AP BIO UNIT 7 STUDY GUIDE
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
who was Darwin and what was his mechanism for evolution
Darwin was a 19th-century naturalist on the HMS Beagle that studied animals. His mechanism for evolution was the species are related by common descent and adaptation to environments results in diversity
Who was Lamark and what were his ideas on evolution
was the first scientist to accept the theory of evolution. He said that complex organisms derived from not complex ones and believed in inheritance of acquired characteristics
homologous vs analogous structures
homologous is an organ or bone that is common in different animals and shows decent from a common ancestor. Analogous structures are similar in structure but the organisms are not from a common ancestor.
Vestigal structures
vestigial structures are organs or genes that have no function. The show decent from a common ancestor because they were once useful but now have no use due to evolution
artificial selection vs natural selection
artificial selection: intentional breeding of animals with desired traits
for natural selection to occur:
organisms have variations
organisms struggle to exist
organisms differ in fitness
organisms become adapted
what is Hardy-Weinberg and what conditions have to be met to keep equilibrium
allele frequencies will be met in all successive gene pools if five conditions are met
no mutations
no gene flow
random mating
no genetic drift
no selection
what evidence for evolution did Darwin not consider
The technology for molecular evidence wasn't around and he wasn't able to see differences in amino acids and so didn't consider it
what is natural selection
the survival of the fittest. It is a process that allows the best-adapted animals to an environment survive
if two fossils are found to be similar but not identical what type of evidence could be used to determine the relatedness
you could use biochemical evidence to compare the amino acid sequences
biogeography
study of the range and geographic distribution of life
transitional forms in the fossil record and what species have transitional forms
Archaeopteryx (150 - 154MYA) link between dinosaurs and birds. A transitional form is one that links an ancestor with its descendants
who was cuvier and what were his thoughts on comparative anatomy
He was a 19th century zoologist that founded the science of paleontology. Beleived in catastrophism because he thought that creation not evolution was correct. When new fossils appeared in an area he said that there was a catastrophe that wiped out all existing species and then new species from another area repopulated it.
Will the cutting off of mice tails eventually lead to shorter tails
this is based in Lamark's theory of acquired characteristics. It is incorrect and we know that characteristics are inquired through evolution not through birth
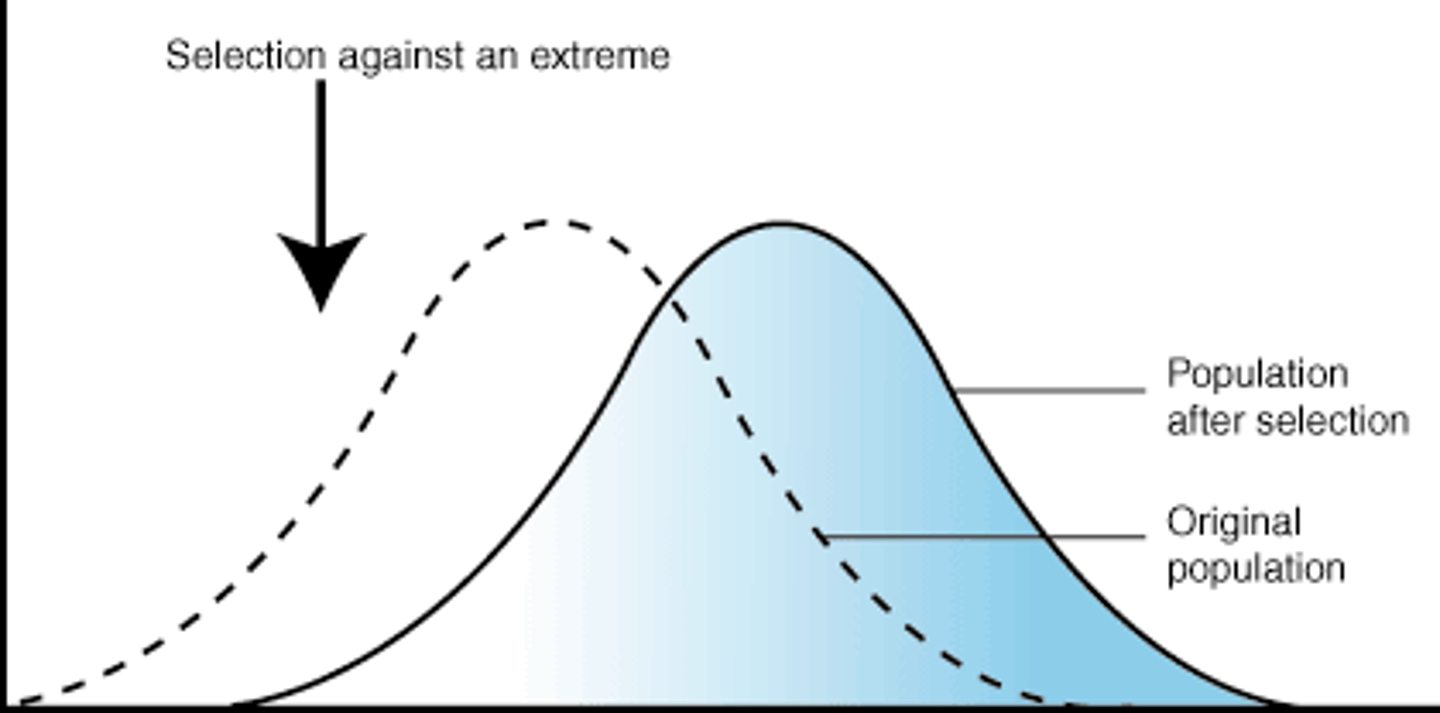
directional selection
when an extreme phenotype is favored and
the curve shifts in that direction
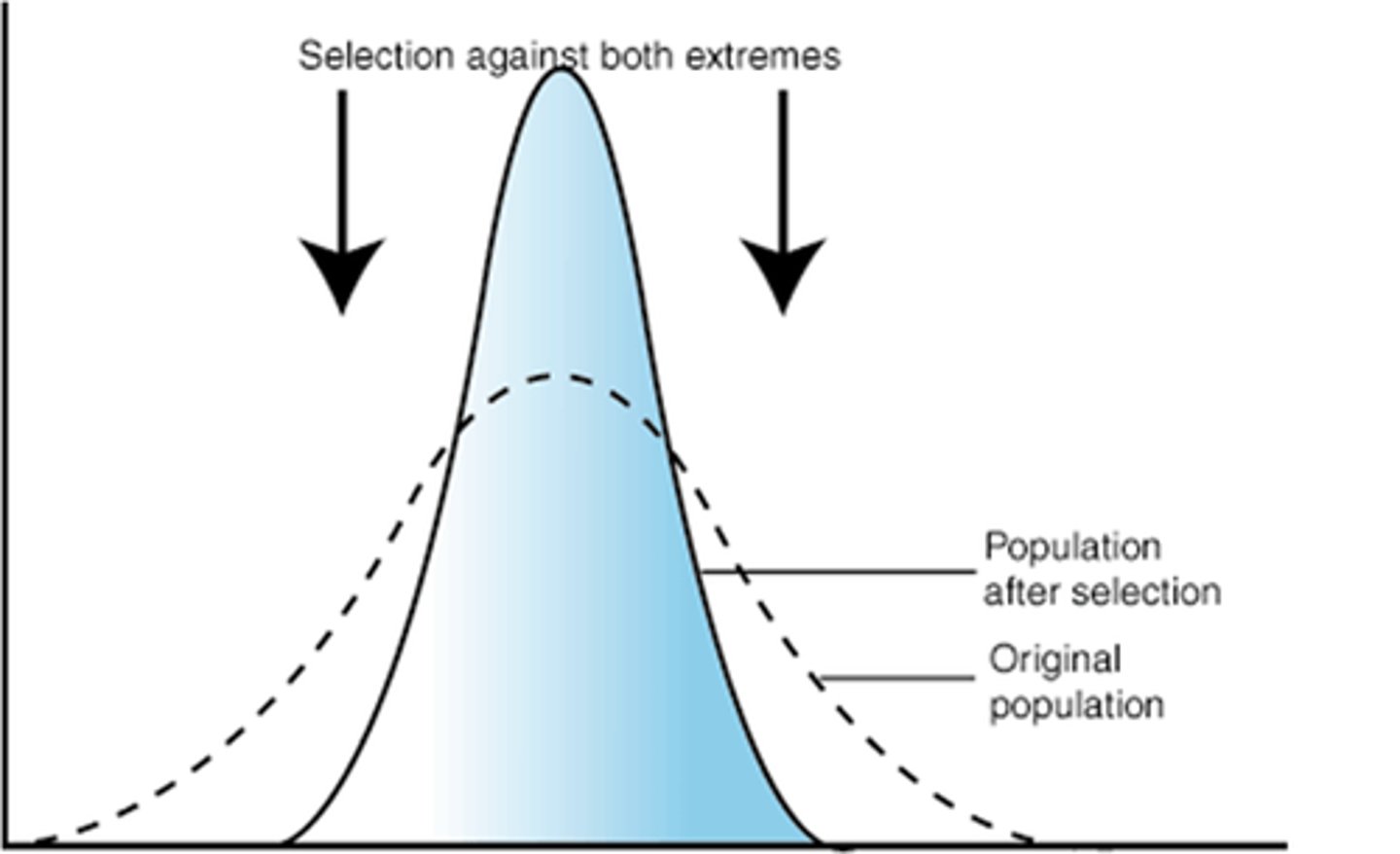
stabilizing selection
when intermediate not extreme phenotypes are favored and the graph is pinched toward the middle
disruptive selection
when two or more extreme phenotypes are favored and therefore make up the population over any intermediates

gene pool
All the genes, including all the different alleles for each gene, that are present in a population at any one time
genetic drift
drift of the allele frequencies away from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
gene flow
introduction of new alleles into the population, non-isolation
founder effect
the founder of an isolated population posses's a gene and then passes it on to his offspring. Due to isolation and inbreeding this gene is more common in this population that outside
micro evolution
evolutionary changes within a population (going against Hardy-Weinberg)
speciation (allopatric and sympatric)
speciation is the creating of a new species due to an inability to reproduce (reproductive isolation)
allopatric: stopping of gene flow due to geographic isolation
sympatric: population developing into two or more groups without geographic isolation
things that lead to reproductive isolation
temporal isolation: mating at different times
behavioral: different rituals to find mates
mechanical: genitalia is not physically compatible
gamete: even if gametes meet they can't fuse to become zygote
habitat: geographic isolation
factors that contribute to the maintenance of variation in a population
mutation, recombination, gene flow, natural selection, and heterozygotes
remember that in Africa heterozygotes for sickle cell are protected against malaria
continental drift in relation to evolution
continental drift is the reason that some species wound up on one continent and then evolved and branched separate to others
what is taxonomy and what are the domains
taxonomy: the act of studying, naming, and clarifying organisms
the three domains are Domain Eukarya, Domain Archea, and Domain Bacteria
kingdom animalia
Eukaryotic and multi-cellula, heterotrophic by ingestion, motile, diploid
kingdom plantae
Eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic by photosynthesis, nonmotile, alternation of generations(life cycle)
kingdom fungi
eukaryotic, multicellular usually, heterotrophic by absorption, nonmotile, haploid
kingdom protista
eukaryotic, multicellular usually, photosynthetic or heterotrophic by various means,motile sometimes by flagella or cillia, various life cycles
what are scientific names and how are by whom are they assigned
genus and species and they are assigned by the Linnean Society
what is a molecular clock and how is it used
a molecular clock is when nucleic acid changes are constant and quantitative and they can be assigned a number of years to a percent difference. 5.1% difference in nucleic acid sequences among song birds = 2.5 MYA
what is phylogeny and what is a phylogenic tree
phylogeny: is the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. a phylogenic tree indicates decent from a common ancestor and each branch indicates a divergence from the common ancestor

cladistics and a cladogram
cladistics: used shared derived characteristics to classify organisms
things to rememer when reading a cladogram: only use shared charactersistscs, simple is better, most divers is farthest to the right, if trait isn't seen in consecutive species then not used
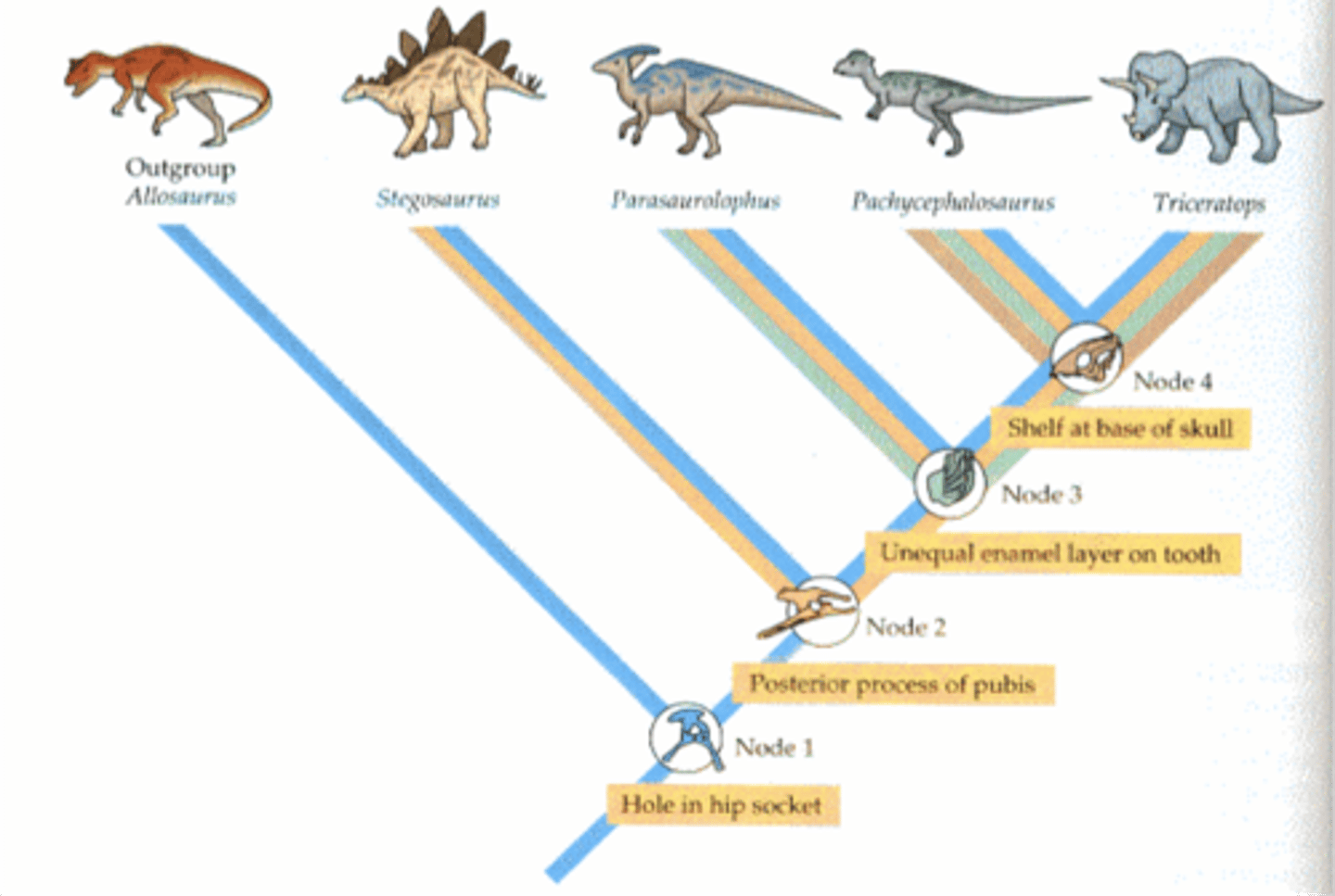
clade
an evolutionary branch of a cladogram that contains a common ancestor and all of its descendants