BSCI201 Biology Flashcards: Pre-Class Quizzes & Terms
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
T/F The two hemispheres of the cerebellum are separated by the longitudinal fissure.
False
T/F In a transverse cross section, both dorsal cavities within the body could be visible.
False
T/F Both the pollex and antebrachial regions are distal to the olecranon.
True
One of the descriptions below is from the perspective of anatomical study, the rest are from a physiological perspective. Select the description below that comes from an anatomical perspective.
a. The innermost lining of the lungs is composed primarily of a thin tissue called simple squamous epithelium.
b. The cell-to-cell connections between heart (cardiac) muscle cells are strong. They hold the tissue together for a life time of forceful contractions.
c. The extremely thin tissue (simple squamous epithelium) of the lungs allows for the quick diffusion of respiratory gases into and out of the body.
d. The direction of blood flow through the heart is directed by one-way valves.
The innermost lining of the lungs is composed primarily of a thin tissue called simple squamous epithelium.
Recall the order of epidermis cellular layers from deepest to most superficial
Deepest
Stratum Basale
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Corneum
Superficial
Your patient has a typical blood pH of 7.35 at their first visit. It is two months later when you draw blood again and the pH is now 7.5.
The blood has undergone an ________ shift and there is a Lower concentration of H+ ions in their blood now _________ than before.
alkaline, lower
The __________ is most closely associated with the cerebellum in embryonic development and remains its primary source of input fibers throughout life.
a. telencephalon
b. midbrain
c. medulla oblongata
d. thalamus
e. pons
f. cerebrum
Pons
In skeletal muscles, the thin filament is composed of
a. calmodulin and myosin
b. actin
c. actin, troponin and tropomyosin
d. myosin
e. actin and tropomyosin
f. myosin and myosin light chain
Actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
T/F In skeletal muscles, the primary neurotransmitter is acetylcholine.
True
T/F The majority of the CSF is produced by the choroid plexus.
False
If damage were to occur to the then there is a strong likelihood that bleeding would occur.
a. Papillary layer
b. Stratum basale
c. All of the listed options
d. Stratum lucidum
e. Two of the listed options
f. Stratum spinosum
Papillary Layer
Indicate the tissue described below.
Your view (at 250x) contains many rectangular shaped cells where each is are longer than they are wide. Each cell has only more than one nucleus. There are cells above and below each other which appear almost directly stacked. Within the cells there are alternating dark and light vertical bands throughout.
Write out the full name of the tissue without any capitalization.
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
T/F In a tissue experiencing high tensile (pulling) stress, we would expect to find intermediate filaments within the cell and desmosomes between neighboring cells.
True
Which of the following is true of epithelial tissue?
a. All of the listed options
b. None of the listed options
c. If the apical surface contains microvilli, the tissue includes the name stratified.
d. The basal surface contains a layer of smooth muscle tissue
e. The tissue does not contain blood vessels
f. If there are 3 layers of cells and the cells near the basal layer are columnar shaped, then the tissue is named stratified columnar epithelium.
The tissue does not contain blood vessels
In which of the following are the cells the oldest/been the longest since they were created?
a. Stratum basale
b. in cells in each of the listed regions were created at the same time
c. Stratum spinosum
d. Stratum granulosum
e. Cannot be determined with the given information
Stratum granulosum
Which of the following is a type of connective tissue proper?
a. none of the listed options
b. Blood
c. Elastic Cartilage
d. Hyaline Cartilage
e. two of the listed options
f. Adipose
Adipose
Name the mitotically active cell which creates the ground substance and fibers of fibrocartilage.
Use only lowercase, singular.
Chondroblast
Which of the following leads to an increase in osteoclast activity?
a. Testosterone
b. None of the listed options
c. Two of the listed options
d. Estrogen
e. Calcitonin
f. Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid Hormone
The skin is a(n) ________________ barrier.
a. Physical
b. Chemical
c. Biological
d. Incomplete
e. All of the listed options
All of the listed options
Which of the following is able to repair following injury?
a. Epidermis
b. Bones in adulthood
c. Bones in childhood
d. All of the listed options
e. only dermis and bones in childhood
f. Dermis
All of the listed options
Which of the following is NOT a function of the integumentary system?
a. All of the listed options are functions of the integument
b. Sensation
c. Protection
d. Blood cell formation
e. Body temperature regulation
Blood cell formation
Which of the following is true in response to skin repair.
a. Granulation tissue lacks capillaries
b. None of the listed options are true
c. A keloid contain a high concentration of elastic fibers
d. Cells from the stratum granulosum regrow the epidermis
e. Scars have a different coloration than neighboring tissues since melanocytes are the first cells to migrate into, and help form, the granulation tissue
None of the listed options are true
Chimpanzees can grasp objects with their feet because their hallux contains a(n) _____________ joint.
Saddle
You are standing in anatomical position, your brachial does not move but you move your antebrachial region in a way that results in your palm facing posteriorly. What movement at a synovial joint was performed?
Pronation
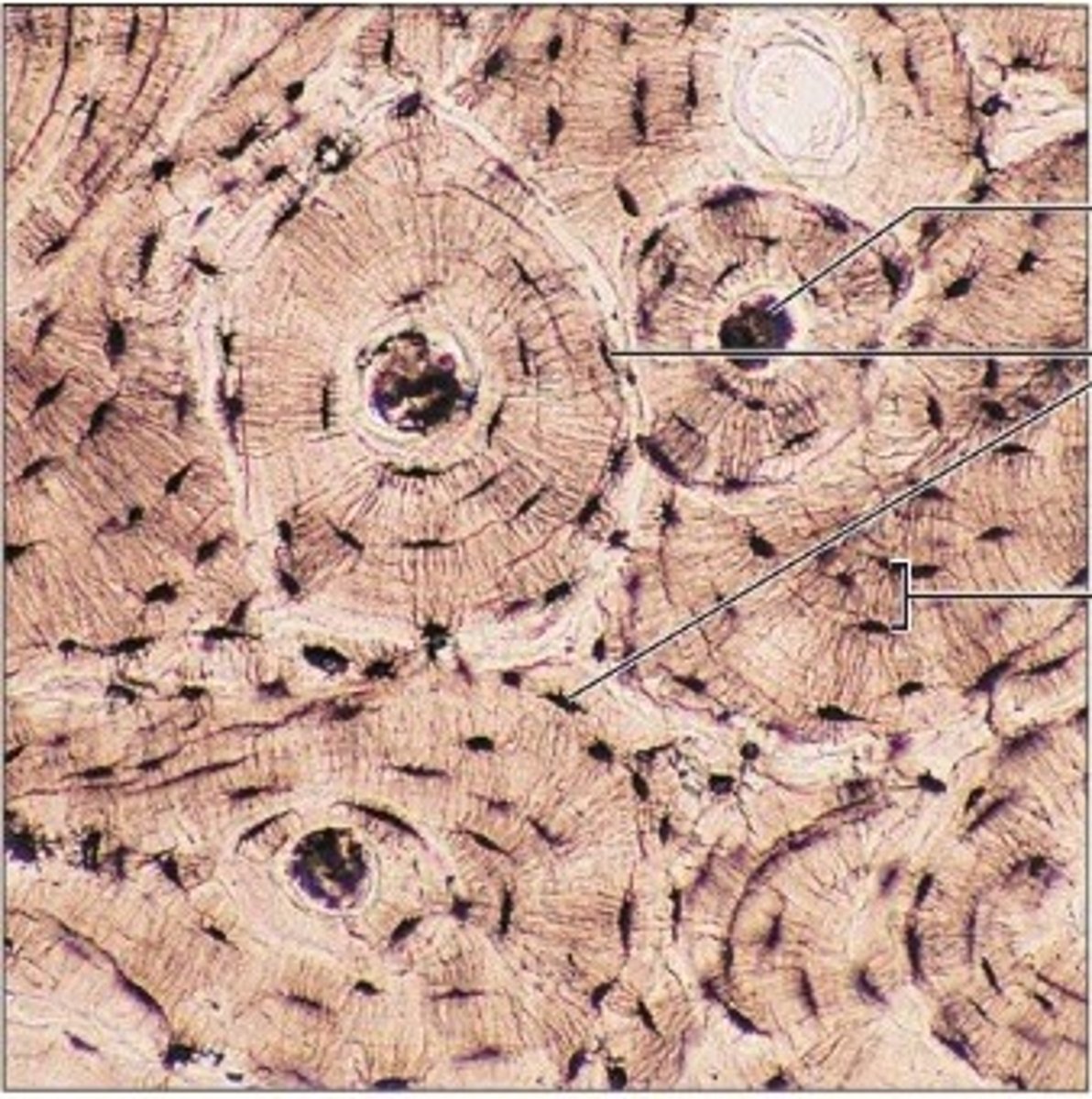
Which of the following is true of the tissue shown in the image below?
a. It is a multicellular exocrine duct
b. It primarily contains chondroblasts
c. It is transitional epithelial tissue
d. It is connective tissue proper
e. It is a type of connective tissue
f. More than one of the listed options
g. It is stratified squamous epithelial tissues
It is a type of connective tissue
Name the type of tissue which send (electrical) impulses throughout the body.
Nervous
The enzyme present in the neuromuscular junction's (NMJ) synaptic cleft that degrades the neurotransmitter is the _________.
a. Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK)
b. Calmodulin
c. Myosin ATPase
d. Acetylcholine esterase
e. Ligand-gated receptor
Acetylcholine esterase
A channel that allows for transport of sodium (Na+), and binds to acetylcholine is classified as a
a. Voltage-gated sodium channel
b. Voltage-gated ligand channel
c. Ligand-gated ion channel
d. Sodium-gated ligand channel
e. Sodium-gated acetylcholine channel
Ligand-gated ion channels
Most of the time, the blood-brain barrier is formed by
a. Ependymal cells
b. Oligodendrocytes
c. Endothelial cells
d. Blood capillaries
e. Astrocytes
Astrocytes
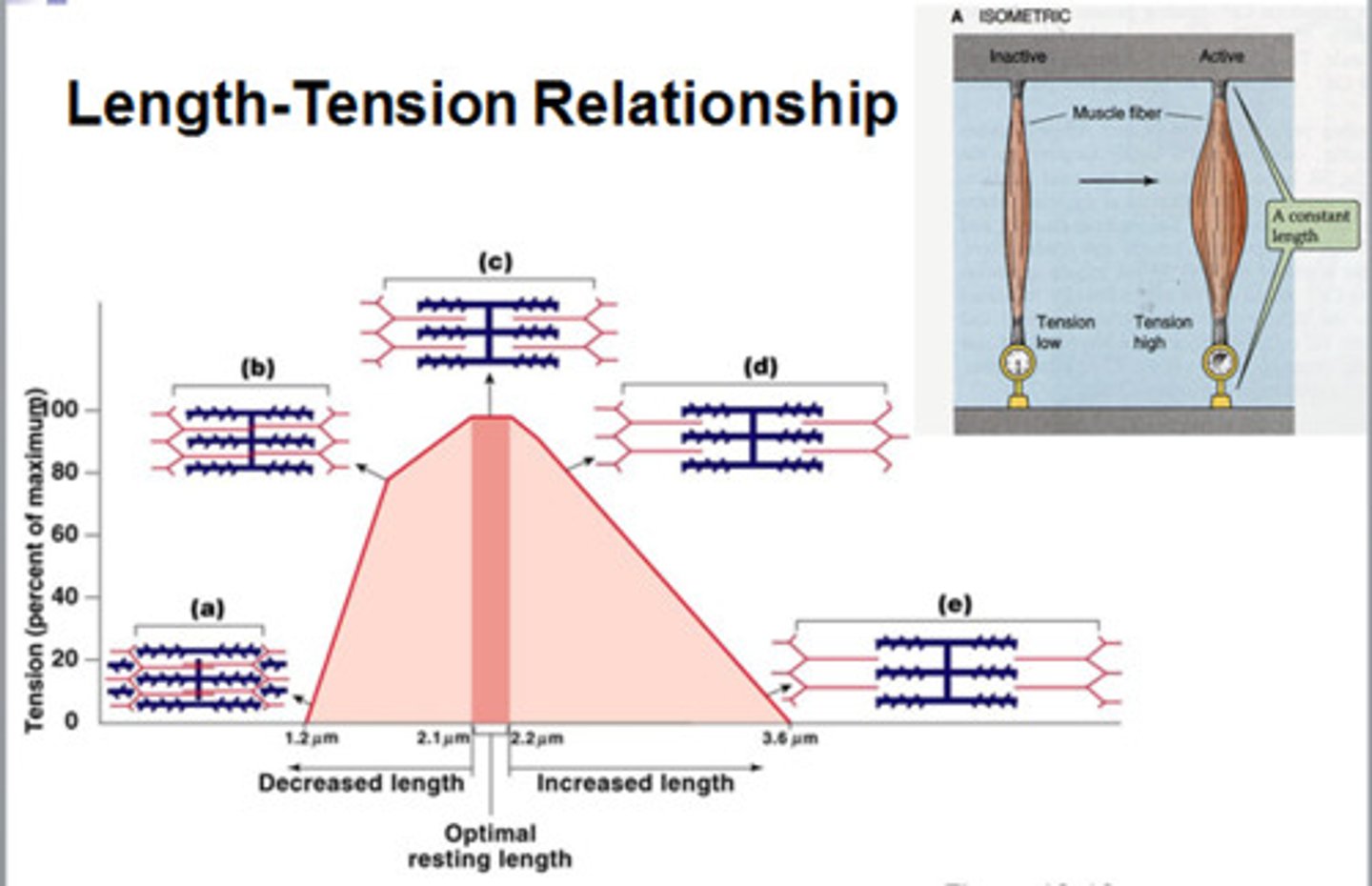
In the Length-tension curve of sarcomere contraction (see image)
a. Point B describes maximal force developed as all myosin tails are in contact with myosin heads
b. Point C describes the maximal length of optimal sarcomere size
c. Point A describes a decrease in force developed as the thin filaments physically hinder each others sliding
d. Point D describes minimal force due to the myosin touching the Z-disc structures
A, B, C, and D appear at the middle top and bottom of the graph in succession
Point C describes the maximal length of the optional sarcomere size
T/F Ca2+ is taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the myofiber through active transport.
True
T/F When a (=single) graded potential is received at one synapse, an action potential is generated at the axon hillock.
True
T/F Projection fibers (=tracts) in the CNS connect the brain to the spinal cord.
True
T/F The spinal cord extends all the way through the sacral region in the vertebral column.
False
T/F An individual with a spinal cord injury inferior to the lumbar enlargement is likely to be paraplegic.
False
T/F At the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), the membrane of the muscle cell is the ______________.
a. Synaptic cleft
b. Postsynaptic cell membrane
c. Axon terminal membrane
d. Presynaptic cell membrane
Postsynaptic cell membrane
At the __________ of the nerve cell, which is the postsynaptic membrane, you are likely to find ___________ channel that will bind neurotransmitters and produce a(n) ________________ potential.
dendrite, ligand-gated Nat+, local graded
Associate the classification to the protein regarding muscles. (only 3 of the answers must be used. Answers can repeat themselves)
Categories are:
Regulatory
Contractile
Structural
Mitotic
Productive
Conductive
Proteins are:
Troponin
Calmodulin
Myosin
MLCK
Actin
Titin
Troponin = Regulatory
Calmodulin = Regulatory
Myosin = Contractile
MLCK = Regulatory
Actin = Contractile
Titin = Structural
What tissue do you expect to find in ligaments connecting two bones?
a. Elastic tissue
b. Reticular tissue
c. Areolar loose connective tissue
d. Dense regular connective tissue
e. Dense irregular connective tissue
Dense regular connective tissue
During bone development, hyaline cartilage becomes bone in long bones through
a. Endochondral ossification
d. Symphyses
c. Intramembranous ossification
e. None of the other options
f. Appositional growth
Endochondral Ossification
During axon regeneration in the PNS, the production of collagen fibers by the endoneurium prior to the formation of the regeneration tube can lead to
a. Sclerotic tissue
b. Keloid tissue
c. Granulation tissue
d. None of the other options
e. Reticular tissue
Sclerotic tissue
T/F The epidural space is located between the dura mater and the arachnoid.
False
T/F The vascularized epithelium found in the bladder is defined as pseudostratified epithelium.
False
The __________________ is protected by the vertebral column; it is wrapped in the _______________ which is/are a thin layer of connective tissue, and does not continue along the _______________________.
spinal cord, pia mater, cauda equina
The pyramids are sensory and motor tracts observed at the ________, where they will cross-over, calling it the ______________________ , and which leads to _______________ organization between the brain and the spinal nerves.
medulla oblongata, decussation of the pyramids, contralateral
The reason why the action potential's conduction direction can only go from the axon hillock to the axon terminal is because
a. The Na+ channels along the axon remain open too long, leading to depolarization.
b. The K+ channels along the axon remain open too long, leading to hyperpolarization.
c. The K+ channels along the axon close up preventing the axon from reaching the resting membrane potential.
d. The Na+ channels along the axon are inactivated during repolarization.
e. The hyperpolarization will not allow another action potential to be fired.
The Na+ channels along the axon are inactivated during repolarization.
Light will first pass through the aqueous humor prior to passing through vitreous humor.
True
Refraction (bending/deflection) of light occurs in _____
a. Ciliary bodies
b. Sclera
c. None of the listed options
d. Cornea
e. Choroid
Cornea
T/F The visual pigment of a cone cell is photopsin, and allows for photic vision.
True
T/F The visual pigment of a rod cell is photopsin, and allows for scotopic vision (scotopia, vision under low-light conditions).
False
T/F Things we see with the left eye are perceived only in the primary visual cortex of the right cerebral hemisphere.
False
Which explains the ability to see the color purple?
a. None of the listed options
b. Both rods and cones are activated simultaneously
c. Some wavelengths activate multiple types of cones
d. Rods provide images in different shades
e. Purple is detected by activation of the N, purple, cone when there is a wavelength of 520nm
f. There are almost twice as many rods as cones in the eye
g. There are specific cones for each color
h. Purple is detected by activation of the N, purple, rod when there is a wavelength of 520nm
Some wavelengths activate multiple types of cones
The color of light is determined by
a. its velocity.
b. its amplitude.
c. how many rods it stimulates.
d. refraction
e. its wavelength.
Wavelength
The retina receives oxygen supply from
a. the hyaloid canal.
b. the pigment epithelium.
c. the sclera.
d. the choroid.
e. the vitreous body.
f. the scleral venous sinus.
The choroid
Which of the following statements about photopic vision (vision of the eye under well-lit conditions) is false
a. it does not employ rhodopsin.
b. it produces fine resolution.
c. it is mediated by the cones.
d. it does not function in starlight.
e. It has a low threshold.
It has a low threshold
The most finely detailed vision occurs when an image falls on a pit in the retina called the
a. optical disc.
b. retina.
c. fovea centralis.
d. macula lutea.
e. hyaloid canal.
fovea centralis
Match the receptor with the stimulus that activates it
a. Chemical
b. Solute concentration of body fluids
c. Pain
d. Pressure and vibration
e. Temperature
Chemical stimulus = Chemoreceptor
Solute concentration of body fluids = Osmoreceptor
Pain = Nociceptor
Pressure and vibration + Mechanoreceptor
Temperature + Thermoreceptor
The blind spot in our visual field occurs because
a. our ocular muscles cannot process movement that allow to have a full 180'radius of field of vision
b. there are certain shapes and color that our cones and rods cannot process.
c. the macula lutea aligns with the optic disc and the path of light.
d. there are no photoreceptors at the back of the retina, where the axons of the retinal ganglion cells exit the retina at the optic disc.
T/F Endolymph is potassium rich and the movement of potassium from the endolymph into the hair cells leads to depolarization.
True
Olfactory receptor cells are____________ cells, with its dendrites projecting_________________ in contact with the ____________________ secreted by ___________________.
bipolar, olfactory cilia, mucus, olfactory glands
Dissolved chemicals (or tastants) stimulate gustatory receptor cells by flowing through ion channels in the plasma membrane or by binding to receptors attached to G-proteins in the membrane.
True
If you wiped your tongue completely dry, you would not be able to have the sense of taste.
True
The bending of hair cells is associate with the sensation of __________________.
Hearing
Gustation is achieved through activation of mechanoreceptors.
False
Associate the structure to the location in the ear
Locations:
External Ear
Middle Ear
Inner Ear
Structures:
Pinna
Eardrum
External auditory canal
Stapes
Malleus
Incus
Semicircular canals
Vestibule
Cochlea
Pinna = External
Eardrum = External
External auditory canal= External
Stapes = Middle
Malleus = Middle
Incus = Middle
Semicircular canals = Internal
Vestibule = Internal
Cochlea = Internal
Several terms have different names for the same structure. Match the 2 names of the same structure.
Common Name:
Eardrum
Pinna
Earwax
Eustachian Tube
Internal Ear
Anatomical Name:
Tympanic Membrane
Auricle
Cerumen
Auditory Tube
Labyrinth
Common Name:
Eardrum = Tympanic Membrane
Pinna = Auricle
Earwax = Cerumen
Eustachian Tube = Auditory Tube
Internal Ear = Labyrinth
Match the characteristics of the soundwave with its physical description.
Physical Aspect:
Wavelength
Pitch
Soundwave Aspect:
Frequency
Amplitude
Frequency = Pitch
Amplitude = Loudness
T/F The receptors for gustation, the gustatory receptor cells, are located in taste buds.
True
Which of the following is part of the middle ear?
a. Pinna
b. Lobule
c. More than one of the listed options
d. Cochlea
e. Semicircular canals
f. Ossicular chain
Ossicular Chain
Which explains the ability to see the color orange?
a. None of the listed options
b. There are specific cones for each color
c. There are almost twice as many rods as cones in the eye
d. Some wavelengths activate multiple types of cones
e. Rods provide images in different shades
Some wavelengths activate multiple types of cones
If smooth muscle function were impaired, which of the following would be most impacted?
a. oval window
b. pupil
c. pigmented layer of the retina
d. external acoustic meatus
e. olfactory epithelium
Pupil
Which of the following occurs due to hyperpolarization?
a. Detection of stimuli which will be interpreted as loud sounds
b. Detection of any stimuli which will be interpreted as sound
c. Detection of stimuli which will lead to vision
d. Detection of stimuli which will be interpreted as quiet sounds
e. Detection of stimuli which will be interested as salty
f. Detection of stimuli which will lead to vision only in low light environments.
g. Detection of stimuli which will be interested as bitter
Detection of stimuli which will lead to vision
In the eye, which of the following first undergoes an electrical change in response to light?
a. Bipolar cells
b. Lens
c. Optic nerve
d. Rods
e. Ganglion cells
Rods
Which of the following is/are in the correct order which sound wave/vibrations pass from the external environment to the internal environment (not all structures will be provided in each option)?
a. Tympanic membrane, oval window, endolymph
b. Pinna, oval window, stapes, basilar membrane
c. Incus, tympanic membrane, organ of Corti
d. Malleus, incus, stapes, tympanic membrane
Tympanic membrane, oval window, endolymph
Which of the following contain endolymph?
a. olfactory epithelium
b. adrenal gland
c. semicircular canals
d. pineal gland
e. none of the listed options
f. all of the listed options
semicircular canals
Batrachotoxin, from poison-dart frogs, reduces (lowers) the threshold for the voltage-gated sodium channels to open by 30-50 mV within motor neurons. Please indicate how this would impact the timing of rigor mortis?
a. It would lead to normal/slow onset of rigor mortis = prevent crossbridge detachment
b. It would lead to normal/slow onset = prevent the activation of the enzyme MLCK
c. It would lead to a sooner onset of rigor mortis = increase the rate of action of ATPase in skeletal muscle
d. It would lead to a sooner onset of rigor mortis = prior to death there would be convulsions due to more ACH release from the motor neuron than normal
e. It would lead to a normal/slow onset of rigor mortis = inhibit the ability to send an action potential
f. It would lead to a sooner onset of rigor mortis = batrachotoxin would irreversibly bind to the acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.
It would lead to a sooner onset of rigor mortis because prior to death there would be convulsions due to more ACH release from the motor neuron than normal
Olfactory receptors are _______ positionally to gustatory cells, and both are type of __________ (receptor).
superior, chemoreceptors
T/F Olfaction is achieved through activation of mechanoreceptors.
False
Refraction (bending/deflection) of light occurs in .
a. Sclera
b. None of the listed options
c. Two of the listed options
d. Ciliary bodies
e. Choroid
f. Cornea
Cornea
Within the cochlea, hair cells are surrounded by sodium-rich endolymph.
False
Which statement is FALSE of endocrine glands
a. Some may have endocrine and exocrine functions
b. They may release hormones in the extracellular fluid or the blood.
c. The impact of their released products will depend on the receptors of the target cell/organ.
d. They use ducts to release their hormones
They use ducts to release their hormones
T/F Hypersecretion of growth hormone in an 23 year old would likely lead to an increase in bone longitudinal growth.
False
Given your understanding of synapses and the chemical signaling action of a neurotransmitter, it is generally considered...
a. autocrine
b. endocrine
c. exocrine
d. Paracrine
Paracrine
A small signaling molecule binds to a G-protein, preventing its activation. What direct effect will it have on signaling that involves cAMP?
a. the phosphorylation cascade will be initiated
b. the hormone will not be able to bind to the hormone receptor.
c. Adenylyl cyclase will not be activated
d. excessive quantities of cAMP will be produced
Adenylyl cyclase will not be activated
T/F Atrial natriuretic peptide is released from the heart which is a secondary endocrine gland.
True
Autocrines are a type of hormone that specialize in local communication.
False
Cytokines are only released from cells within the immune system.
False
The release of follicle stimulating hormone occurs due the actions of another hormone, Gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
True
Which of the following travels the furthest (from site of release to target) through the body?
Hormones
Which of the following is not a primary endocrine gland?
a. More than one of the listed options
b. Thyroid gland
c. Pancreas
d. Kidney
e. Pineal gland
Kidney
Name the hormone released from the pituitary gland which causes smooth muscle contractions in the uterus and the ductus deferens (also known as Vas deferens).
a. Oxytocin
b. Progesterone
c. Gonadotropin releasing hormone
d. Testosterone
Oxytocin
Which of the following hormones contributes tot he regulation of the body's fluid and electrolyte balance?
a. adrenocorticotropic hormone
b. antidiuretic hormone
c. calcitonin
d. luteinizing hormone
Antidiuretic hormone
T/F The pancreas is a primary endocrine gland and releases glucagon.
True
When blood calcium levels are low, PTH stimulates
a. a reduction in calcium absorption from the intestines
b. the activity of osteoclasts
c. urinary excretion of calcium by the kidneys
d. the activity of osteoblasts
the activity of osteoclasts
The adrenal glands are attached superiorly to which organ?
a. thyroid
b. heart
c. Kidneys
d. Liver
Kidneys
What cells secrete melatonin?
a. pinealocytes
b. melanocytes
c. epithelial cells
d. retinal cells
If the parathyroid glands where removed, which of the following would be the most likely to be impacted?
a. Serum (blood) calcium homeostasis
b. Age of first menstrual cycle in females
c. Ovulation
d. Milk production
e. Sleep/Wake cycles
Serum (blood) calcium homeostasis
Which of the following is released from the posterior pituitary?
a. The hormone that stimulates osteoclasts
b. The hormone which if is released in high amounts in adults leads to acromegaly
c. The hormone that triggers the release of follicle-stimulating hormone
d. The hormone involved with milk ejection response
The hormone involved with milk ejection response
A scientist has discovered a new lipid-soluble hormone. Given this information, which of the following is most likely true regarding this hormone?
a. It's receptor will be located on the plasma membrane
b. It will be released from red blood cells
c. Large amounts will need to be secreted to compensate for its short-half life
d. It will be bound to a transport protein in the blood
e. It will travel across a synaptic/neuromuscular cleft to reach its target organ
It will be bound to a transport protein in the blood
Antidiuretic hormone is released from the ___________________ gland and travels through the bloodstream to act on the its target organ the ___________ . This results in an increase of water in the _________________.
posterior pituitary gland, kidney, blood