Chapter 8 - Reactivity Trends
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
group 2 electron configuration
has 2 electrons on the outer s-sub shell - 2s orbital (s2)
-when these electrons are lost they form 2+ ions
-are reducing agents
group 2 redox reactions with OXYGEN
all react with oxygen to form a metal oxide
-metal is oxidised and oxygen is reduced
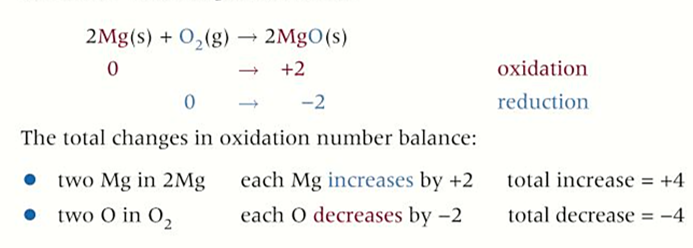
group 2 redox reactions with WATER
all react with water to form an alkaline hydroxide and hydrogen gas
-reactivity of elements increases as you go down
-metal is oxidised and hydrogen is reduced (only in gas)

group 2 redox reactions with DILUTE ACIDS
all react with a dilute acid to form a salt and hydrogen gas
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
-reactivity of elements increases as you go down
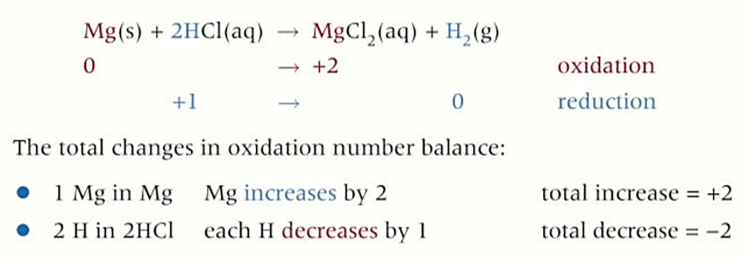
why does the reactivity increase as you go down group 2?
the atomic radius increases as the electron shielding increases so nuclear attraction decreases so it is easier to lose the outer electrons so ionisation energies decrease
group 2 oxides -reactions with water
1) oxide and water react to release hydroxide ions and form an alkaline solution of metal hydroxide
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca2+ + 2OH-
2) when solution becomes saturated a solid precipitate will be formed
Ca2+ + 2OH- → Ca(OH)2(s)
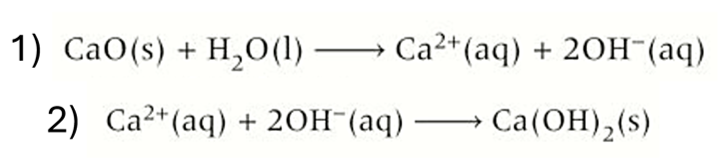
solubility of hydroxides in group 2 + experiment
increases as you go down group 2 due to greater concentration of OH- ions
experiment:
1) add a spatula of each group 2 oxide to water in a test tube
2) shake mixture with bung on - will have saturated solution of metal hydroxide with some undissolved white solid
3) measure pH of group - colour change
USES of group 2 compounds as bases
-neutralising acidic soil - increases pH of soil
Ca(OH)2 + 2H+ → Ca2+ + 2H2O
-used as antacids for treating acid indigestion - hydrochloric acid in stomach reacts with metal hydroxide and forms neutral substance
Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + 2H2O
group 7 electron configuration
has 2 electrons on the outer s-sub shell and 5 electrons on the outer p-sub shell - s2p5
-when an electron is gained they form 1- ions
-are oxidising agents
trend in BOILING POINT in group 7
increases as you go down
-more electrons so stronger London forces so more energy needed
trend in REACTIVITY in group 7
decreases as you go down
-atomic radius increases as electron shielding increases so nuclear attraction decreases so harder to gain 1 electron for full outer shell
colour of group 7 elements AT ROOM TEMP + PRESSURE
-chlorine = green gas
-bromine = red-brown liquid
-iodine = grey-black solid
colour of group 7 elements IN WATER
-chlorine = pale green
-bromine = orange
-iodine = brown

colour of group 7 elements IN CYCLOHEXANE
is used as they dissolve more readily so easier to tell colours
-chlorine = pale green
-bromine = orange
-iodine = violet

halogen-halide displacement reactions
-shows the trend in reactivity in group 7
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCl + Br2 - turns from pale green to orange
2KI + Br2 → 2KBr + I2 - turns from orange to brown/violet
2KI + Cl2 → 2KCl + I2 - turns from pale green to brown/violet
halogen-halide displacement reactions -IONIC equations
2Br-+ Cl2 → 2Cl- + Br2
2I-+ Br2 → 2Br- + I2
2I-+ Cl2→ 2Cl-+ I2
disproportionation + examples
redox reaction where the same element is oxidised and reduced
-EXAMPLES:
Cl2 + H2O → HCl +HClO
Cl2 + 2NaOH → NaCl + NaClO + H2O - conditions needed for bleach = cold and dilute sodium hydroxide
-Cl goes from 0 to -1 and +1
BENEFITS of chlorine
-kills bacteria
-ensures safe water supply
RISKS of chlorine
-toxic gas
-respiratory irritant
-chlorinated hydrocarbons can cause cancer
test for AMMONIUM ions
-add dilute sodium hydroxide and warm
-if ions are present will produce ammonia gas which has a sharp smell
ammonia gas = turns damp red litmus paper blue
equation: NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) → NH3(g) + H2O(l)
test for CARBONATE ions
-add dilute nitric acid
-if ions are present will fizz as carbon dioxide gas is released
equation: CO32-(aq) + H+(aq) → CO2(g) + H2O(l)
test for SULFATE ions
-add barium nitrate solution
-if ions are present will form a white precipitate
equation: SO42-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) → BaSO4(s)
test for HALIDE ions
-add silver nitrate solution
-if ions are present a precipitate will form - silver chloride = white, silver bromide = cream, silver iodide = yellow
equation: Cl-(aq) + Ag+(aq) → AgCl(s)
FURTHER test for halide ions
-using ammonia solution
-silver chloride = dissolves in dilute ammonia solution
-silver bromide = dissolves in concentrated ammonia solution
-silver iodide = does not dissolve in any ammonia solution
ORDER of tests for qualitative analysis
1) ammonium or carbonate
2) sulfate
3) halide