🦴 | Chapter 6: Skeletal System and Bone Physiology
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering major terms and concepts from Chapter 6 on the skeletal system, including bone structure, cells, growth processes, hormonal regulation, disorders, and fracture repair.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
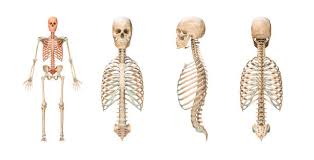
Axial Skeleton
Skeletal division including skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage.
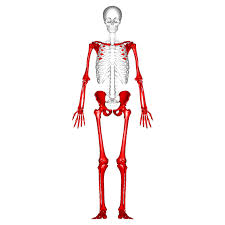
Appendicular Skeleton
Skeletal division of limbs and girdles (pectoral/pelvic).
Structural Support (Skeletal Function)
Provides body framework and attachment for soft tissues/organs.
Protection (Skeletal Function)
Encloses and safeguards vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
Leverage (Skeletal Function)
Muscles use bones as levers to produce movement.
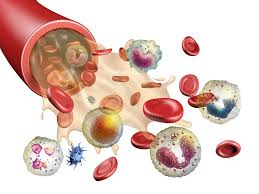
Blood Cell Production
Formation of blood cells in red bone marrow (hematopoiesis).
Mineral and Lipid Storage
Reservoir for calcium, phosphate, and lipid reserves (yellow marrow).
Sutural Bone
Small, flat bone found between the flat bones of the skull.
Irregular Bone
Bone with complex shape, e.g., vertebrae and pelvic bones.
Short Bone
Small, boxy bone such as carpal and tarsal bones.
Flat Bone
Thin, parallel surfaces; forms roof of skull, ribs, sternum, scapulae.
Long Bone
Elongated bone; found in limbs such as femur, humerus, tibia.
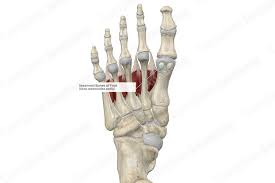
Sesamoid Bone
Small, seed-shaped bone that develops in tendons; example: patella.
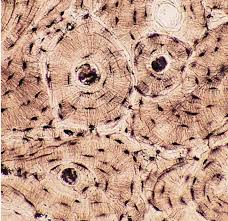
Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue)
Connective tissue composed of cells and an organic-inorganic extracellular matrix.
Collagen Fibers
Organic component (≈35%) that provides tensile strength and flexibility to bone.
Hydroxyapatite
Inorganic mineral salts (≈65%) that give bone its hardness and compressive strength.
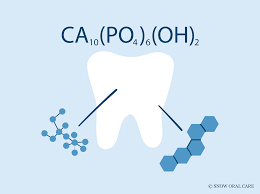
Osteogenic Cell
Bone stem cell producing osteoblasts; found in periosteum/endosteum.
Osteoblast
Bone-forming cell; secretes osteoid for bone mineralization.
Osteocyte
Mature bone cell in lacuna; maintains matrix via canaliculi.
Osteoclast
Dissolves bone matrix via osteolysis, releasing calcium and phosphate.
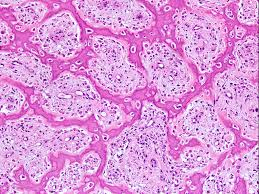
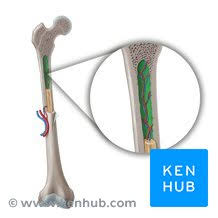
Compact Bone
Dense outer bone layer composed of osteons; provides strength for weight bearing.
Spongy (Cancellous) Bone
Internal lattice of trabeculae; lighter and houses red or yellow marrow.
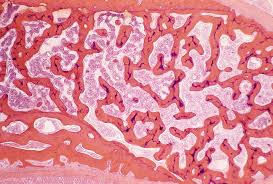
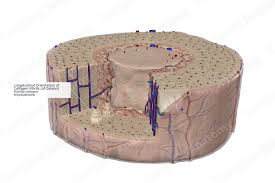
Osteon (Haversian System)
Structural unit of compact bone consisting of concentric lamellae around a central canal.
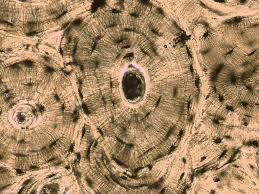
Lamellae
Concentric rings of calcified matrix in an osteon.
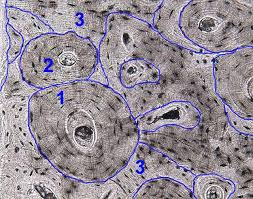
Lacuna
Small cavity housing an osteocyte within bone matrix.
Canaliculi
Microscopic canals that connect lacunae and allow nutrient/waste exchange.
Central (Haversian) Canal
Channel in the center of an osteon containing blood vessels and nerves.
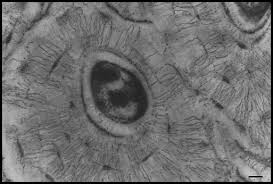
Trabecula
Thin struts or plates forming the lattice of spongy bone.
Diaphysis
Shaft of a long bone composed mainly of compact bone surrounding the medullary cavity.
Metaphysis
Narrow region connecting diaphysis to epiphysis; contains growth plate in children.
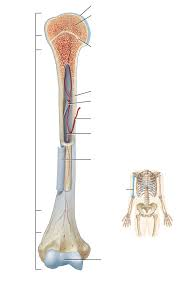
Epiphysis
Expanded end of long bone, mostly spongy bone.
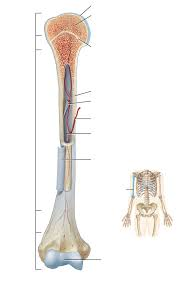
Epiphyseal Line
Adult bone mark from epiphyseal plate, indicating ceased growth.
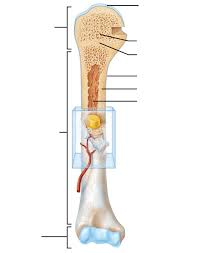
Articular Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage covering epiphyses where bones articulate, reducing friction.
Medullary Cavity
Central cavity within diaphysis containing red or yellow marrow.
Periosteum
Fibrous membrane covering bone (except joints), containing osteogenic cells and vessels.
Endosteum
Thin membrane lining medullary cavity and trabeculae; site of bone growth and remodeling.
Nutrient Artery
Major vessel entering the diaphysis to supply bone tissue.
Endochondral Ossification
Process in which hyaline cartilage is replaced by bone; forms most skeletal bones.
Intramembranous Ossification
Bone development from mesenchymal tissue; forms flat bones like skull and clavicle.
Ossification
General process of bone formation by osteoblasts.
Appositional Growth
Bone growth in diameter via addition of new bone at the periosteal surface.
Interstitial Growth
Lengthwise growth of long bones occurring at the epiphyseal plates.
Pituitary Growth Failure
Short stature due to insufficient growth hormone during childhood.
Marfan Syndrome
Genetic disorder causing excessive cartilage formation; results in tall stature and long limbs.
Gigantism
Excess growth hormone before puberty leading to extreme height.
Acromegaly
Excess growth hormone after epiphyseal closure causing bone thickening in face, jaw, hands.
Internal Callus
Spongy bone and cartilage bridge forming inside the medullary cavity during repair.
External Callus
Cartilage and bone collar forming around the outside of a fracture site.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Hormone that raises blood calcium by stimulating osteoclasts, kidneys, and intestines.
Calcitonin
Thyroid hormone lowering blood calcium through osteoclast inhibition
Calcitriol
Active form of vitamin D that increases intestinal absorption of calcium.
Red Bone Marrow
Hematopoietic tissue producing red and white blood cells and platelets.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Adipose-rich marrow serving as an energy reserve.
Osteoid
Unmineralized organic matrix secreted by osteoblasts.
RANKL (Receptor Activator of Nuclear factor κB Ligand)
Signal from osteoblasts promoting osteoclast differentiation.
Bone Remodeling
Continuous bone turnover for structural adaptation and calcium balance.