Chemistry: Chemical reactions
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Name the 3 types of energy transfer and briefly describe each. Name one example
each.
each.
* Radiation: Radiation is the transfer of heat energy through space by electromagnetic radiation.
* Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat energy from one substance to another or within a substance.
* Convection: Convection is the transfer of heat energy in a fluid or gas. This type of heating is most commonly seen in the kitchen with a boiling liquid.
* Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat energy from one substance to another or within a substance.
* Convection: Convection is the transfer of heat energy in a fluid or gas. This type of heating is most commonly seen in the kitchen with a boiling liquid.
2
New cards
Radiation examples:
* Ultraviolet light from the sun
* A burning candle emits radiation in the form of heat and light
* Radio waves, microwaves, visible light, Lasers, etc
* A burning candle emits radiation in the form of heat and light
* Radio waves, microwaves, visible light, Lasers, etc
3
New cards
Conduction examples:
* A lizard warming its belly on a hot rock
* The heat from a stovetop transferring into a metal pot of water
* A blacksmith heating up a sword in hot coals, and the heat transferring up through the metal
* The heat from a stovetop transferring into a metal pot of water
* A blacksmith heating up a sword in hot coals, and the heat transferring up through the metal
4
New cards
Convection examples:
* Boiling water (heats up, gets less dense, floats to the top of the pot and is replaced with cold water)
* Fire heating up air - air expands, loses density, rises
* Sea or land breeze caused by difference in pressure
* Fire heating up air - air expands, loses density, rises
* Sea or land breeze caused by difference in pressure
5
New cards
Describe an extreme weather condition and relate this to global warming. Why is the
phenomenon getting worse with higher temperatures?
phenomenon getting worse with higher temperatures?
A warming climate can increase the risk of both submarine (underwater) and aerial (above ground) landslides, thereby increasing the risk of local tsunamis. The melting of permafrost (frozen soil) at high latitudes decreases soil stability, making it more susceptible to erosion and landslides
6
New cards
What is needed for a combustion reaction to take place? What are the products?
Reactants: Oxygen, heat (energy), fuel
\
Products: CO2 + H20
\
Products: CO2 + H20
7
New cards
Exothermic reaction:
Exothermic process releases heat (energy) into its surroundings
\
On graph: Up to down
\
On graph: Up to down
8
New cards
Endothermic reaction:
Endothermic process absorbs heat (energy) from its surroundings in order to take place
\
On graph: Down to up
\
On graph: Down to up
9
New cards
Exothermic reaction examples:
* Burning of a Candle
* Burning of Sugar
* Creation of an ice cube (water → ice)
* Burning of Sugar
* Creation of an ice cube (water → ice)
10
New cards
Endothermic reaction examples:
* Melting of an ice cube (ice → water)
* Cooking an egg
* evaporation
* Cooking an egg
* evaporation
11
New cards
Is a combustion reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Exothermic
12
New cards
Explain why the mass of ash in a combustion reaction is less than the mass of wood.
Does this observation show that the Law of conservation of mass is false?
Does this observation show that the Law of conservation of mass is false?
the oxygen was torn off of the wood and burned, this means a lot of the wood dispersed into the surrounding area. The ash is simply the leftovers. No mass was destroyed, simply transmuted
13
New cards
Name the 5 types of chemical reactions
* Synthesis
* Decomposition
* Single replacement
* Double replacement
* Combustion
* Decomposition
* Single replacement
* Double replacement
* Combustion
14
New cards
Synthesis
A + B → AB
15
New cards
Decomposition
AB → A + B
16
New cards
Single Displacement
A + BX → AX + B
17
New cards
Double Displacement
AB + XY → AX + BY
18
New cards
Combustion
Carbon Compound + O2 → CO2 + H2O
19
New cards
Double Displacement
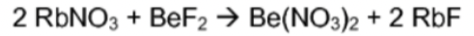
20
New cards
Single Displacement
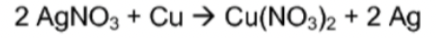
21
New cards
Combustion
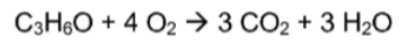
22
New cards
Synthesis
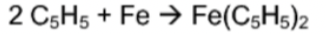
23
New cards
Describe the difference between an exothermic and endothermic reaction
An exothermic process releases heat, causing the temperature of the immediate surroundings to rise. An endothermic process absorbs heat and cools the surroundings.
24
New cards
When ammonium chloride is added to water, a chemical reaction takes place and
the temperature decreases. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
the temperature decreases. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic because it dissolves
25
New cards
Endothermic reactions in medicine or technology:
* Ice pack
* Baking cake
* Baking cake
26
New cards
Exothermic reactions in medicine or technology:
* Fuel combustion in planes
* Burning coal in a forge
* Burning coal in a forge
27
New cards
Molar Mass abbreviation:
M
28
New cards
Mass abbreviation:
m
29
New cards
Mole abbreviation:
n
30
New cards
Unit for molar mass:
g/mols
31
New cards
Unit for Mass:
grams
32
New cards
Unit for Moles:
Mols and/or Moles
33
New cards
m = ?
m = n x M
34
New cards
n = ?
n = m/M
35
New cards
M = ?
M = m/n