1 - phonology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Diachronic study of language
The study of language over time
Synchronic study of language
The study of language at a certain point in time.
Descriptive Phonology
to describe how people speak
("people say/ write ...")
Prescriptive/normative Phonology
to tell people how to speak
("people shouldn't...")
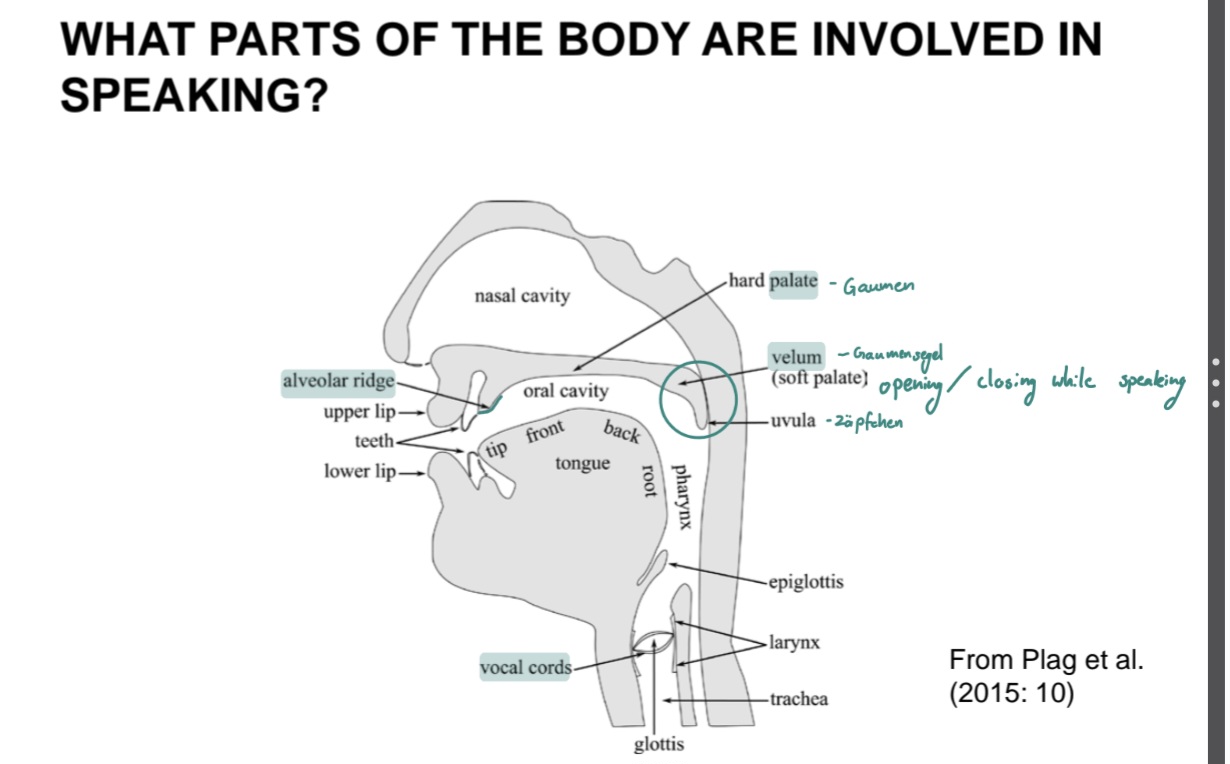
describe what parts are used in producing sounds
what do we call letters in Linguistics
graphemes
what do we call sounds?
Phones
no obstruction of airstream =
vowls
obstruction of airstream=
consonats
places of articulation (8)
− bilabial (lips)
− labio-dental (lips +teeth)
− dental(teeth)
− alveolar (aveolar ridge, behind teeth)
− palato-alveolar
− palatal (hard pallate, upper part of oral cavity)
− velar (velum, opening to nasal cavity)
− glottal (glottis, in vocal cords)
manners of articulation: (5)
plosive; complete obstruction of airstream, explosion
fricative; incomplete air obstruction, friction
affricative: plosive+ fricative, air stop followed by air Release w friction
nasals: obstruction of oral cavity, velum lowered, air through nose
approximates; incomplete obstruction- no audible friction
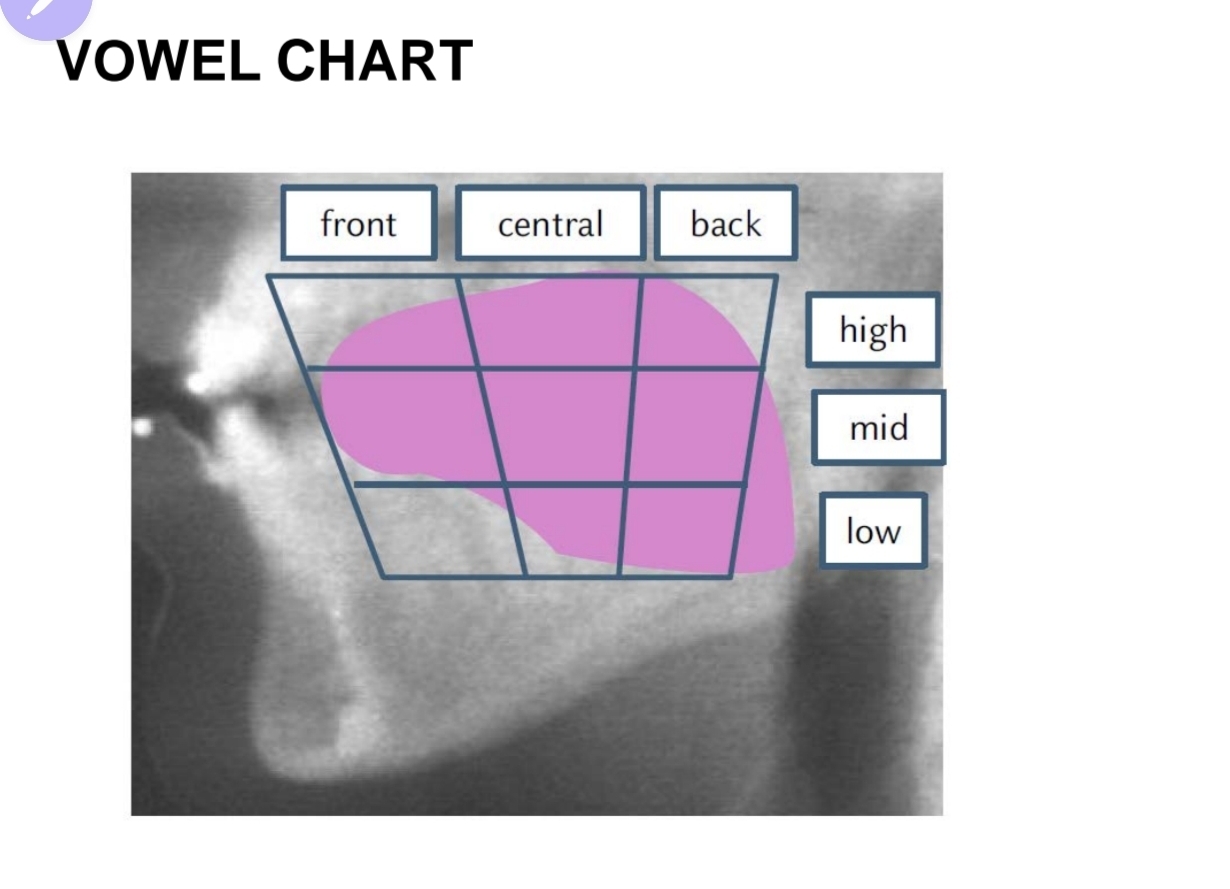
how do we classify vowls?
Vowl classification
• tounge position (hight and frontness)
• lip rounding
• vowl lenght
what are DIPHTHONGS
• 2 tounge positions (complex vowels)
• one sound
• eigther closing or centering
• no centering in AE
eɪ, aɪ, ɔɪ, əʊ, oʊ, aʊ, ɪə, ʊə, eə
What are the key differences between phonetics and phonology?
Focus:
Phonetics → Concrete phones (physical sound)
Phonology → Abstract phonemes (sound categories)
Nature:
Phonetics → Continuous, gradient detail
Phonology → Discrete, categorical contrasts
Transcription:
Phonetics → Narrow [brackets], e.g. [pʰ]
Phonology → Broad /slashes/, e.g. /p/
Features Encoded:
Phonetics → All articulatory/acoustic properties
Phonology → Only functionally relevant ones that change meaning
what is a phoneme?
Smallest meaning-differentiating unit
Different sound instances (phones) may belong to same abstract concept (phoneme)
− Sounds that belong to the same phoneme cannotchange the meaning of a word
minimal pair
only one sound differs --> changes meaning
- rest is identical
Allophones
systematic variatopn that realise one phoneme
- cannot occur in the same enviorment (complemetary distribution)
- superman methaphora
exp. /l/ —> articulated or dark ɫ
What does a Syllable consits of?
Syllable:
- one vowl
- no fixed number of cosonats
- onset:
- nucleus
- coda
what is nucleus, coda and onset?
Syllable:
- onset: preceding nucleus
- nucleus: vowel or diphong, important part
- coda: following the nucleus
open syllable:
no coda
closed syllable:
end in at least one consonat
maximal onset rule
as many consonats in onset as possible
onset: rise in sonority, coda: fall in sonority
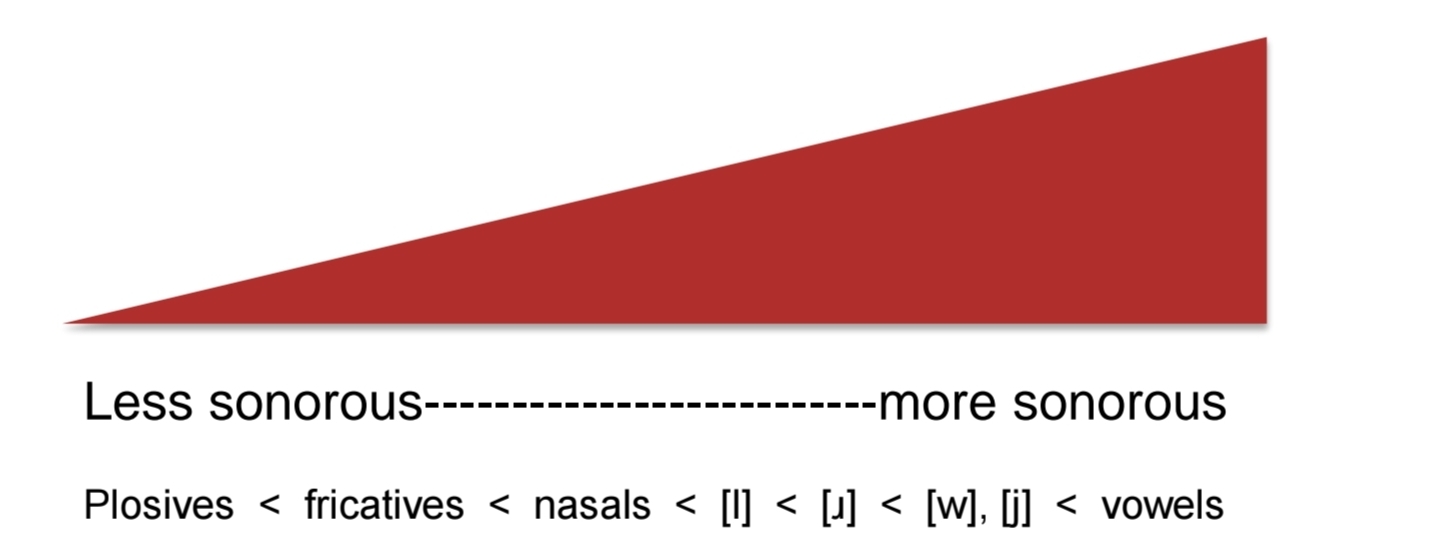
sonority
clear audibility/ prominece of a sound
sonority sequencing principle
sonority rises (in onset) towards nucleus (peak) then falls in coda