AP Psychology - Unit 1 Vocabulary - Chapter 1 Vocabulary #2
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
VOCAB QUIZ #2 ON 9/23/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Agonist
a molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action
Antagonist
a molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action
Endocrine system
the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands and fat tissue that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Hormones
chemical messages that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
Psychoactive drug
a chemical substance that alters the brain, causing changes in perceptions and moods
Substance use disorder
a disorder characterized by continued substance use despite significant life disruption
Depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body function
Tolerance
the diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of the drug, requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug’s effects
Addiction
an everyday term for compulsive substance use (and sometimes for dysfunctional behavior patterns, such as out-of-control gambling) that continue despite harmful consequences
Withdrawal
the discomfort or distress that follow after discontinuing an addictive drug or behavior
Barbiturates
drugs that depress central nervous system activity, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment
Opioids
opium and its derivatives; they depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
Stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
Nic-a-teen
seeing celebrities, such as singer Lily Allen, vaping or smoking to tempt young people in the vulnerable teen and early-adult years to imitate. in 2017, over 1/3 of youth-rated movies showed smoking
The “Hug Drug”
MDMA, also known as Ecstasy and often taken at clubs, produces a euphoric high and feelings of intimacy. repeated use can destroy serotonin-producing neurons, impact memory, and permanently deflate mood
Hallucinogens
psychedelic (“mind-manifesting”) drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
Near-death experience
an altered state of consciousness reported after a close brush with death (eg. cardiac arrest); often similar to drug-induced hallucinations
Biological psychology
the scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes. (some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists)
Biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
Level of analysis
the differing complementary views, from biological to psychological to social-cultural, for analyzing any given phenomenon
Neuroplasticity
the brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
Lesion
tissue destruction.
brain lesions may occur naturally (from disease or trauma), during surgery, or experimentally (using electrodes to destroy brain cells)
EEG (electroencephalogram)
an amplified recording of the waves or electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface. these waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
MEG (magnetoencephalography)
a brain-imaging technique that measures magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity
CT (computed tomography) scan
a series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure
PET (positron emission tomography) scan
technique for detecting brain activity that displays where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. MRI scans show brain anatomy
fMRI
technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fMRI scans show brain function as well as structure
Understanding the non-WEIRD brain
most neuroscience research studies people from WESTERN, EDUCATED, INDUSTRIALIZED, RICH, and DEMOCRATIC populations (WEIRD)
Hindbrain
consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum; directs essential survival functions, such as breathing, sleeping, and wakefulness, as well as coordination and balance
Midbrain
found atop the brainstem; connects the hindbrain with forebrain, controls some motor movement, and transmits auditory and visual information
Forebrain
consists of the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus; manages complex cognitive activities, sensory and associative functions, and voluntary motor activities
Brainstem
the central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
Medulla
the hindbrain structure that is the brainstem’s base; controls heartbeat and breathing
Thalamus
the forebrain’s sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Reticular formation
a nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus; it filters information and plays an important role in controlling arousal
Cerebellum
the hindbrain’s “little brain” at the rear of the brainstem; its functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory
Limbic system
neural system located mostly in the forebrain — below central hemispheres — that includes the amygdala, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland; associated with emotions and drives
Amygdala
two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion
Hypothalamus
a limbic system neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system, and is linked to emotion and reward
Hippocampus
a neural center located in the limbic system; helps process explicit (conscious) memories — of facts and events — for storage
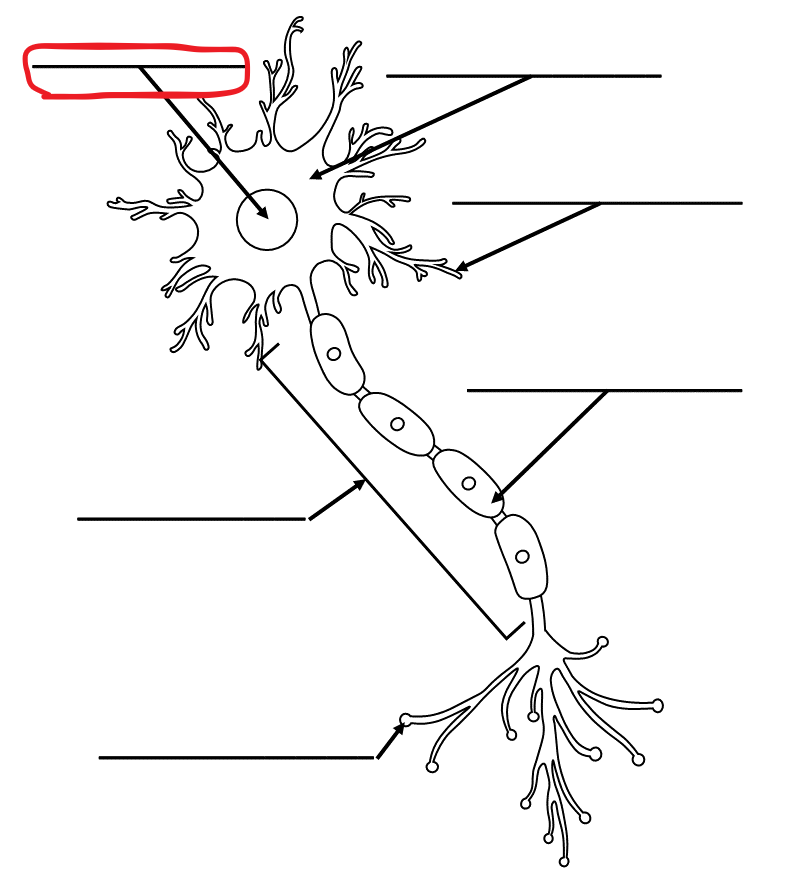
What is the term for this part of the neuron?
Nucleus
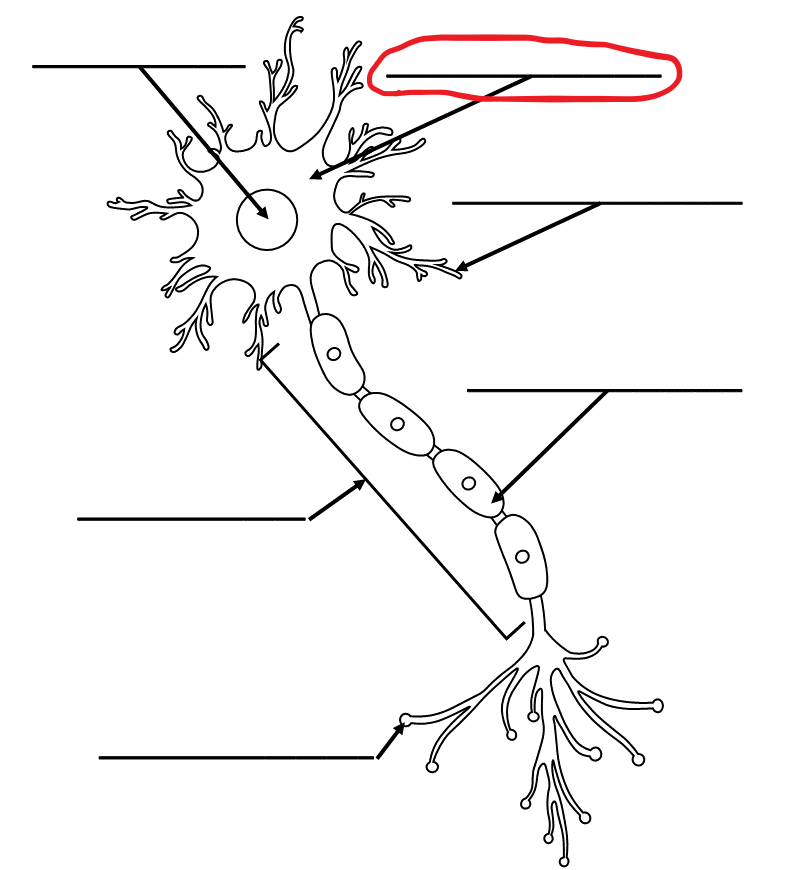
What is the term for this part of the neuron?
Cell Body/Soma
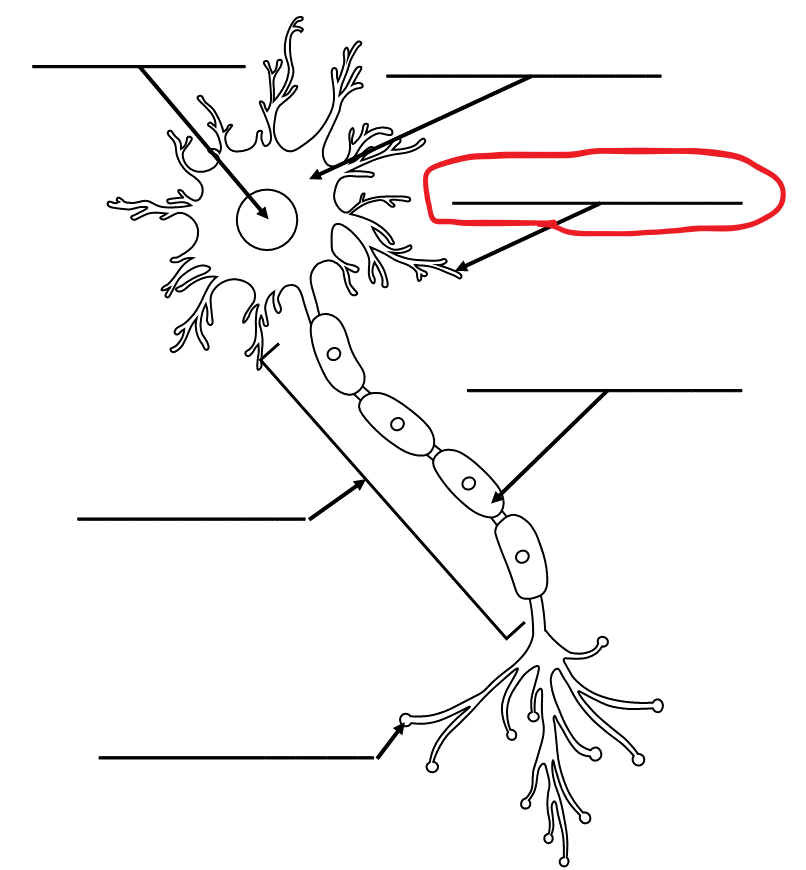
What is the term for this part of the neuron?
Dendrite
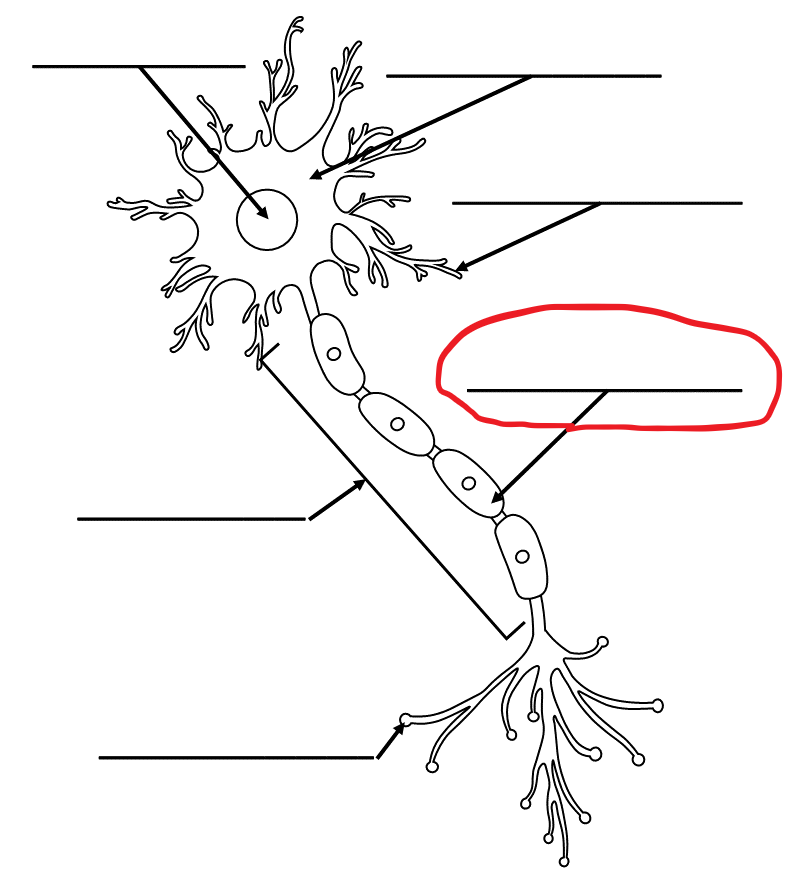
What is the term for this part of the neuron?
Myelin Sheath
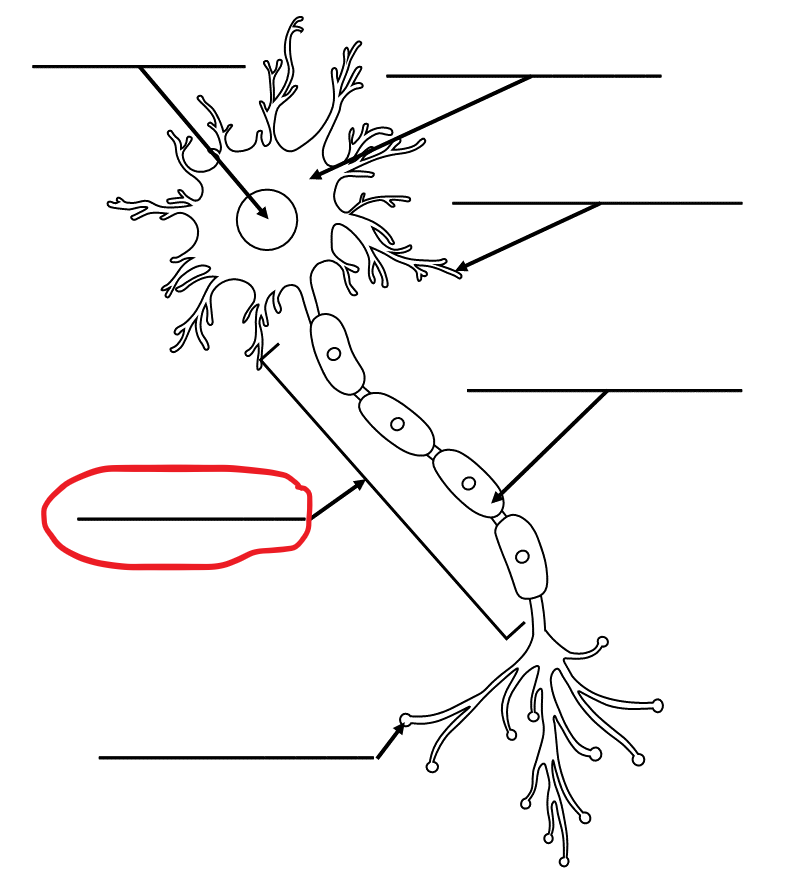
What is the term for this part of the neuron?
Axon
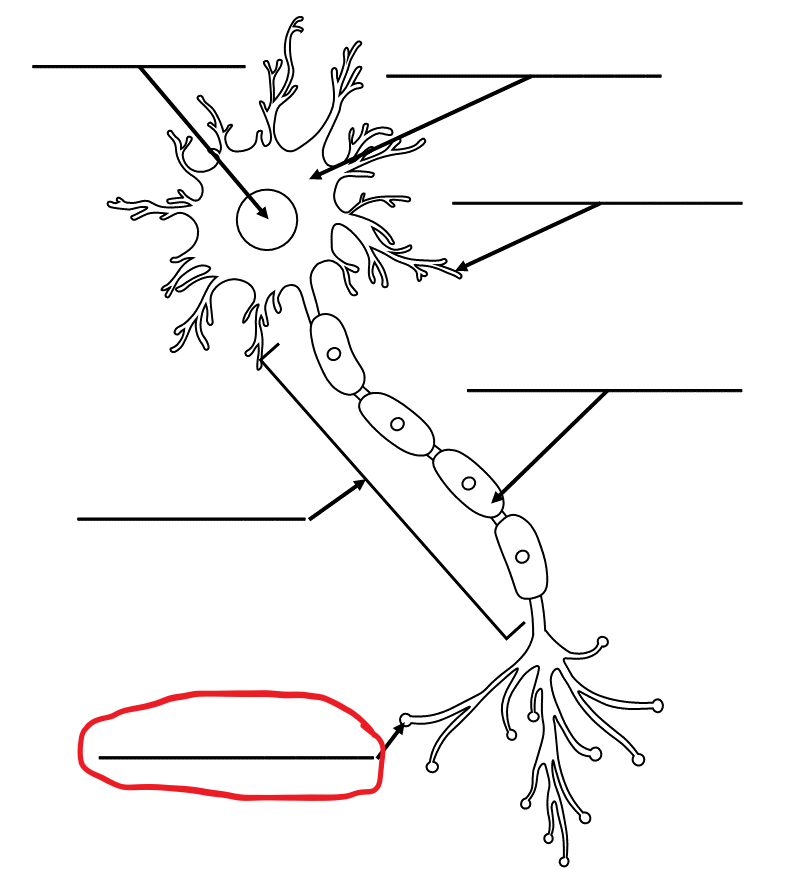
What is the term for this part of the neuron?
Terminal Buttons