
(e.g., DNA ligase)
Proteases
catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, but at different sites
Chymotrypsin is considered
a model enzyme for the study of catalytic mechanisms and is involved in protein digestion.
Chymotrypsin Mechanism involves
acid base catalysis
acyl-enzyme covalent intermediate
hydrolysis
catalytic triad in serine proteases
Serine, Histidine and Aspartic acid work together to facilitate peptide bond cleavage.
Functional groups within the active site
contribute to catalysis
Vmax
is the maximum velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
chymotrypsin is an example of
non-allosteric behavior
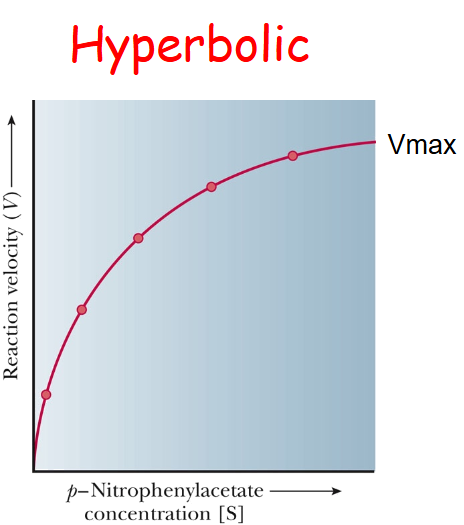
Non-allosteric graph
Hyperbolic
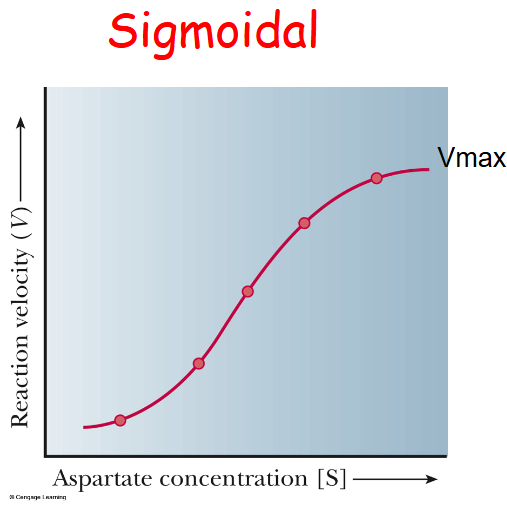
Allosteric graph
Sigmoidal
The Michaelis constant = KM
the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of its maximum value.
KM can be used to help evaluate
specificity of an enzyme
for a substrate (if it obeys M-M conditions)
small Km
indicates high affinity of the enzyme for the substrate.
Big Km
indicates low affinity of the enzyme for the substrate.
Variations in KM have physiological consequences
like aldehyde dehydrogenase, where the weakened mitochondria isoform missing causes symptoms like facial flushing and rapid heart beat while the stronger form is more effective in metabolizing acetaldehyde.
What does kcat mean?
turnover number, because it describes the
number of rxns a molecule of enzyme can catalyze per
second under optimal condition.
What does kcat /KM mean ?
Catalytic Efficiency or Specificity Constant which describes an enzymes
preference for different
substrates
Catalytic perfection
is when kcat/ KM = diffusion rate
A bigger kcat/KM means
the enzyme is more efficient at catalyzing reactions.
Allosteric Enzymes are
“information sensors” that often regulate flux of metabolic pathways
Aspartate Transcarbamoylase
an allosteric enzyme that senses concentrations of CTP to “inhibit” or ATP to “activate” the enzyme
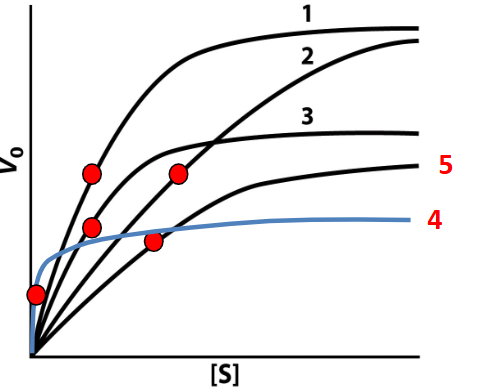
Competitive inhibition in a graph
KM bigger #, =“weaker” substrate affinity 2
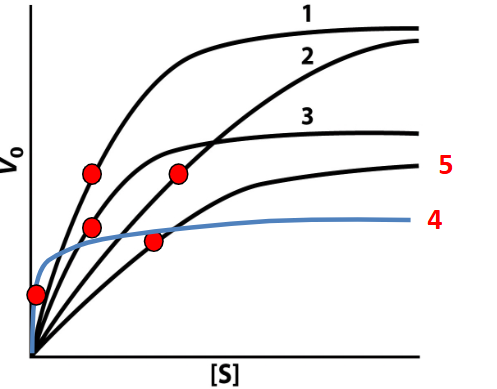
Non-competitive inhibition in a graph
decreasing the maximum reaction rate (Vmax) without affecting the affinity (KM) for the substrate. 3
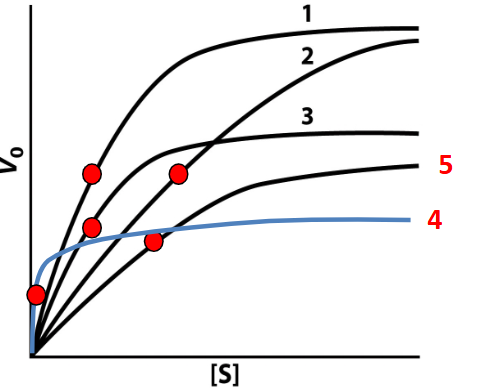
Un-competitive inhibition
occurs when an inhibitor binds only to the enzyme-substrate complex, preventing conversion to product, which decreases both Vmax and KM. 4
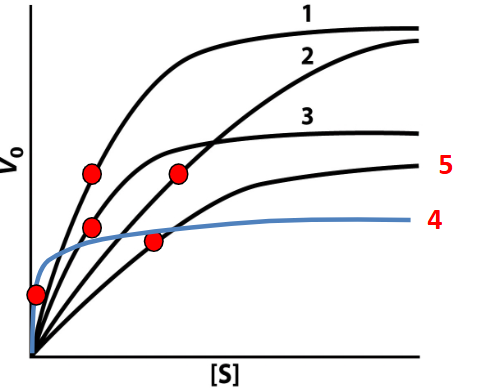
Mixed inhibition graph
is characterized by a decrease in Vmax and a change in KM depending on the affinity of the inhibitor for the enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex. 5
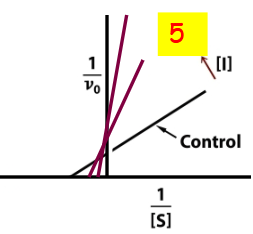
Double-reciprocal (Lineweaver-Burk) plot
where y intercept is 1/vmax
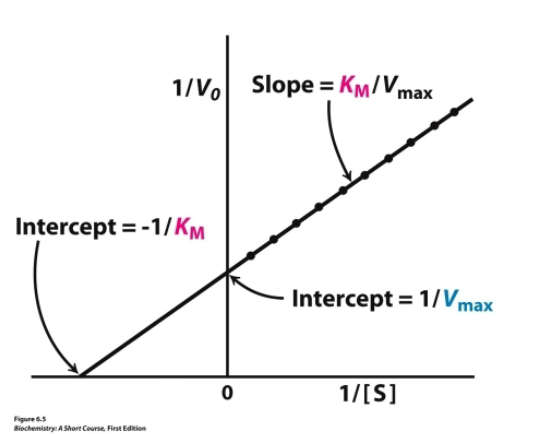
Competitive inhibition double reciprocal plot
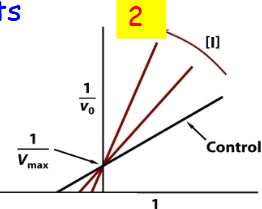
non-competitive double reciprocal plot
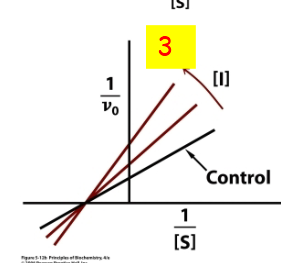
uncompetitive double reciprocal plot
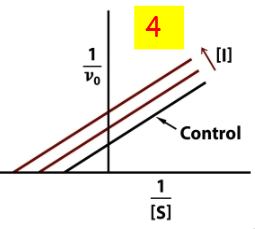
Mixed competition double reciprocal plot