Lipids - Food Components and Health
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
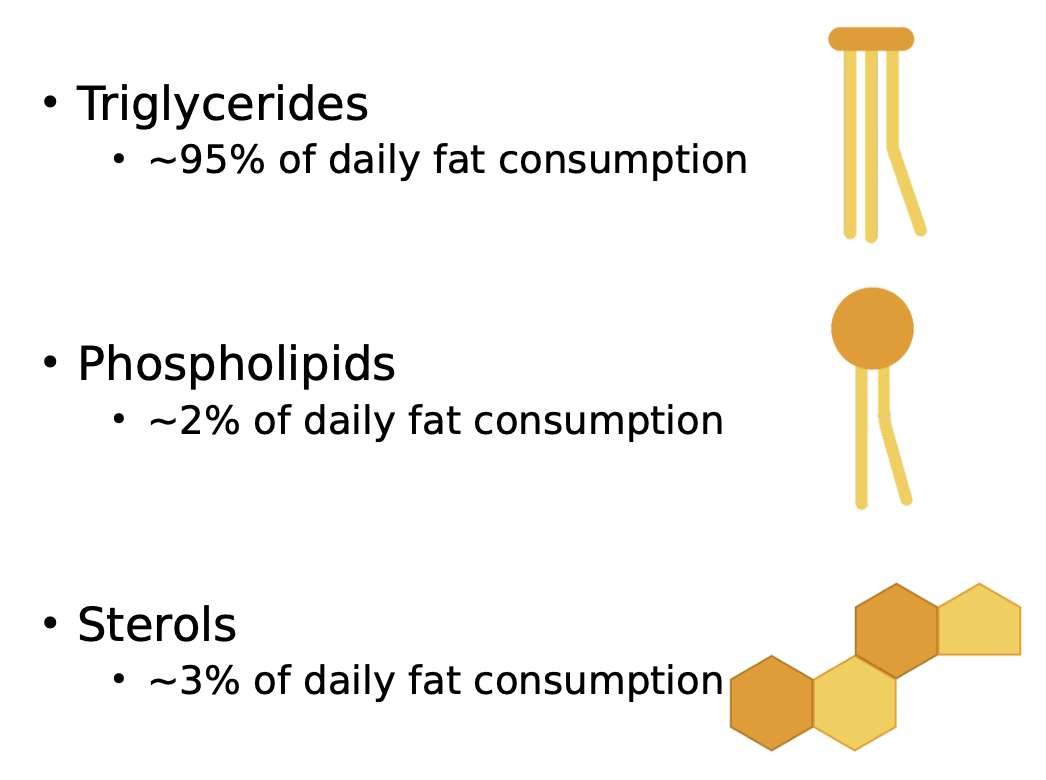
What are the tree types of dietary lipids?
The three dietary lipids are Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols.
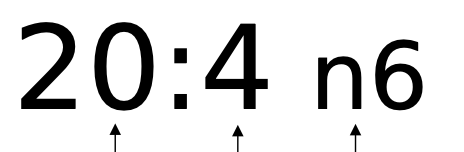
How does the n/omega-Designation work?
The first number is the amount of carbons. The second number (after double point) is the amount of double bonds. The number after the n is the carbon number at which the double bonds start.
COUNTS FROM METHYL END!!
How does the delta-Designation work?
The first number is the amount of carbons. The second number (after double point) is the amount of double bonds. The numbers after the delta is the carbon numbers at which the double bonds start.
COUNTS FROM CARBOXYL END!!
Why are the fatty acid composition of a triglyceride important?
They are important because this composition affects the firmness and stability.
A high degree of saturated acids → Solid at room temperature, less prone to oxidation (spoilage).
A high degree of unsaturated acids → Liquid at room temperature, more prone
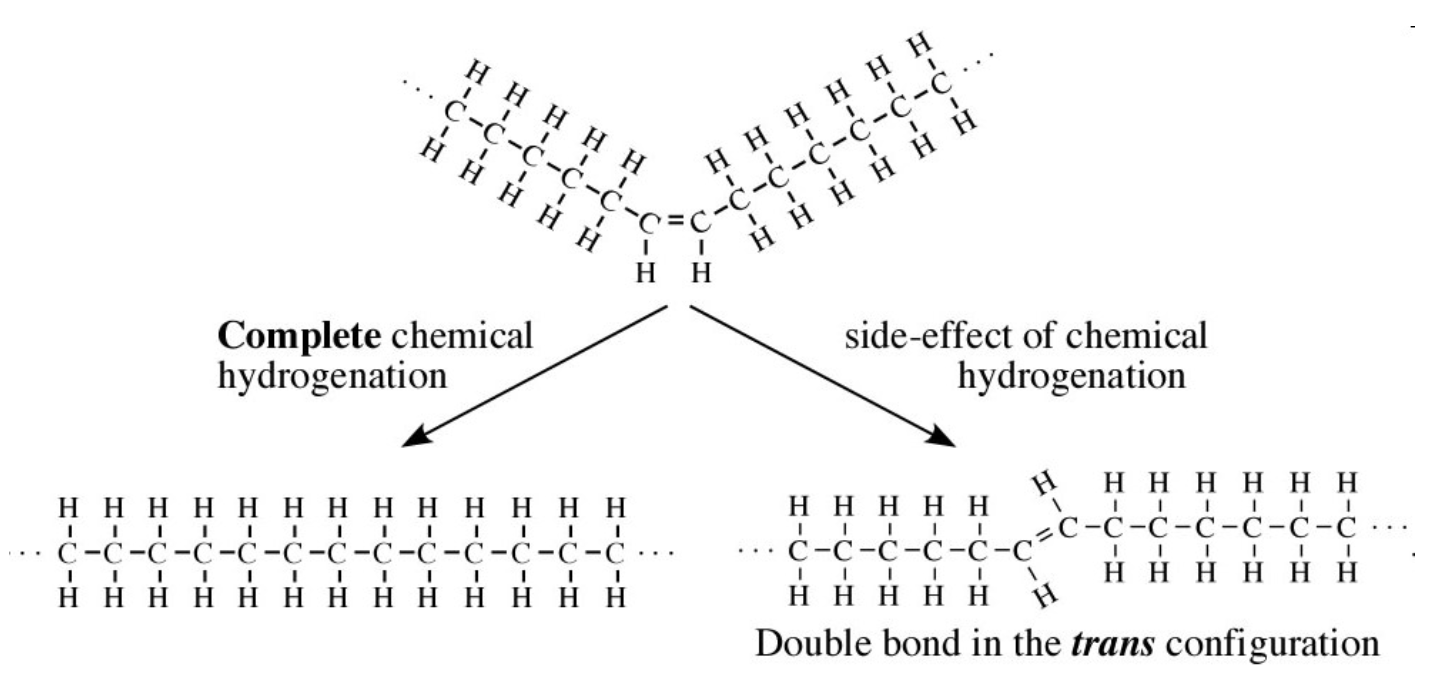
What is hydrogenation and why is it useful?
Hydrogaenation is the process of converting unsaturated fatty acids in saturated. Hydrogens are added. This helps to make oils less prone to spoilage.
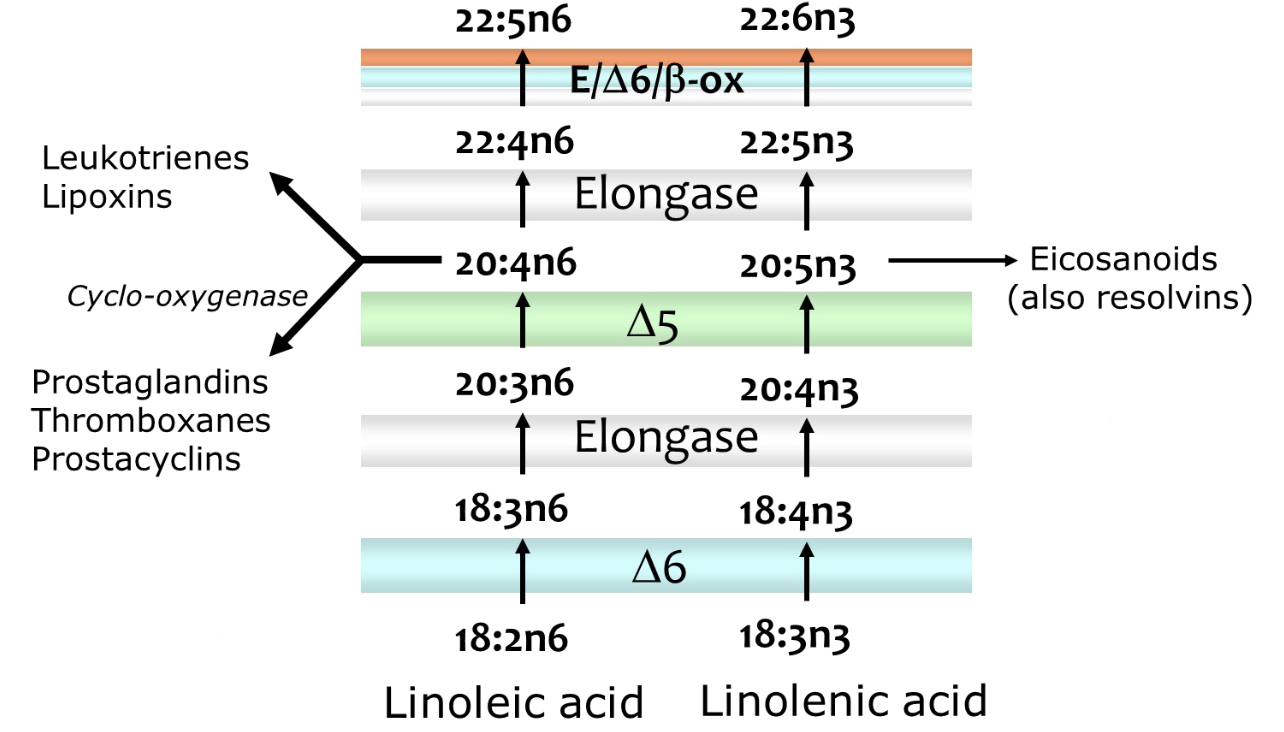
Which fatty acid do we obtain from diet and why are they essential?
We obtain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids from diet. They are essential because we need them to synthesize bioactive molecules.
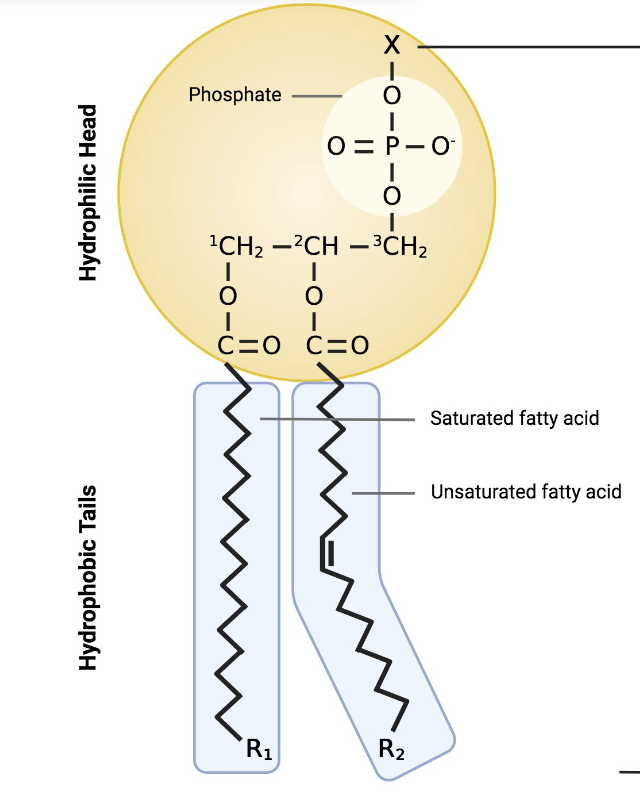
What is the structure of phospholipids?
The phospholipid uses a glycerol backbone with a hydrophilic phosphate head and two hydrophobic fatty acids tails.
What is a sterol?
A sterol is a fat soluble molecule. Cholesterol is an example and can only be found in animal products.
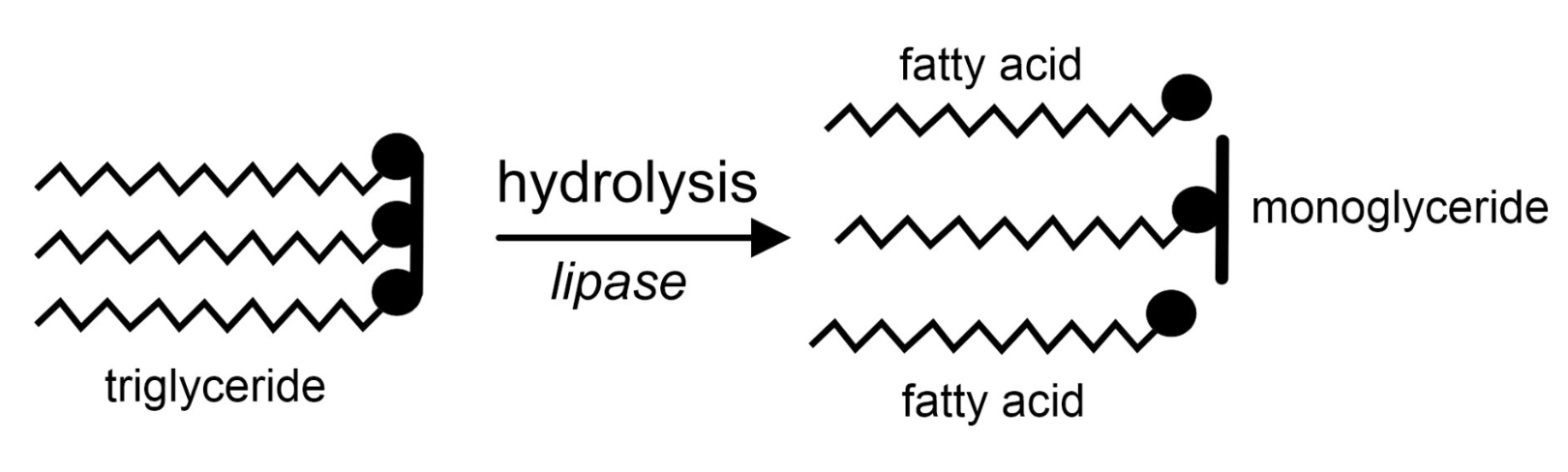
Through which process is fat digested?
Fat is digested through hydrolysis by lipase. It hydrolyses triglycerides to monoglycerides and free fatty acids.