Axial Bone Markings
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
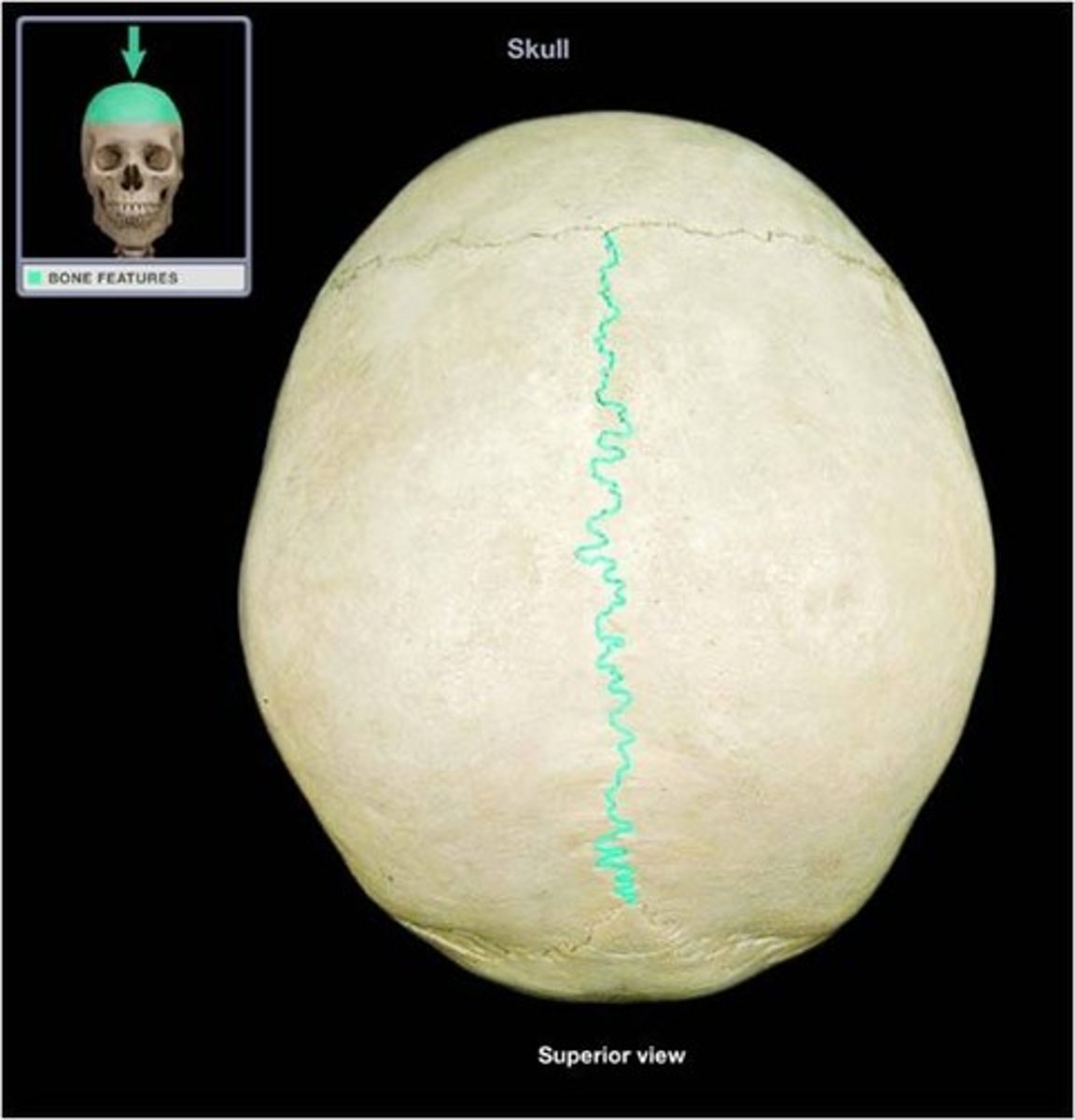
What part is this?
sagittal (cranial vault)
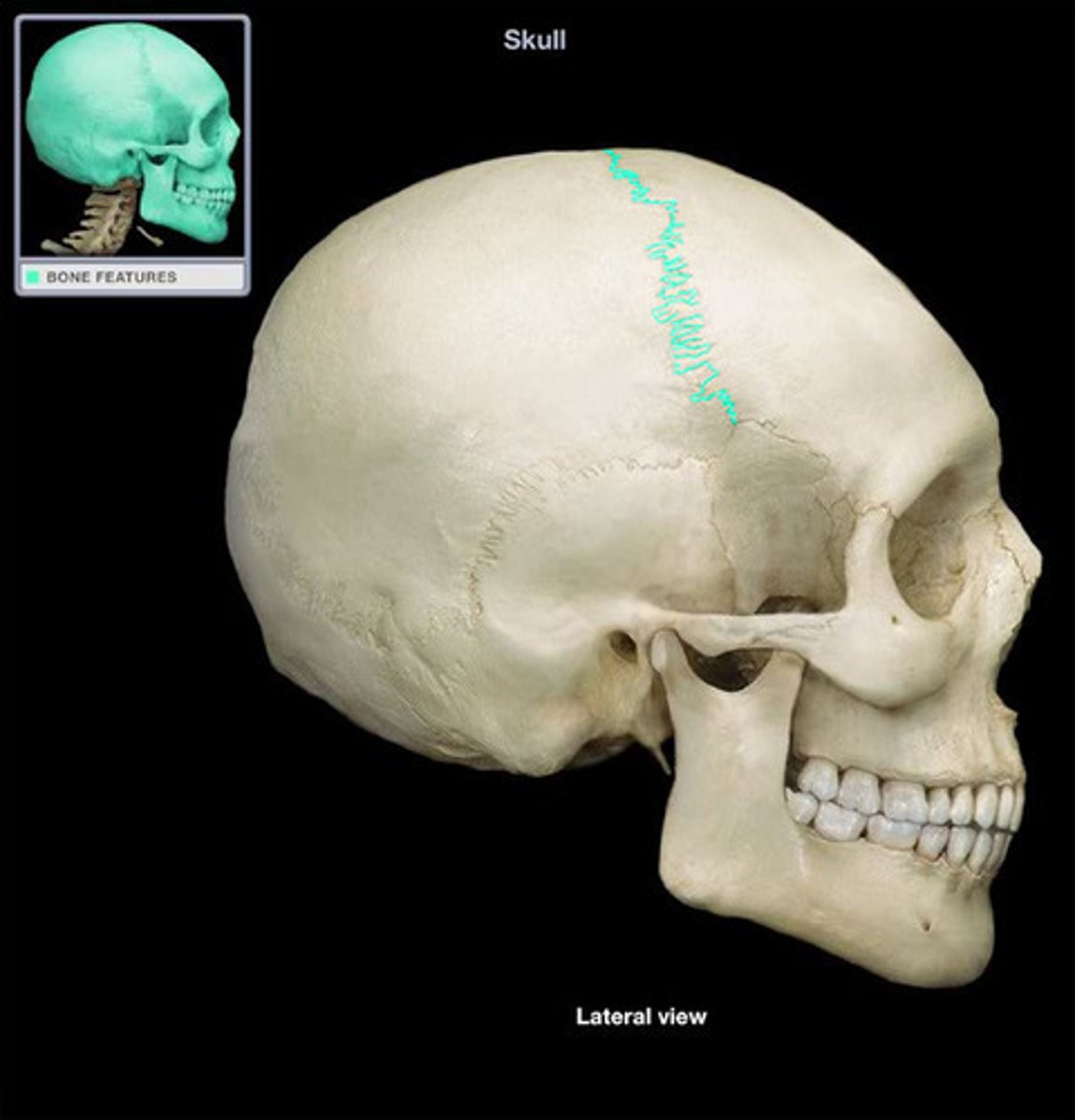
what sutures is this?
Coronal (cranial vault)
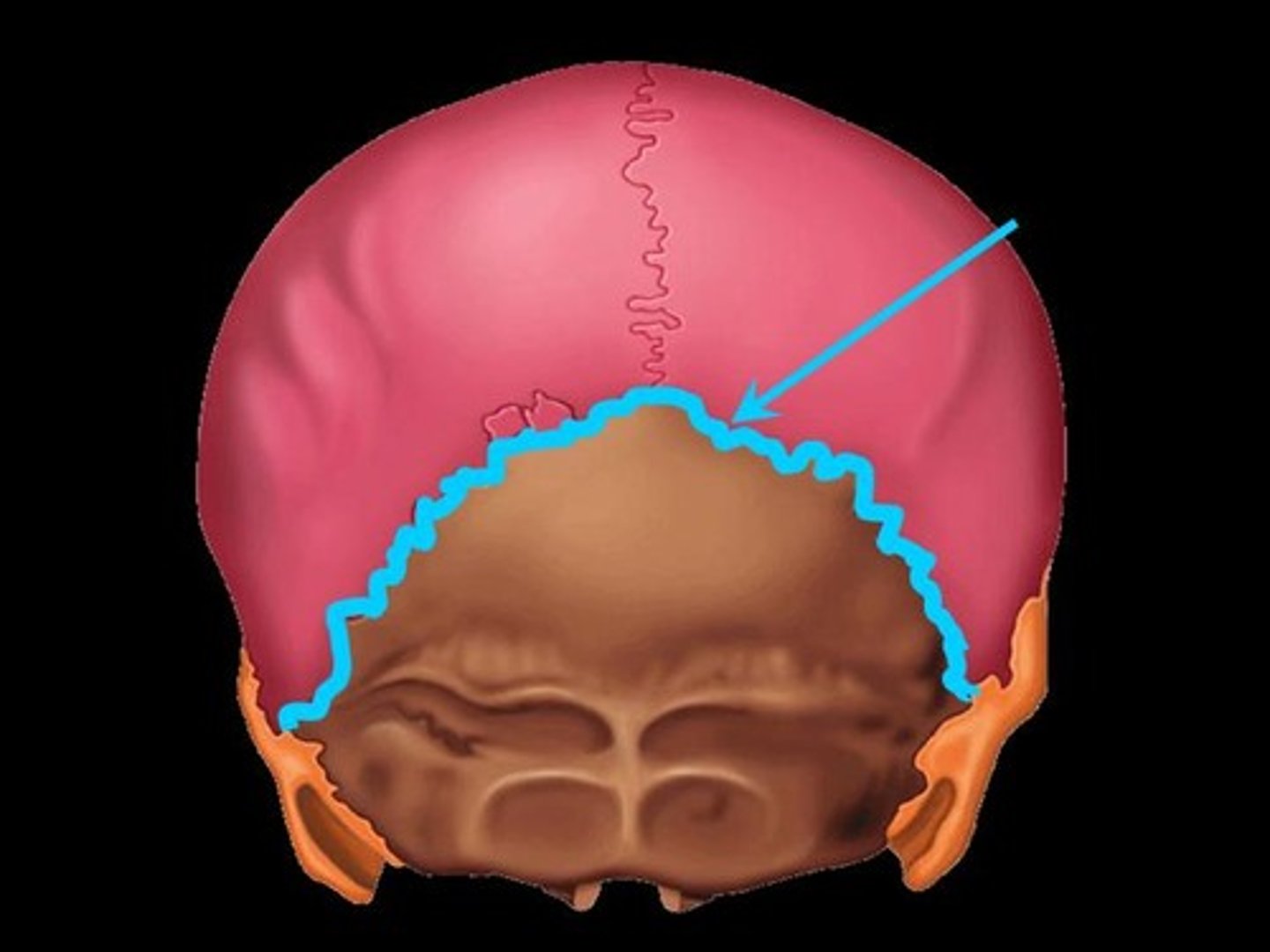
what sutures is this?
Lamboid (cranial vault)
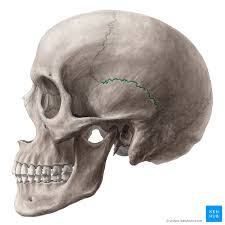
what sutures is this?
Squamous
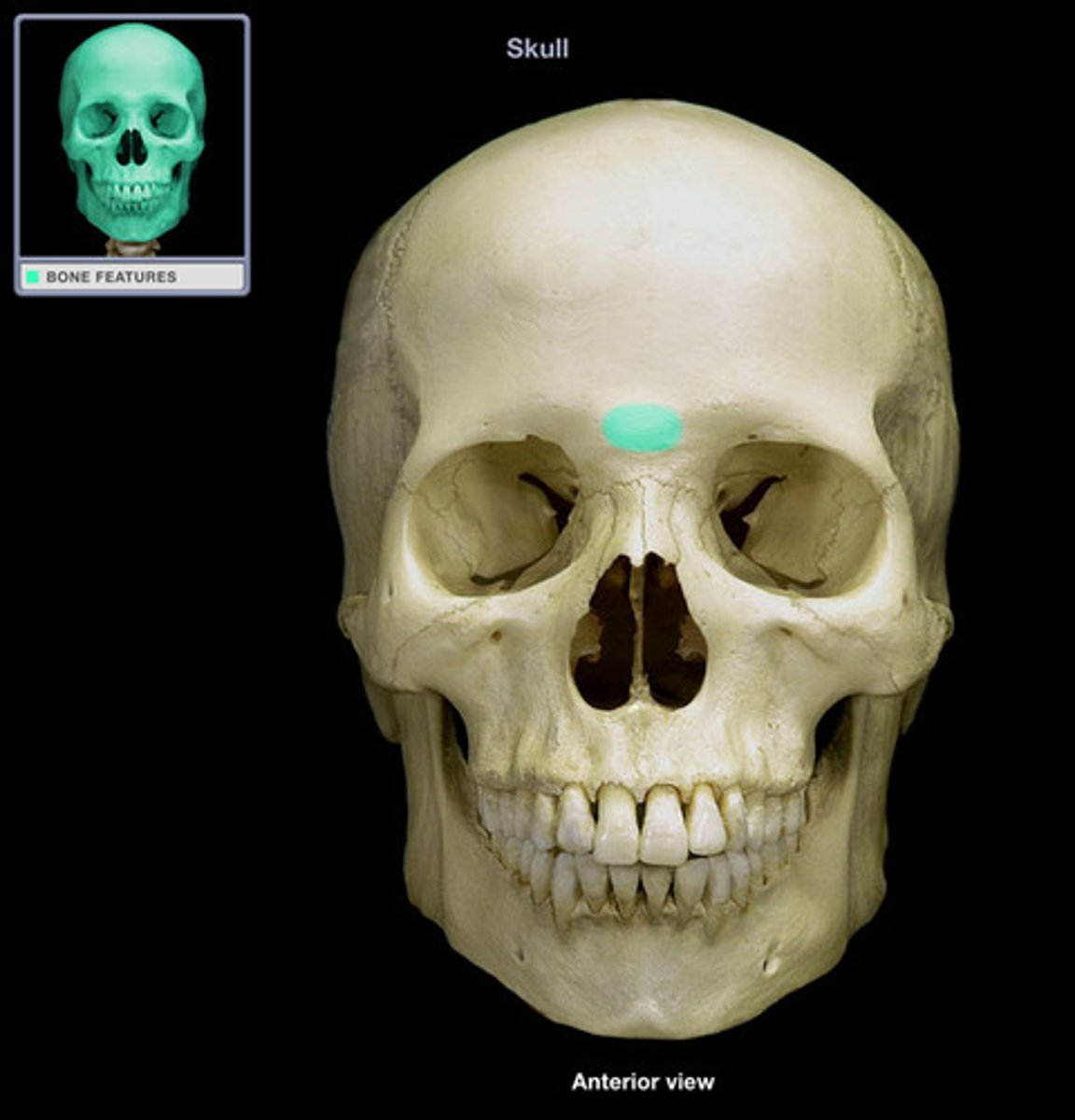
what is this?
glabella (frontal bone)
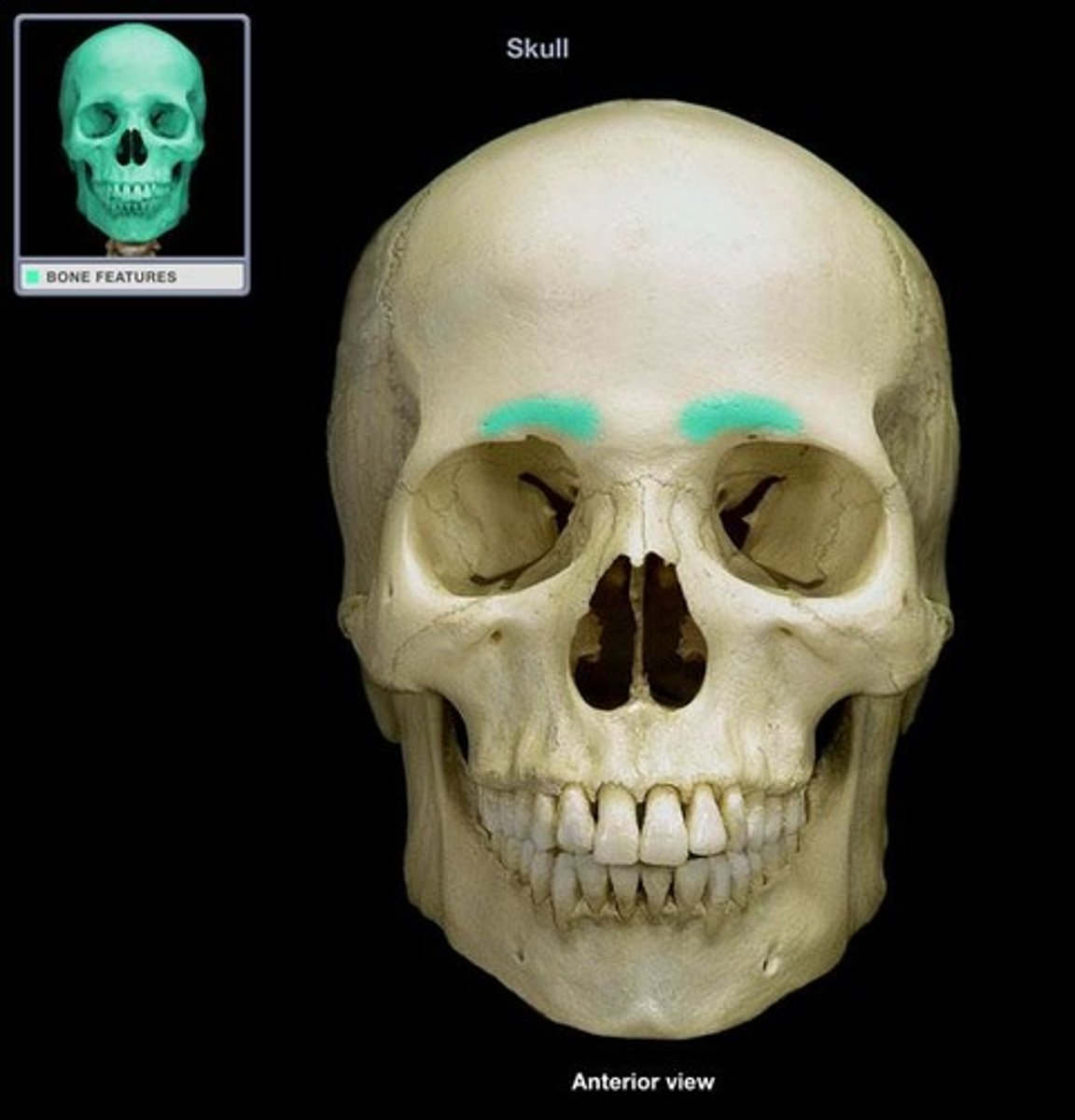
the superior rim of the eye sockets.
supraorbital margins (frontal bone)
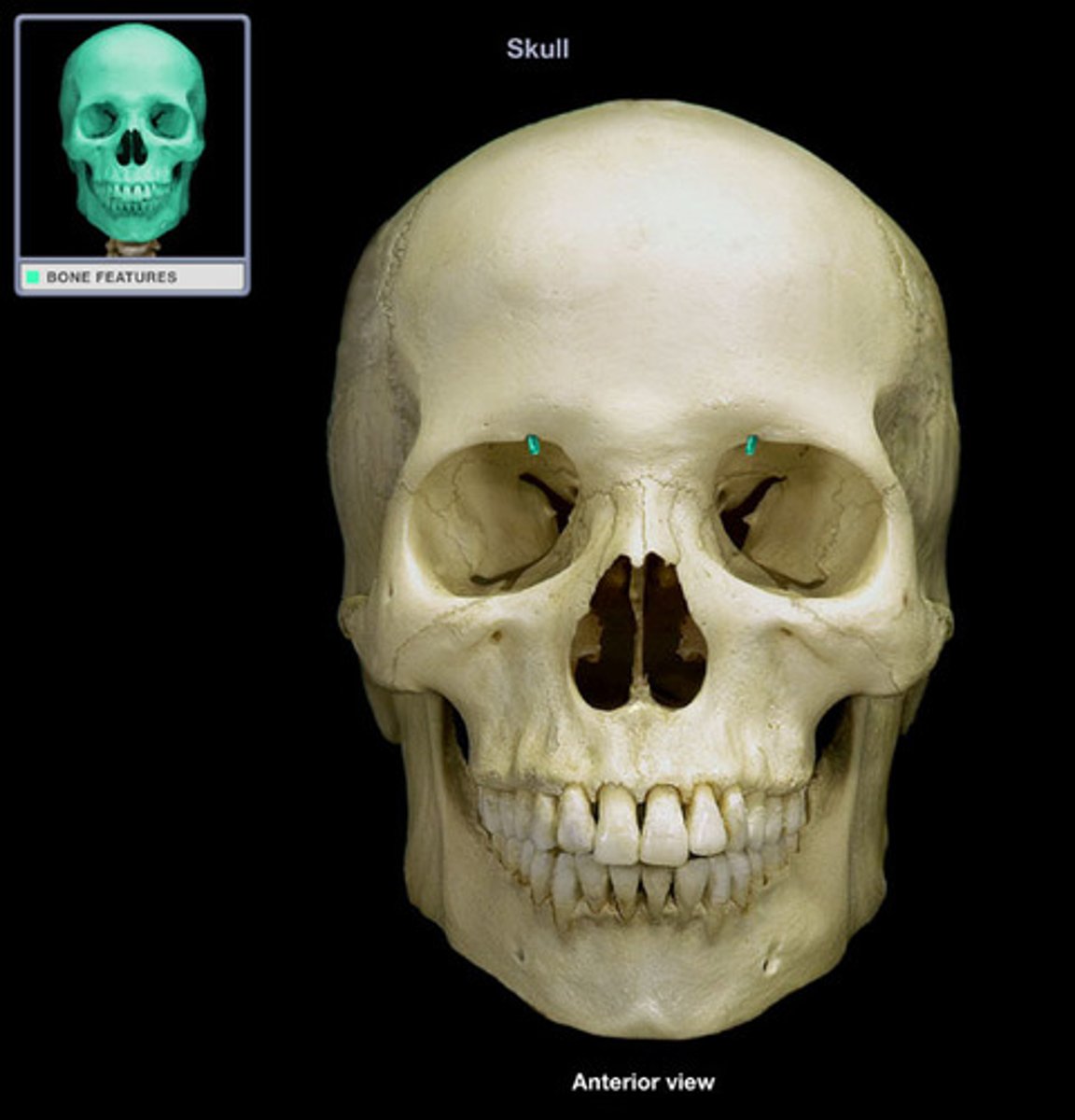
opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass
supraorbital foramen (frontal bone)
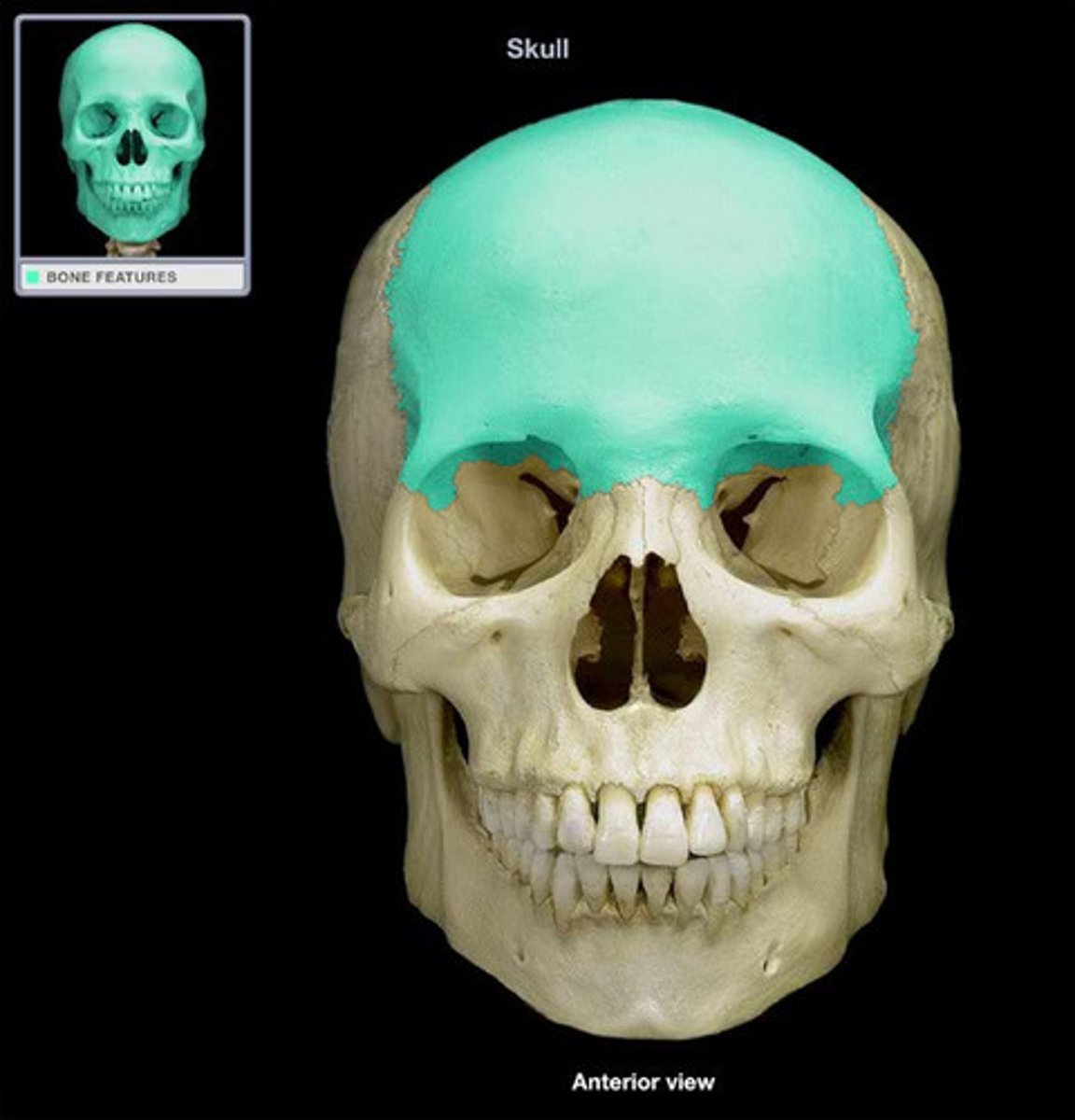
holds the frontal lobe of the brain
anterior cranial fossa (frontal bone)
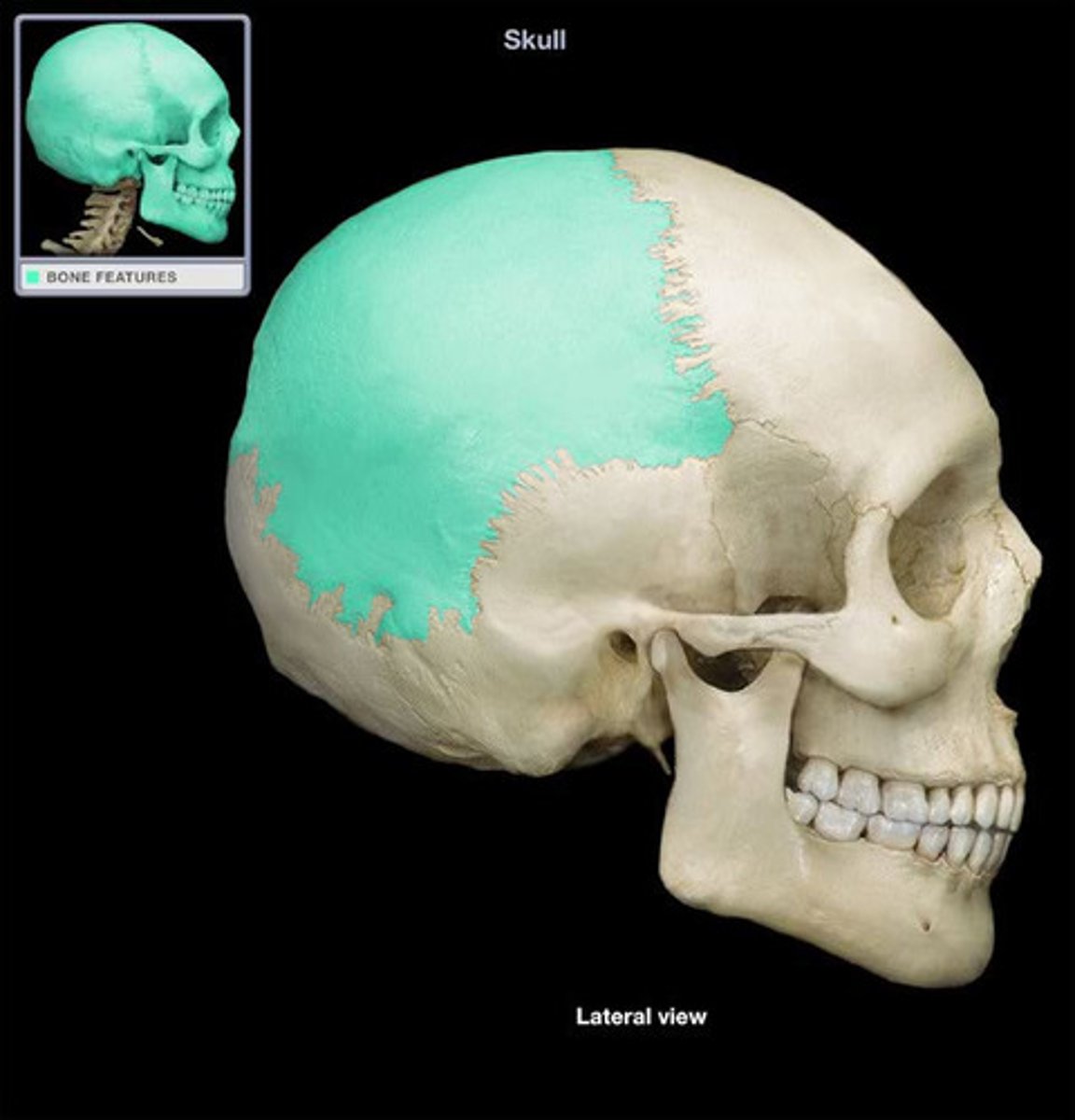
either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium
parietal bone
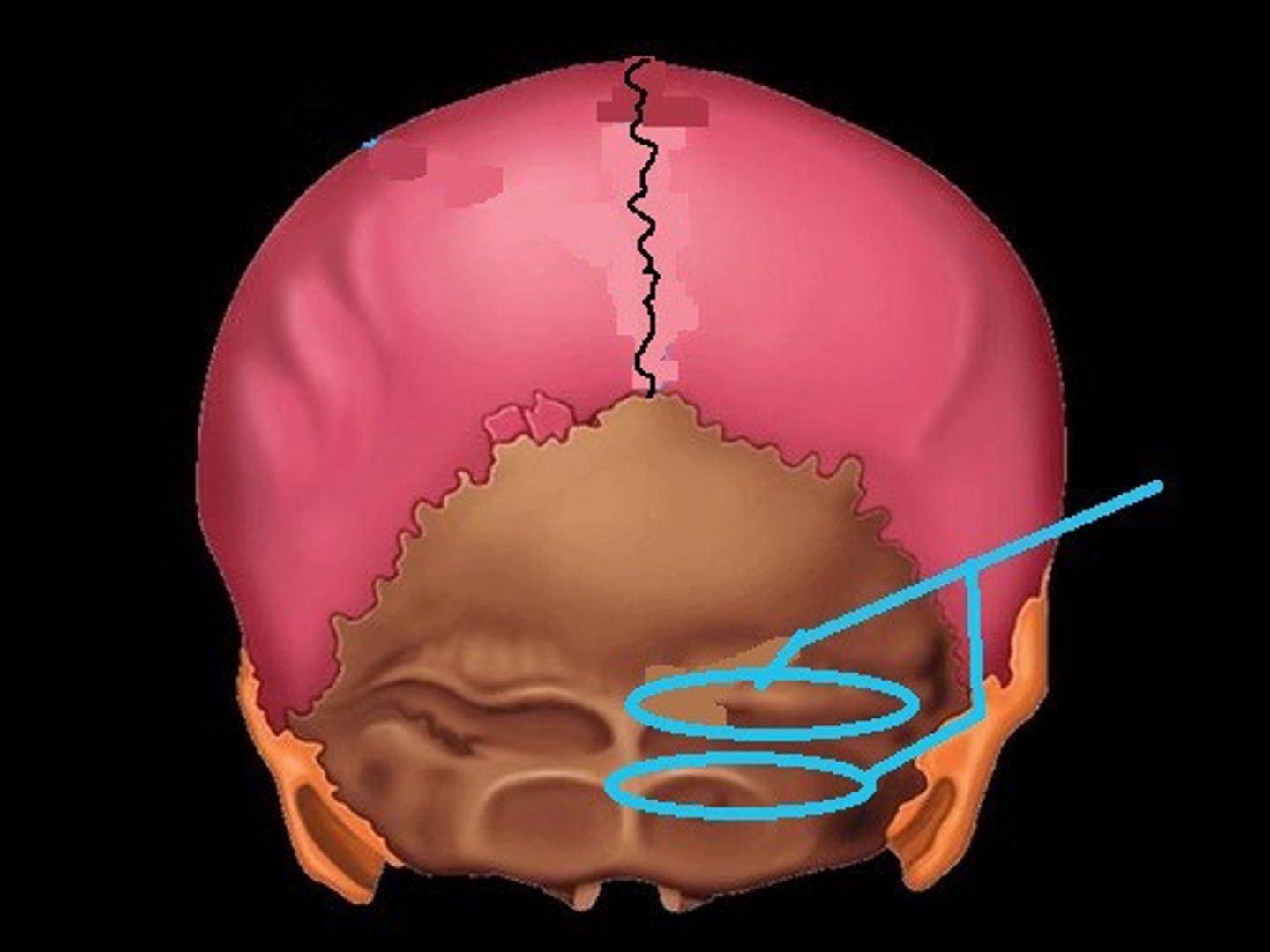
4 curved lines on the external surface of occipital bone
nuchal lines (occipital bone)
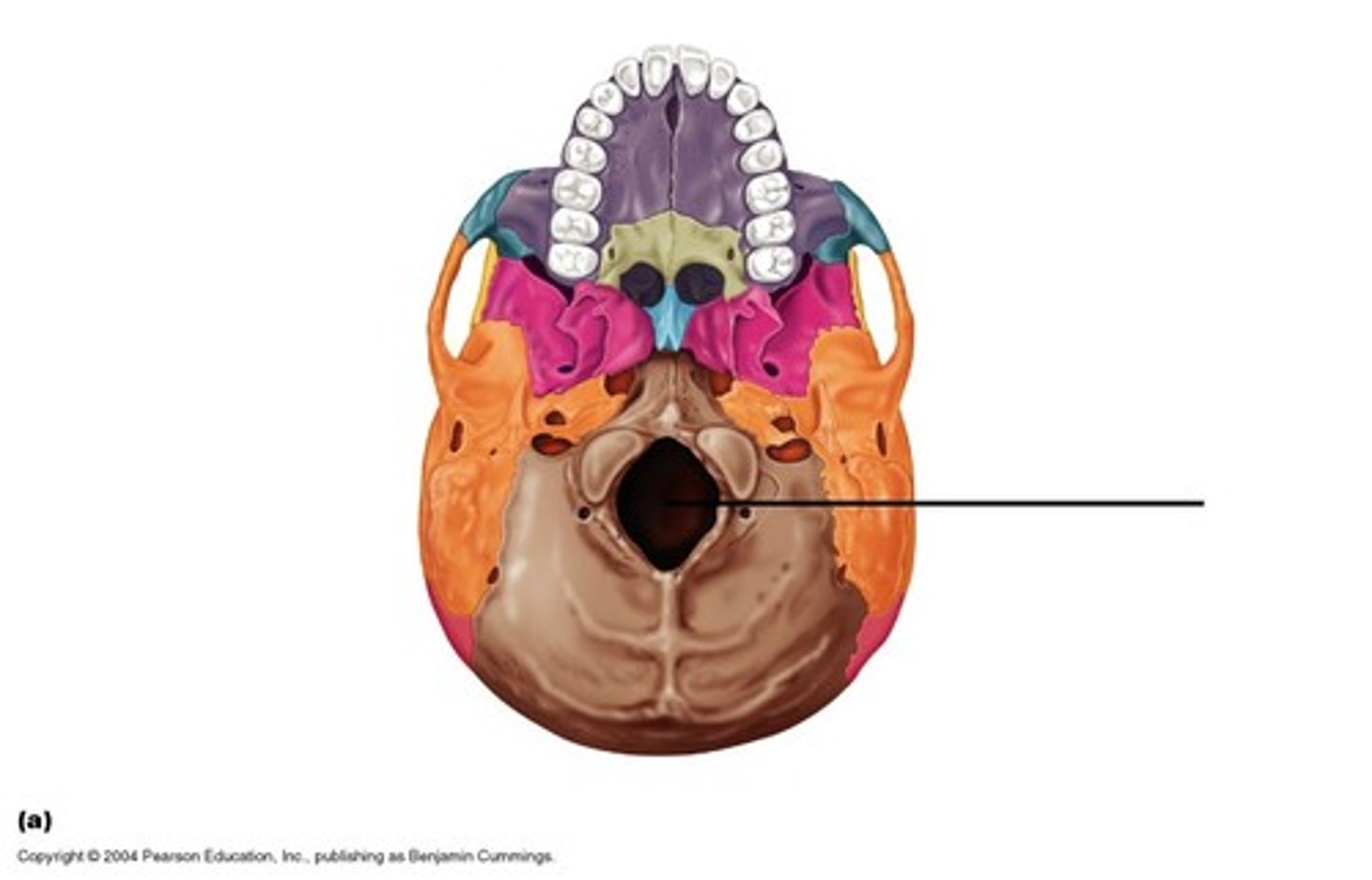
A large opening at the base of the skull through which the brain connects to the spinal cord.
foramen magnum (occipital bone)
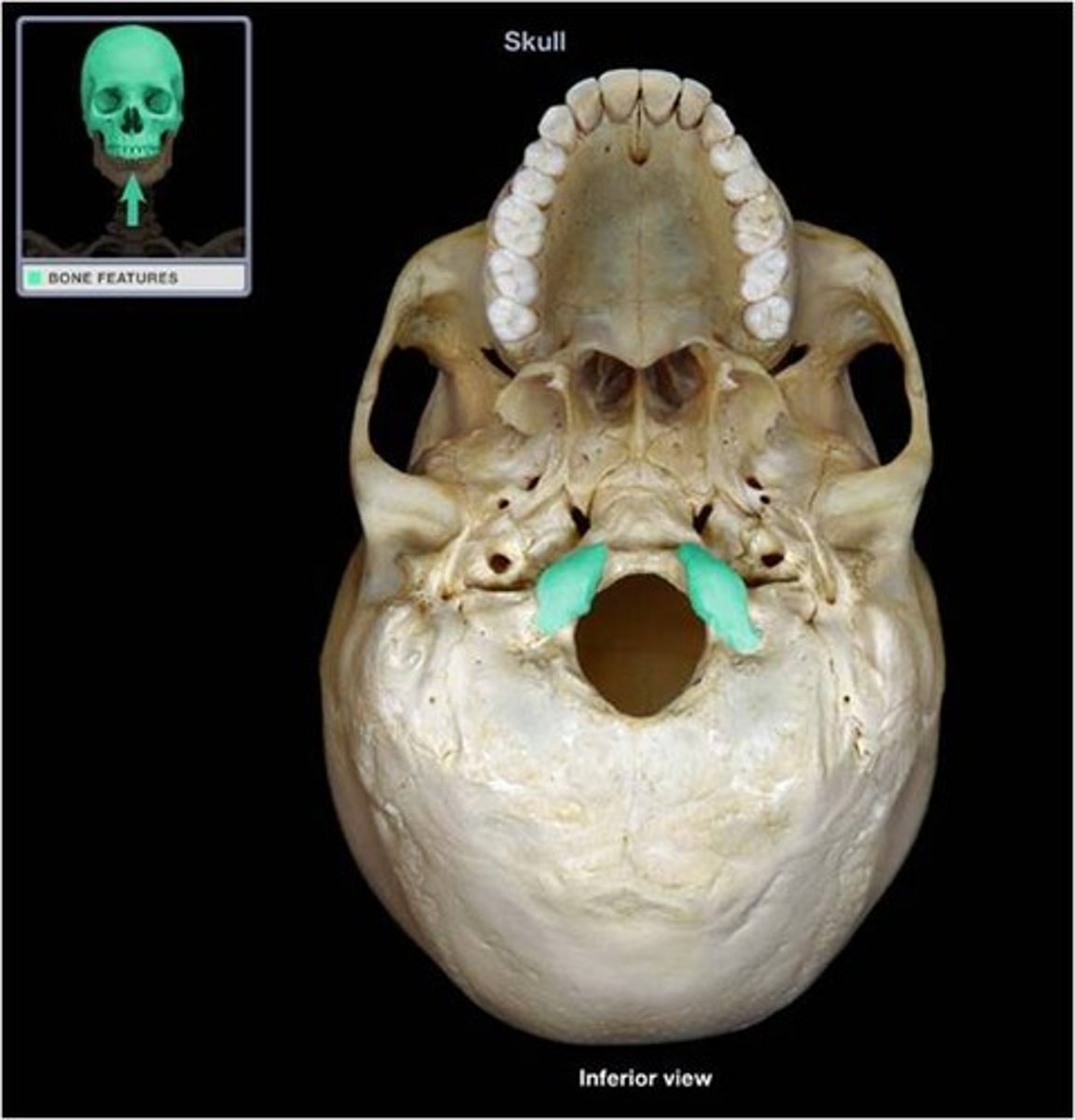
Rounded projections lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas)
occipital condyles (occipital bone)
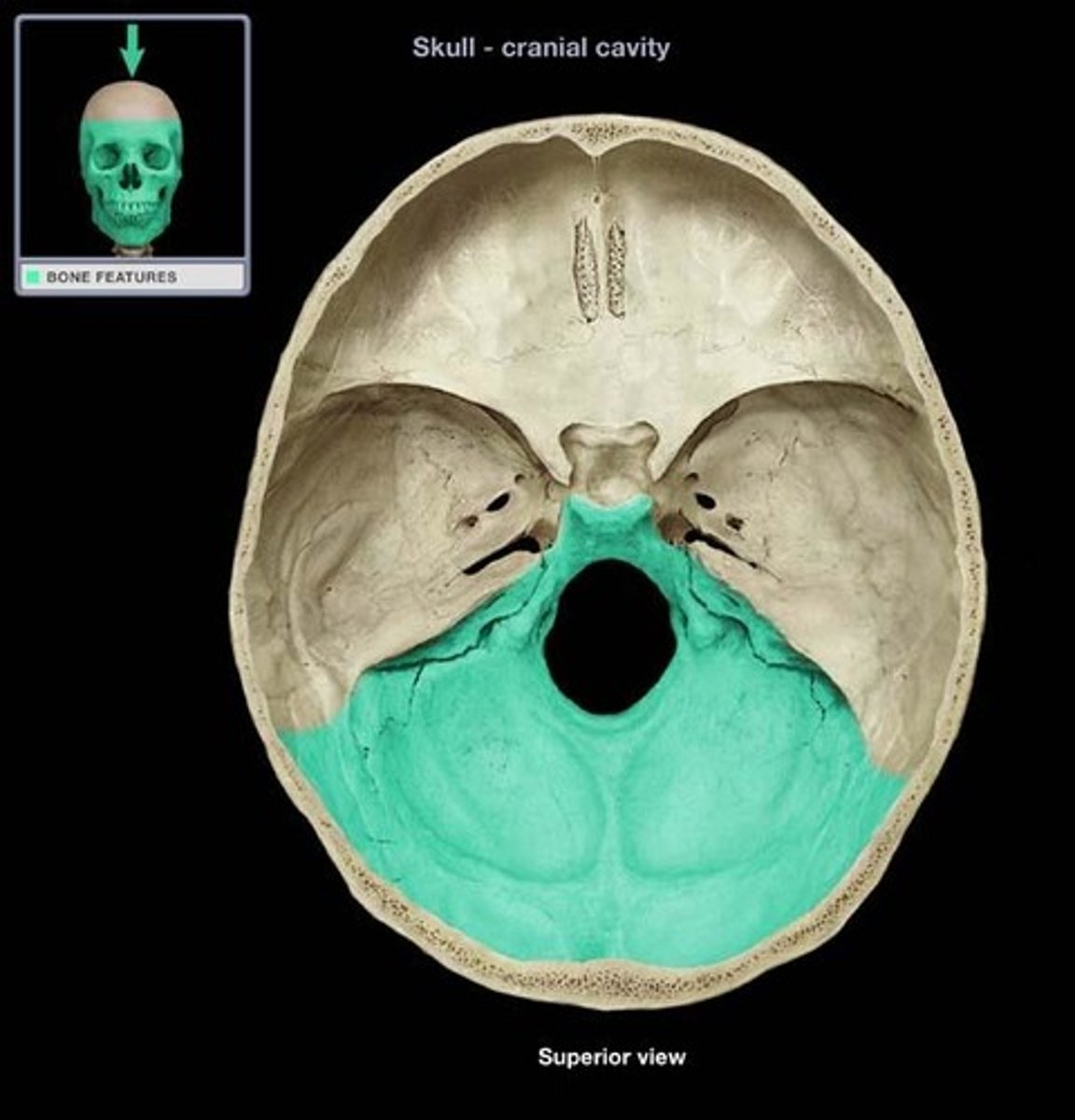
supports the cerebellum of the brain
posterior cranial fossa (occipital bone)
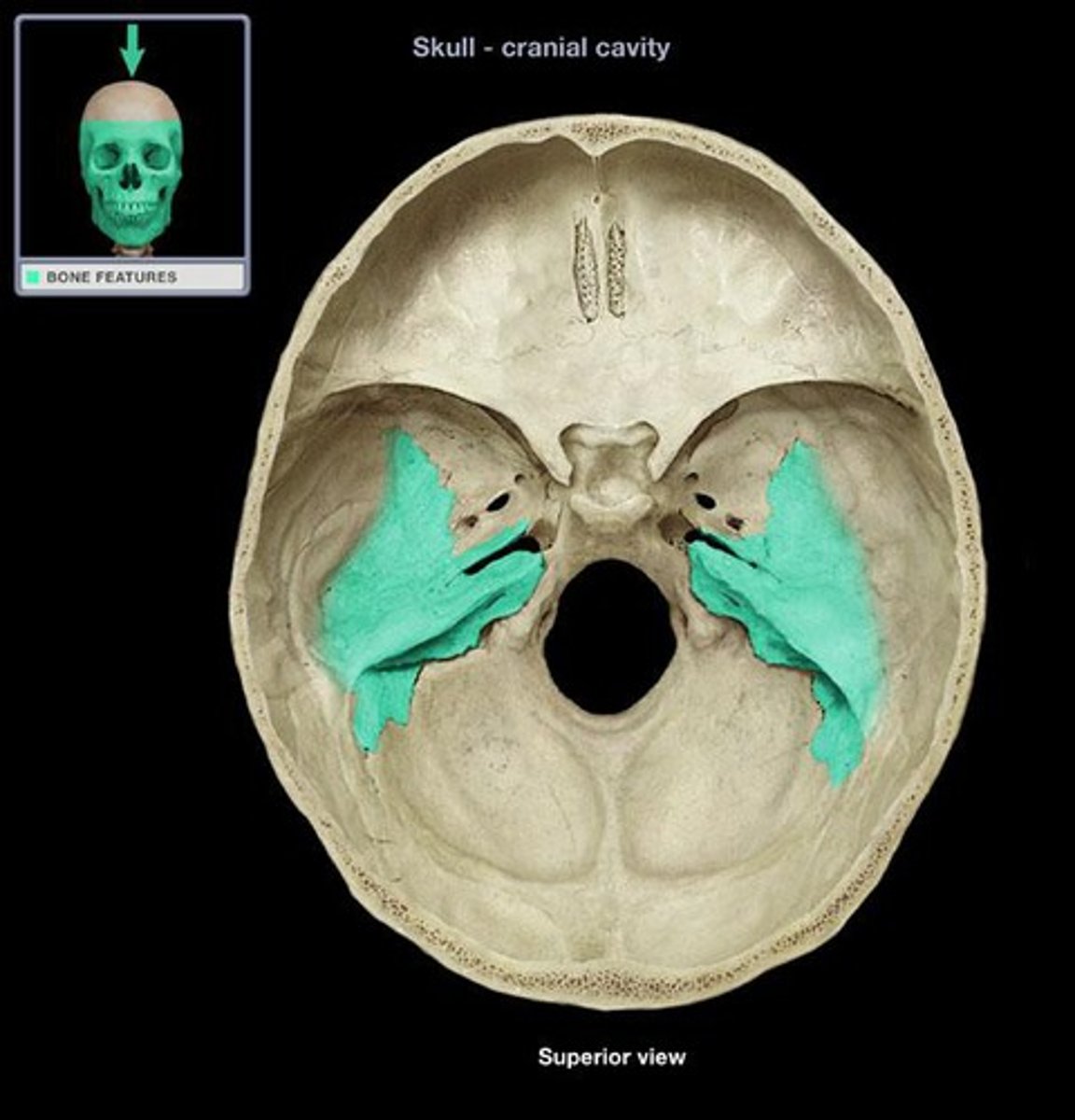
flat; above ear
squamous portion (temporal bone)
raised portion on top section of skull towards bottom
petrous portion (temporal bone)
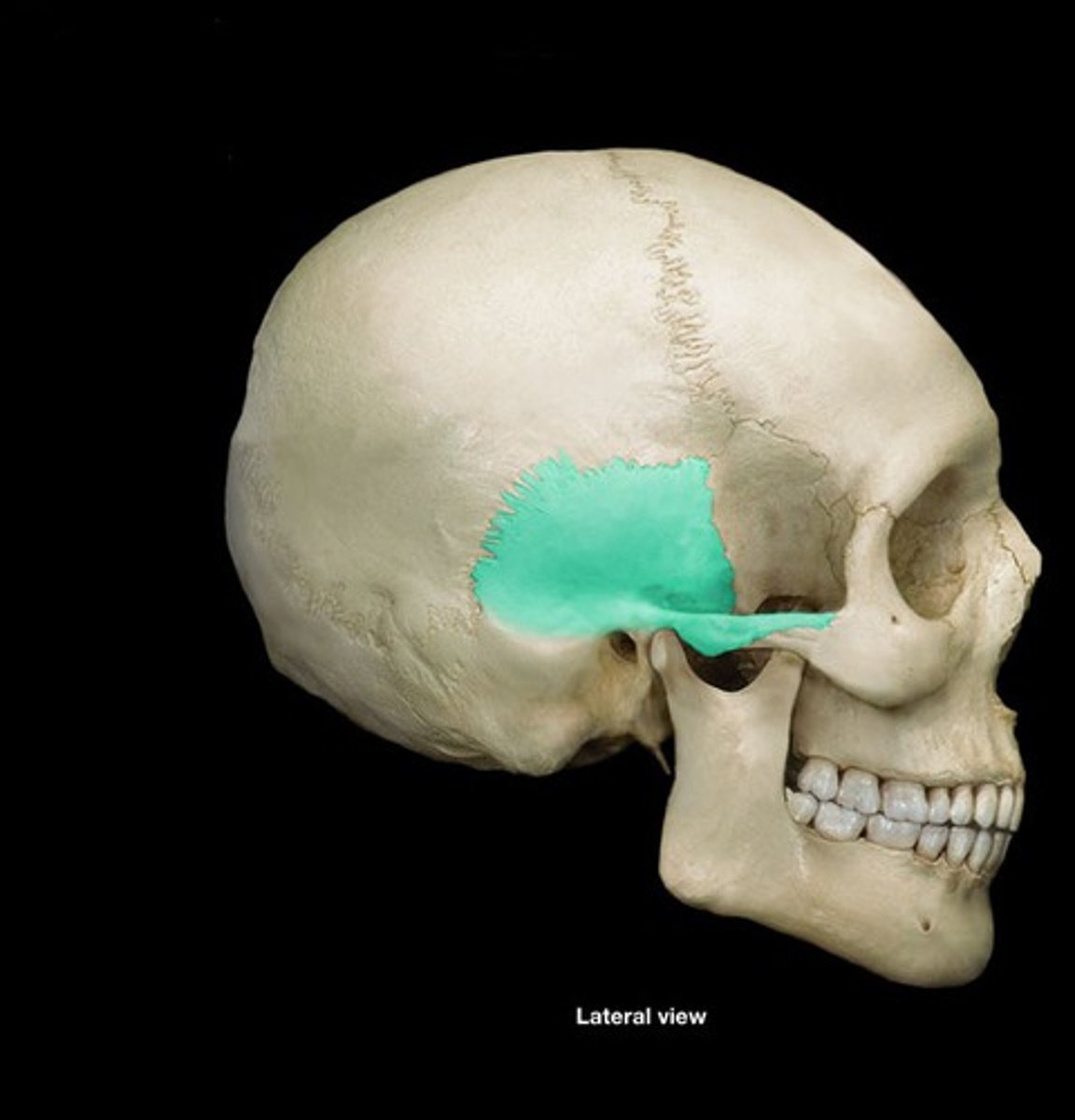
a projection of the temporal bone that forms part of the zygoma
zygomatic process (temporal bone)
pole-like process extending downward from the temporal bone on each side of the skull
styloid process (temporal bone)
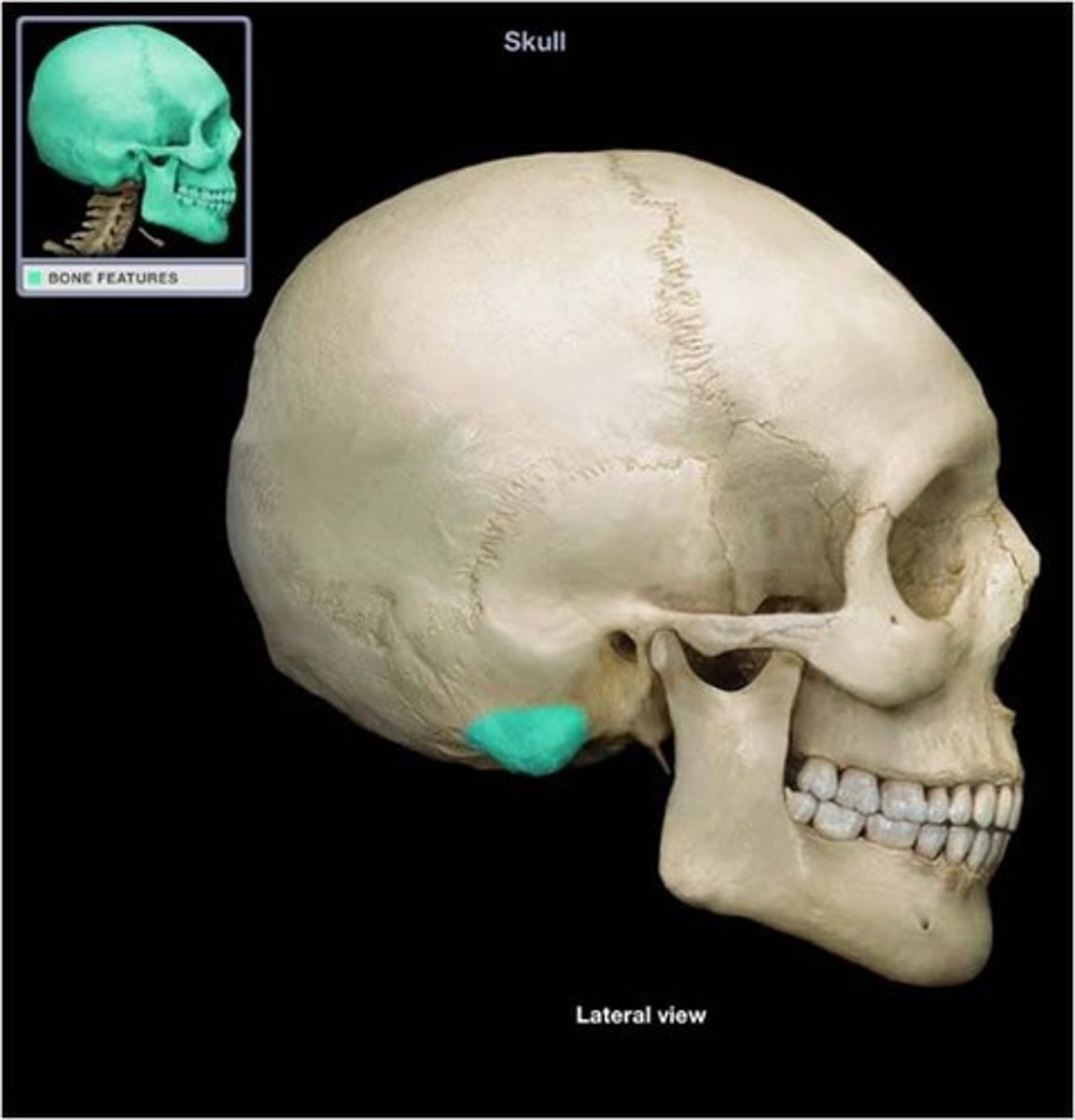
round projection on the temporal bone behind the ear
mastoid process (temporal bone)
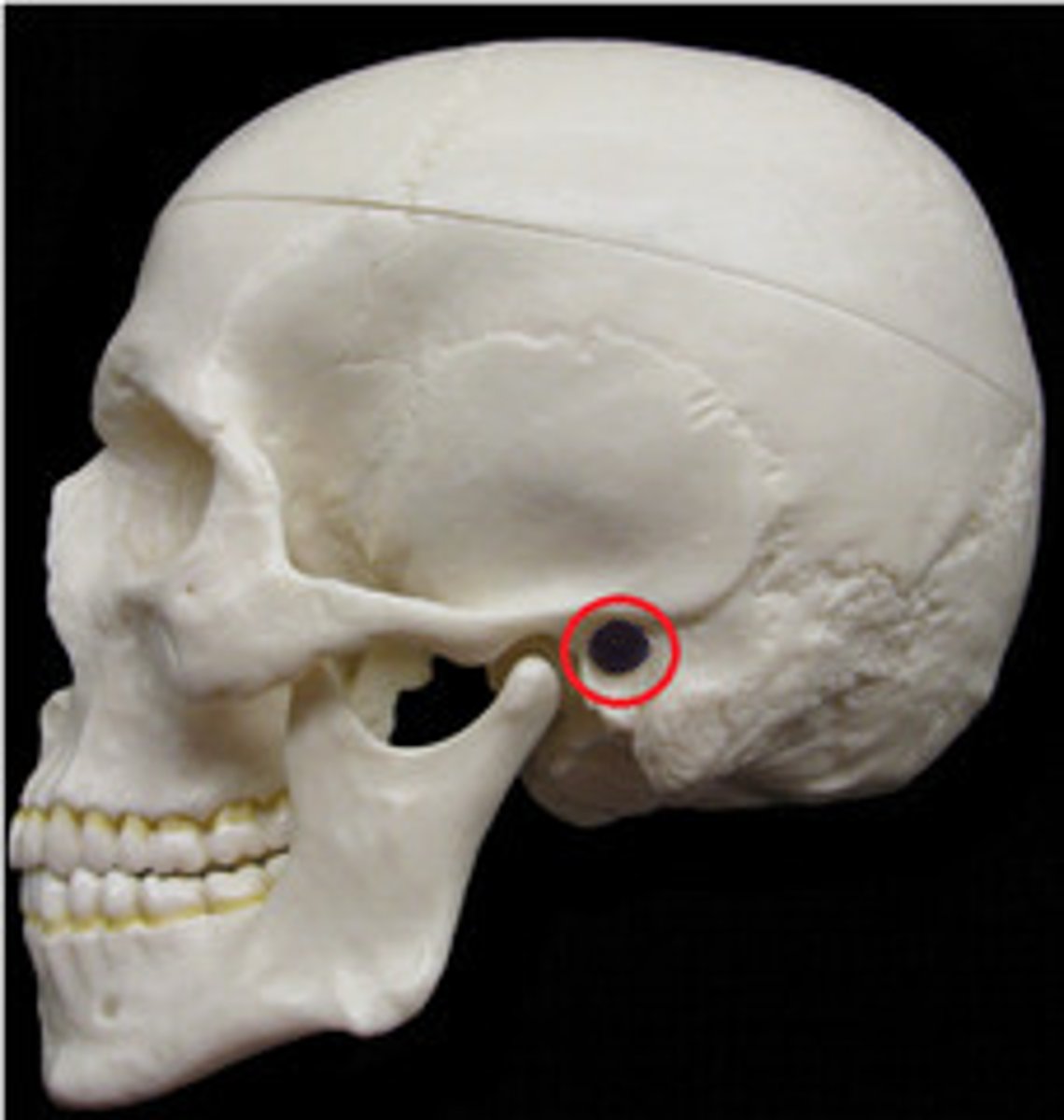
ear canal
external auditory meatus (temporal bone)
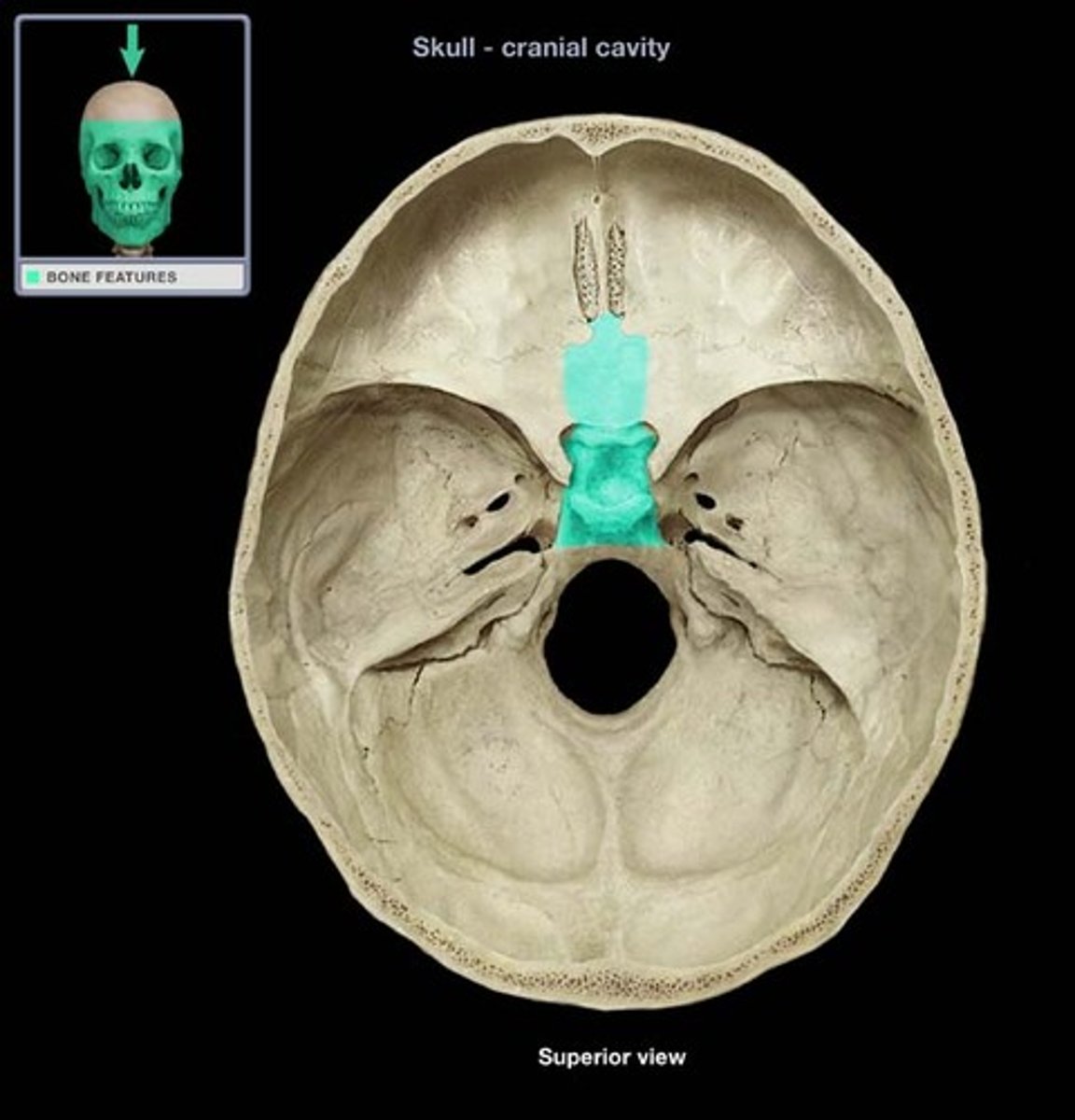
central section of sphenoid
body of sphenoid bone
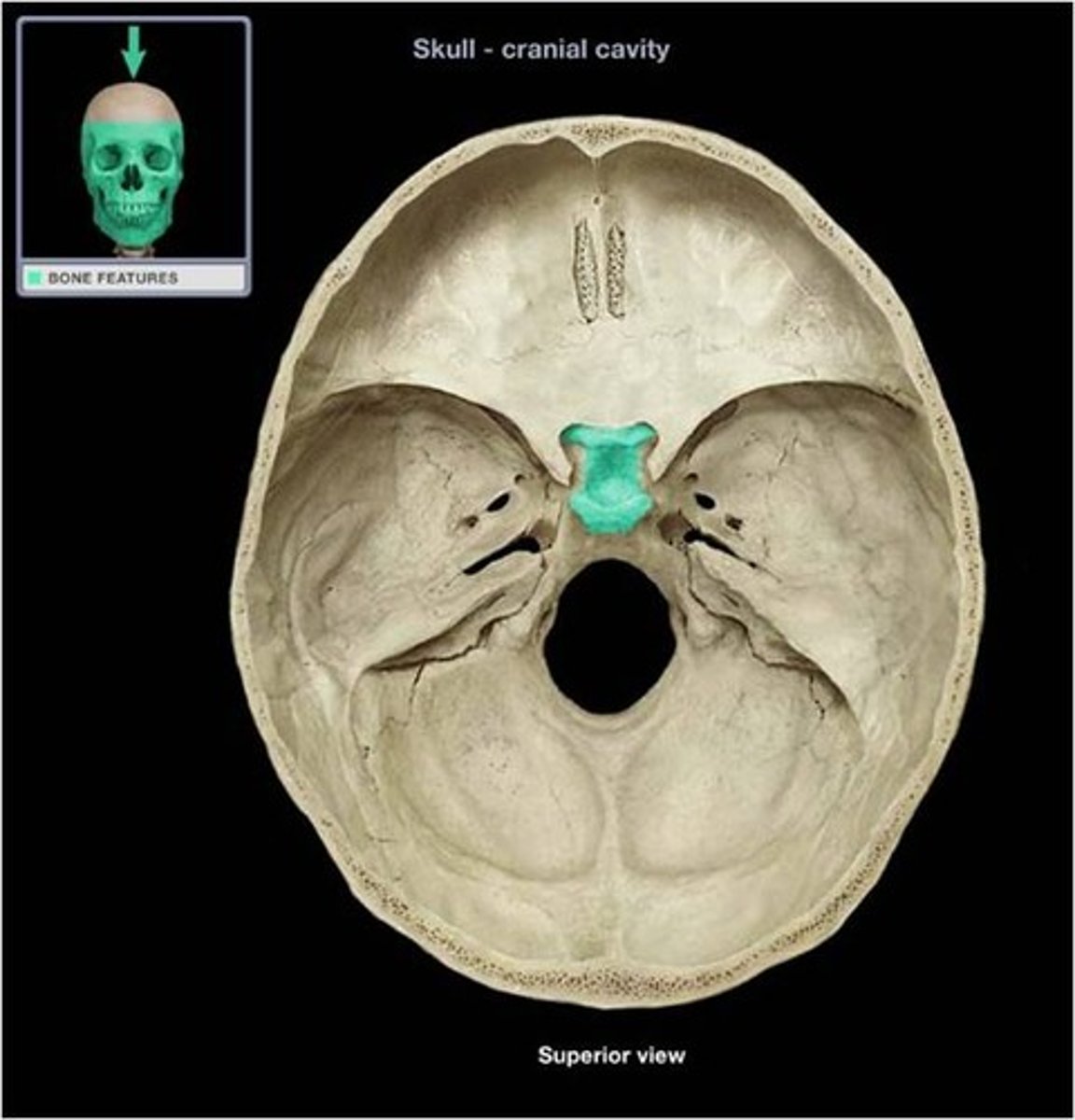
what is this
stella turcica of sphenoid bone
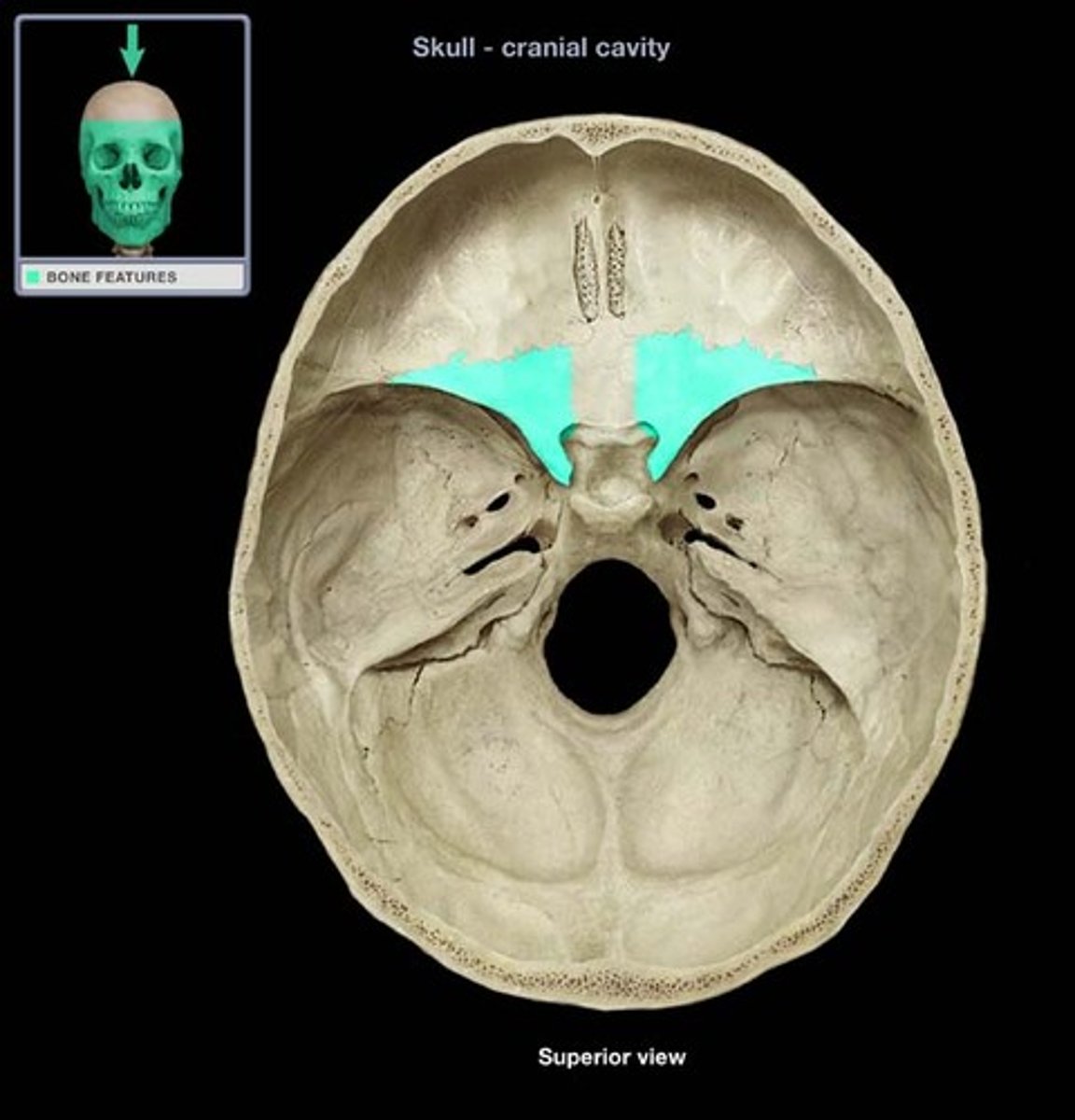
One of two side wings extending from the body of the sphenoid bone
lesser wing of sphenoid bone
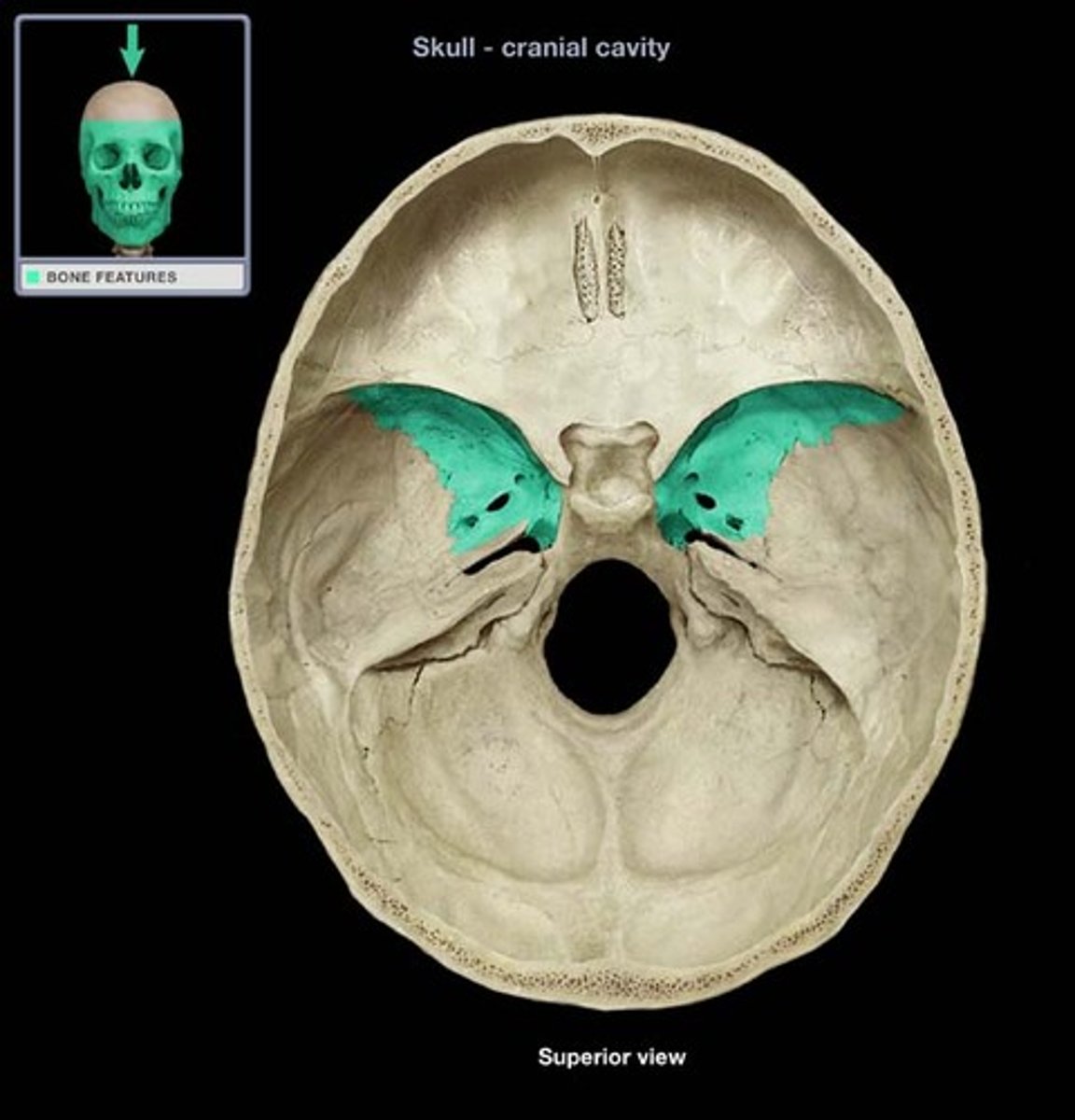
posterior and inferior to lesser wing on the interior of the skull, also visible in the posterior orbit and lateral side of the skull
greater wing of sphenoid bone
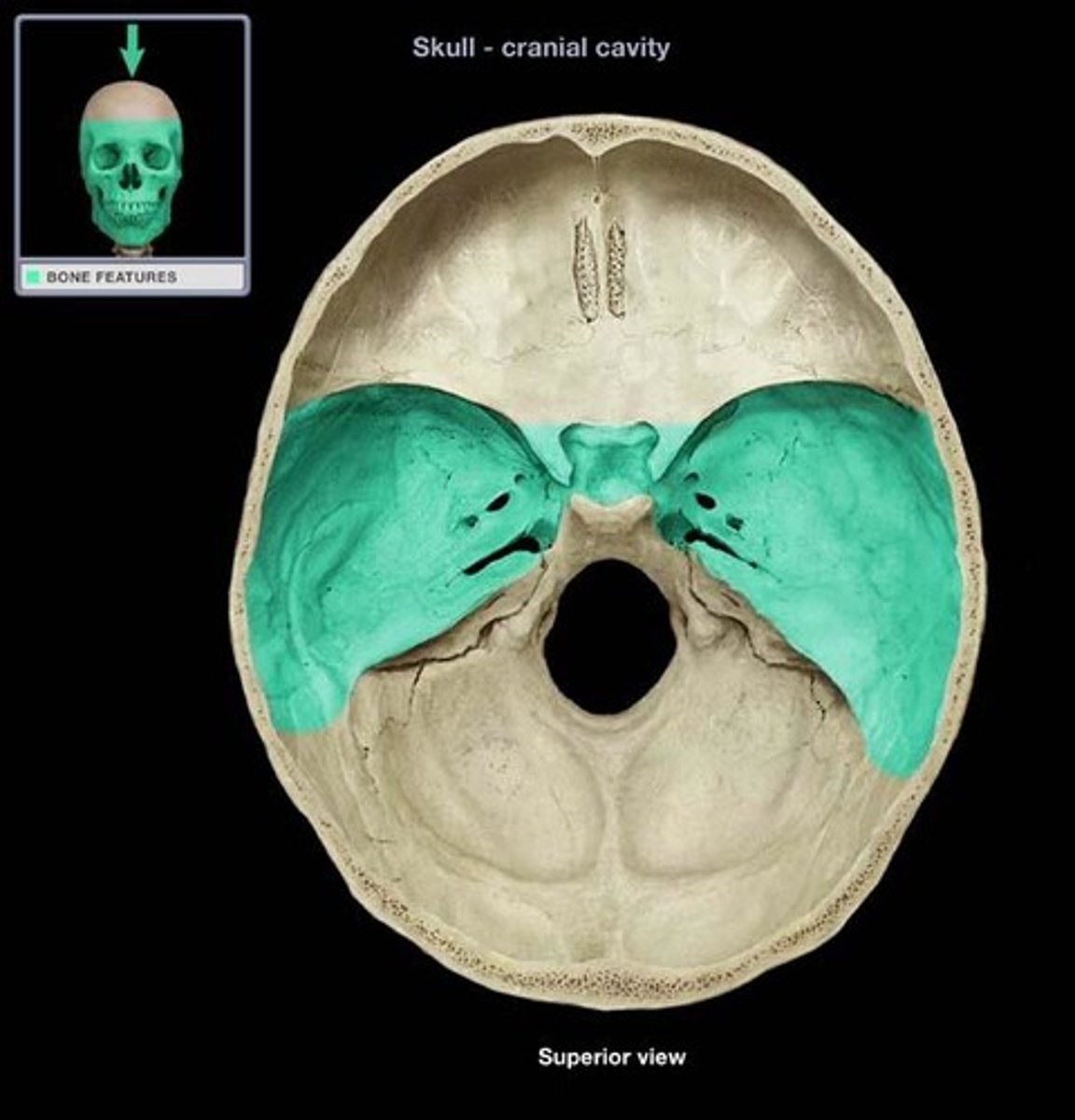
what is this
middle cranial fossa of sphenoid bone
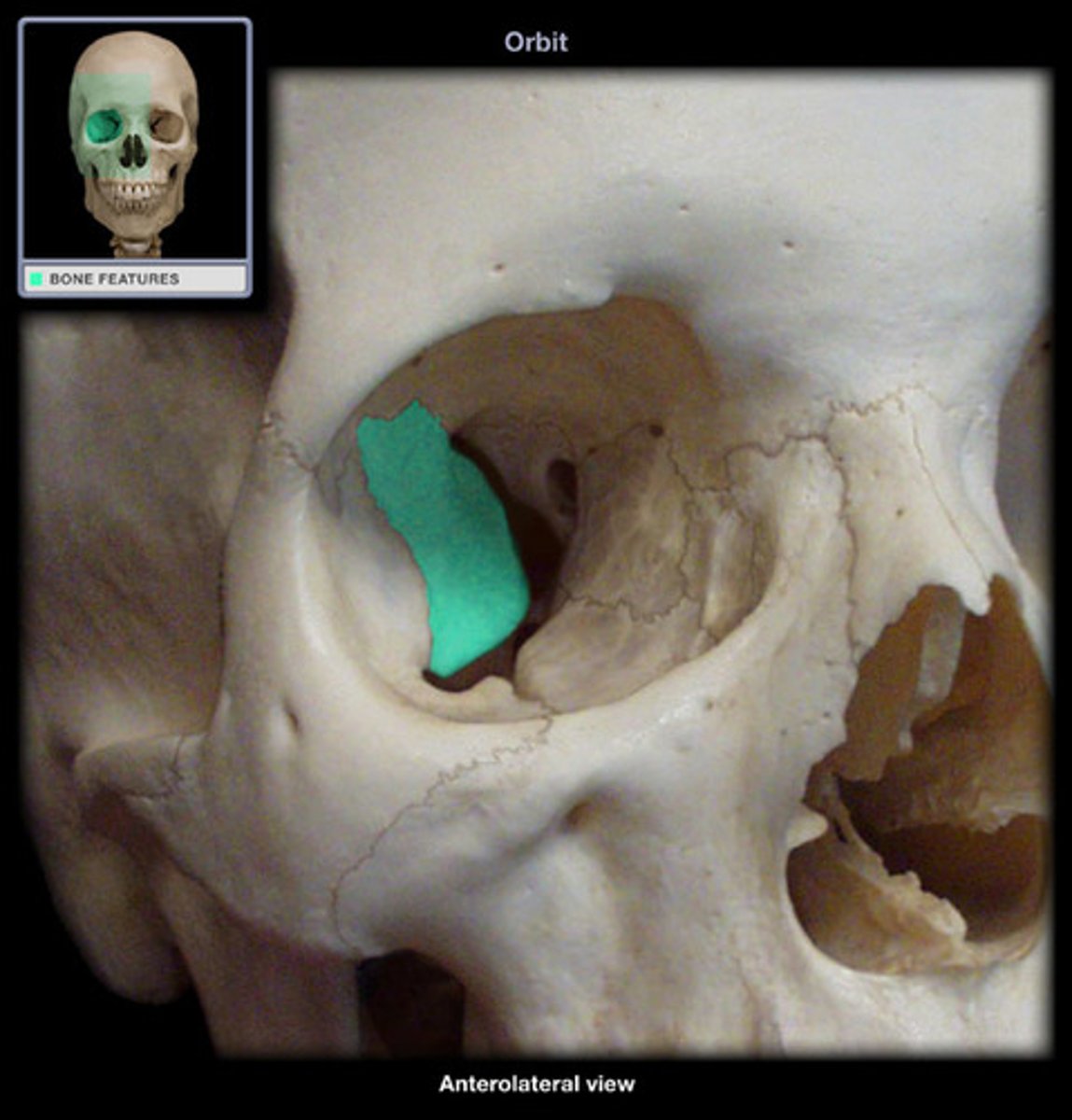
- eye socket
orbital surface of sphenoid bone
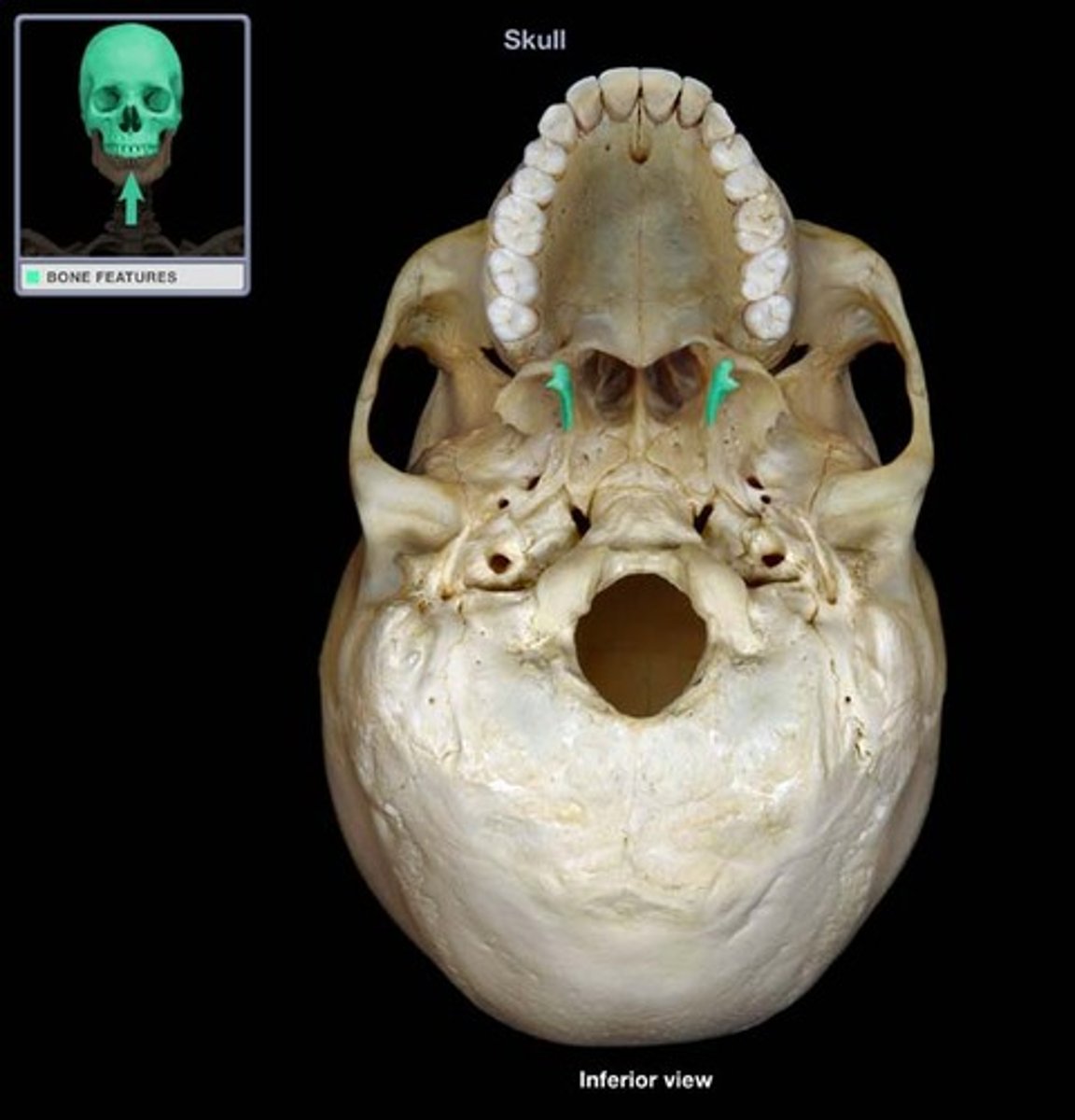
point of attachment for muscles of mastication (chewing)
medial pterygoid plates
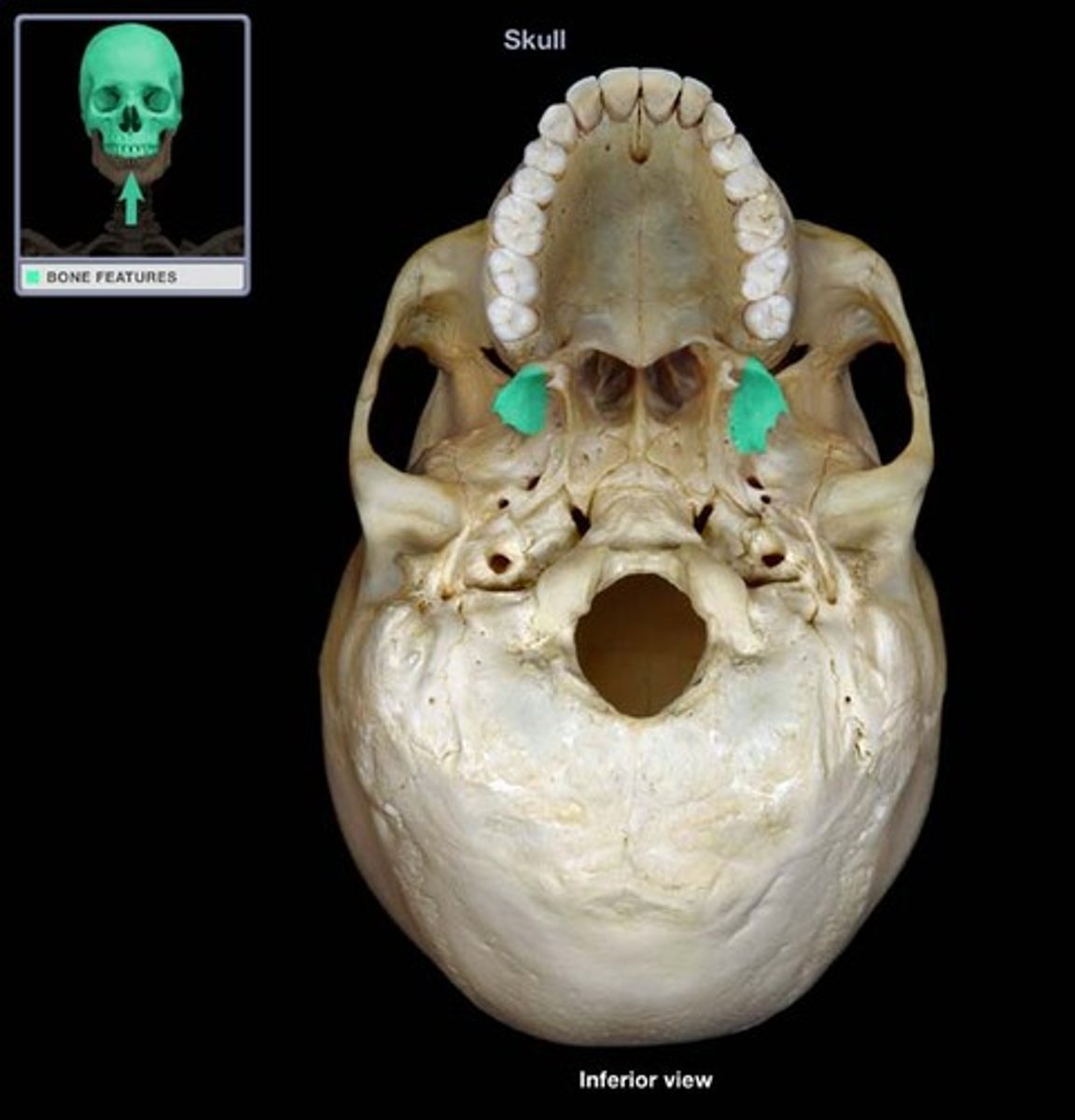
point of attachment for muscles of mastication (chewing)
lateral pterygoid plates
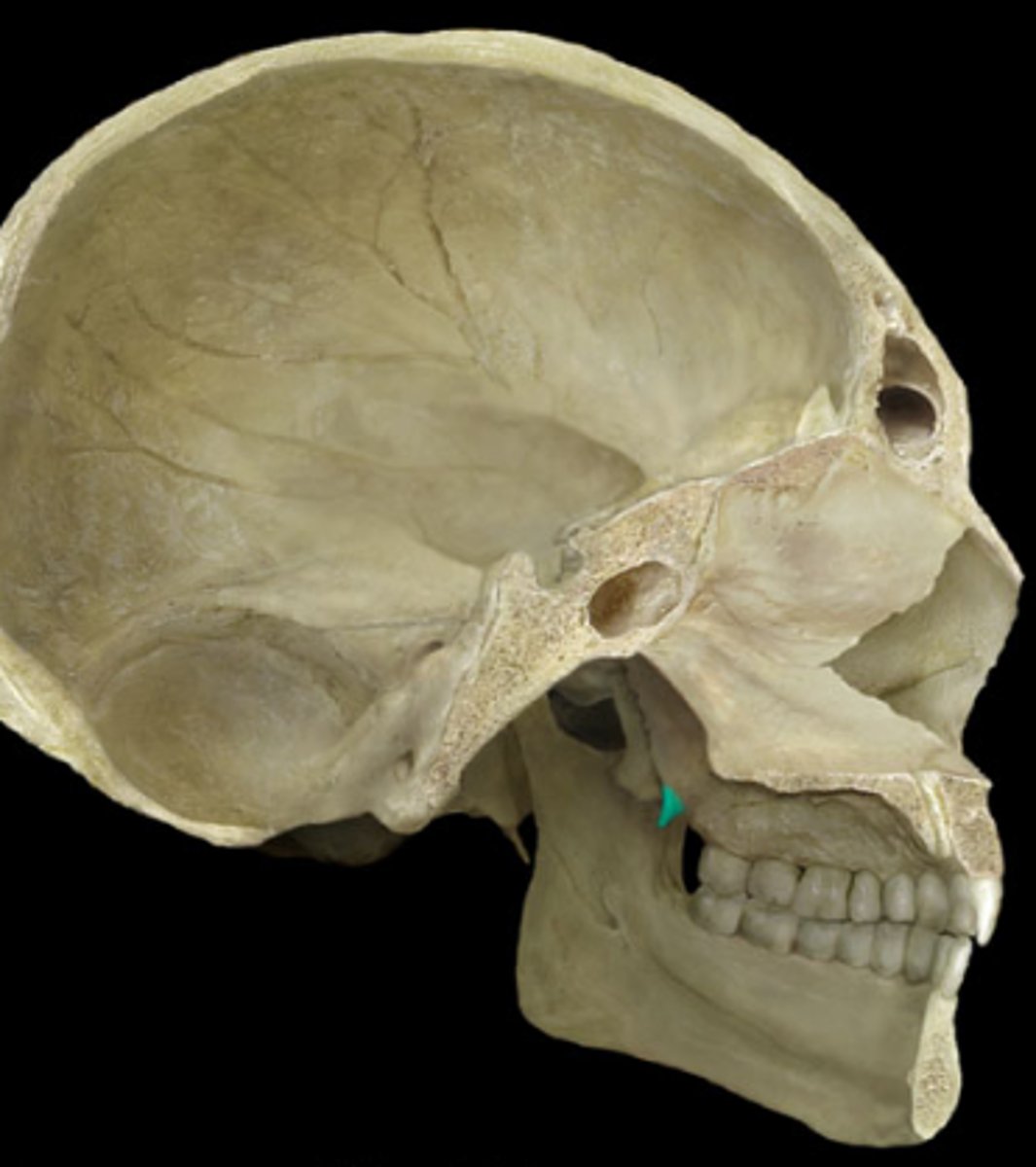
hook-shaped process
hamulus of sphenoid bone
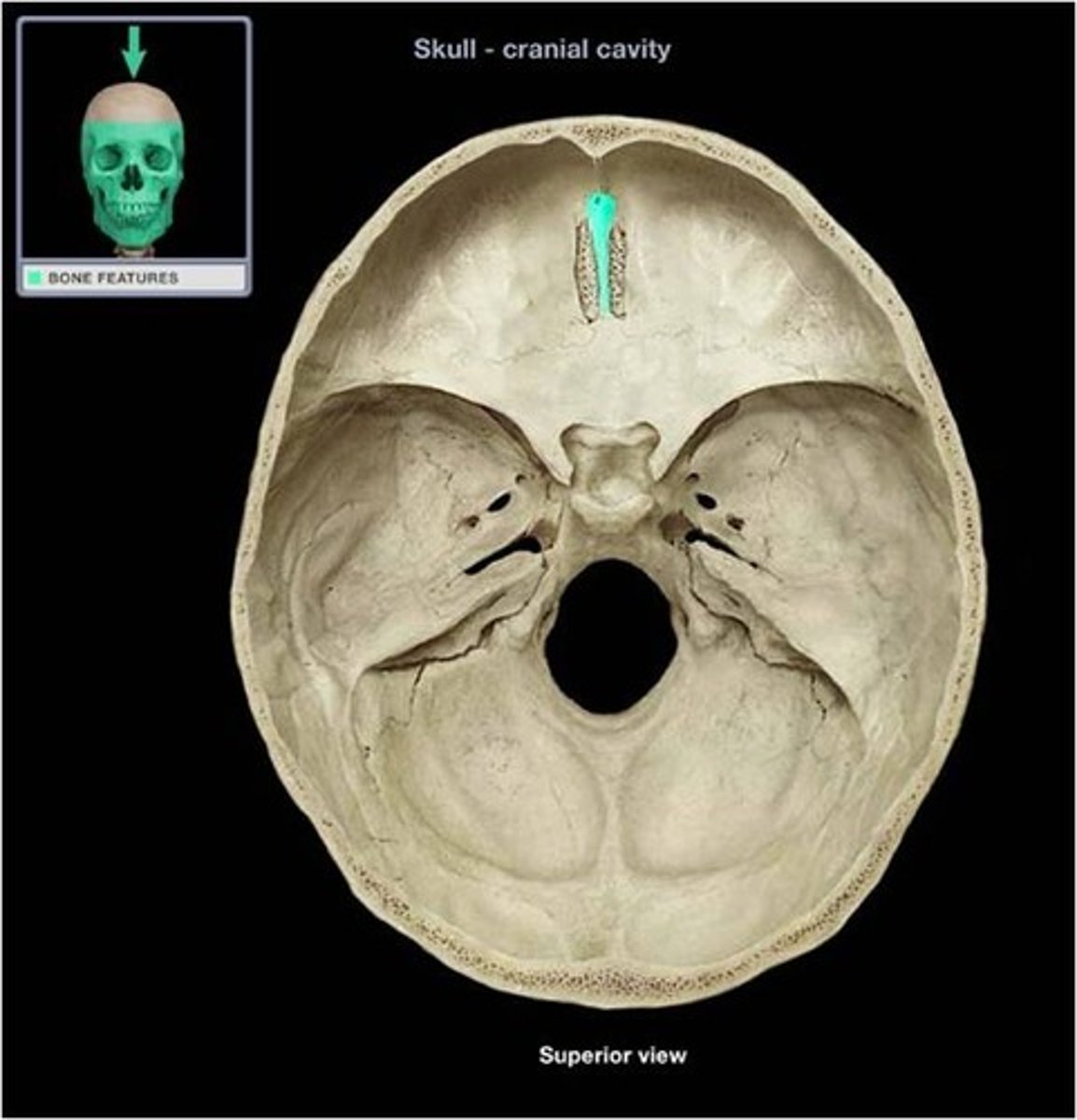
Structure of the ethmoid bone that projects superiorly from the cribriform plate. It's named is derived from "rooster's comb"
crista gali
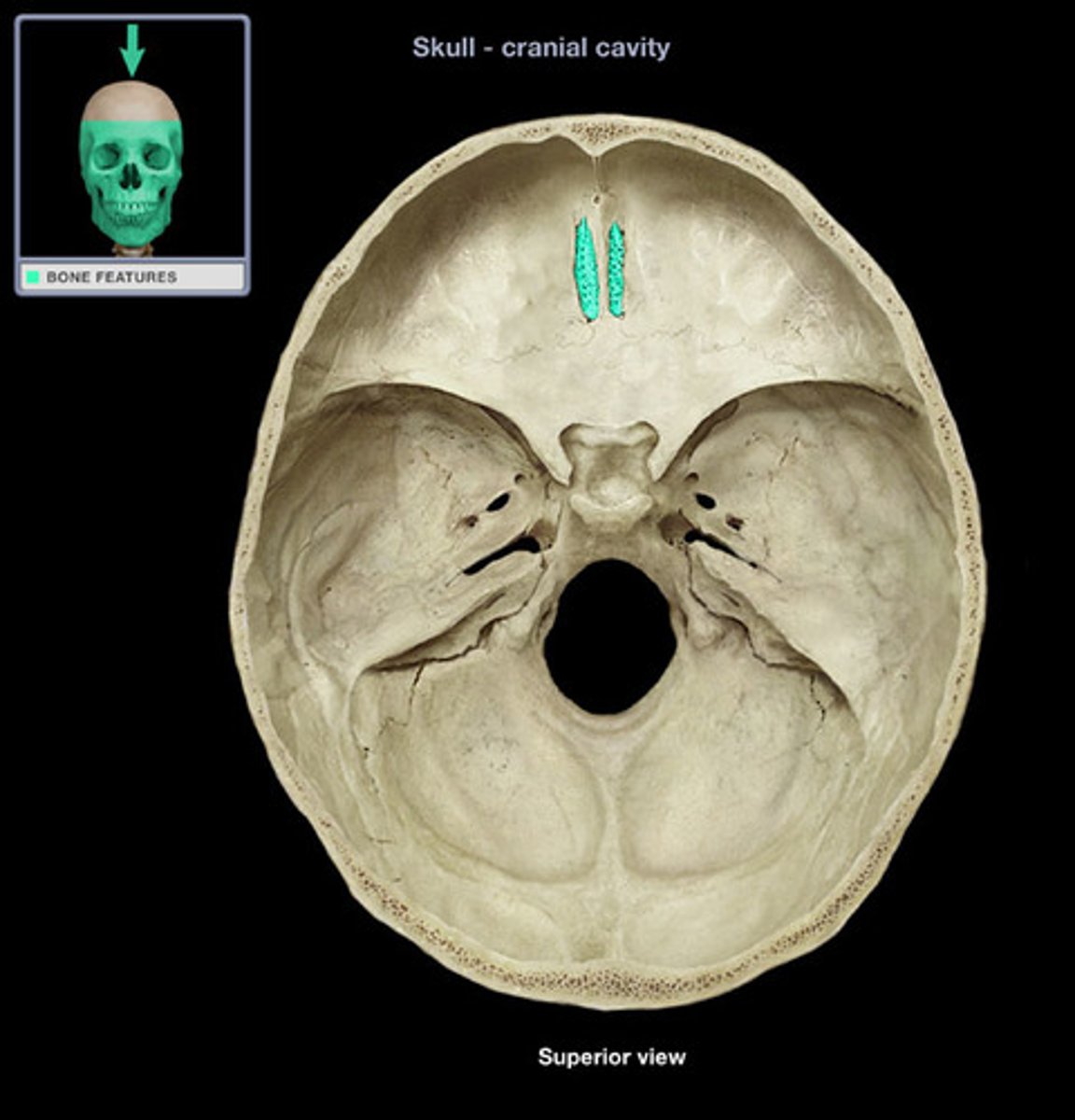
The horizontal plate of the ethmoid bone separating the cranial cavity from the nasal cavity.
cribriform plate
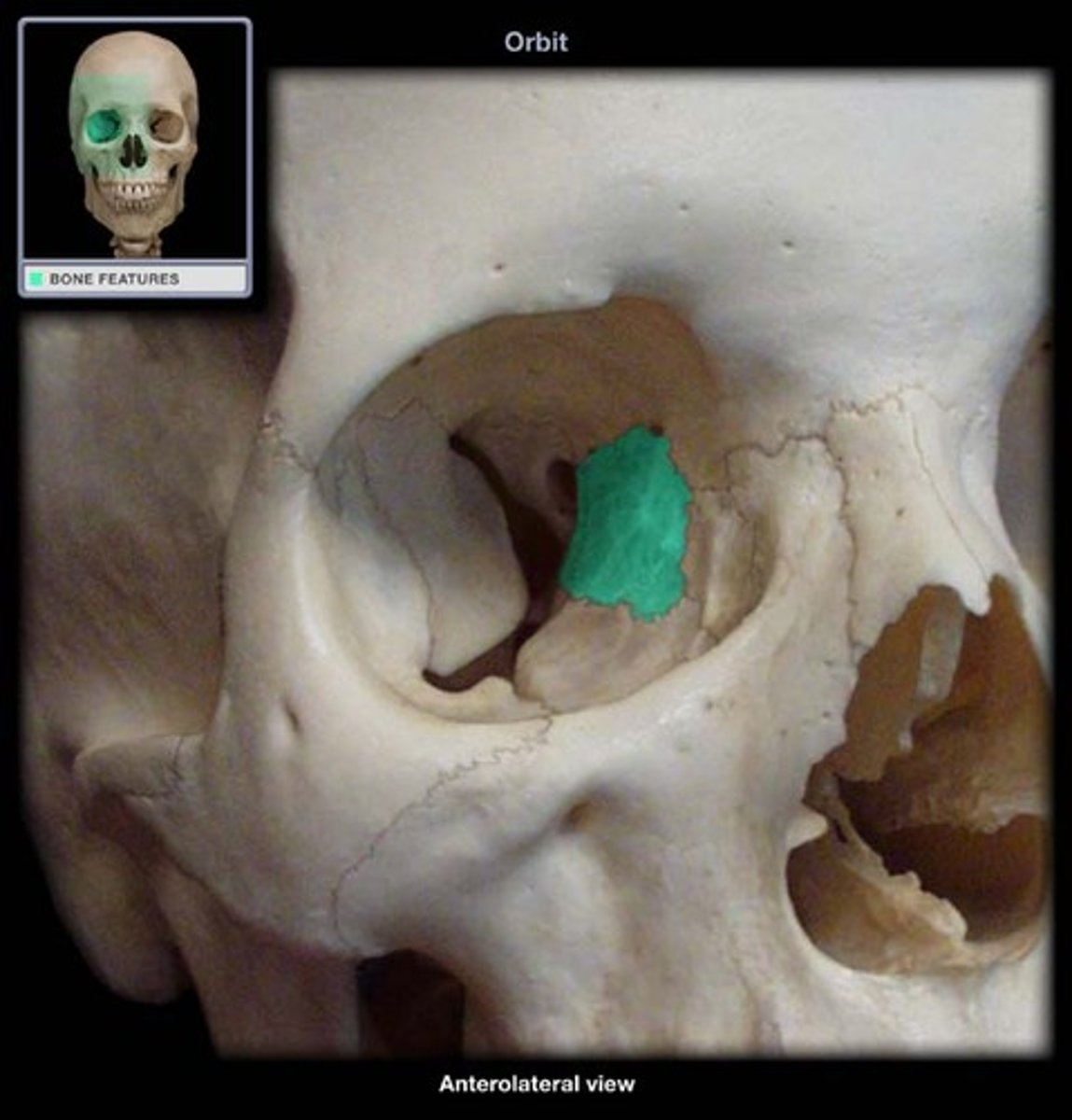
smooth plates which form the medial walls of the eye sockets
orbital plate in ethmoid bone
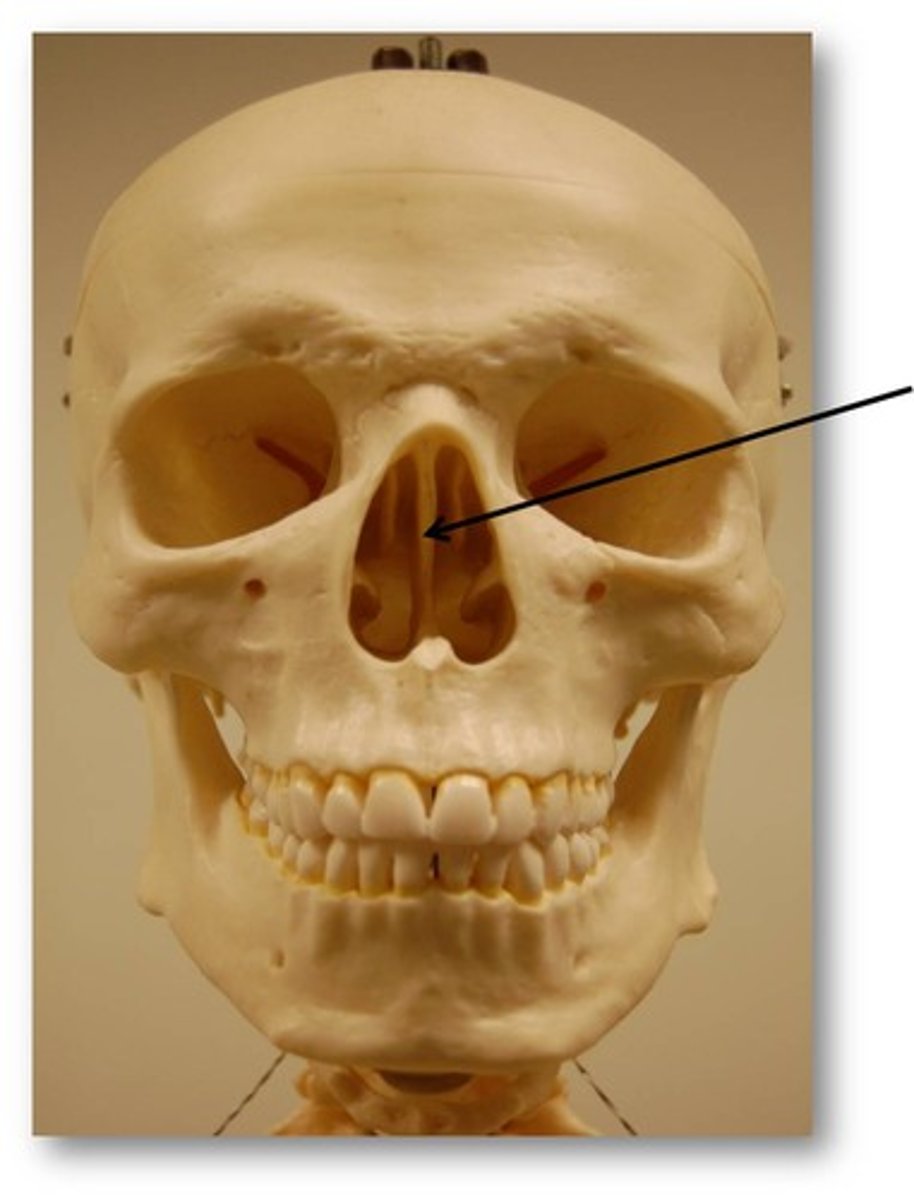
forms superior part of nasal septum
perpendicular plate in ethmoid bone
frontal process in maxillae
lateral bony framework of nose and lateral wall of nasal cavity
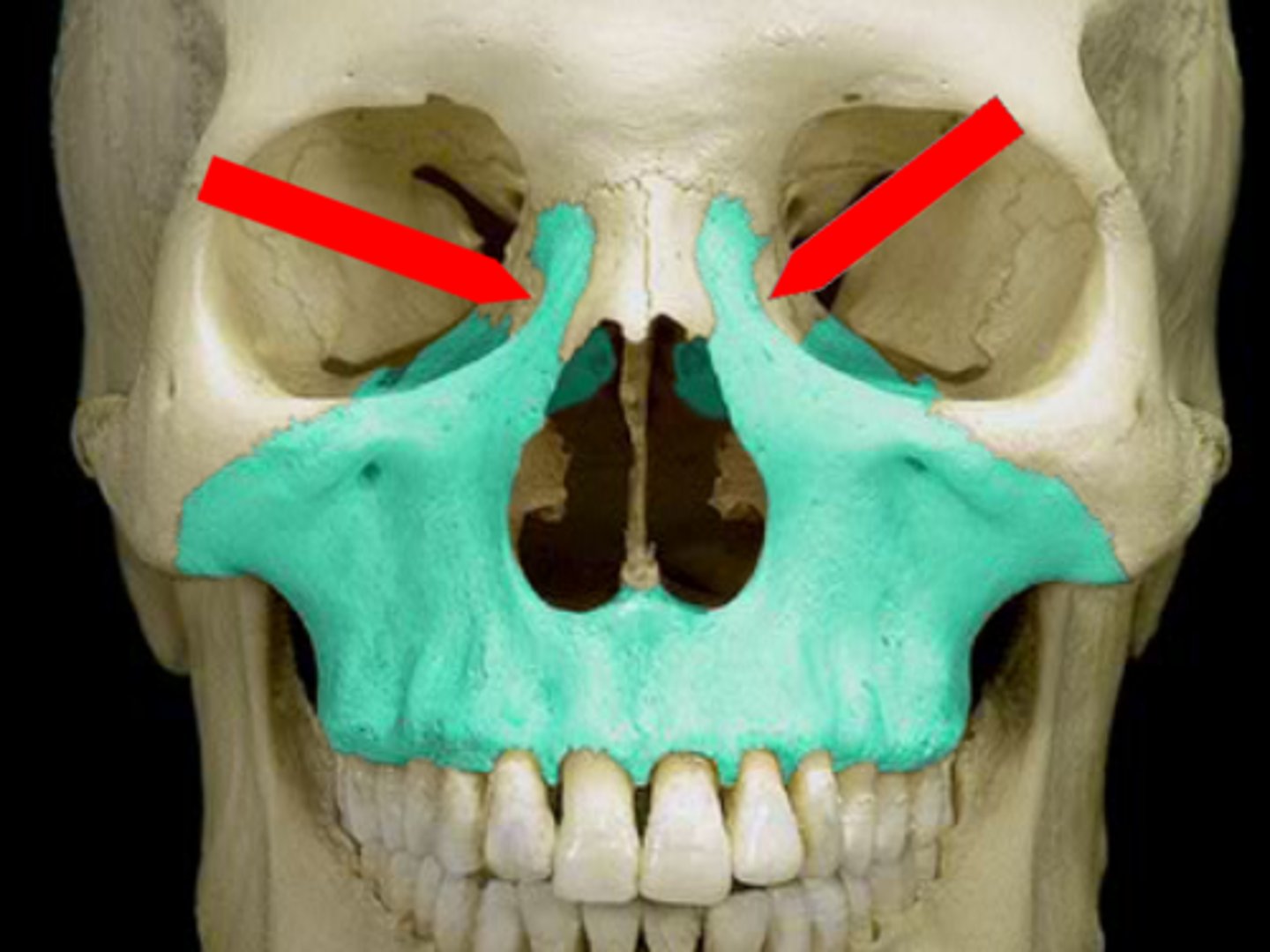
what is this?
lacrimal notch in maxillae
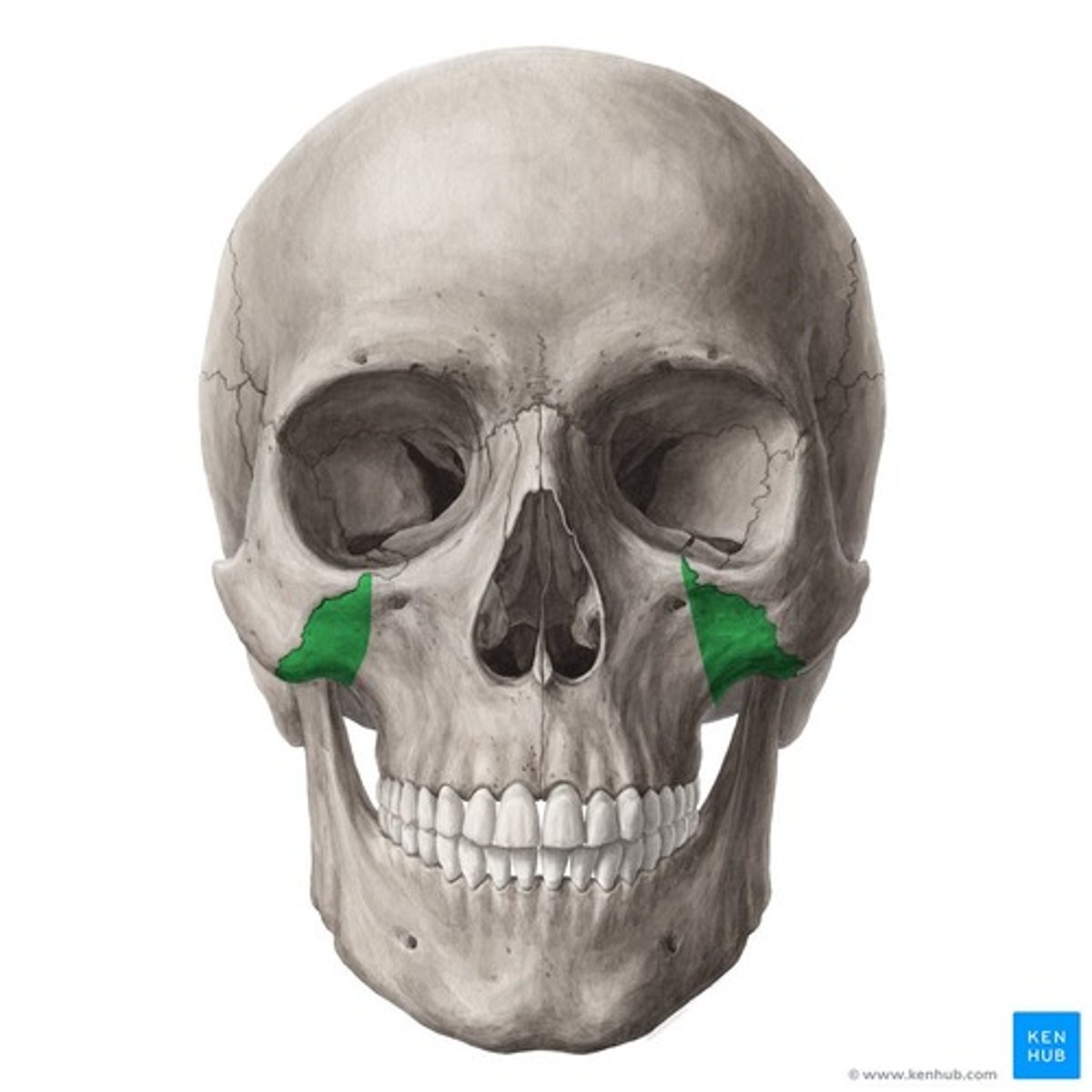
meets zygomatic bone, forms part of inferior orbital rim and orbital floor
zygomatic process in maxillae
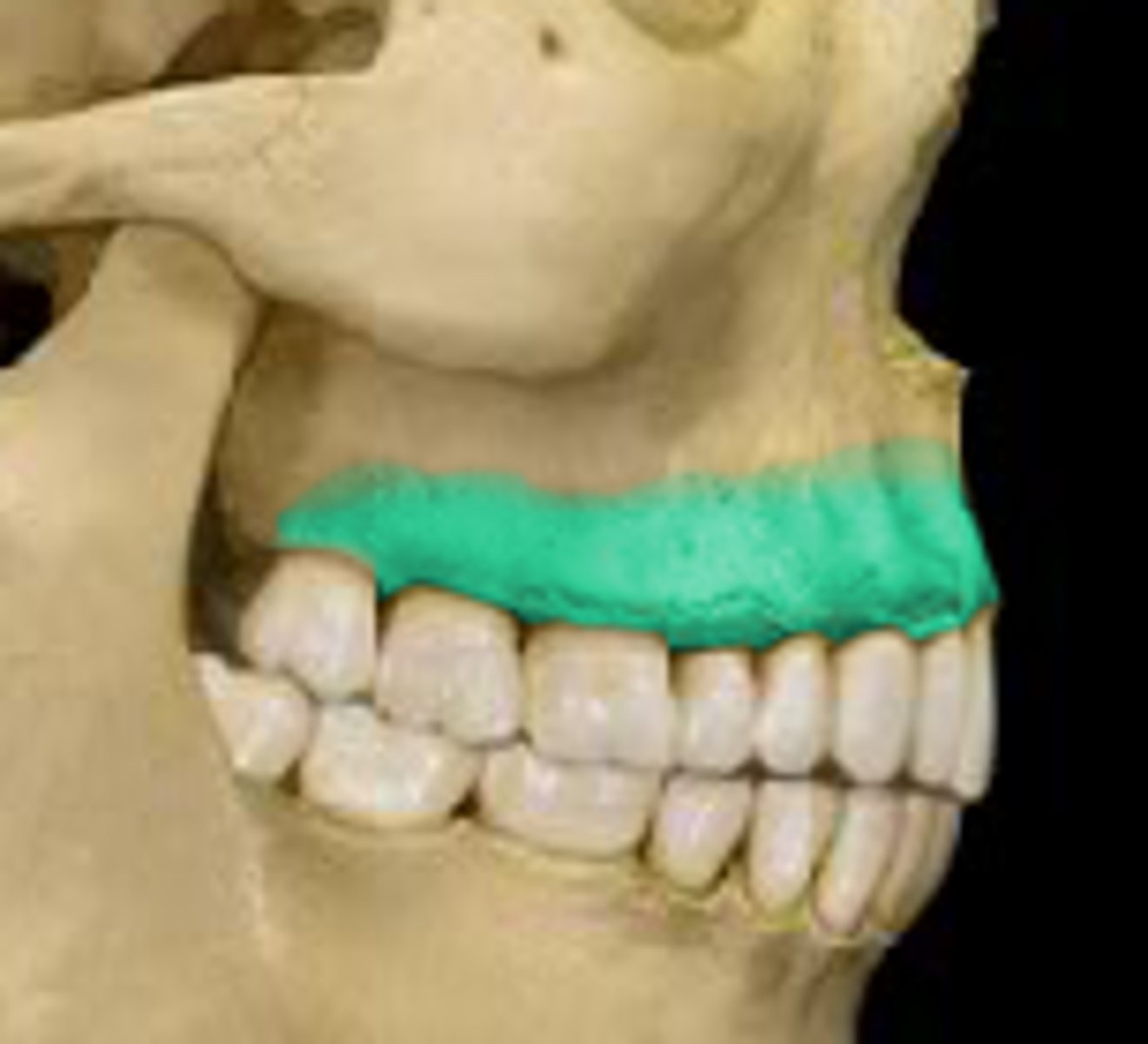
Portion of the maxillary bones that form the support for teeth of the maxillary arch
alveolar process in maxillae
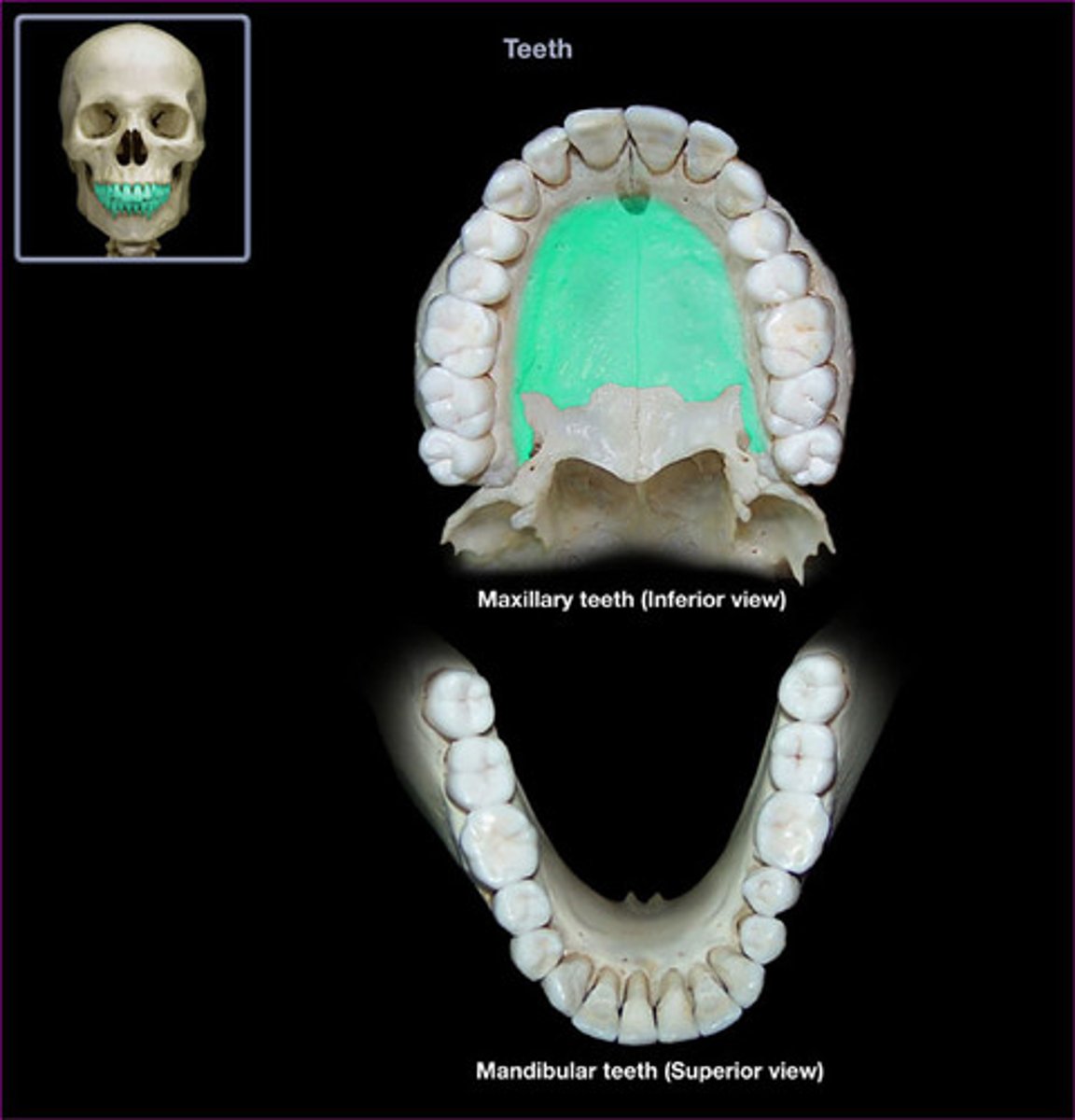
roof of the mouth
palatine process in maxillae
what is this?
sinus in maxillae
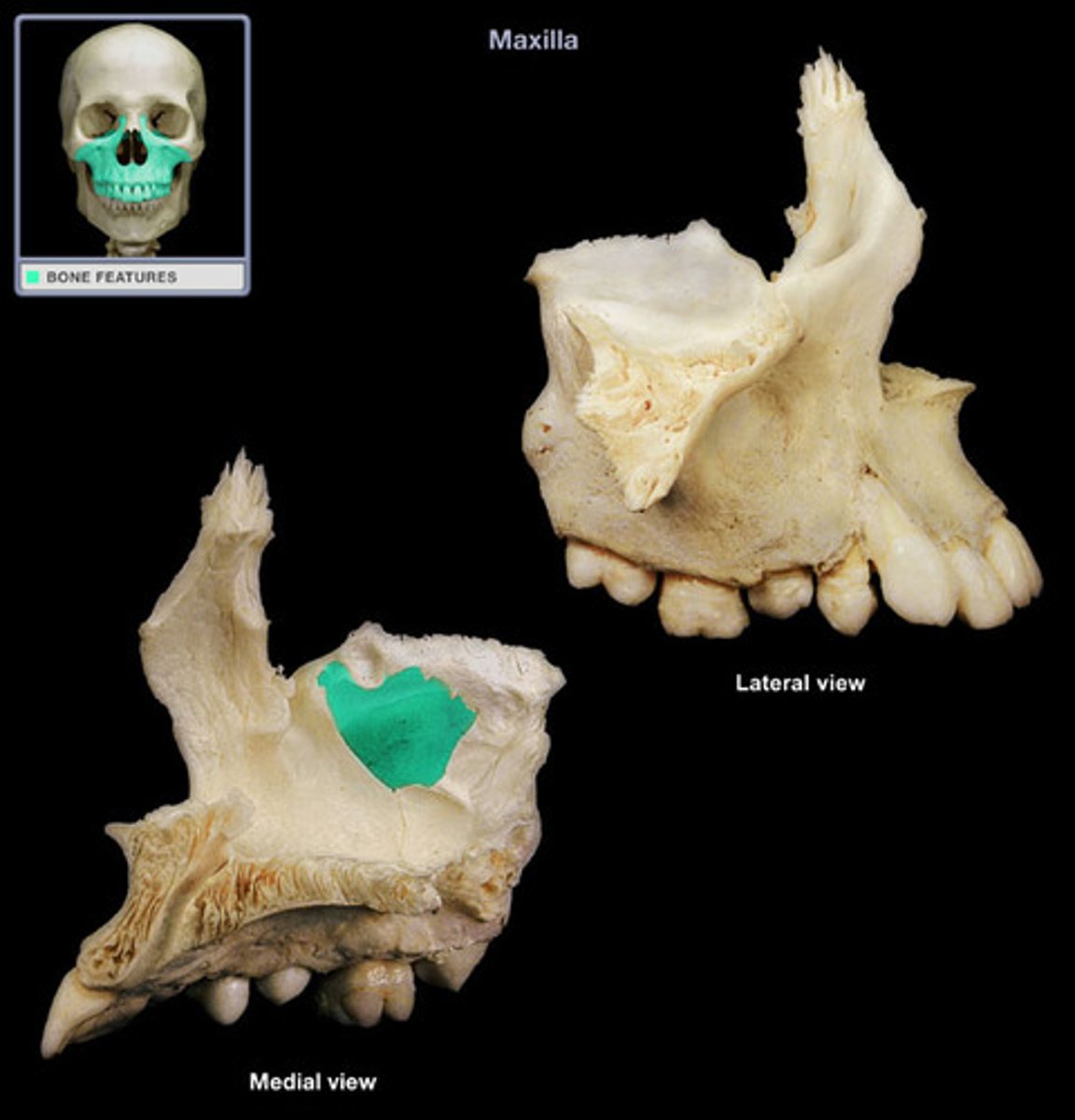
forms the lateral wall of the orbit and it articulates with the frontal bone
frontal process in zygomatic bone
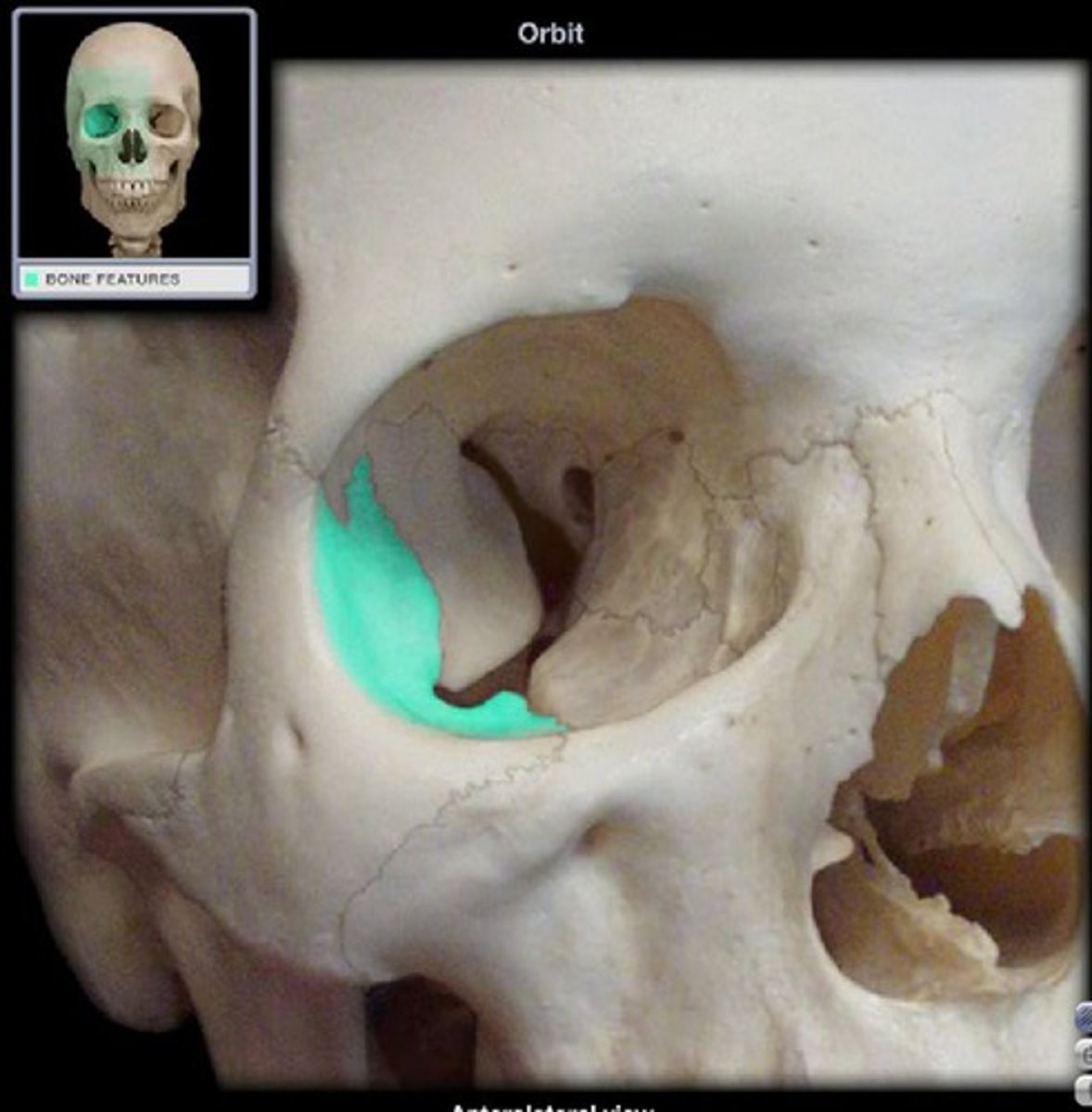
lateral surface of eye orbits
orbital surface in zygomatic bone
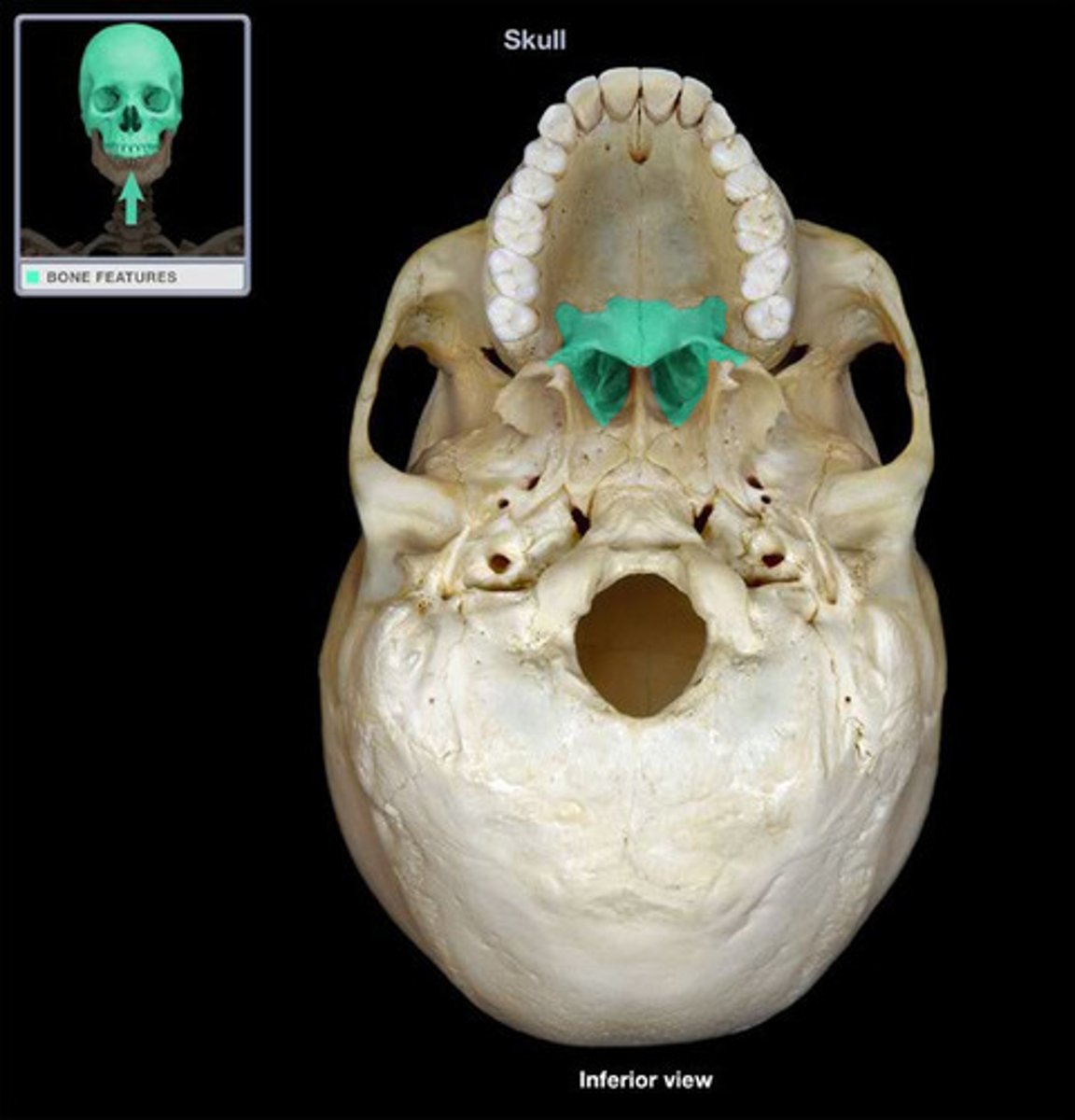
either of two irregularly shaped bones that form the back of the hard palate and helps to form the nasal cavity and the floor of the orbits
Palatine bone (horizontal plate)
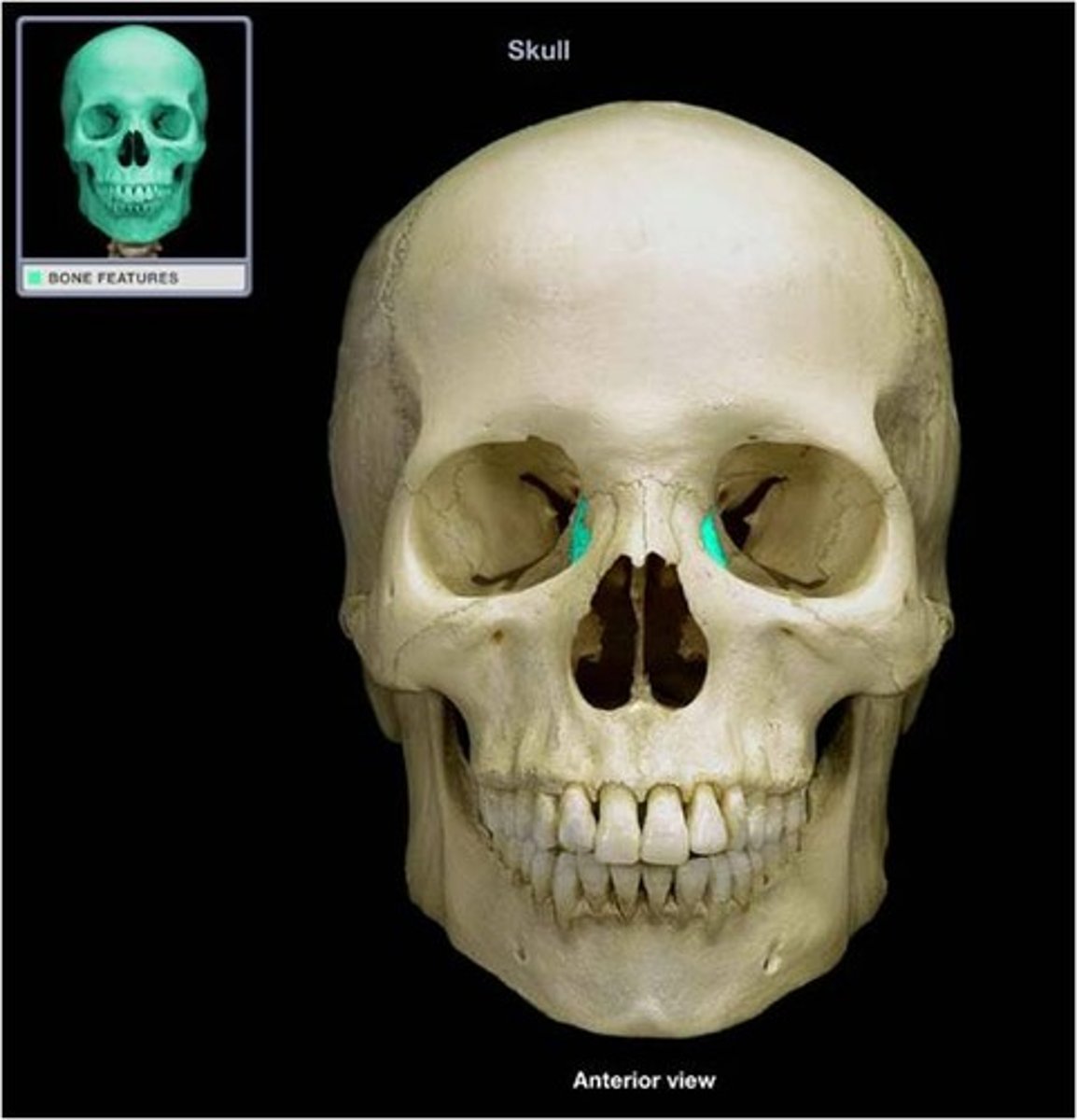
thinnest and most fragile bones in the entire body
lacrimal and nasal bones
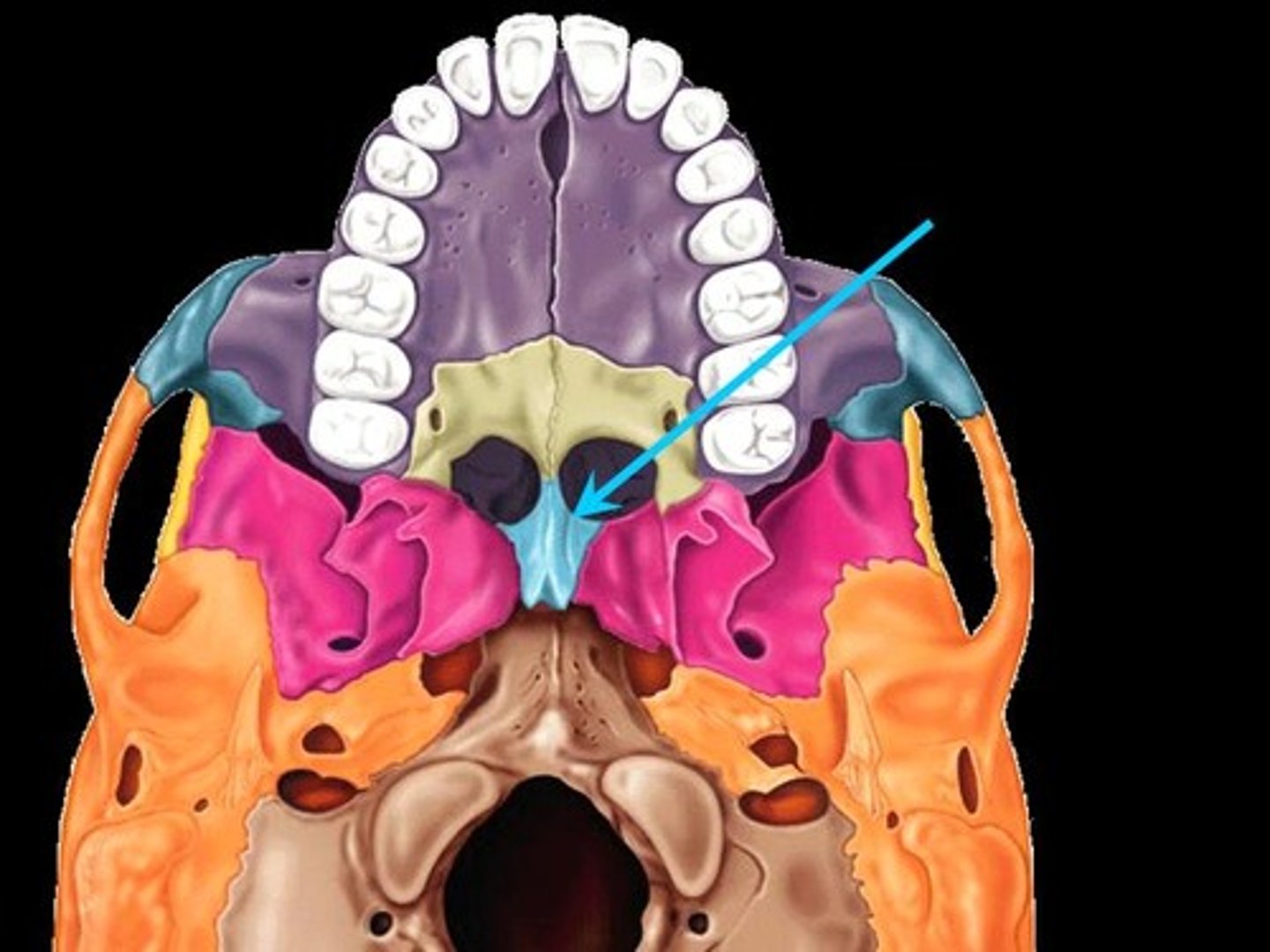
located on either side of the midline groove on the superior surface of the vomer. Is the thickest part of the vomer
vomer (ala)
lower jaw: body, angle, ramus, coronoid process, condylar process, mandibular condyle, alveolar process, mental and mandibular foramen
mandible
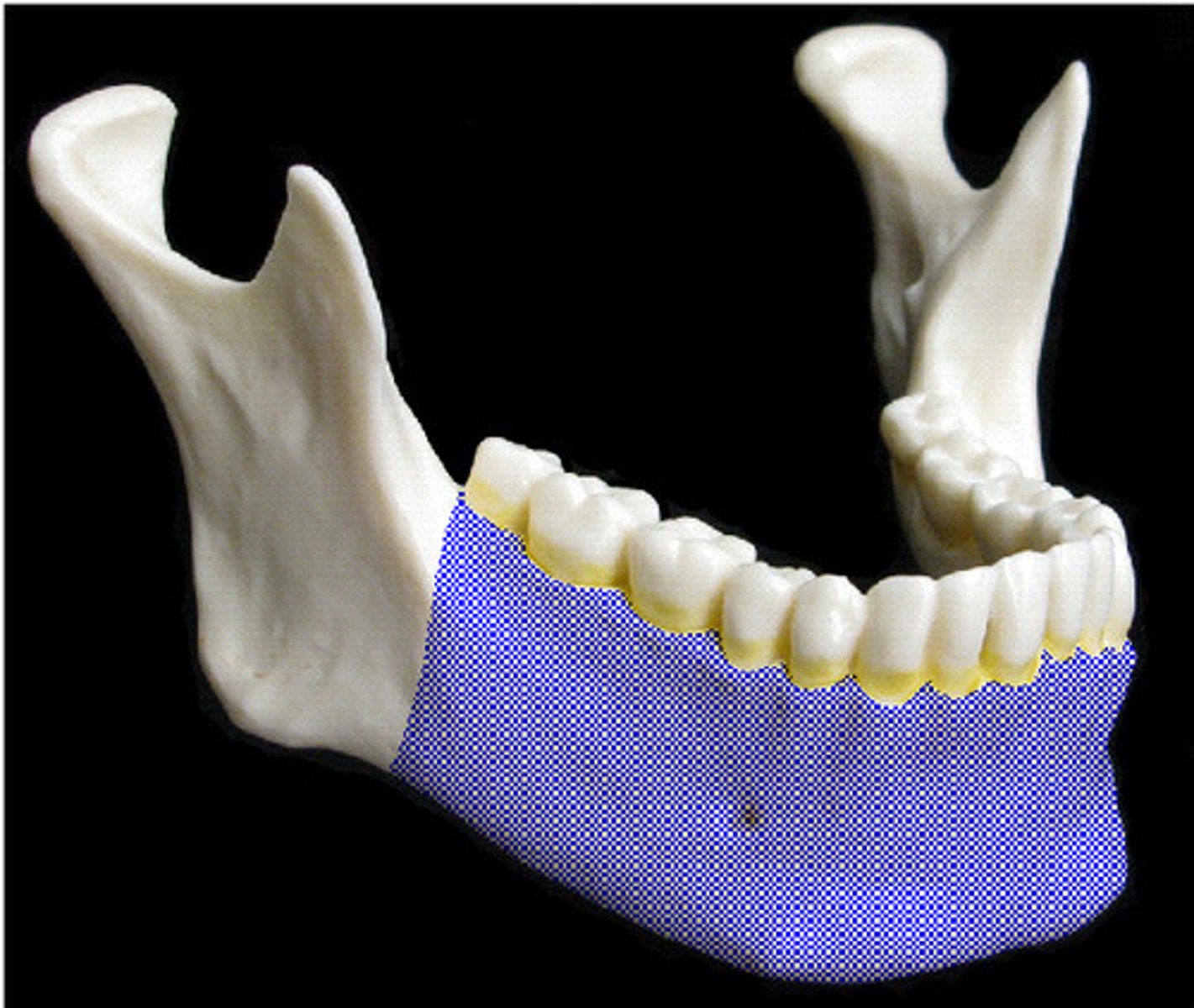
the horizontal portion of the lower jaw
body in mandible
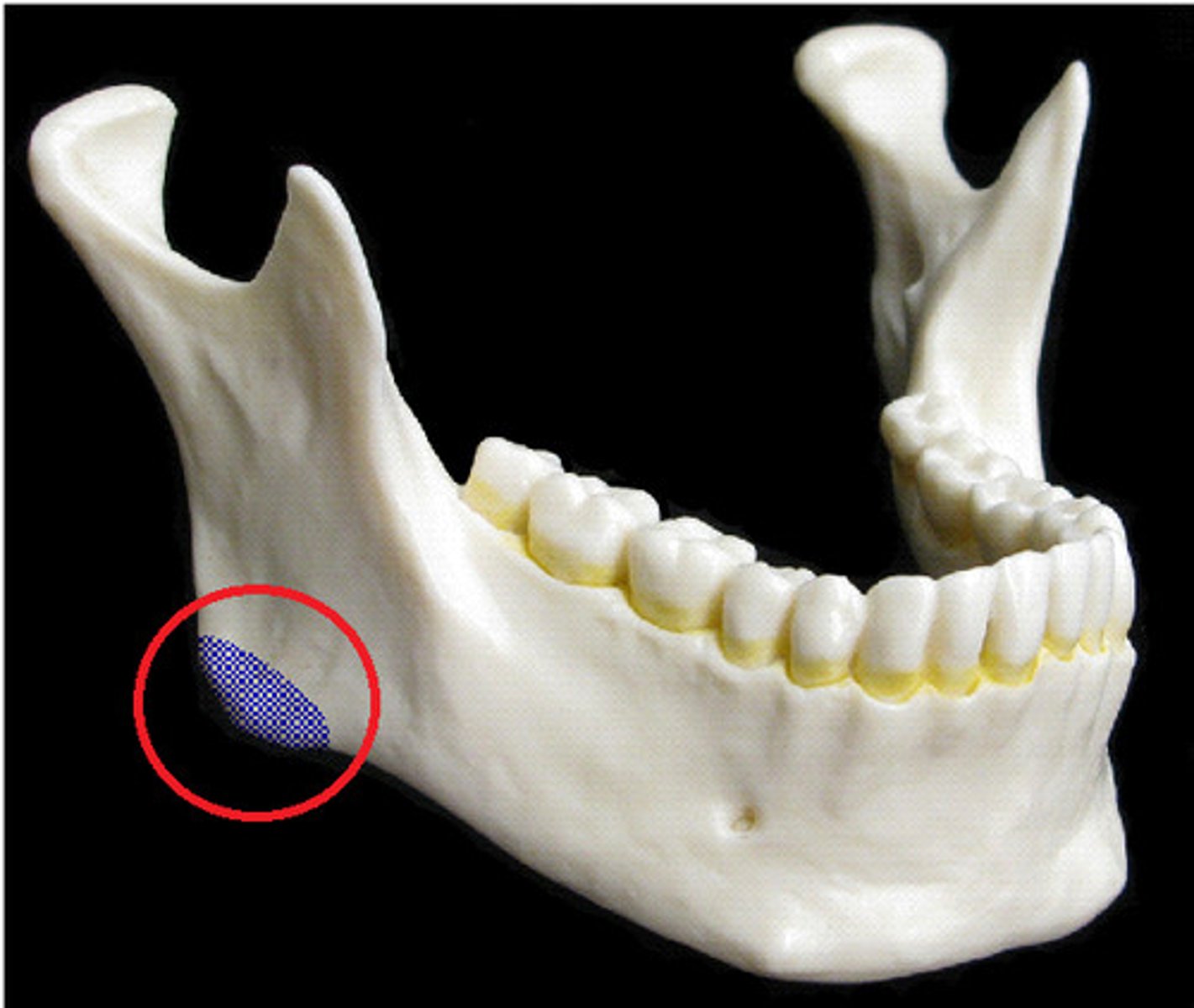
what is this?
angle in mandible
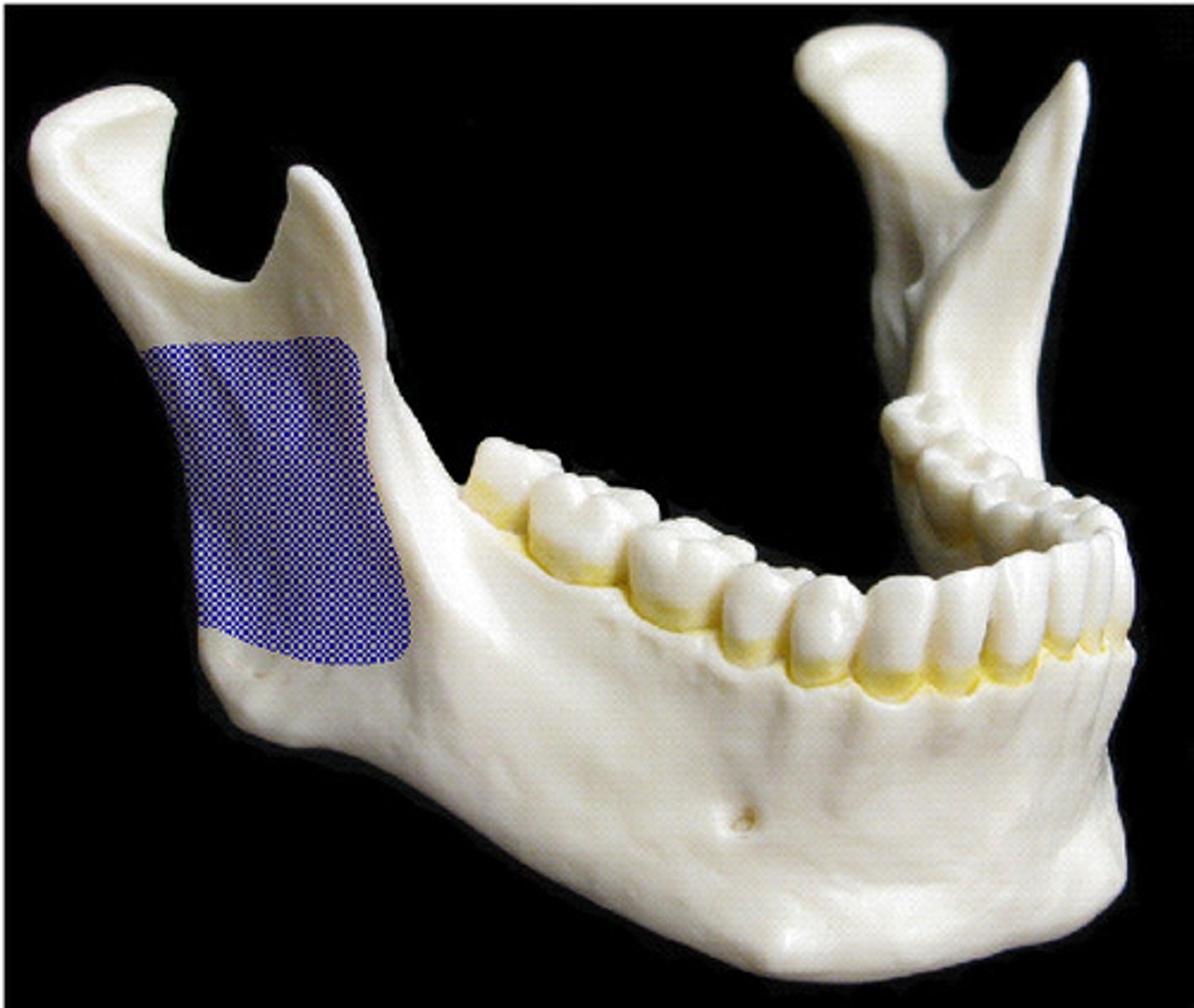
vertical part of mandible
ramus in mandible
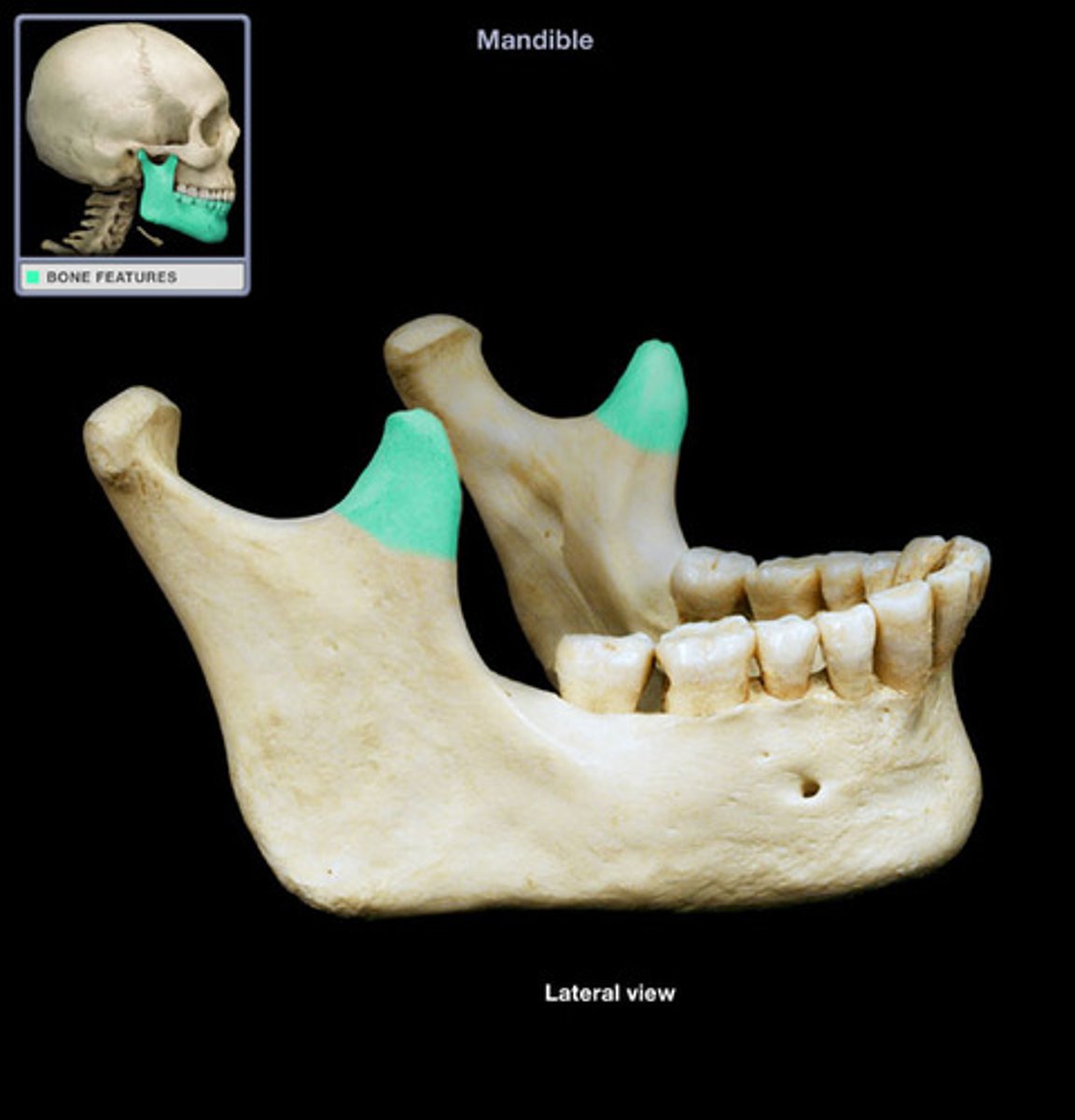
flattened upward projection from the anterior margin of the mandibular ramus
coronoid process in mandible
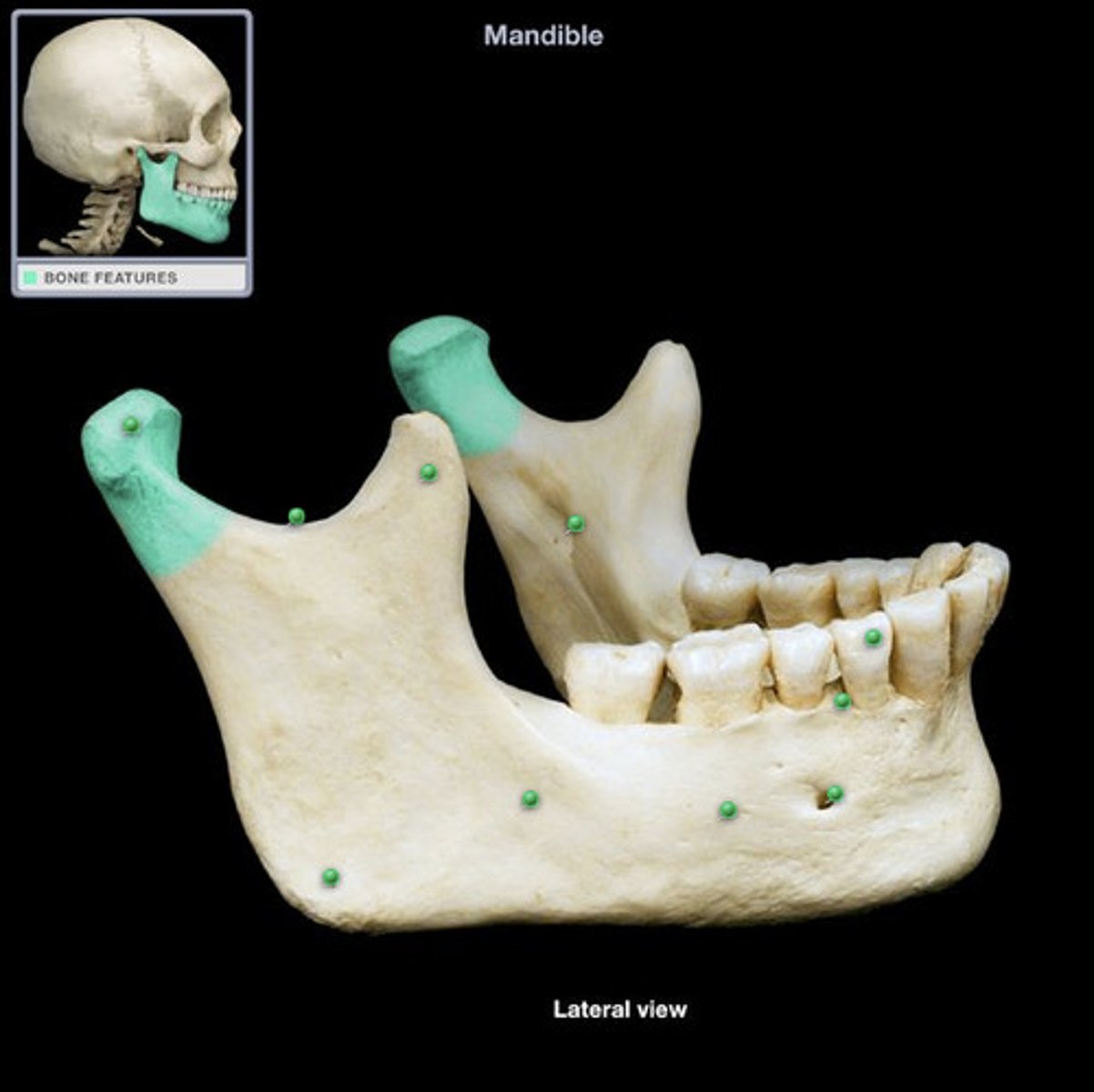
articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
mandibular condyle in mandible
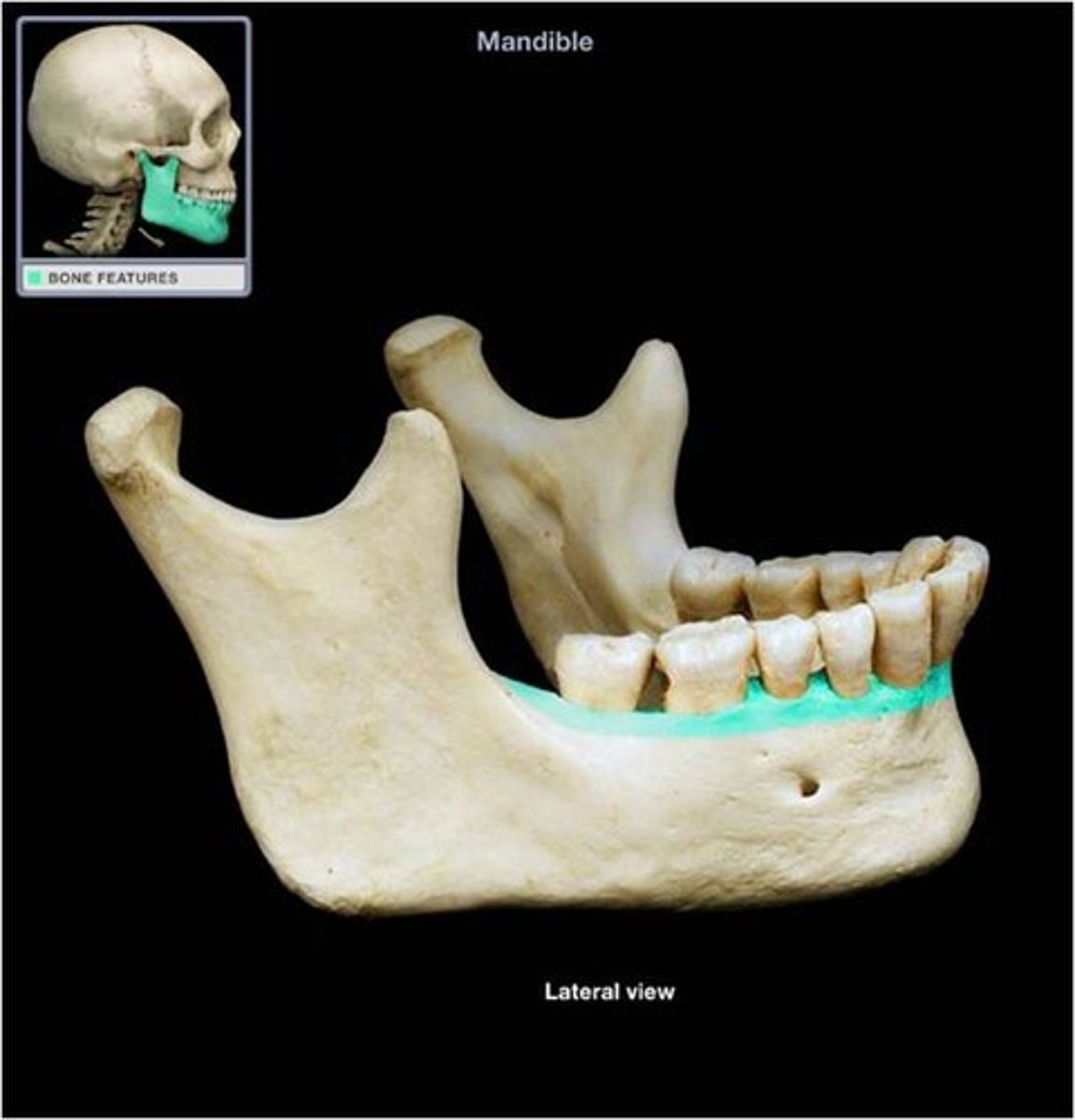
supports the lower teeth
alveolar process in mandible
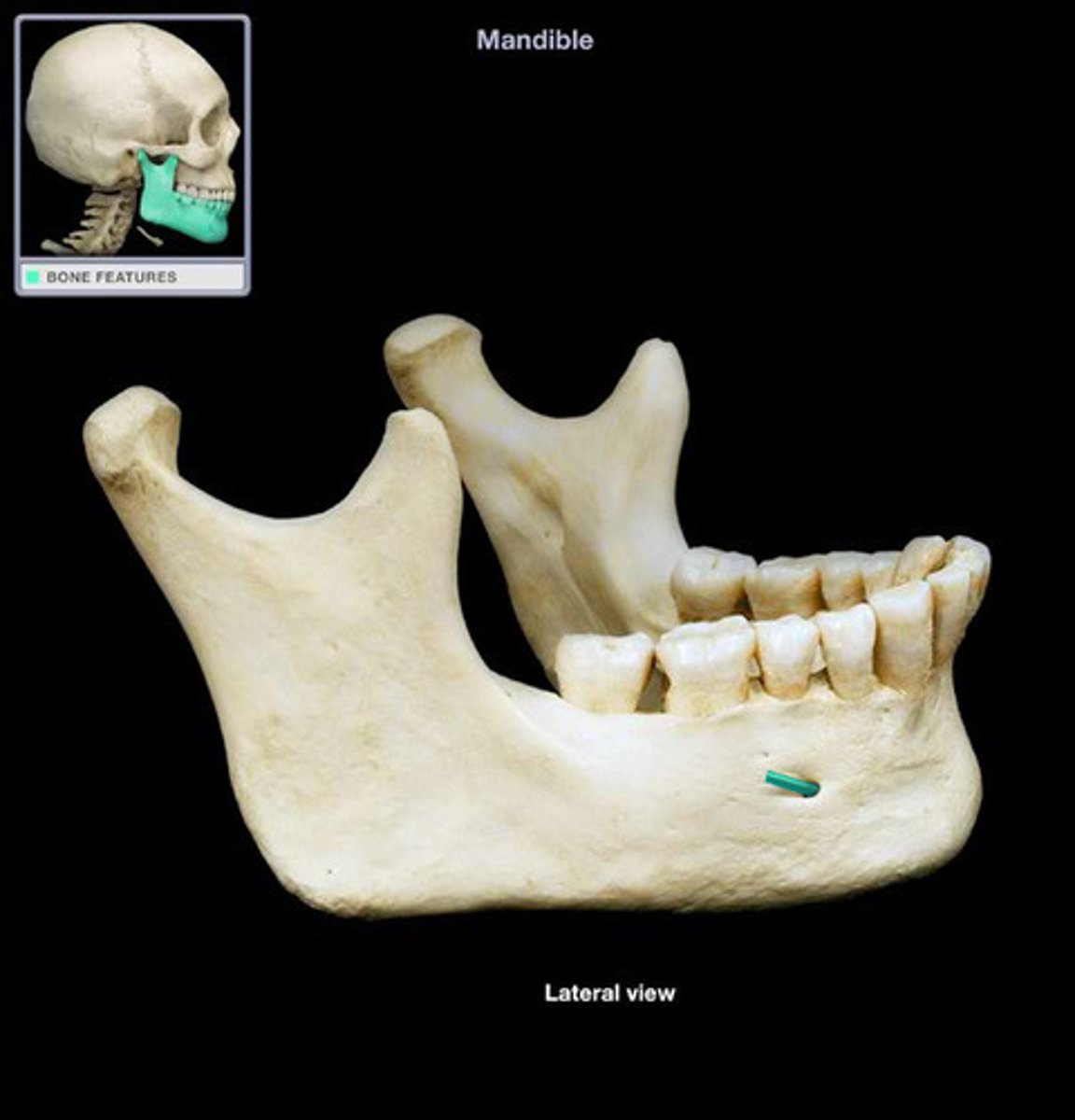
holes in which the cranial nerves travel
mental and mandibular foramen
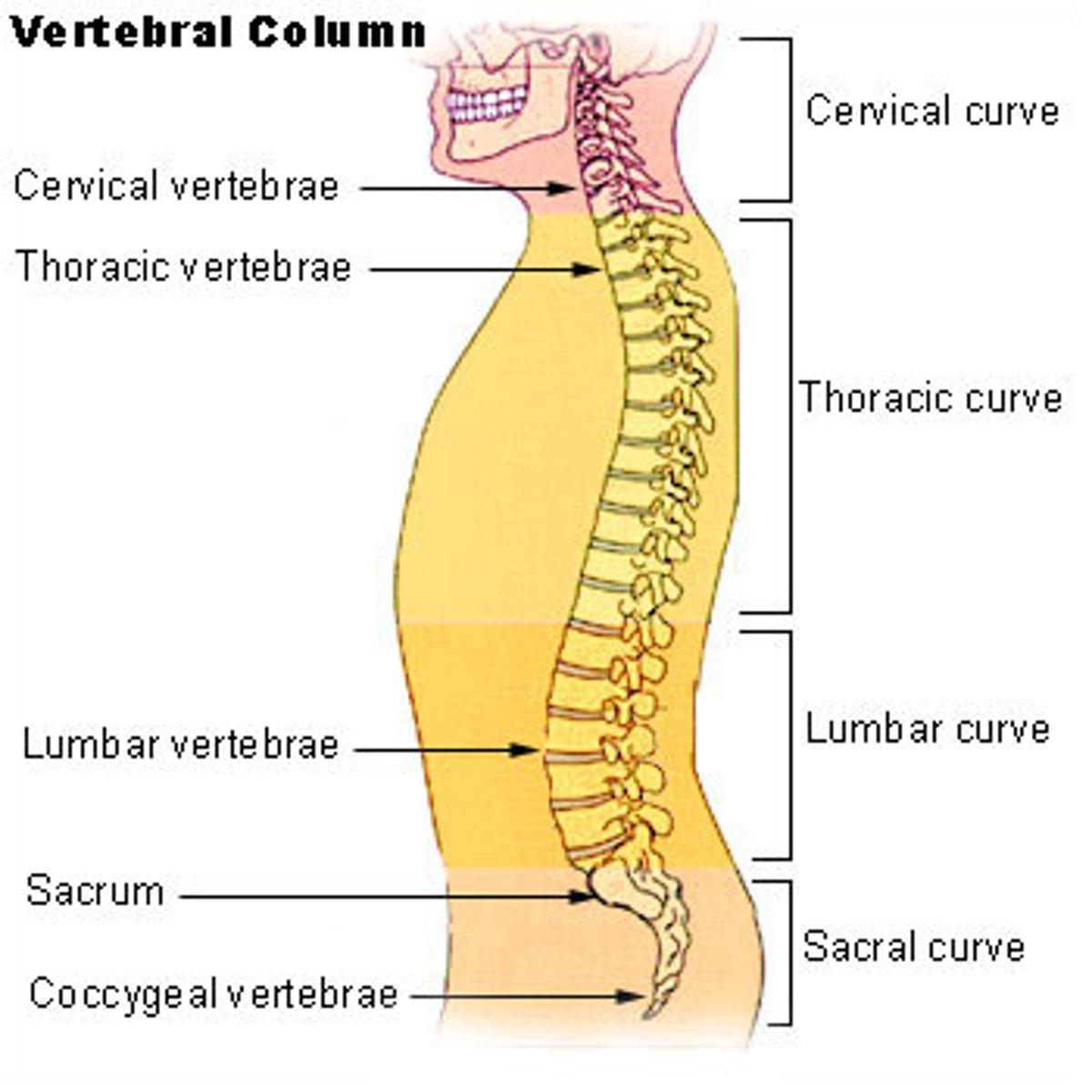
articulated vertebral column, individual vertebra, regional vertebrae,
vertebral column
articulated vertebral column
vertebral canal
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral curvatures
spinal nerves
intervertebral foramen
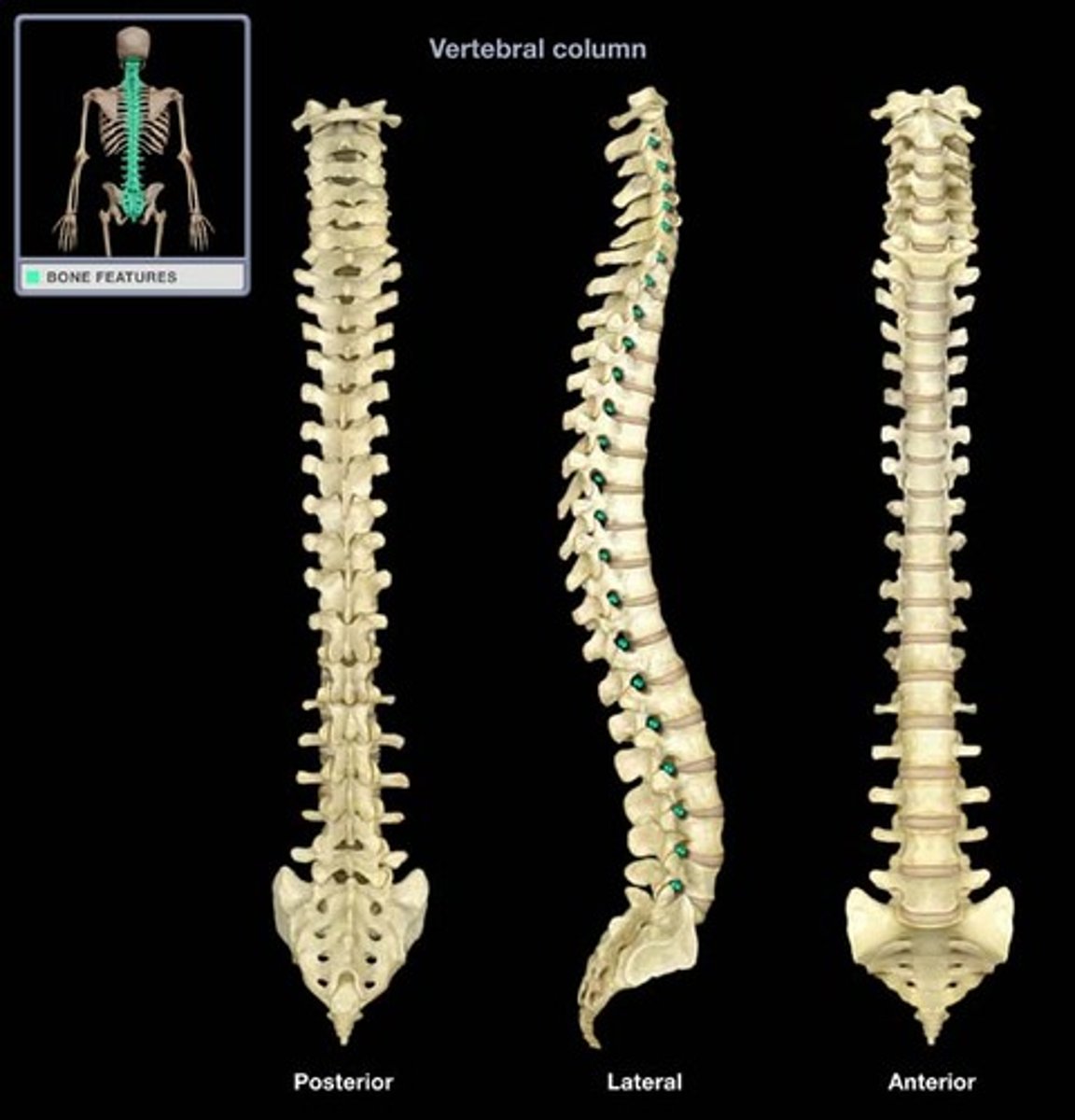

what is this?
intervertebral foramen (articulated vertebral column)
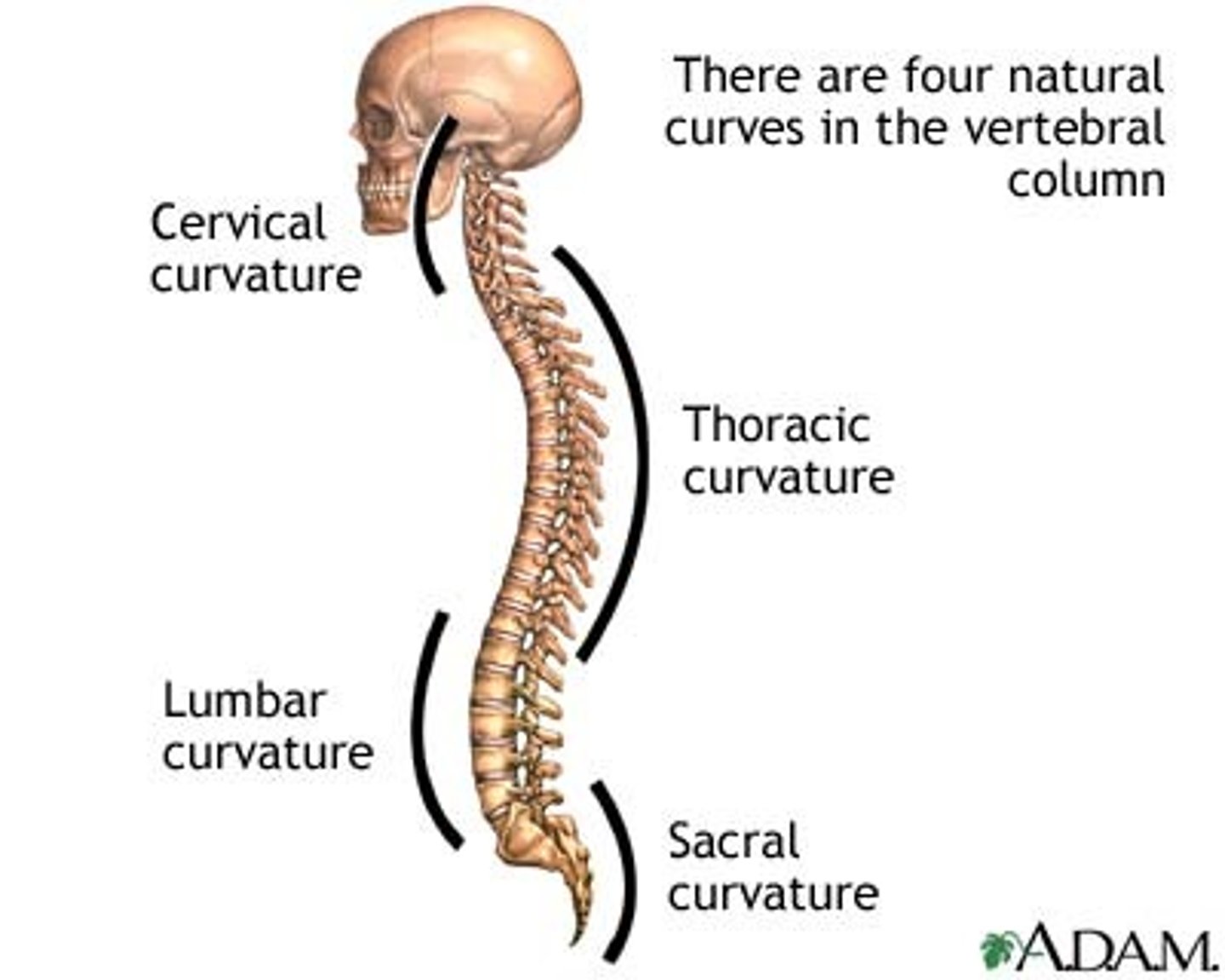
the four curvatures of the vertebral column
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, curvatures
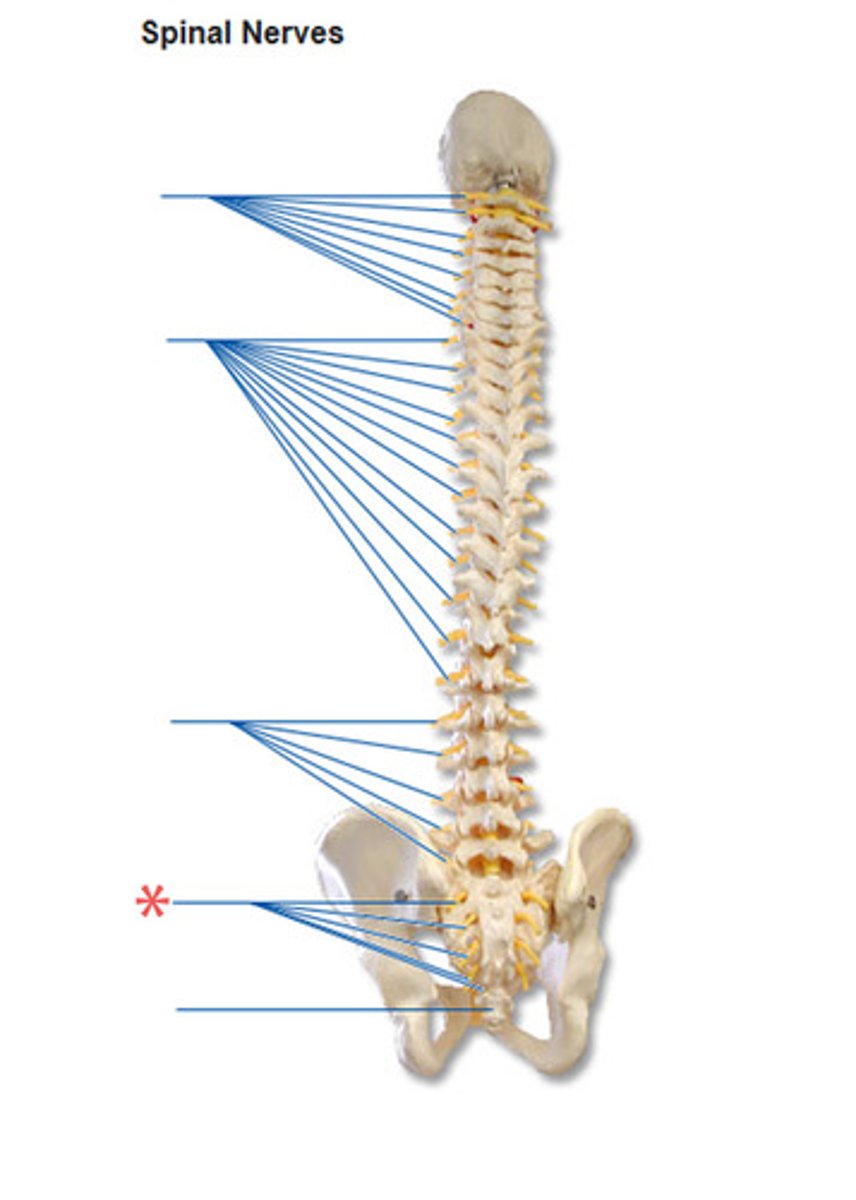
carry impulses to and from the spinal cord
spinal nerves
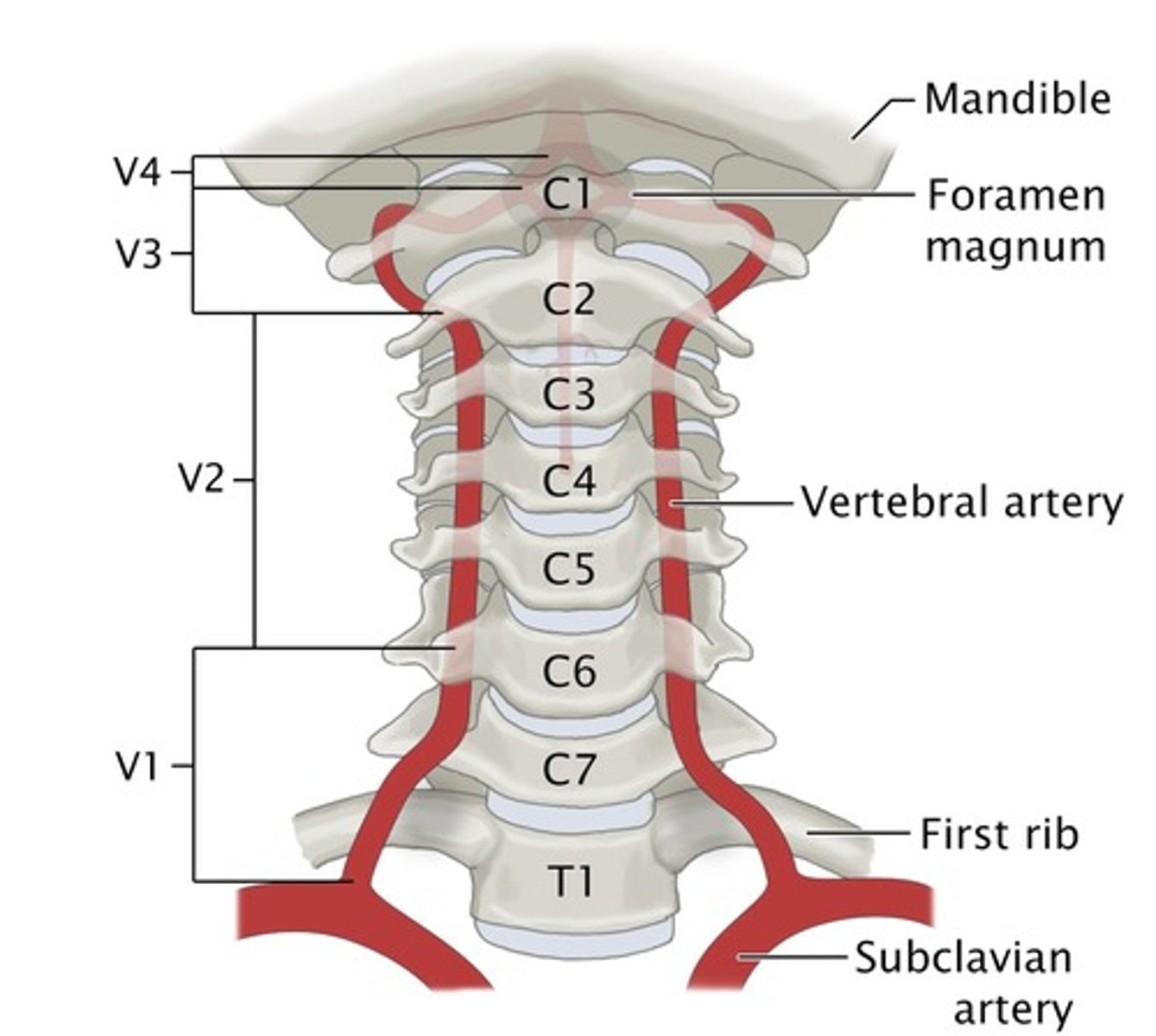
Arteries that ascend the vertebrae, enter the base of the skull, and join together to form the basilar artery.
vertebral arteries (articulated vertebral column)
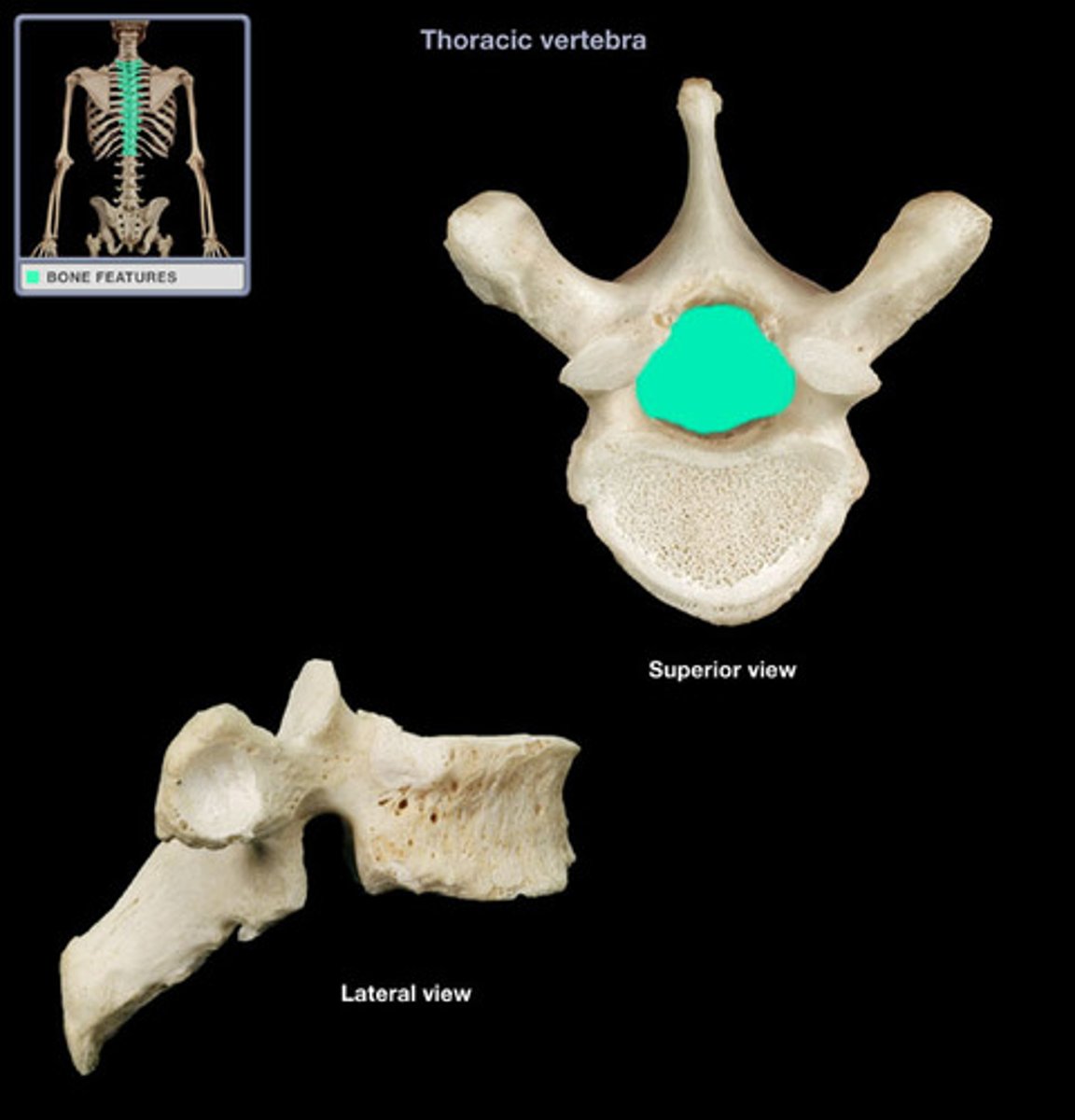
opening for spinal cord
vertebral foramen in vertebrae
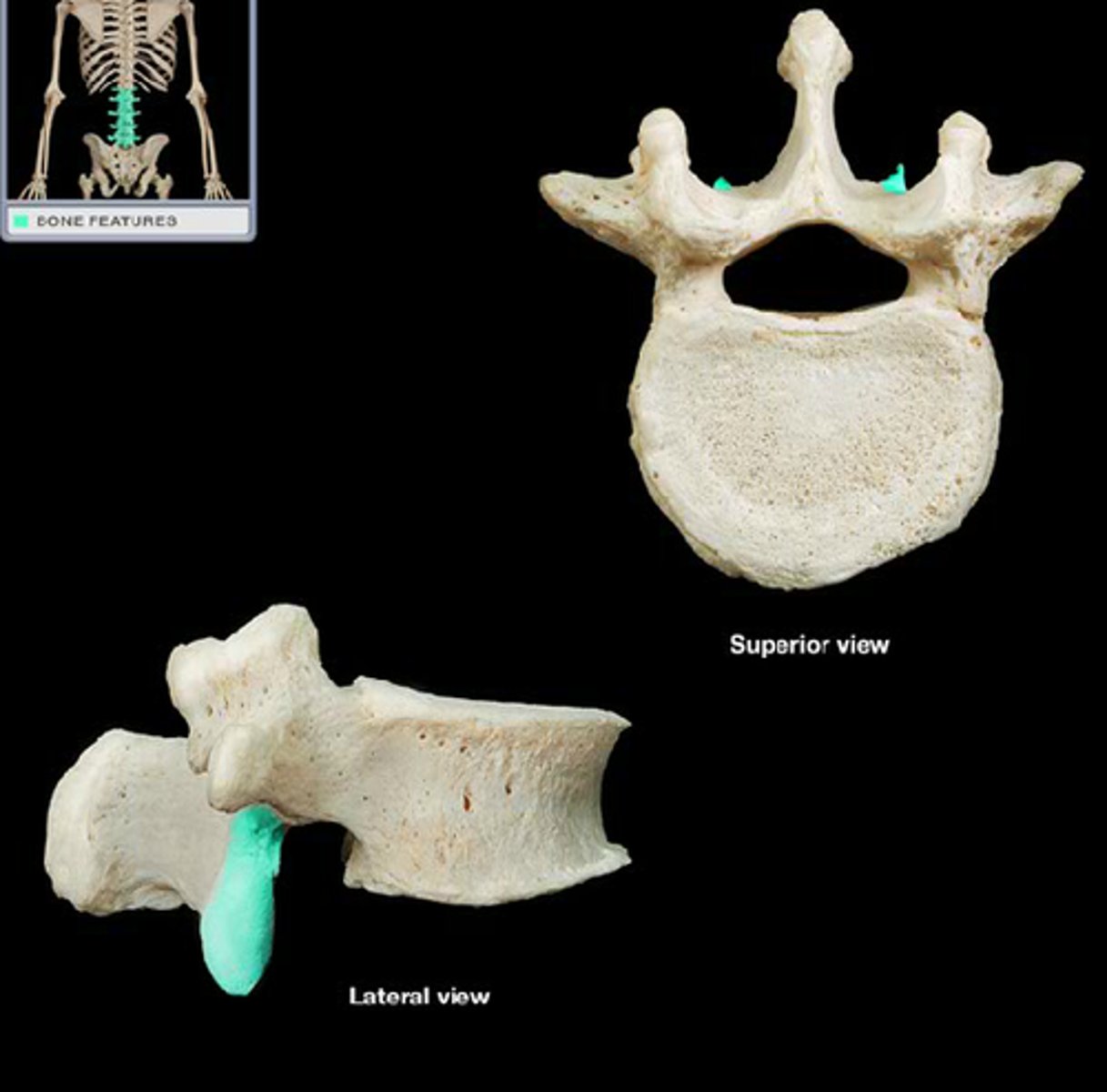
The portion of the vertebrae that points out laterally. Remember the Transverse Plane.
transverse process in vertebrae
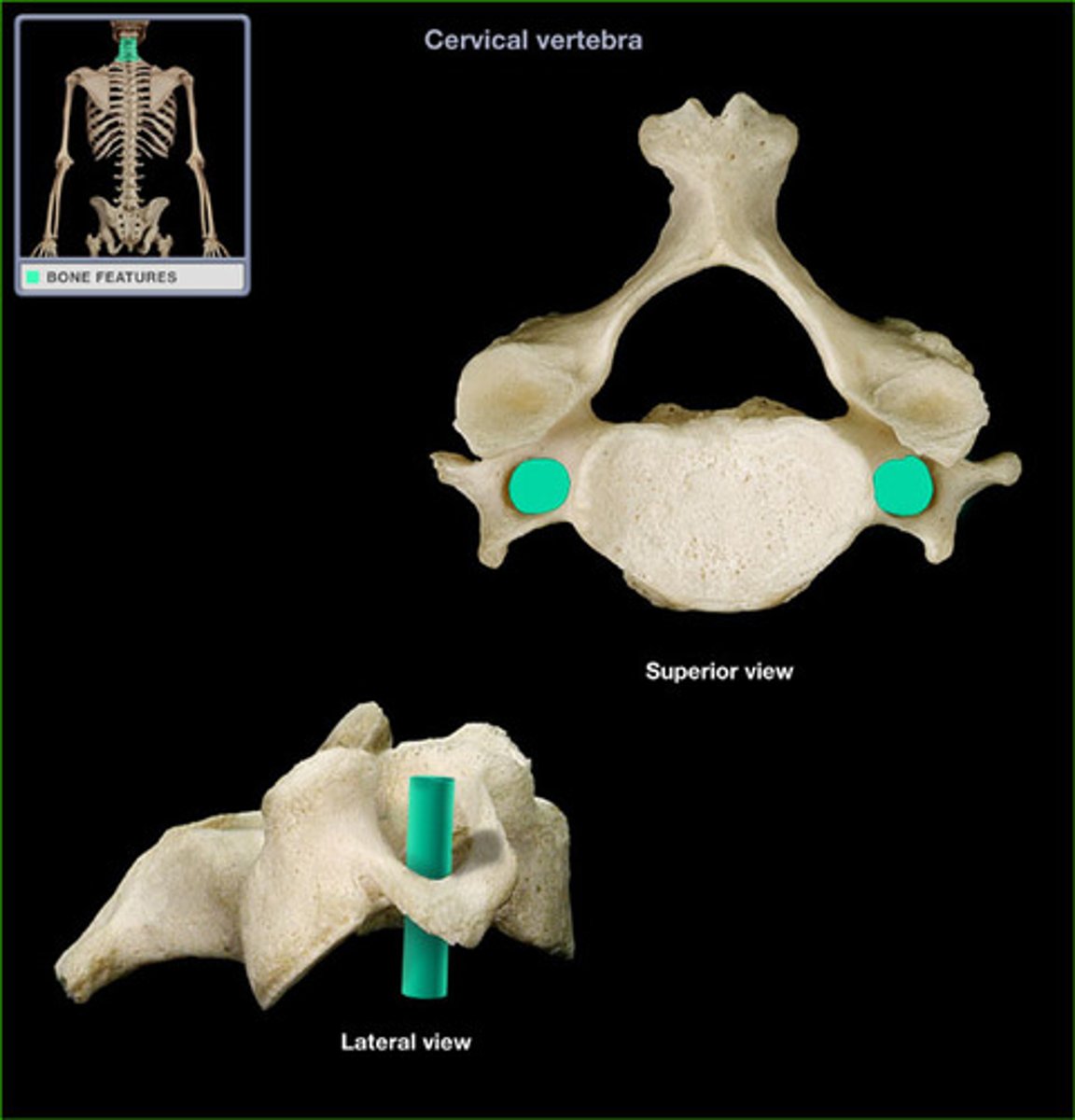
Where does the vertebral artery enter so that it can continue on to the brain?
transverse foramen in vertebrae

The portion of the vertebrae that sticks out posteriorly.
spinous process in vertebrae
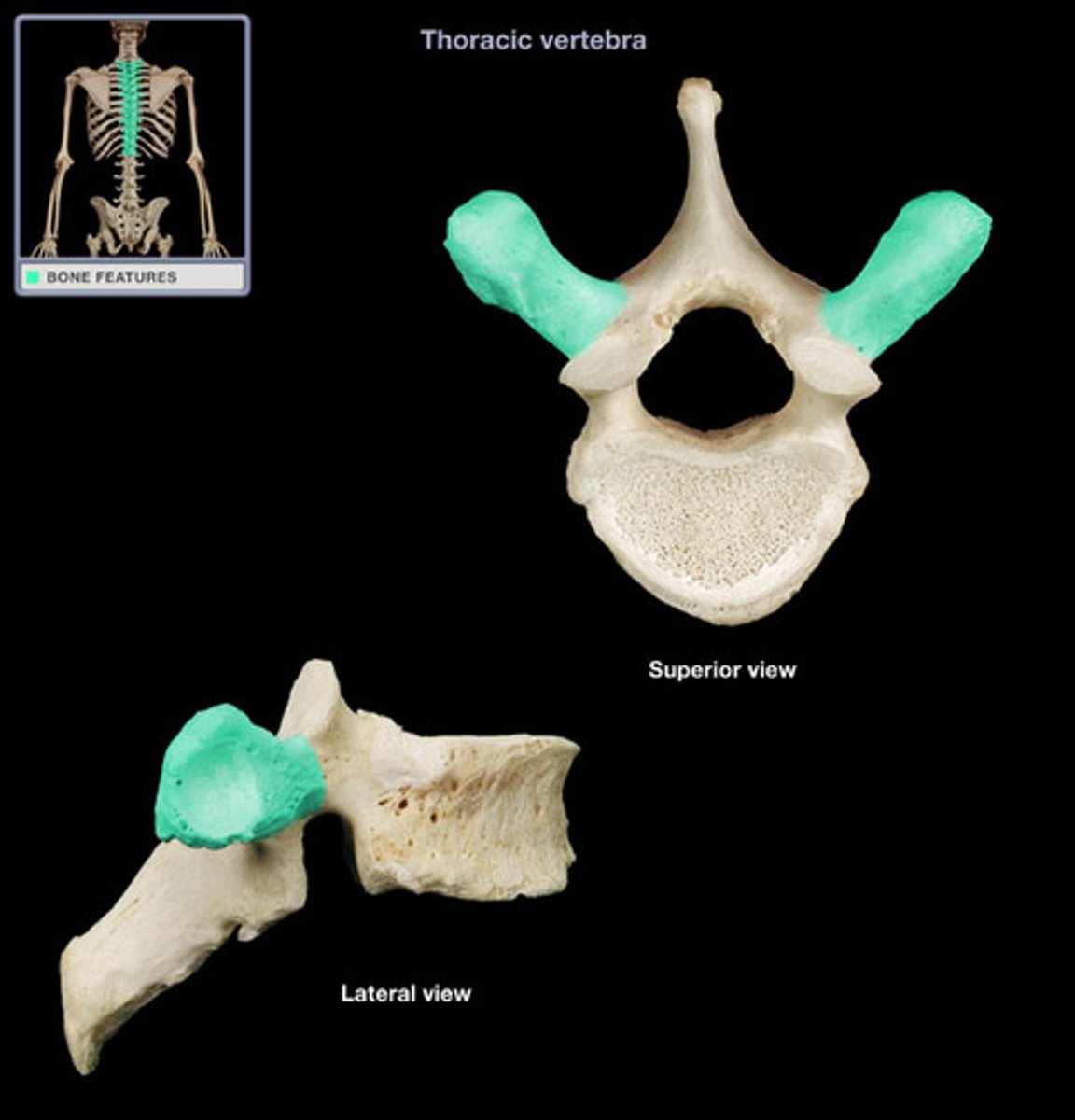
-Location: Superior to pedicles and intermediate to the transverse processes and vertebral body of the vertebrae
-Articulates with: Inferior articular process of the next vertebra just superior to the current vertebra
*Think of the connected rungs of a ladder. The superior articular processes act in this way with the inferior articular processes
superior articular process in vertebrae
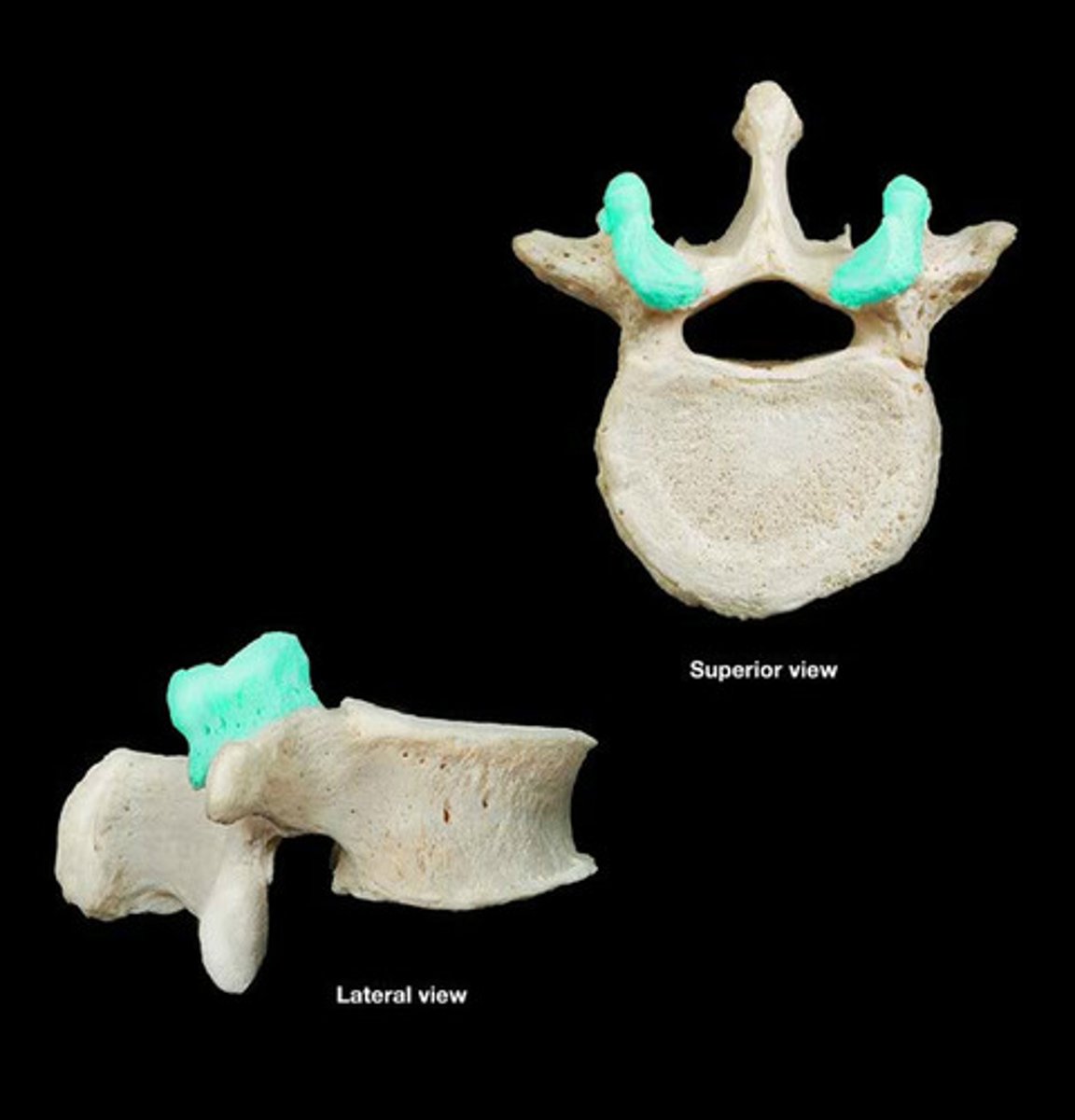
articular process that arises at the junction between the pedicles and laminae; projects caudally
inferior articular process (vertebrae)
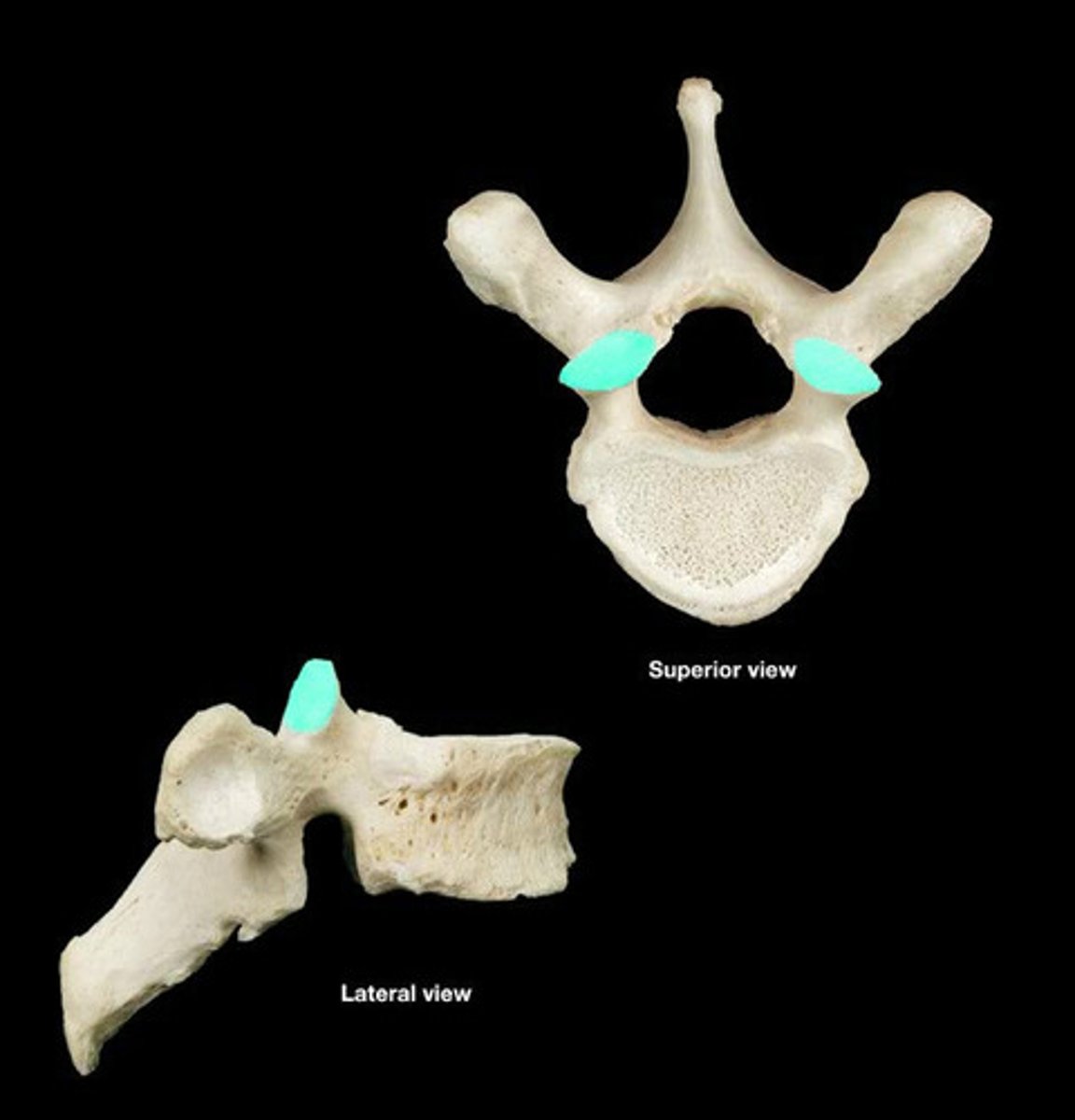
articulate with the inferior articular facets of superior vertebrae
superior articular facets
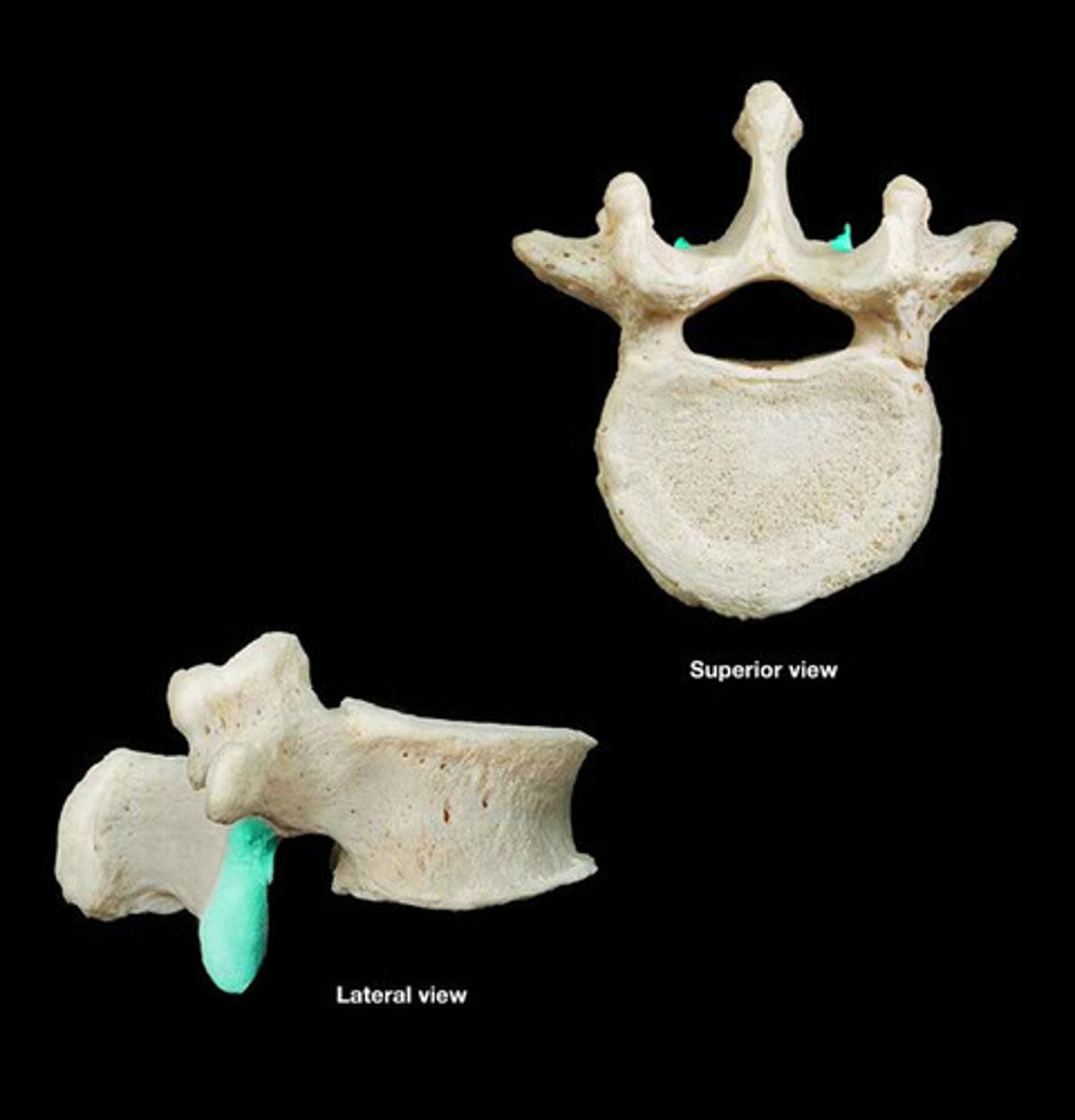
articulate with the superior articular facets of inferior vertebrae
inferior articular facets
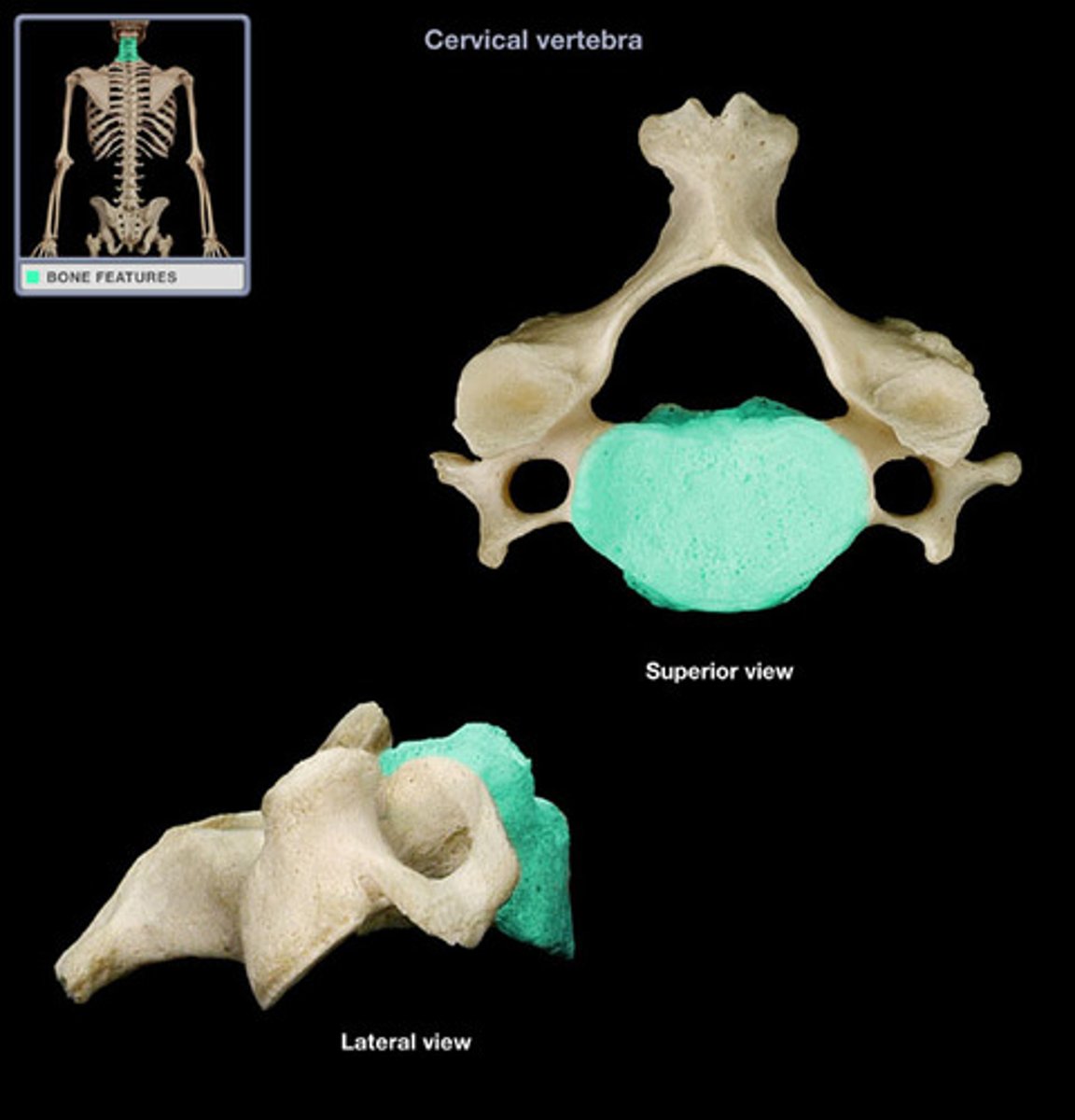
the thick, disc-shaped anterior portion which is the weight bearing portion
body of vertebrae
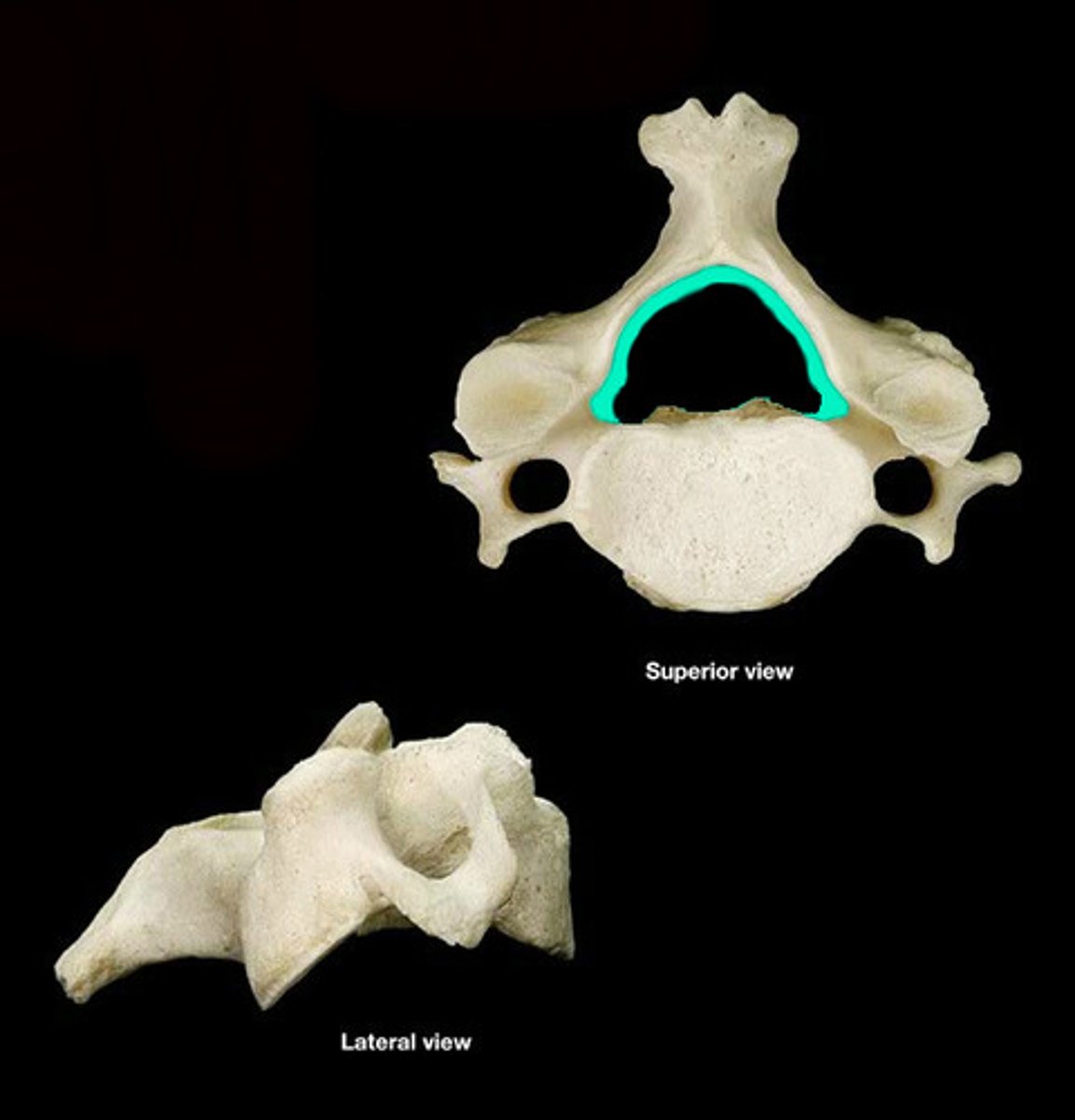
protects the spinal cord
vertebral arch
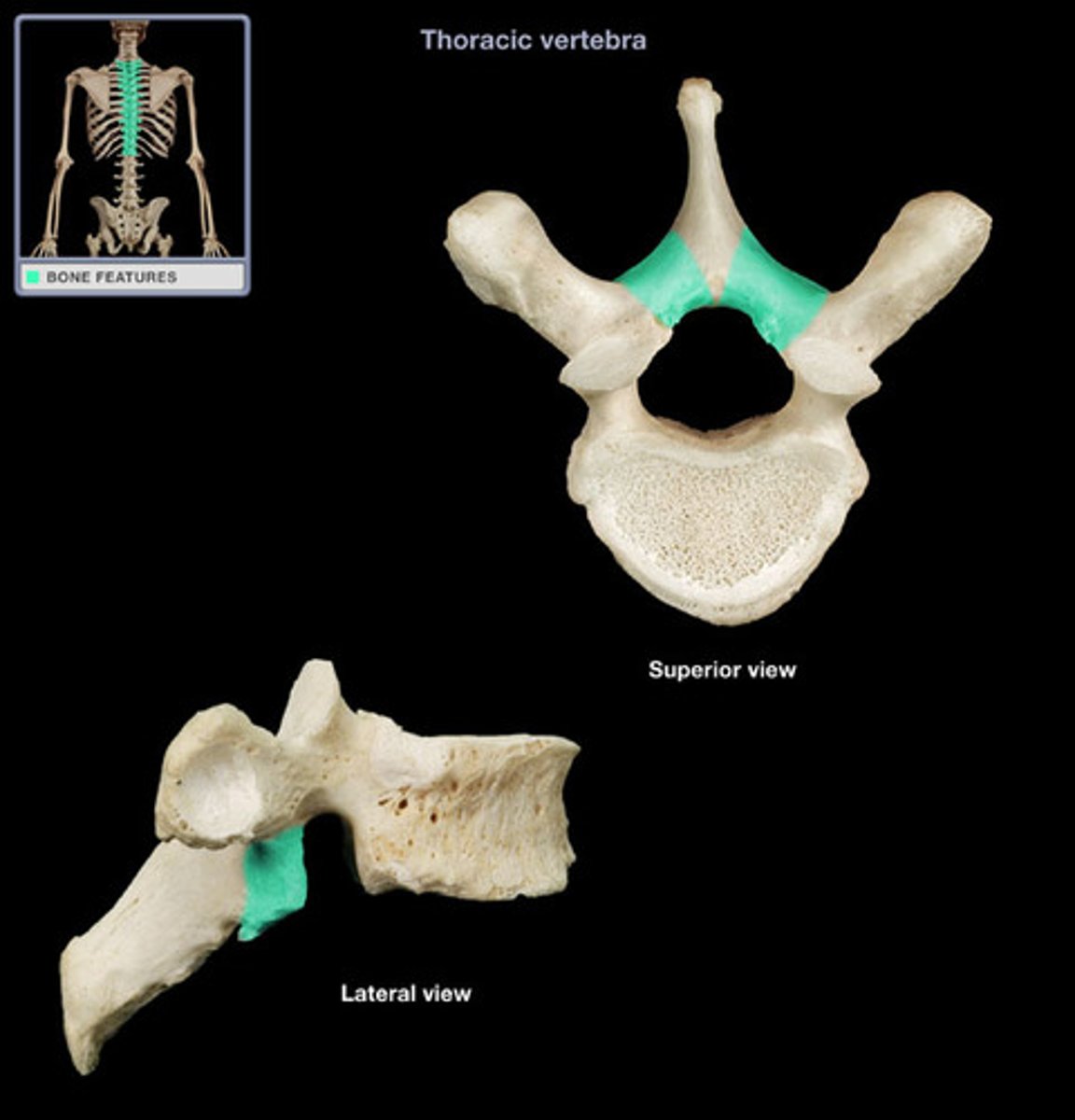
A thin layer or flat plate of a vertebra between the transverse process and the spinous process.
lamina (vertebrae)
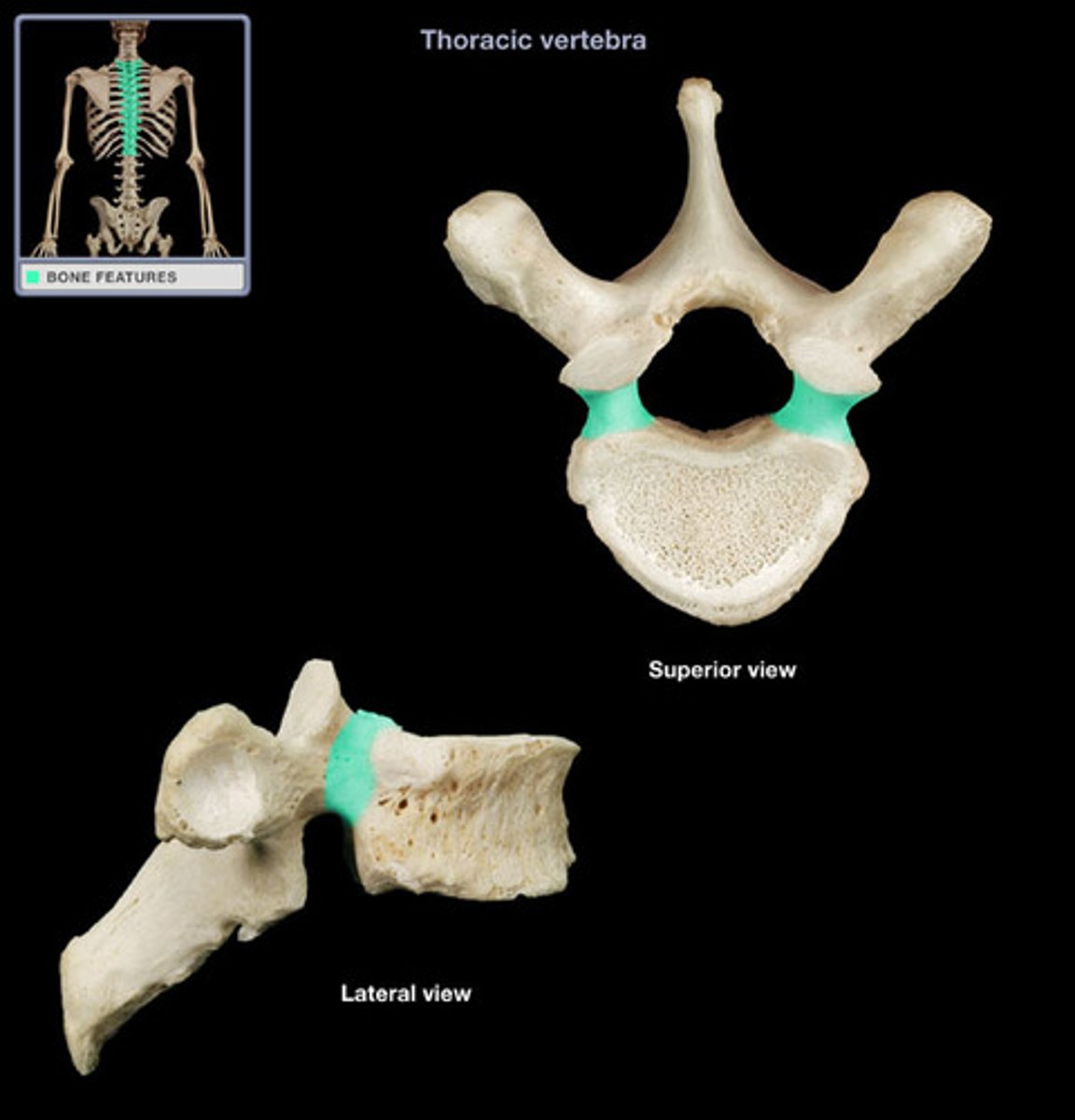
attached to and extends posteriorly on either side of the body
pedicle (vertebrae)

transverse foramen, dens, bifed
cervical region contains
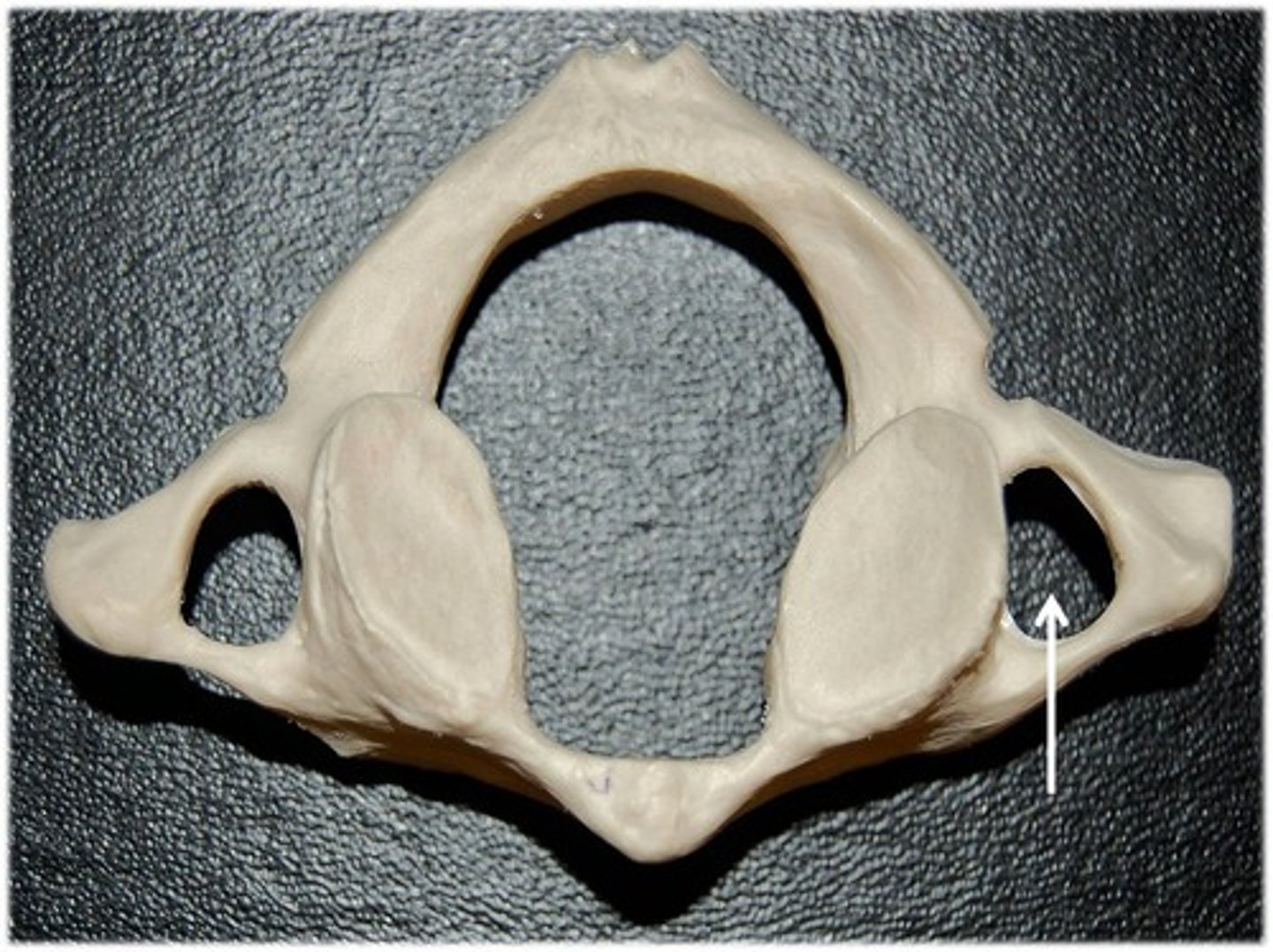
what is this?
transverse foramen (cervical region)
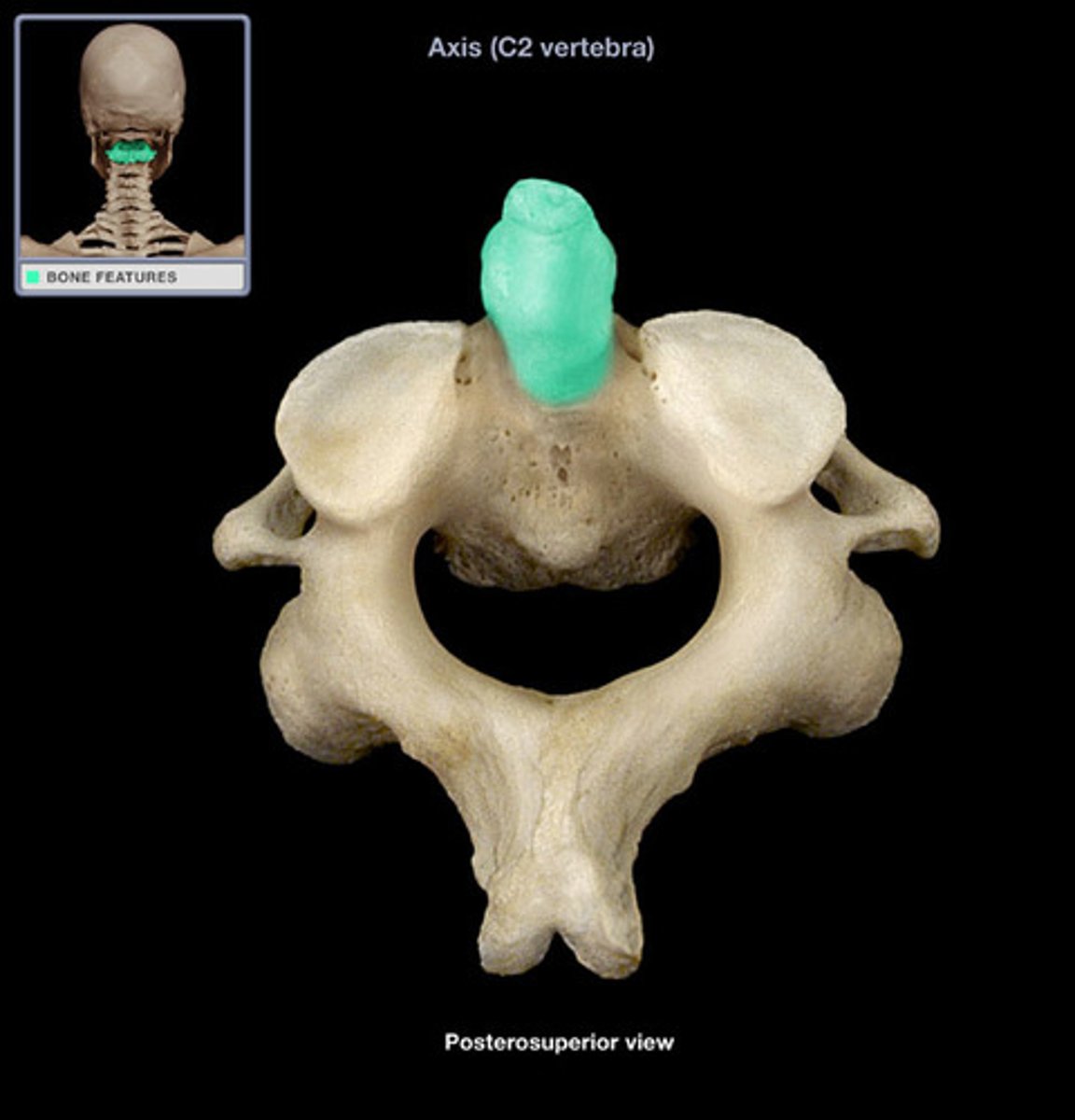
what is this
dens (cervical region)
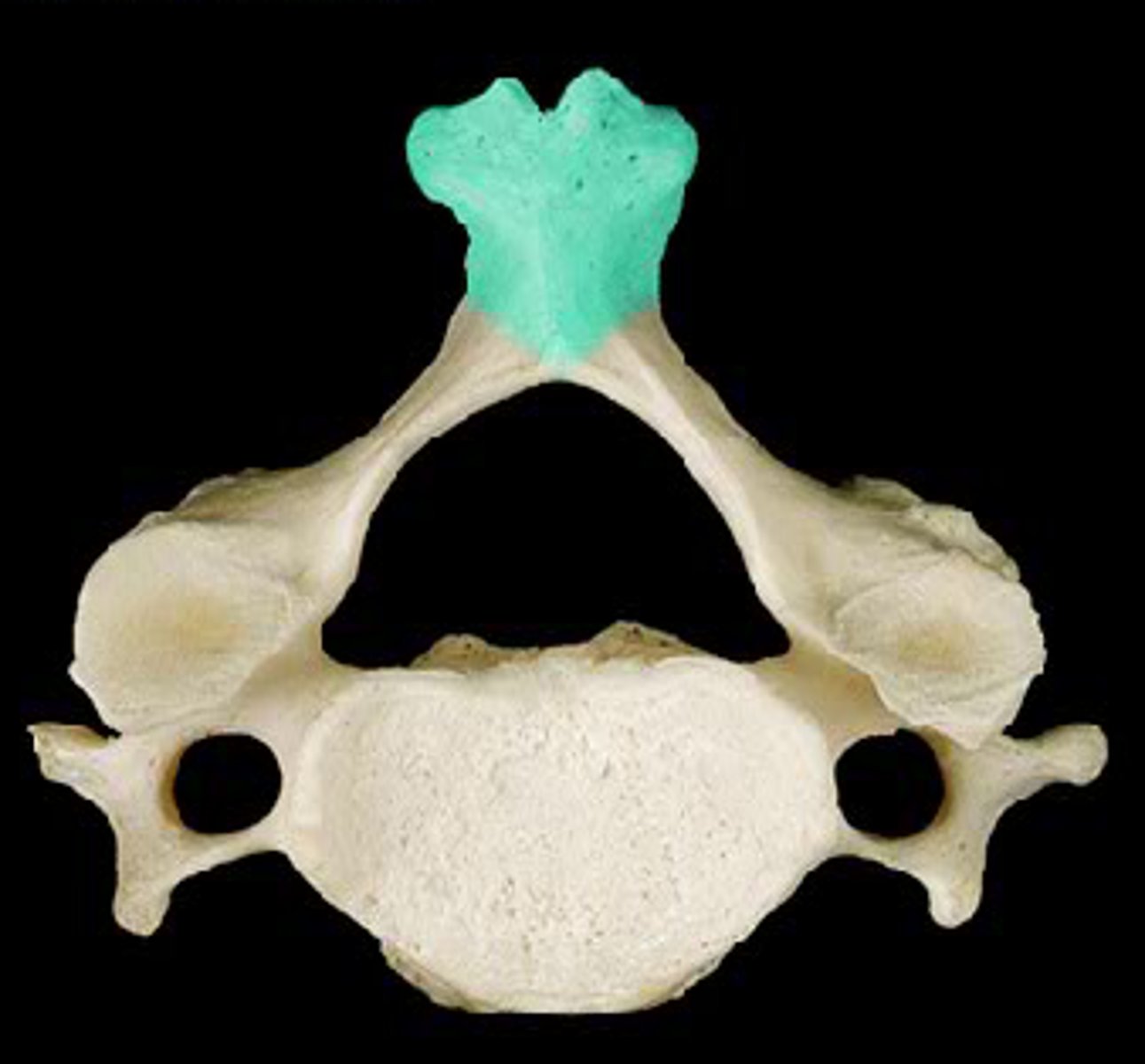
what is this
bifid (cervical region)
what is this
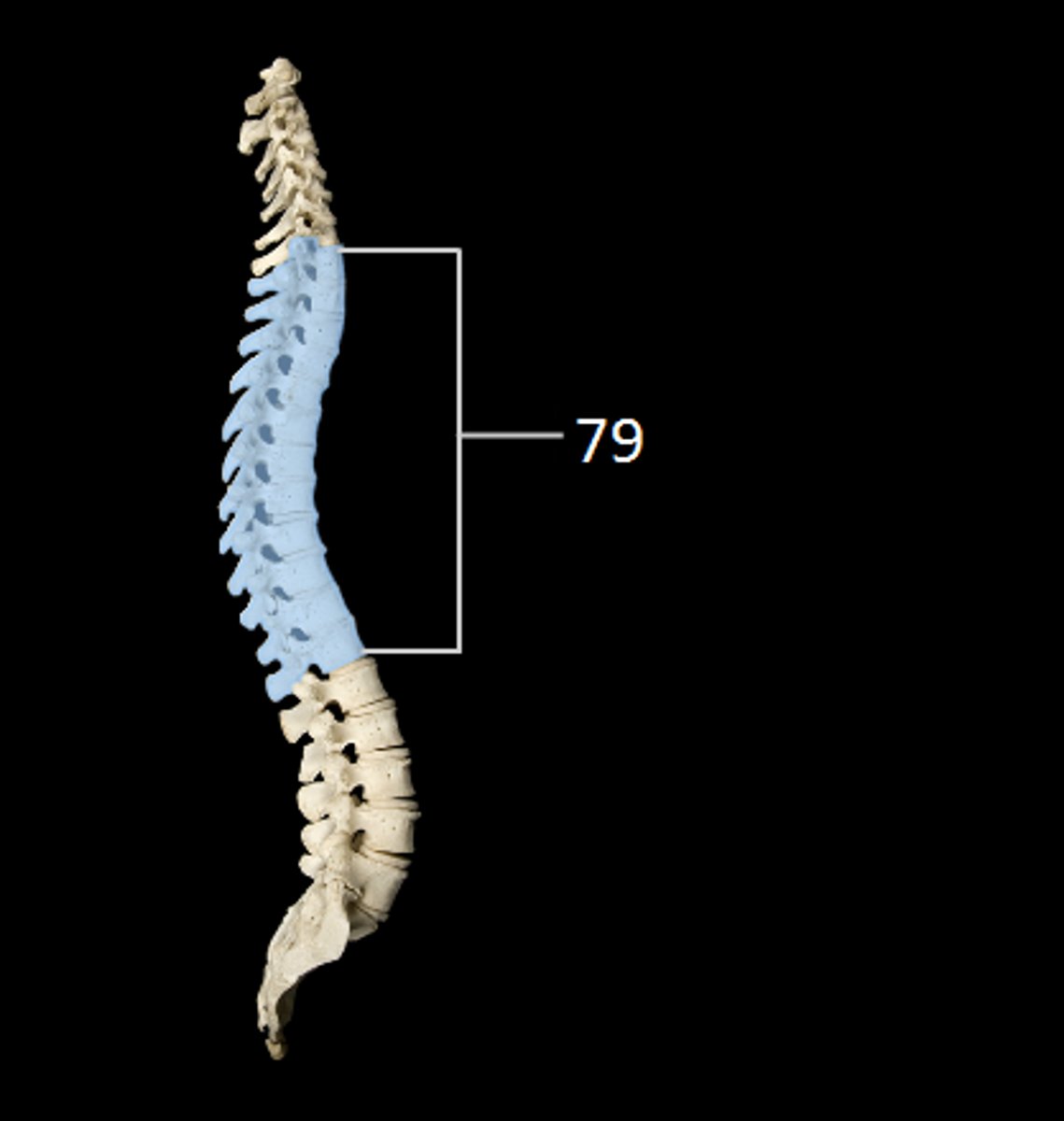
thoracic region
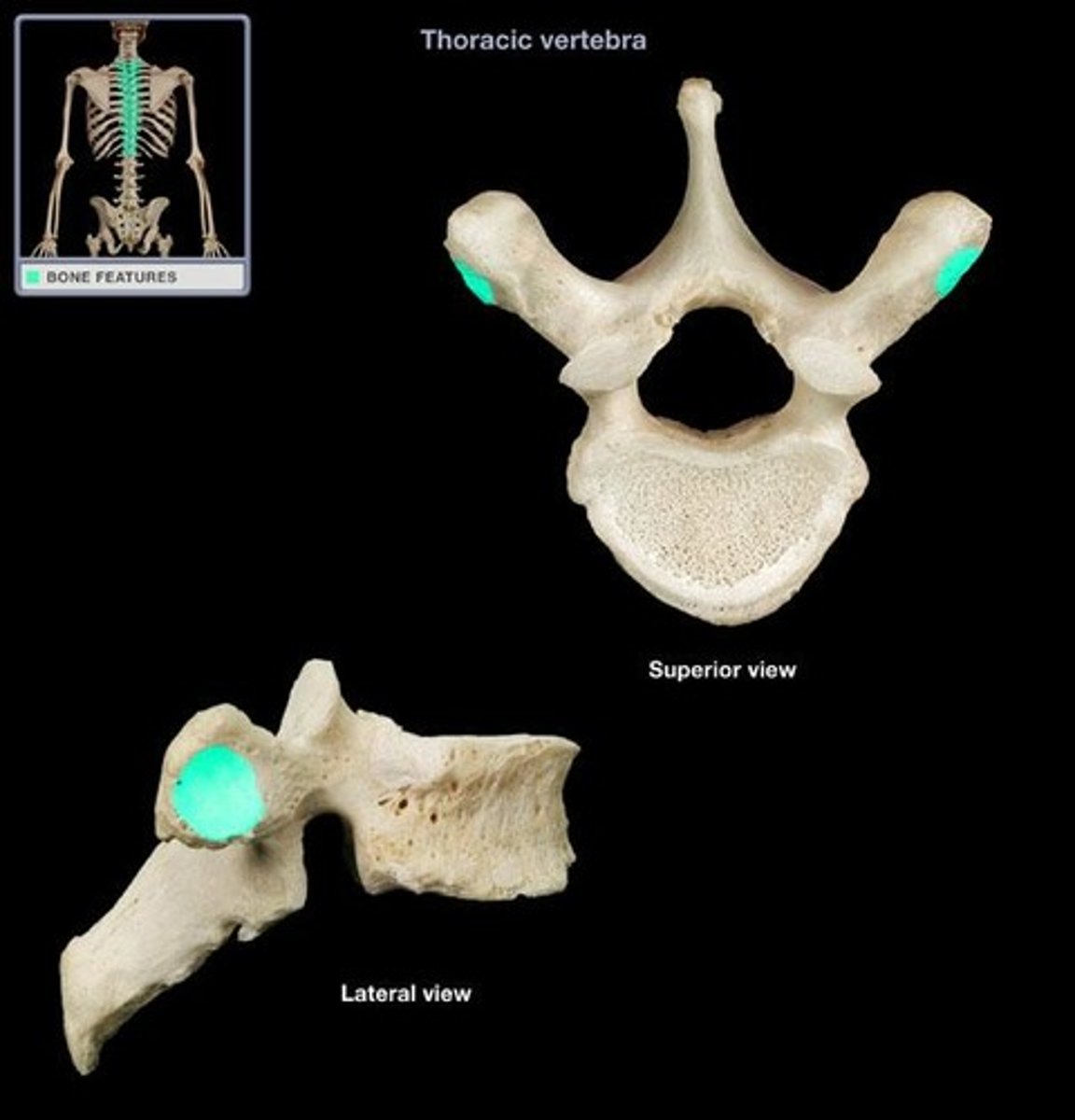
what is this
facets for rib articulation
tailbone
- Sacral foramina—(anterior and posterior)
-Sacral crest
-Sacral canal
-Sacral promontory
sacral region
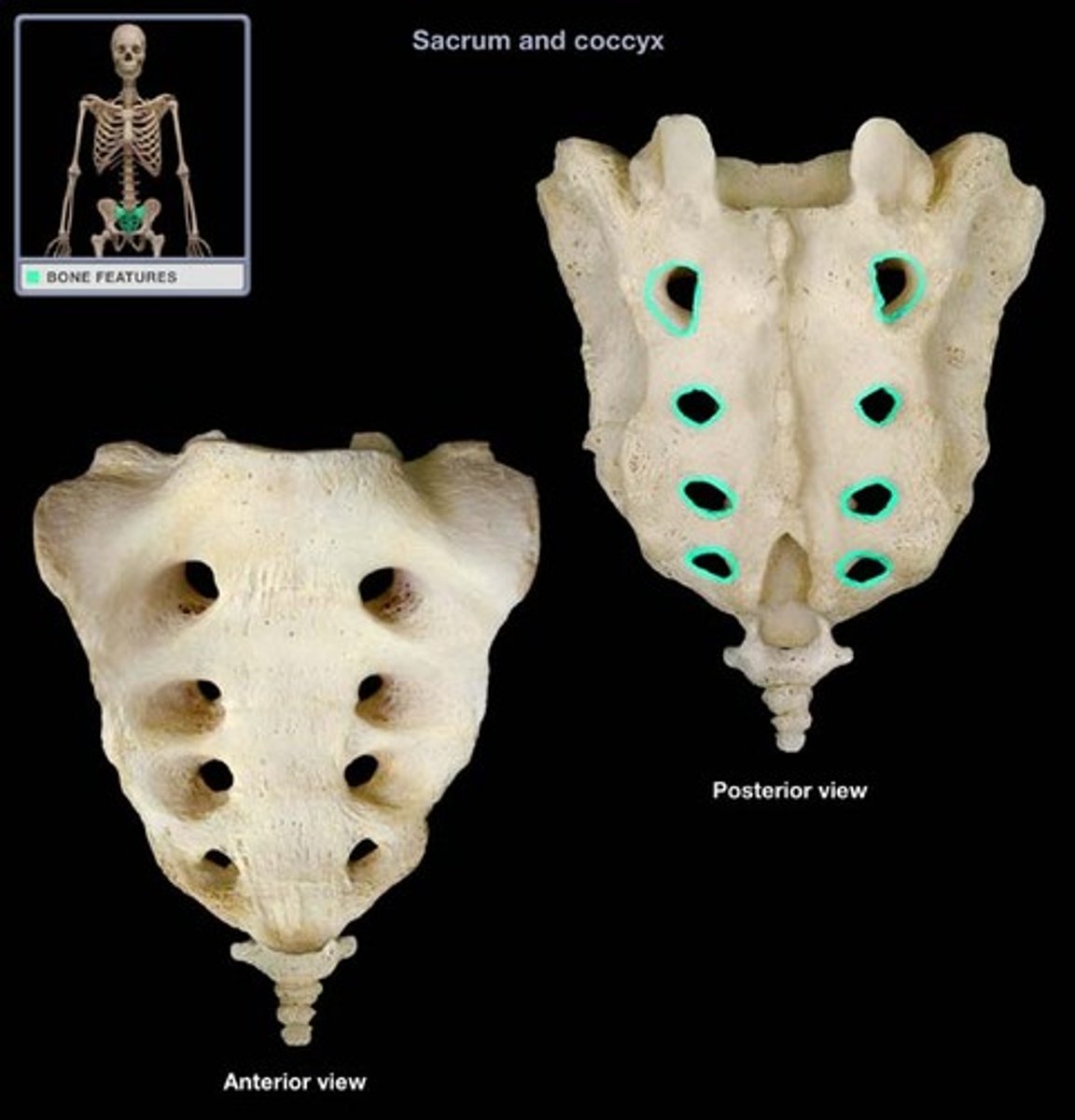
Four ridges (lines of fusion) cross the anterior part of the sacrum, and sacral foramina are located at either end of these ridges. There foramina allow blood vessels and nerves to pass
sacral foramina (anterior and posterior)
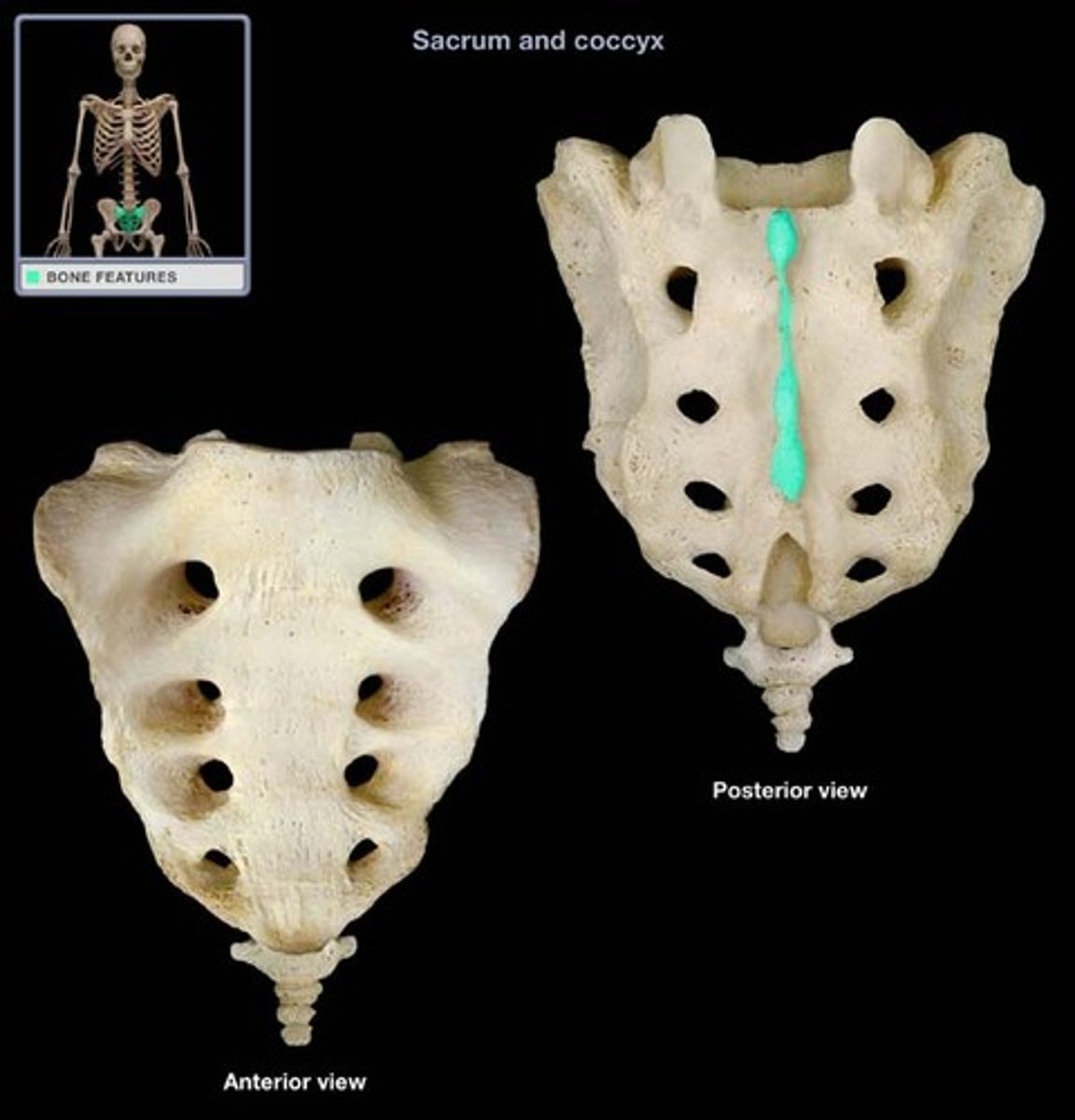
raised midline down center of sacrum
sacral crest
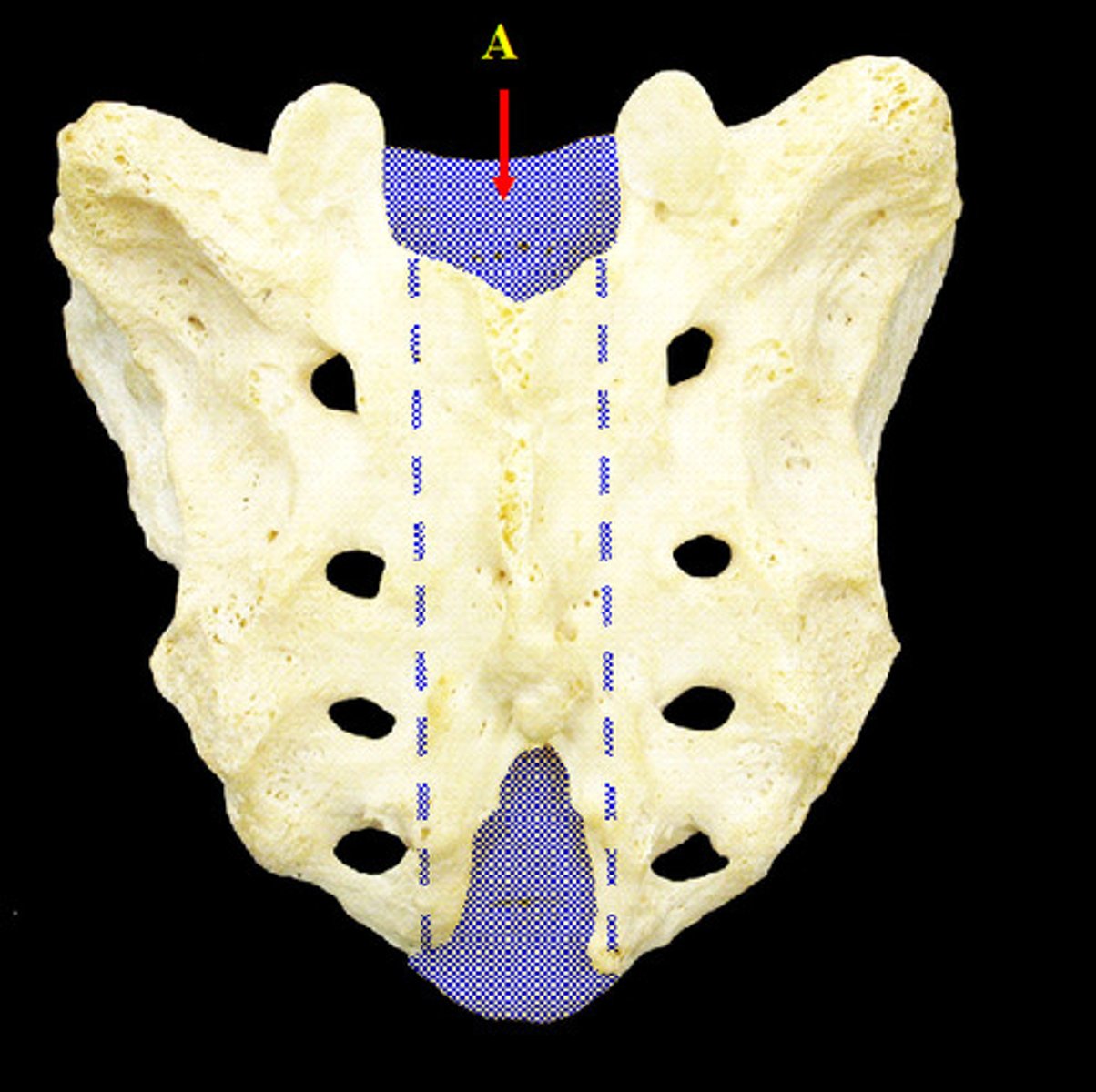
central canal transmitting the dorsal and ventral roots of spinal nerves S1 to S6 and the coccygeal spinal nerve.
sacral canal
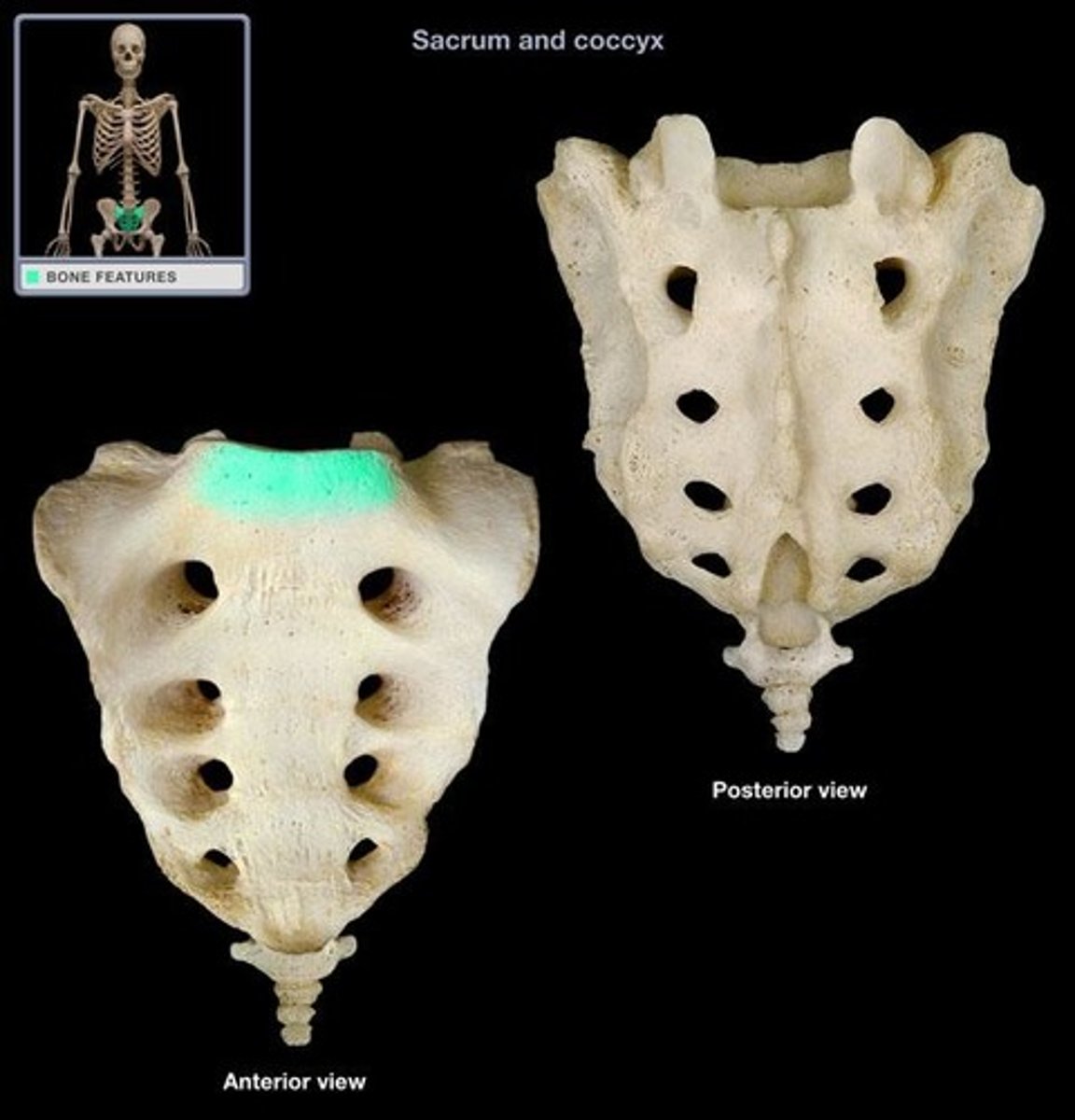
Where the first sacral vertebrae bulges into pelvic cavity
sacral promontory
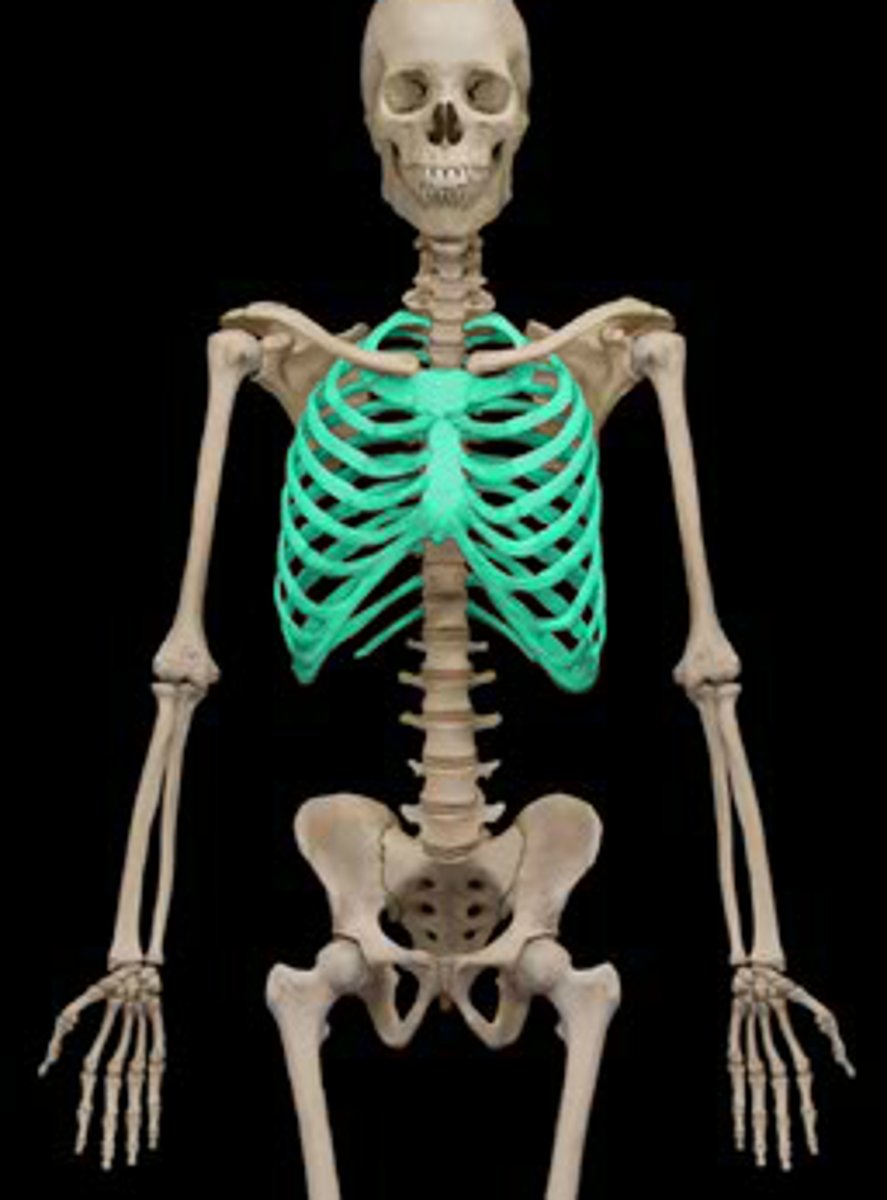
ribs and sternum
thoracic cage
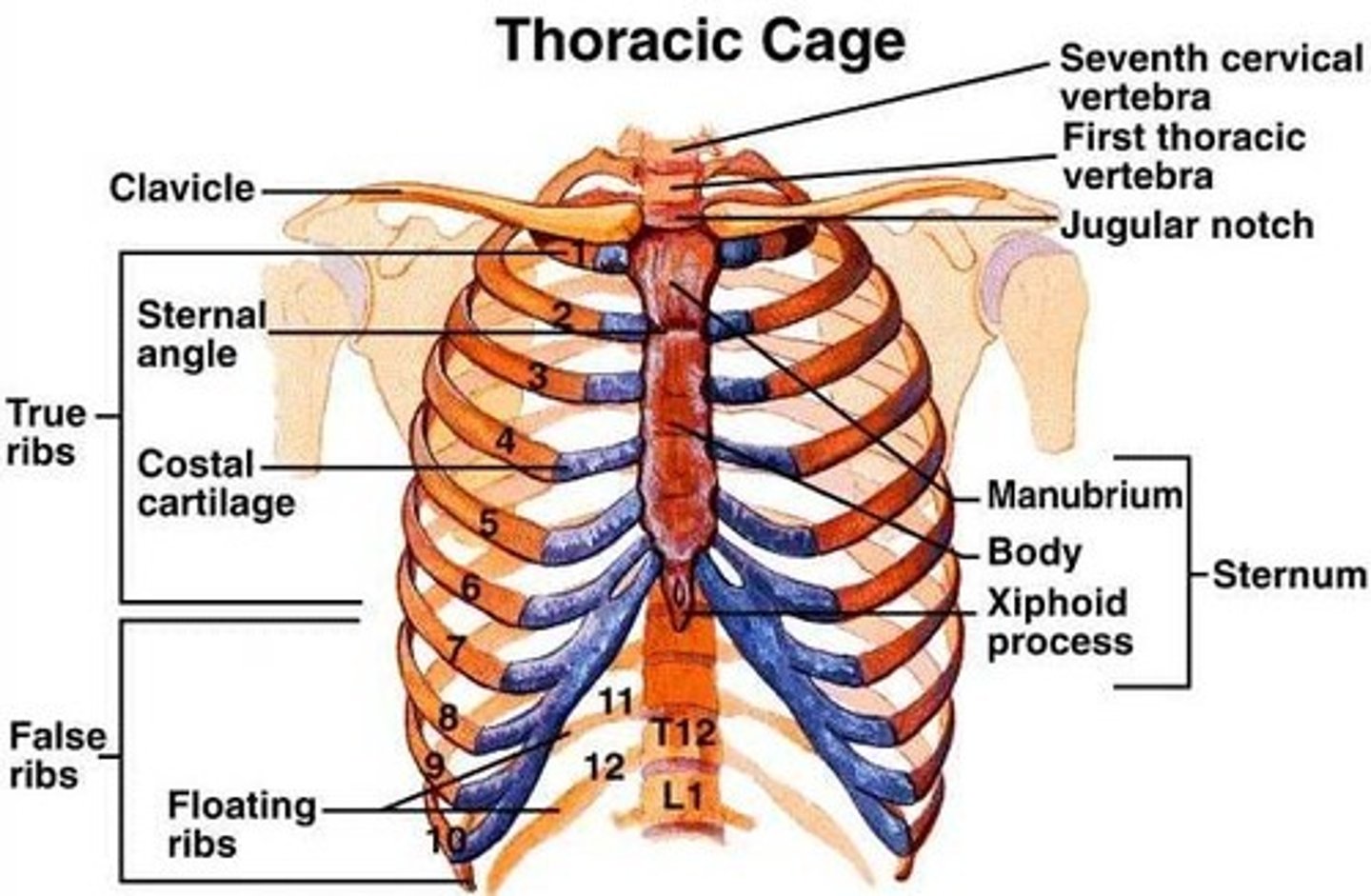
true ribs 1-7
vertebrosternal ribs
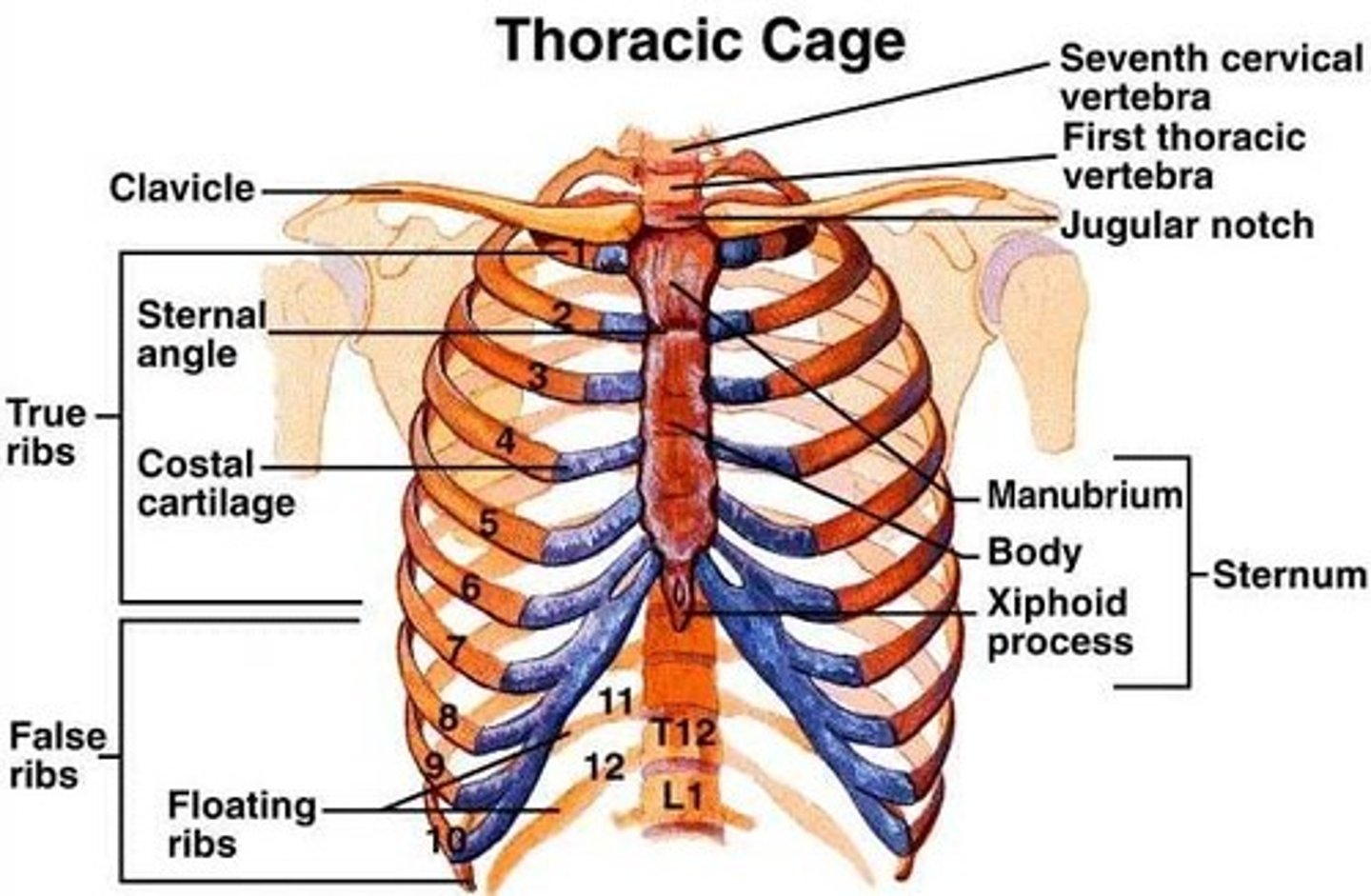
"False Ribs" 8-10
Vertebrochondral ribs
vertebrosternal vs vertebrochondral ribs
Vertebrosternal ribs are the true ribs that directly connect to the sternum, while vertebrochondral ribs are the false ribs that connect to the sternum indirectly via cartilage.
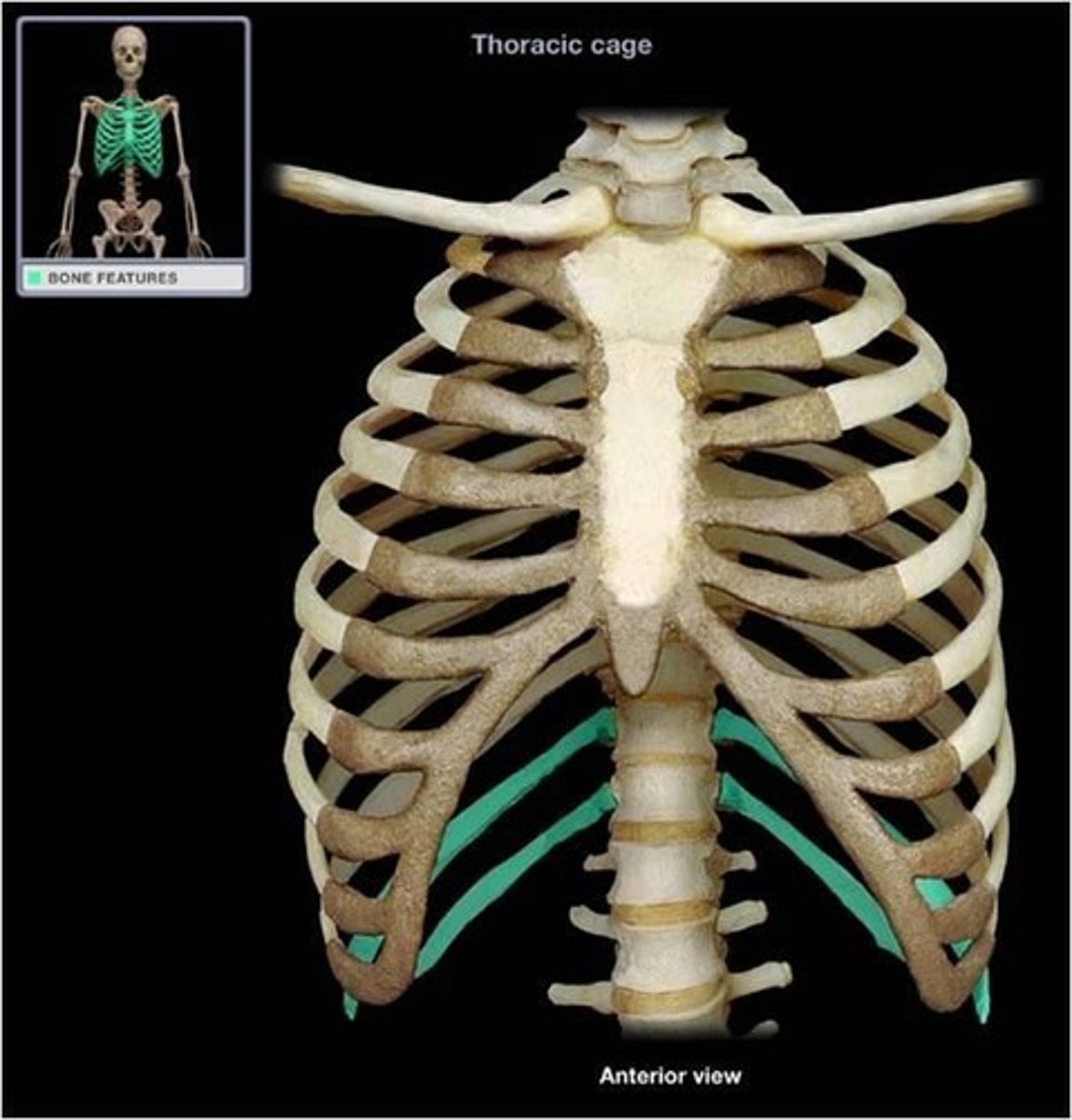
floating ribs 11-12
vertebral ribs
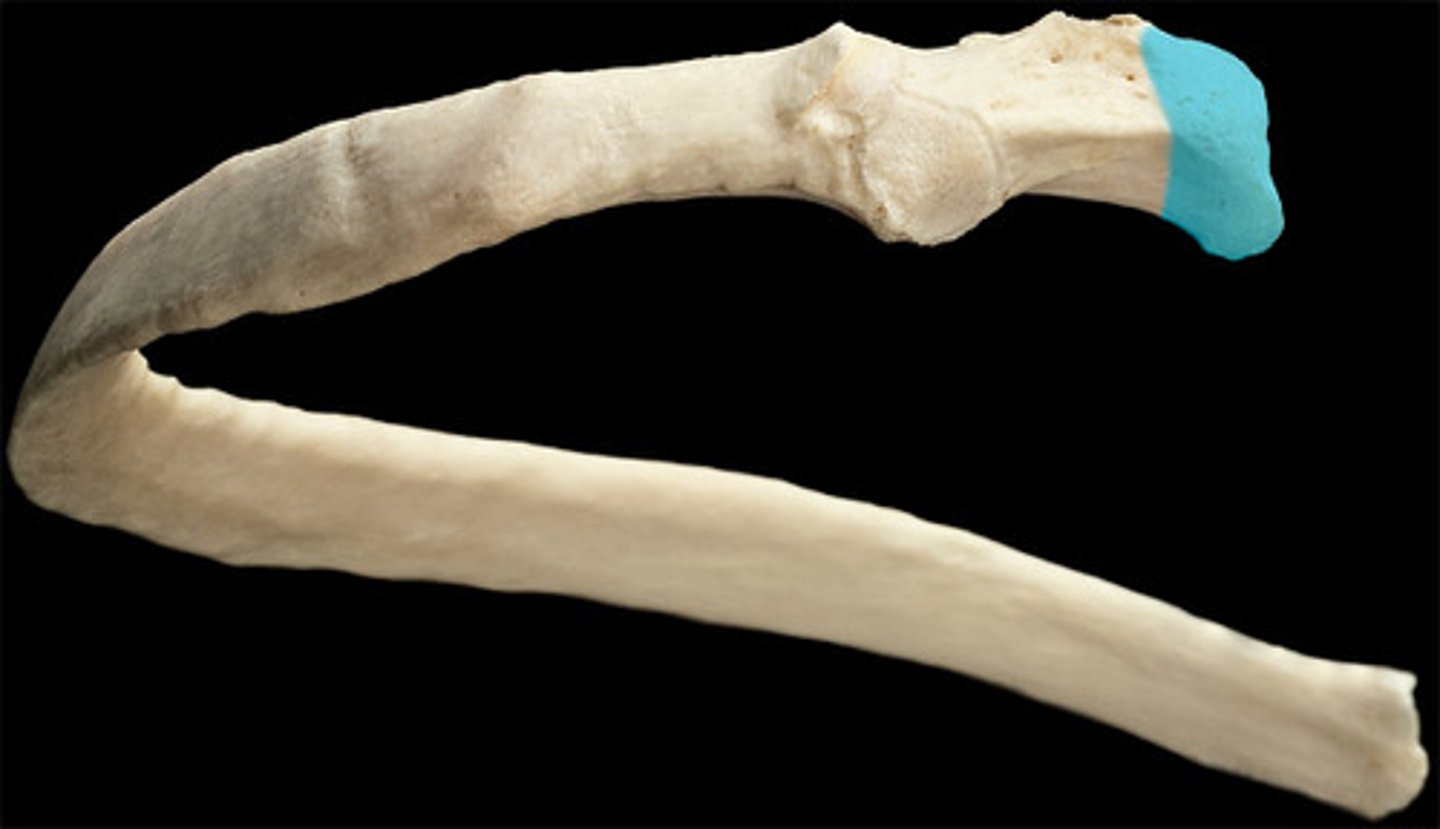
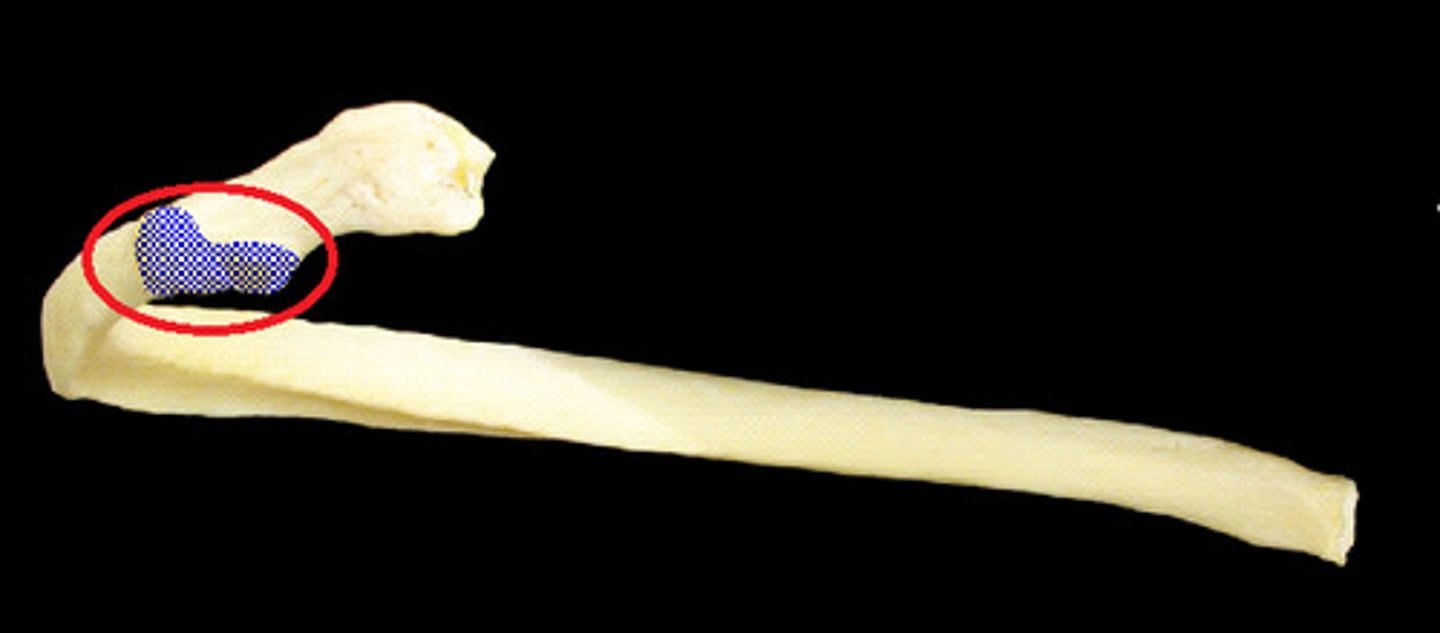
connects to vertebrae, end of rib
head (ribs)
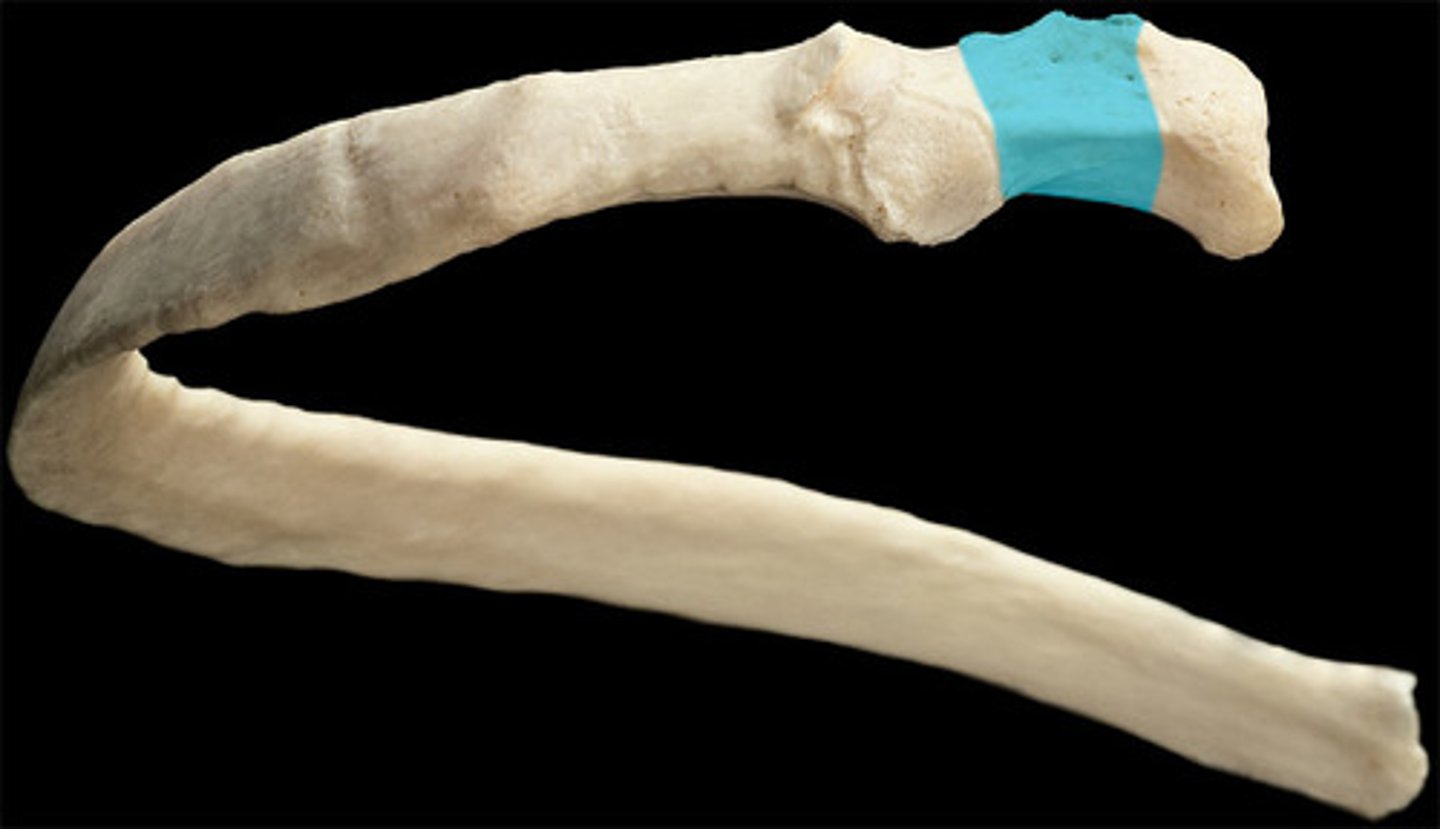
lies between head and tubercle
neck (ribs)

articulates with transverse process
rib tubercle
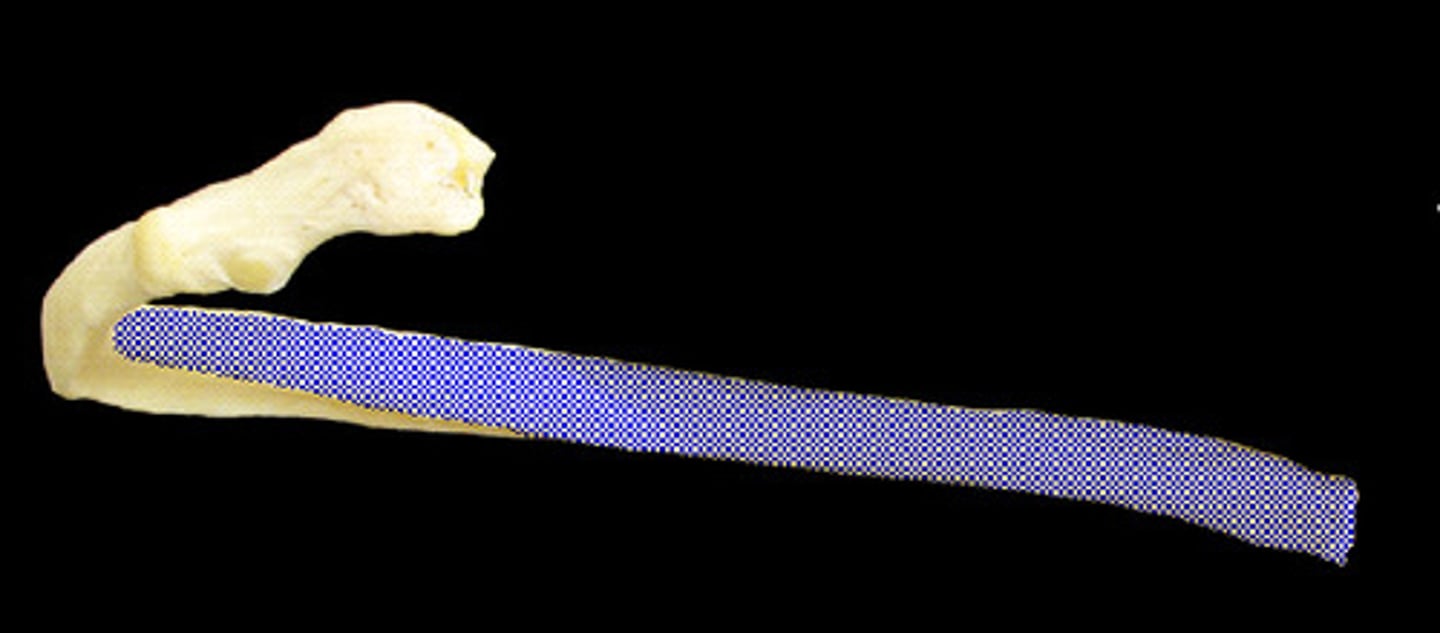

the body of the rib
shaft (rib)
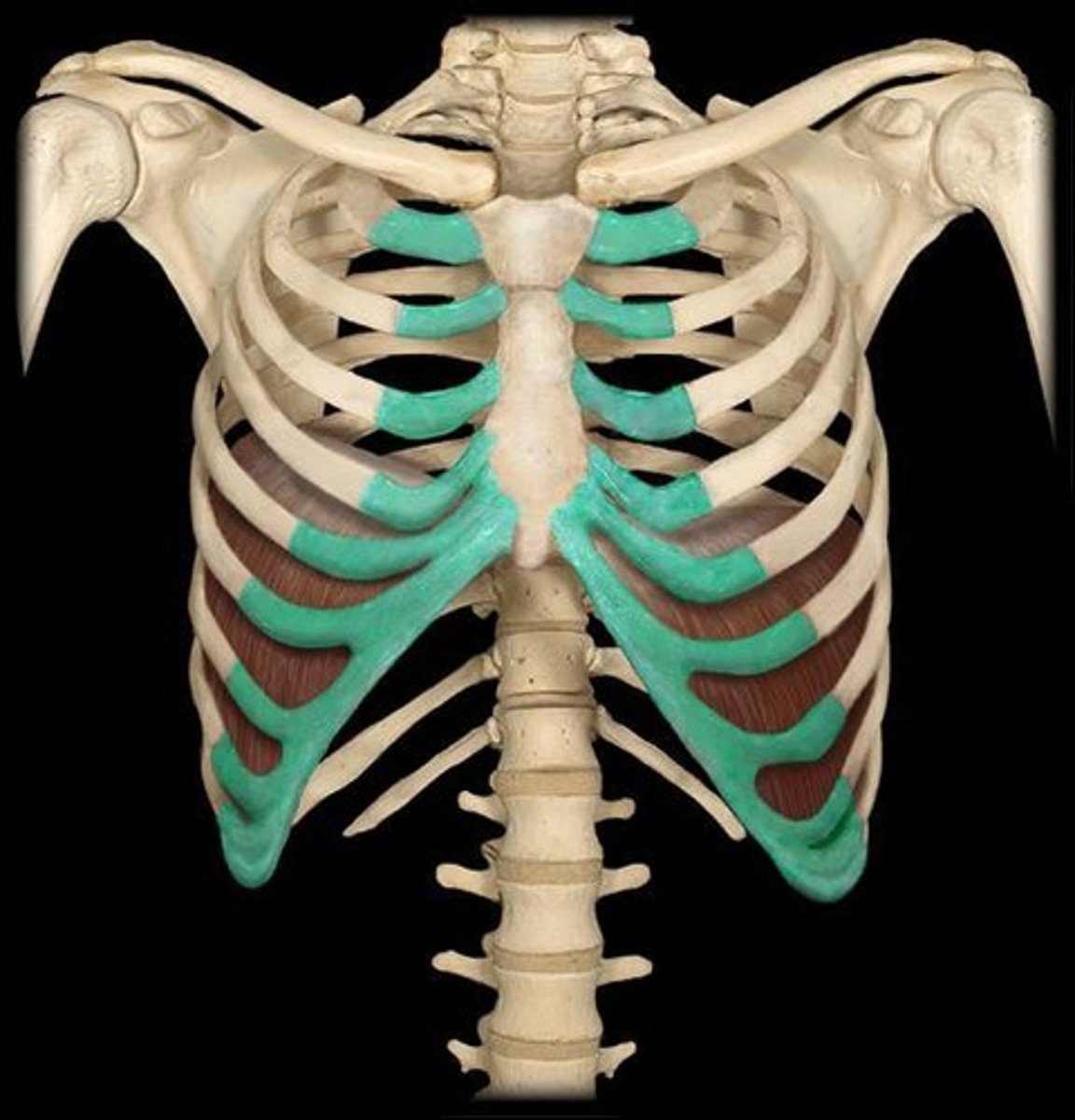
connect the ribs to the sternum (breastbone)
coastal cartilages (rib)
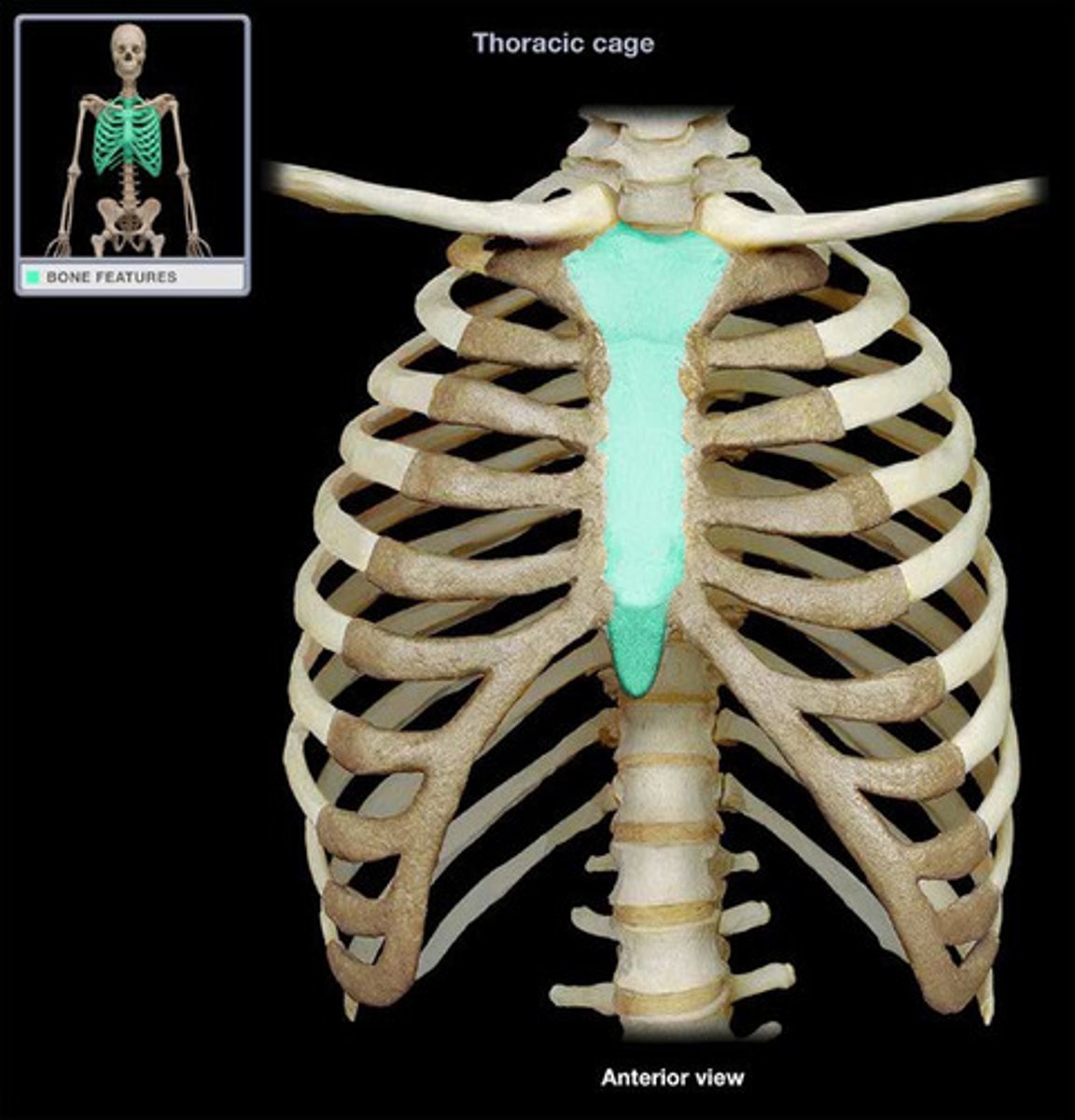
- manubrium
- sternal body
- xiphoid process
sternum contains
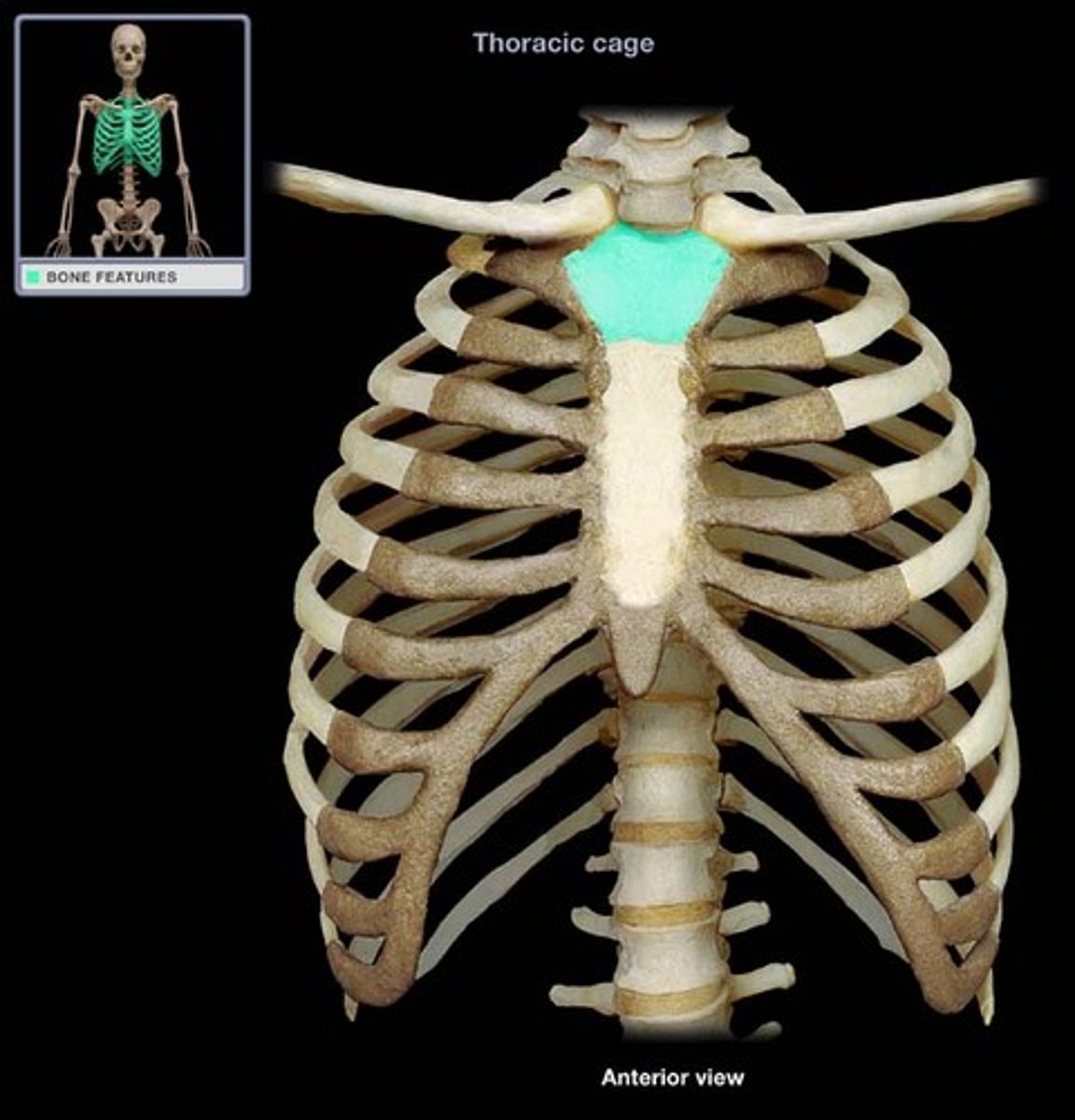
top of sternum
manubrium (sternum)
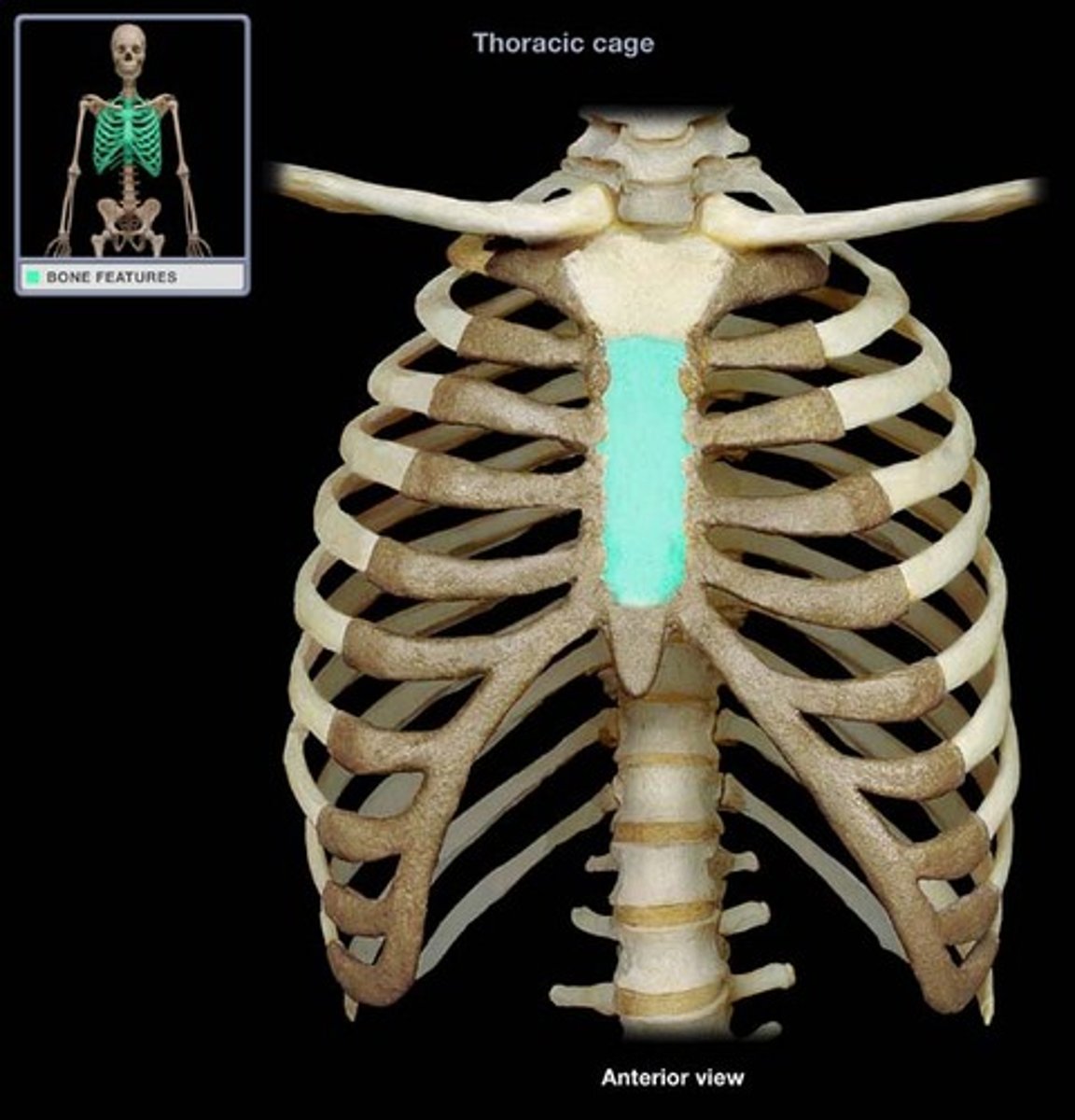
-Tongue-shaped
-Attaches to the manubrium
-Attaches to costal cartilages of ribs 2-7
sternal body (sternum)
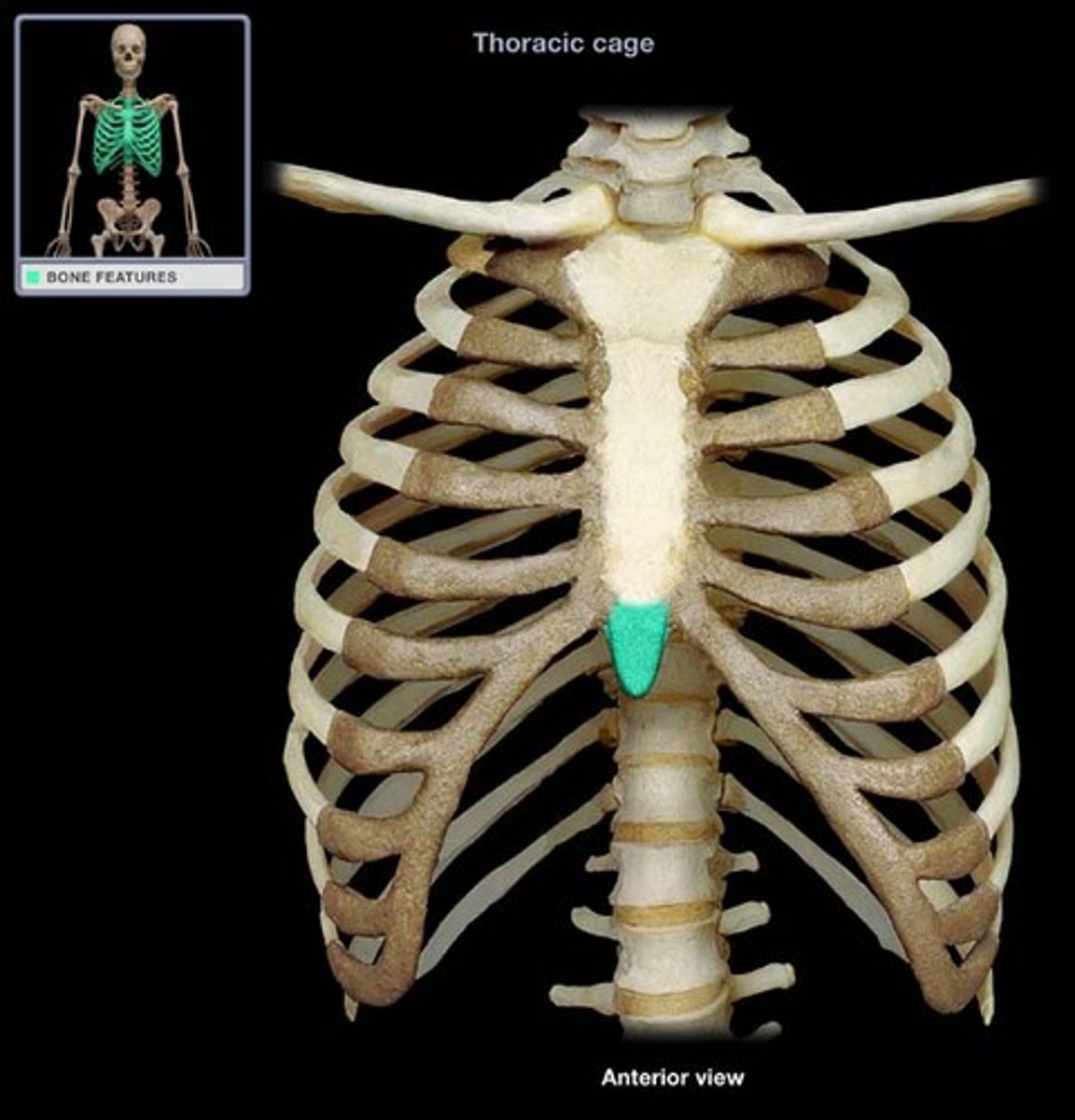
bottom of sternum
xiphoid process (sternum)
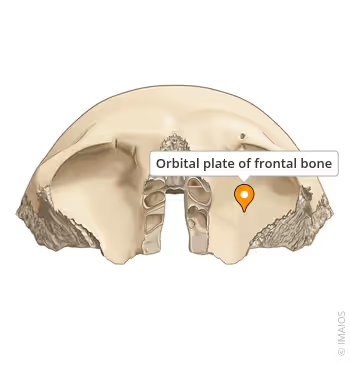
what is this?
orbital surface
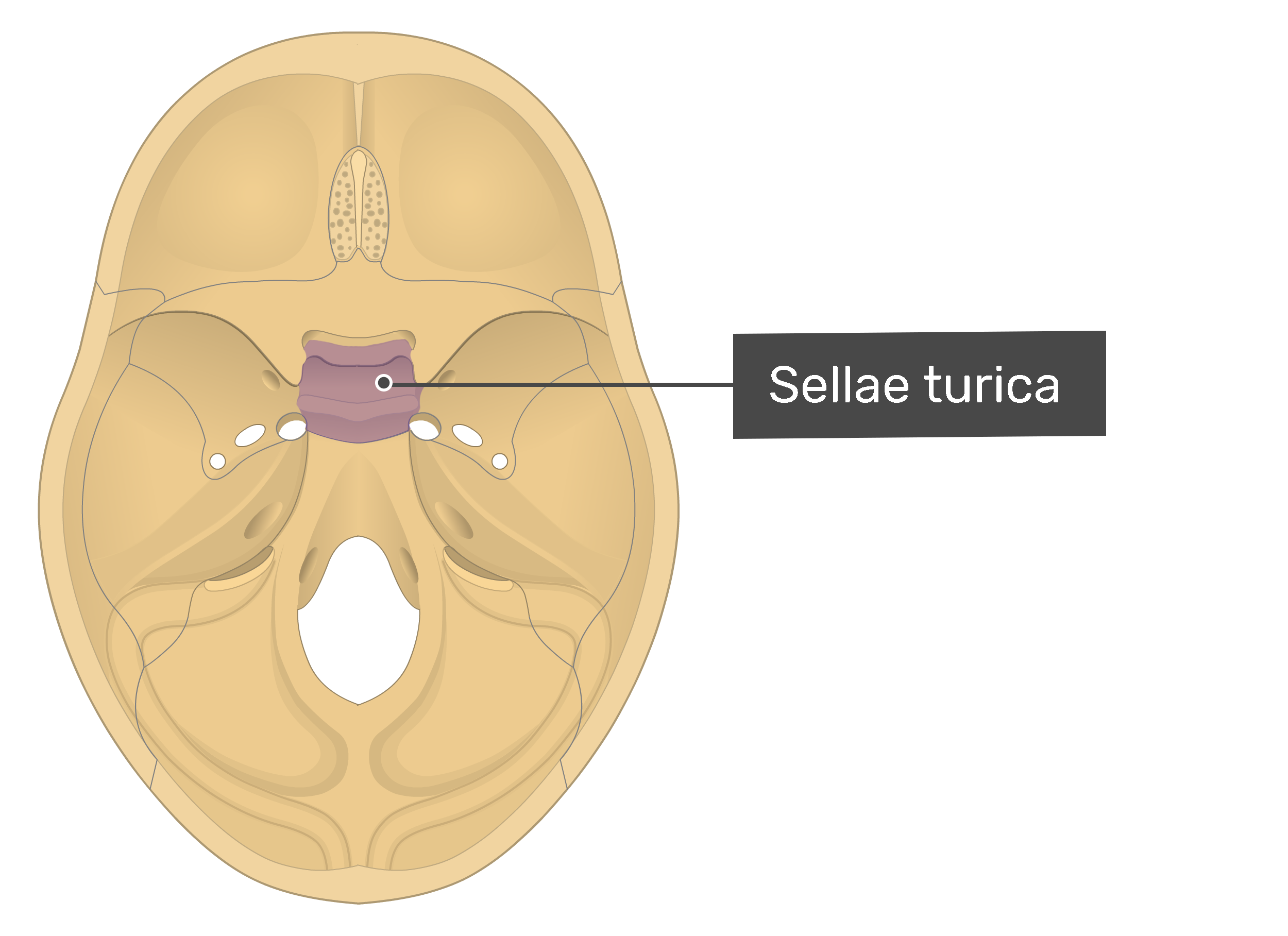
what is this?
sella turcica
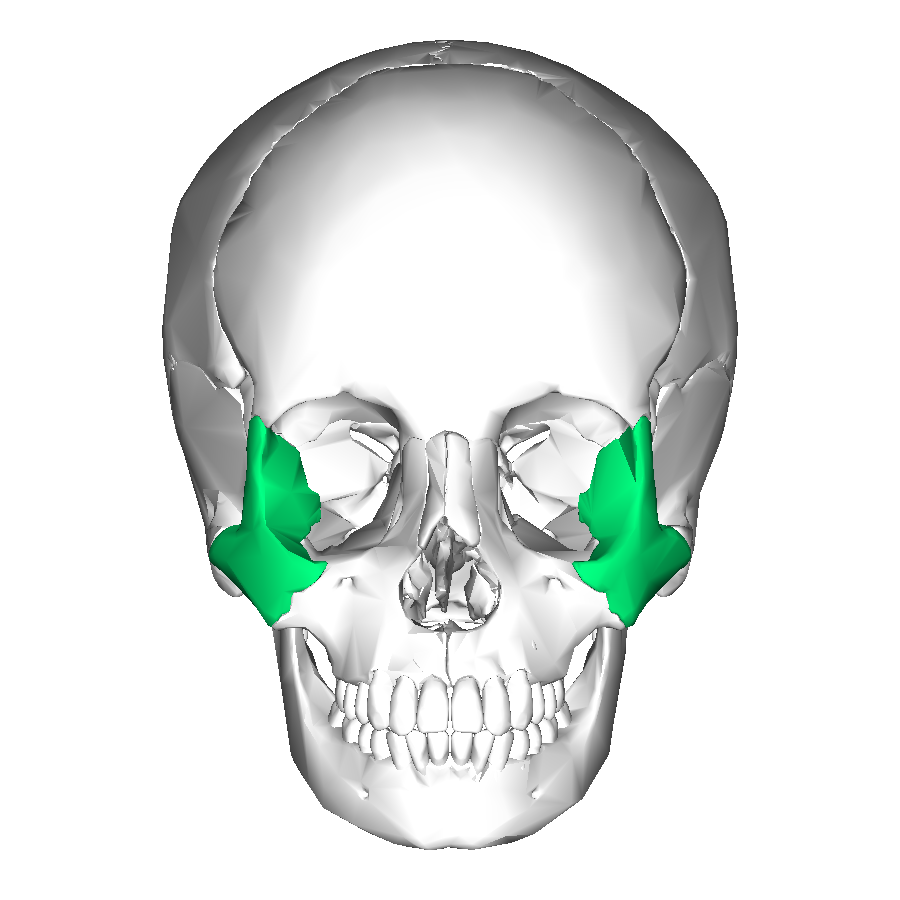
what is this?
zygomatic bone
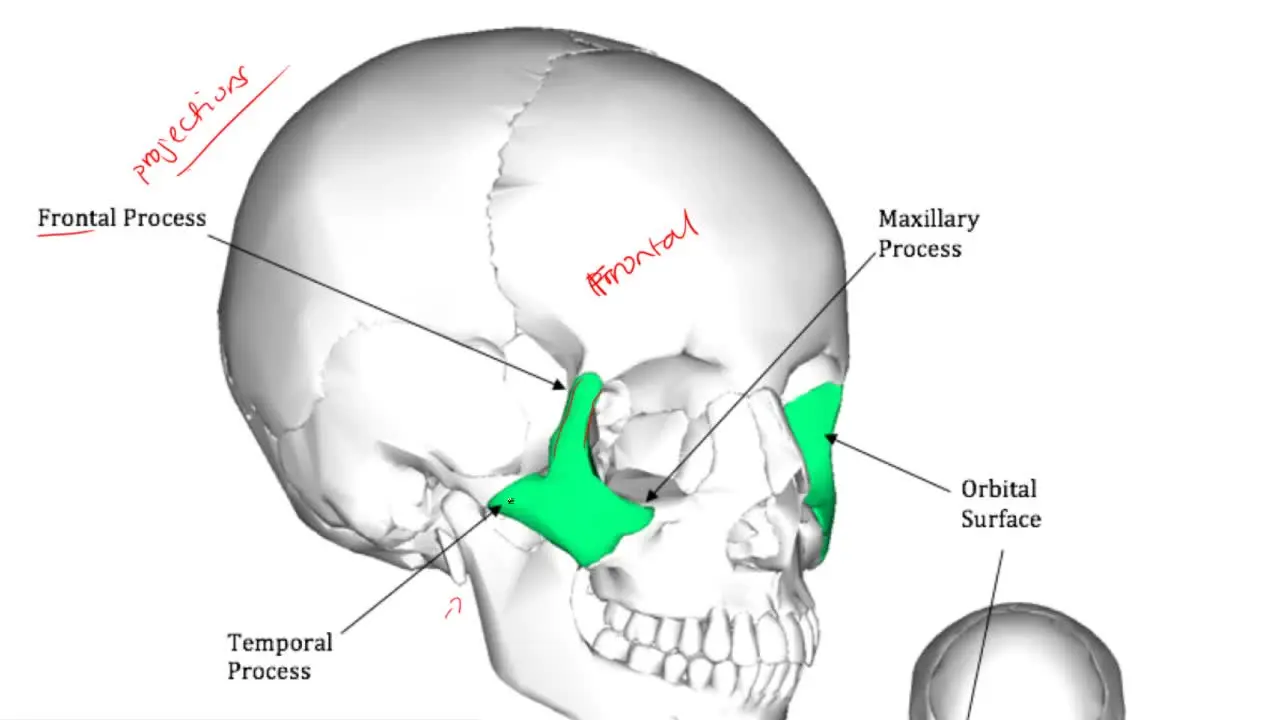
what is this?
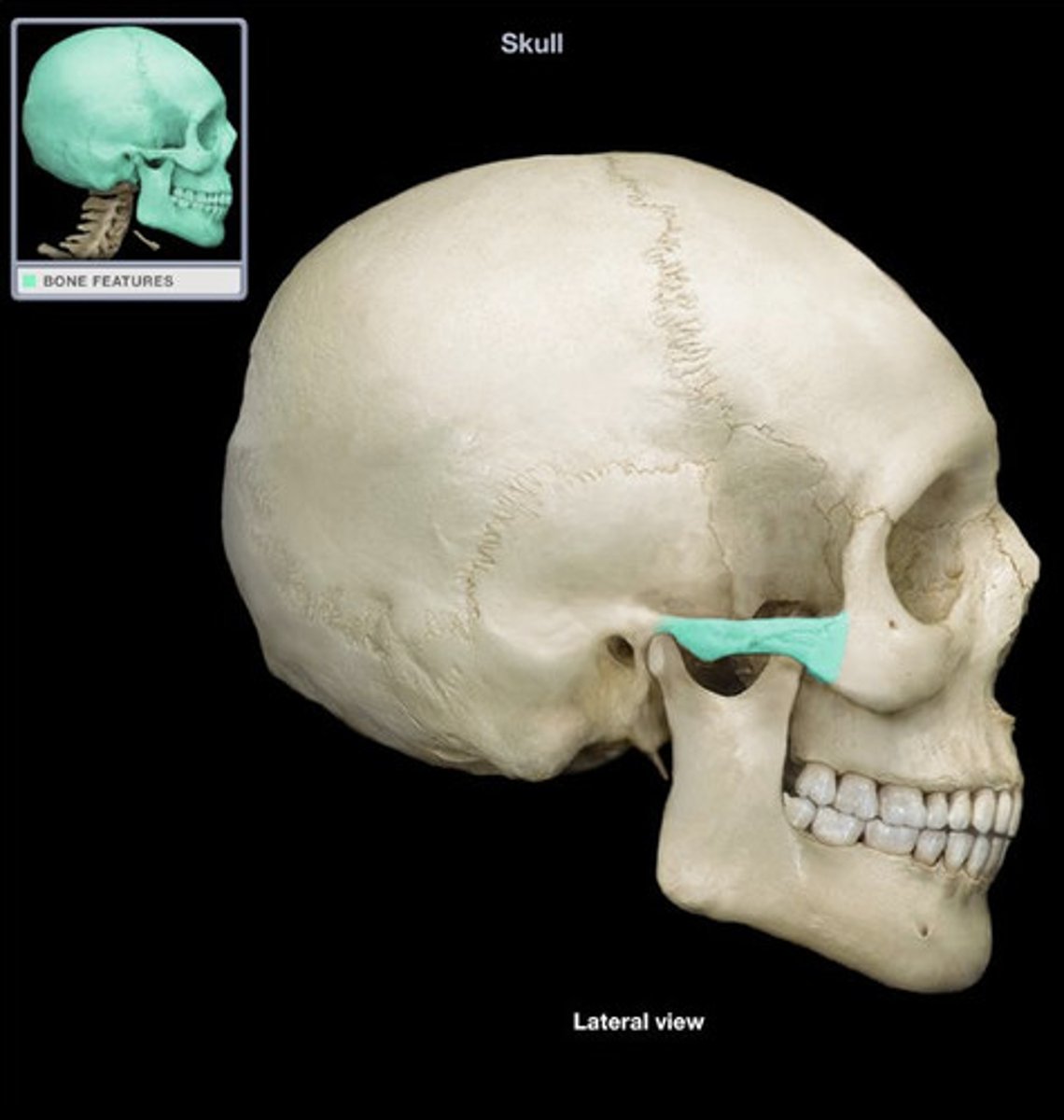
temporal process
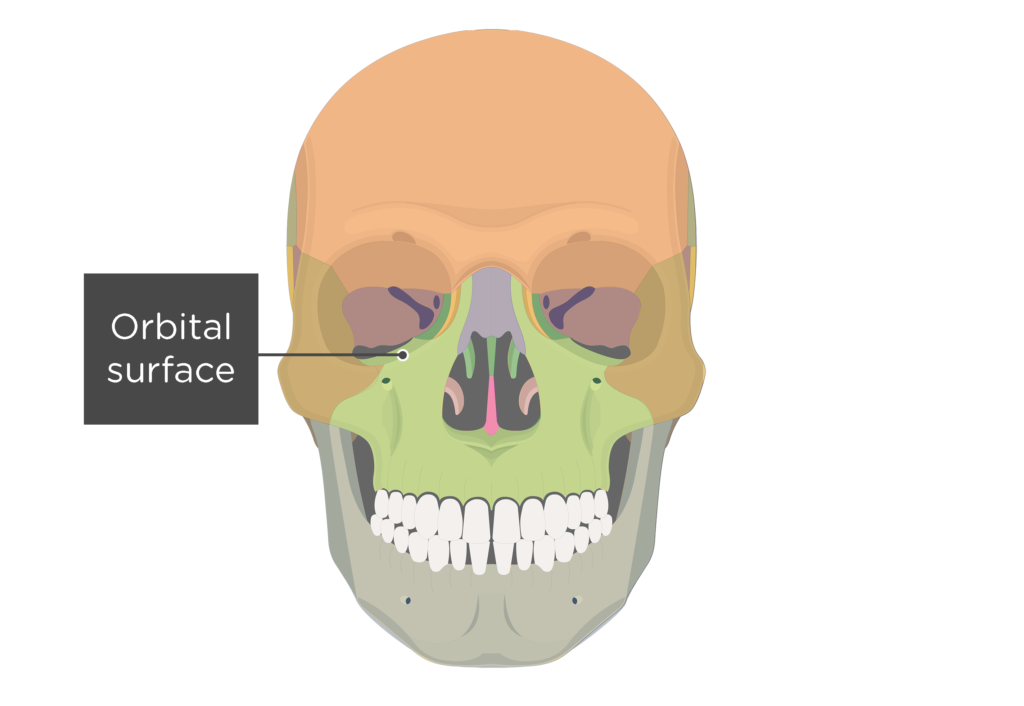
what is this?
orbital surface
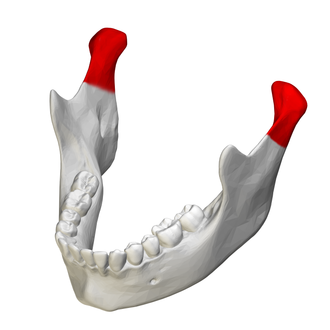
what is this?
condylar process