Week 6 - Scapula, Clavicle, and Upper Limbs
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
scapula
shoulder bone
composes part of the shoulder girdle
scapular (spine)
ridge on the posterior surface of the scapula
muscle attachment
supraspinous fossa
depression superior to spine
supraspinatus lies here as well as arteries and nerves
infraspinous fossa
depression inferior to spine
infraspinatus lies here
subscapular fossa
depression on the posterior aspect of the scapula (the part that faces toward your innards)
subscapularis lies here
acromion process/acromion
projection from the lateral end of the scapular spine
muscle attachment; articulates with the acromial end of the clavicle
coracoid process
projection of bone from the superior border of the scapula, anterior view
muscle attachment
glenoid fossa/cavity
hollow end on scapula
forms the shoulder joint
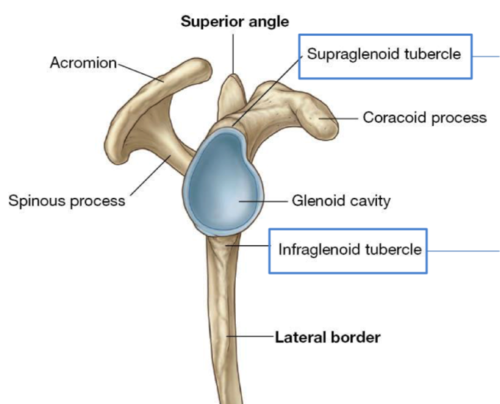
supraglenoid tubercle
surface superior to the glenoid fossa, looks like a smooth bump
attachment for the origin of the long head of biceps brachii
infraglenoid tubercle
inferior to the gleniod fossa, looks more like a small depression
attachment for the origin of the long head of the triceps brachii
clavicle
your collar bone
composes part of the shoulder girdle
sternal end
this end of the clavicle is medial with a rounded edge; the bumps right above your sternum
articulates with the sternum
acromial end
this end of the clavicle is lateral with a flattened edge; this end is closest to your shoulders where the acromion is
articulates with the acromion
conoid tubercle
bump on the posterior aspect of the clavicle seen from the inferior view, closest to the acromial end; greater directional ID point
ligament attachment
glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint)
this joint refers to area running from the glenoid fossa(/cavity) to the head of the humerus
shoulder girdle
this body part is composed of the clavicle, scapula, and humerus; where the arm fits
brachium
upper arm; from axilla to elbow
movement
humerus
bone of upper arm
head
the rounded proximal end of the humerus
articulates with glenoid cavity of scapula to form the glenohumeral joint
anatomical neck
the portion separating the head from the main body of the humerus; above the greatter and lesser tubercle
surgical neck
portion below the greater and lesser tubercle on the humerus
greater tubercle
large bony knob on the anterior surface of the humerus, close to the anatomical neck, lateral to the lesser tubercle
attachment of rotator cuff muscles
crest of greater tubercle of humerus
a raised ridge continuing down the anterior surface of the humerus directly from the greater tubercle
attachment point for pectoralis major
lesser tubercle
smaller bony knob on the anterior surface of the humerus, close to the anatomical neck, medical to greater tubercle
attachment of rotator cuff muscles
crest of lesser tubercle humerus
a raised ridge continuing down the anterior surface of the humerus directly from the lesser tubercle
attachment of the latissimus dorsi and teres major
intertubercular sulcus
groove between greater and lesser tubercles
attachment of latissimus dorsi and pectoralis major muscles
deltoid tuberosity
large bump on the main shaft or body of the humerus
attachment of the deltoid
trochlea
pully shaped knob on distal surface of humerus
articulates with trochlear notch on forearm
capitulum
rounded knob on distal surface of humerus
articulates with head of radius on forearm
olecranon fossa
big divot on posterior side of humerus
articulates with olecranon process
radial fossa
fossa directly above the capitulum; anterior aspect of humerus
articulates with radial head
coronoid fossa
fossa directly above trochlea
stabilizes elbow joint, prevents over flexing
medial epicondyle
rough process medial to trochlea
attachment of most flexor muscles in antebrachium
lateral epicondyle
rough process lateral to capitulum, seen prominently from posterior aspect, lateral to olecranon fossa
attachment of most extensor muscles in antebrachium
antebrachium
the forearm
proximal radioulnar joint
the head of the radius articulating with the radial notch of the ulna
distal radioulnar joint
the medial surface of the ulna articulating with the ulnar notch of the radius forms what joint
radius
the smaller of the two forearm bones (subunit of antebrachium)
head
disc-shaped proximal end of the radius
articulates with capitulum and radial notch
neck
portion beneath the head of the radius
radial tuberosity
rough medial projection distal to the head of the radius
attachment of biceps brachii muscles
styloid process of the radius
pointed end on the distal end of radius, sits laterally
ligament attachment
ulnar notch of the radius
notch on the medial aspect of the distal end of the radius; opposite of styloid process
articulates with the medial surface on the distal end of the ulna to form the distal radioulnar joint
ulna
the larger of the two forearm bones (subunit of antebrachium)
trochlear notch
a notch shaped like a large C on the ulna
articulates with the trochlea
olecranon process
the large proximal end of the ulna
attachment of triceps brachii muscle
coronoid process
small anterior projection at proximal end of ulna, inferior to trochlear notch
attachment of brachialis muscle
radial notch
small depression lateral side of proximal end of ulna
articulates with head of radius to form the proximal radioulnar joint
styloid process of the ulan
pointed end on the distal end of the ulna
ligament attachment
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
the 4 muscles of the rotator cuff