2 - Wound Healing 2024 (Rush Surgery)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
80%
The tensile strength of a wound only reaches only about _____% of uninjured issue
Zinc
Zinc is a necessary cofactor of RNA and DNA polymerase, and deficiencies have been linked to poor early wound healing.
Deficiency in _______ (vitamin) results in delayed early wound healing
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
FGF is mitogenic for endothelial cells, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and myo- blasts; stimulates wound contraction and epithelialization; and induces the production of collagen, fibronectin, and proteoglycans. It is an important mediator of angiogenesis
___________ (growth factor) stimulates wound contraction
Stage __ pressure ulcers arerepresented by the presence of non- blanching erythema of intact skin
Stage I
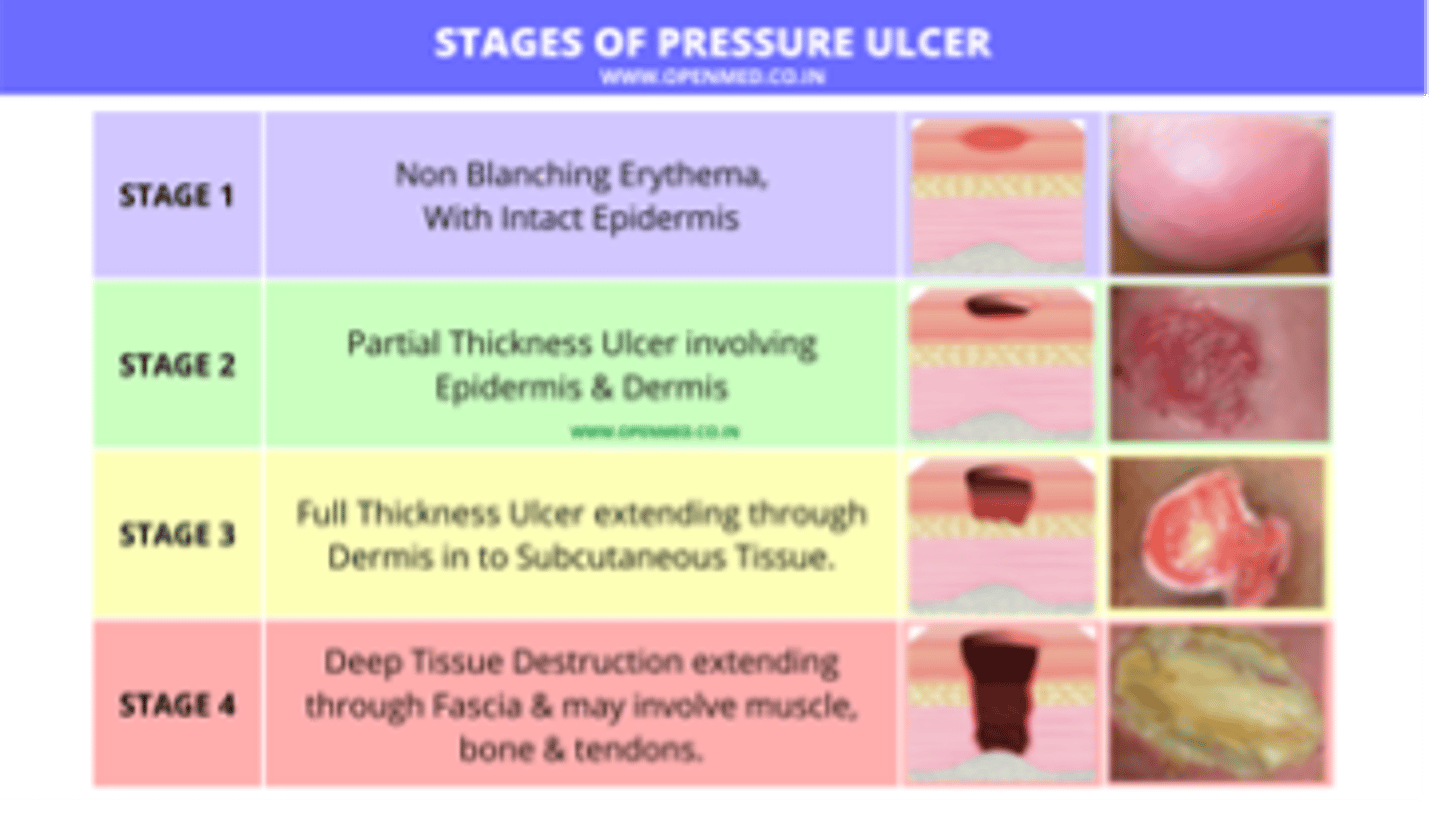
Stage ___ pressure ulcers are characterized by partial-thickness skin loss involving the epidermis or dermis
Stage II
Clinically, the ulcer is manifested as a blister, abrasion, or shallow crater
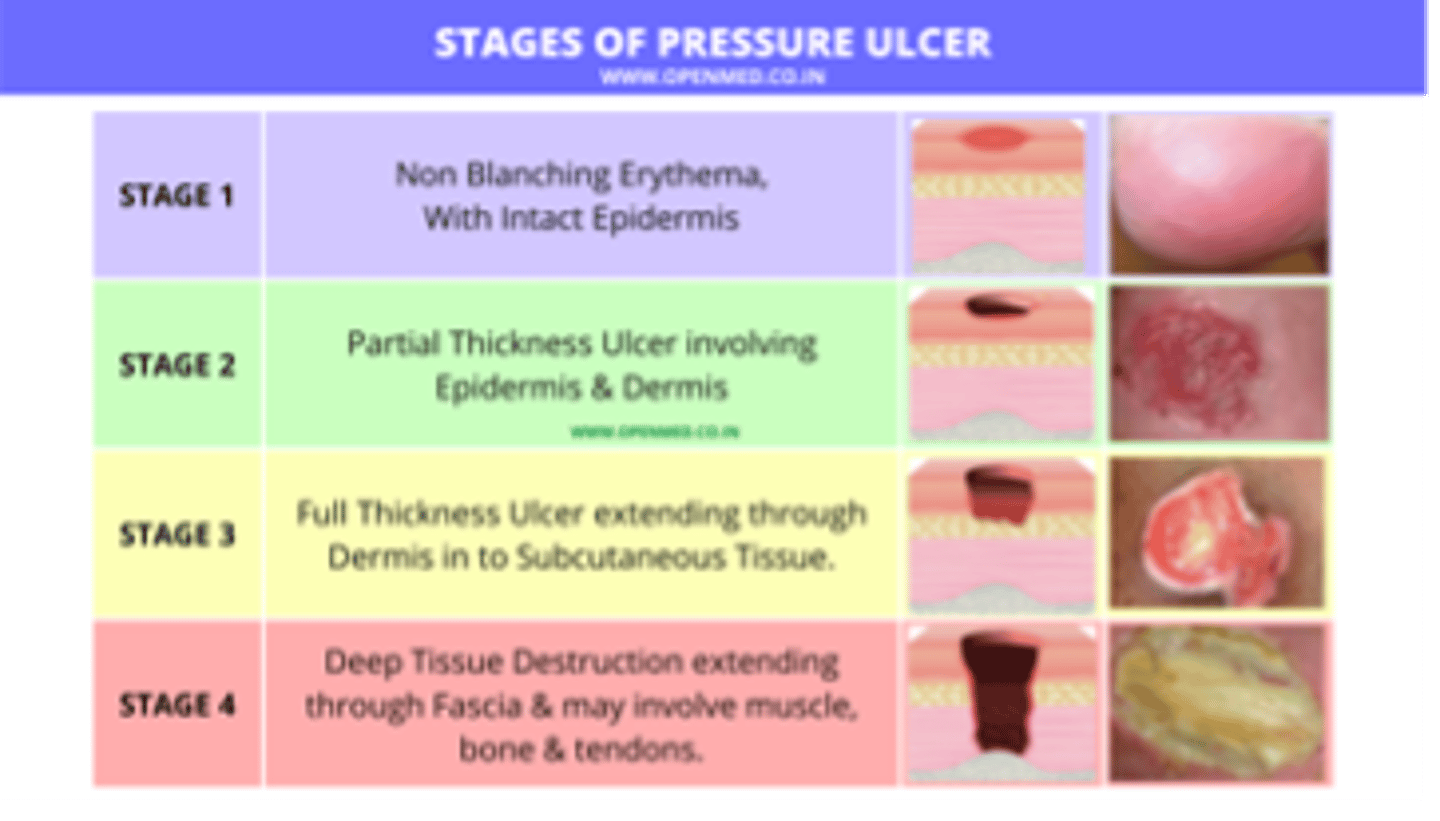
Stage ___ pressure ulcers are full-thickness skin loss with involvement of the underlying subcutaneous tissue and may extend down to but not through underlying fascia
Stage III
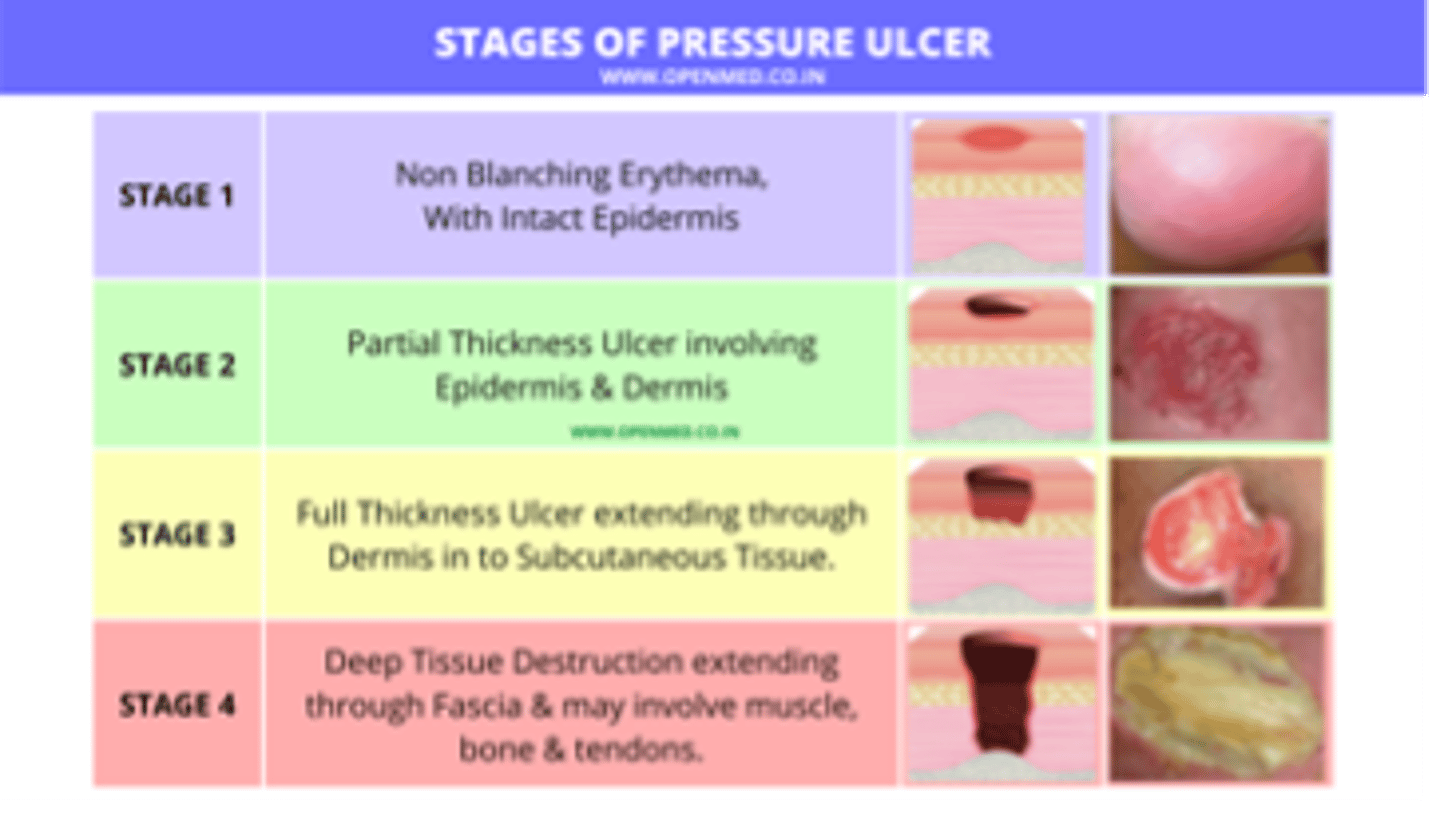
Stage _____ pressure ulcers represent full-thickness skin loss with extensive destruction or tissue necrosis of underlying structures, which may include muscle and bone.
Stage IV
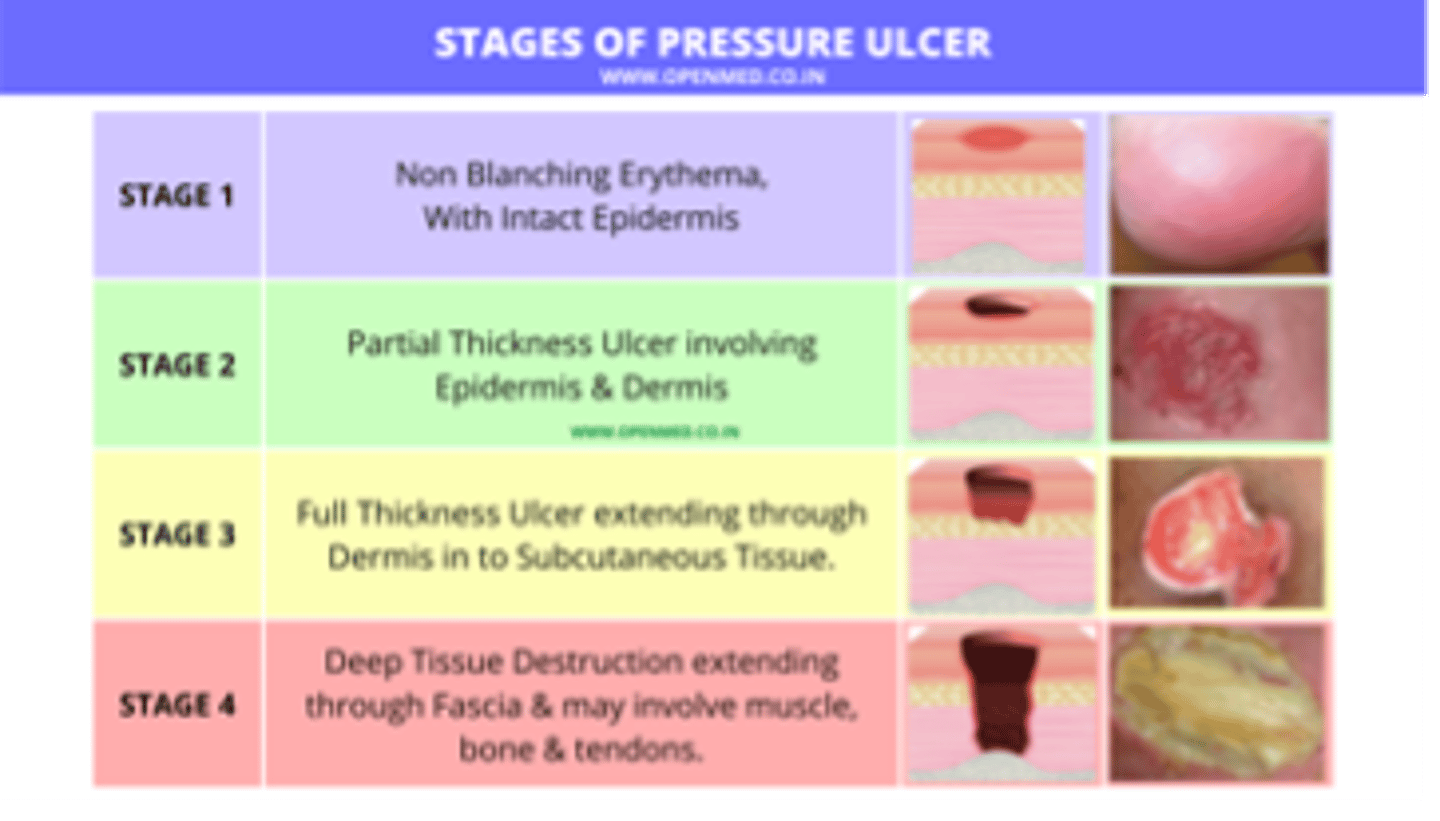
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is required for normal calcium metabolism, but it is also involved in promoting immune function in the skin
Vitamin ____ serves an immunomodulatory role in wound healing.
Proliferative phase
During this phase granulation tissue is formed through angiogenesis, fibroplasia, and epithelialization
It is during the ______ phase of wound healing that the scaffolding for tissue repairis laid.