Chapter 18, Lesson 5: Platelets and the Control of Bleeding
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 18, Lesson 5 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Hemostasis
The cessation of bleeding with platelets
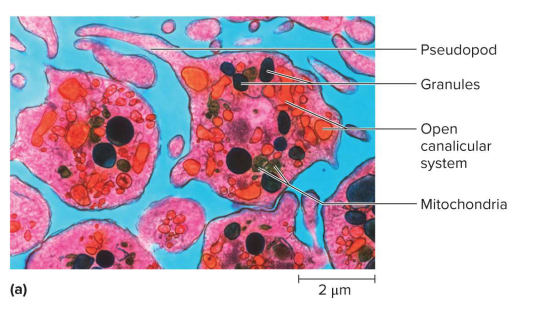
Platelets
Small fragments of megakaryocytes in bone marrow with no nucleus and granules with secretions; moves in ameboid manner with foot (pseudopod)
Open canicular system
The internal system of channels that open onto the platelet surface
Platelet functions
Secrete vasoconstrictors to reduce blood loss
Create platelet plugs to seal small breaks
Secrete procoagulants (clotting factors)
Attract neutrophils to inflamed sites
Dissolve clots when necessary with enzyme
Thromobopoiesis
The production of platelets
Thrombopoietin
A chemical that triggers stem cells to become megakaryoblasts, which replicate DNA to become megakaryocytes
Megakaryocytes
Cells 100 micrometers in diameter in the bone marrow; fragments split off to become platelets
Platelet life span
5 to 6 days
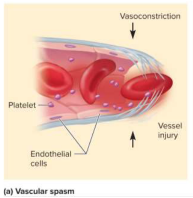
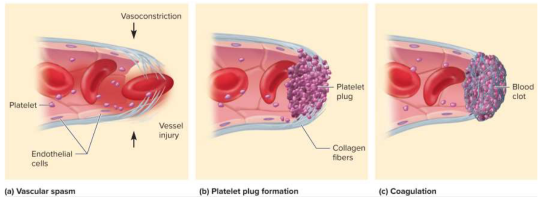
Vascular spasm
The first step in hemostasis that constricts blood vessels quickly before platelet plugs and clotting
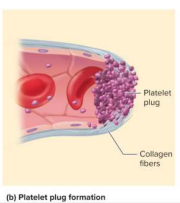
Platelet plug formation
The second step in hemostasis where platelet pseudopods (feet) stick together to form a platelet plug
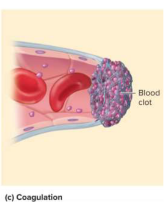
Coagulation (clotting)
The last defense against bleeding which uses clotting factors to aid in clotting
Clot retraction
The stoppage of clots where clots compact
Bleeding time
Aids in measuring coagulation efficiency
Hemophilia
A family of hereditary disease characterized by deficiencies of one clotting factor or another; blood cannot clot most effectively and is often sex-linked recessive
Thrombosis
Abnormal formations of a clot in an unbroken vessel; can be very harmful in vital organs to cause tissue death
Clot management
Done through prevention (vitamin K antagonists to prevent factor production) or dissolution of clots