GOVT 0402 - Topic #2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Last updated 10:17 PM on 2/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
What is Leadership?
* Is defined as the ability to inspire confidence and support among the people on whose competence and commitment performance depends.
* Involves influencing others to achieve objectives important to them and the organization.
* Contributes to organizational effectiveness through the use of desirable personal attributes to achieve good results.
* Involves influencing others to achieve objectives important to them and the organization.
* Contributes to organizational effectiveness through the use of desirable personal attributes to achieve good results.
2
New cards
Effective Leadership =
Attributes x Results
3
New cards
Leaders are _______
– Visionary
– Passionate
– Creative
– Flexible
– Inspiring
– Innovative
– Courageous
– Imaginative
– Experimental
– Independent
– Passionate
– Creative
– Flexible
– Inspiring
– Innovative
– Courageous
– Imaginative
– Experimental
– Independent
4
New cards
Managers are _______
– Rational
– Consulting
– Persistent
– Problem-solving
– Tough-minded
– Analytical
– Structured
– Deliberate
– Authoritative
\- Stabilizing
– Consulting
– Persistent
– Problem-solving
– Tough-minded
– Analytical
– Structured
– Deliberate
– Authoritative
\- Stabilizing
5
New cards
Some examples of leadership theories are _______
1. Trait Theory
2. Behavioural Theories
3. Contingency Theories
4. Contemporary Theories
6
New cards
Trait Theory can be defined as _______
* This theory seeks to explain that @@**personality**@@**,** @@**social**@@**,** **physical** or @@**intellectual traits**@@ differentiate leaders from non-leaders.
* People inherit certain qualities and traits that make them better suited to leadership.
* Traits are personal characteristics of the individual including physical characteristics, intellectual ability and personality.
* People inherit certain qualities and traits that make them better suited to leadership.
* Traits are personal characteristics of the individual including physical characteristics, intellectual ability and personality.
7
New cards
Cognitive Skills are _______
* Mental abilities and knowledge
* Problem-solving skills
* Imagination, creativity, and a willingness to experiment
* Technical and professional competence (knowledge of the business)
* Problem-solving skills
* Imagination, creativity, and a willingness to experiment
* Technical and professional competence (knowledge of the business)
8
New cards
Personality Traits are _______
* Enthusiasm
* Self-confidence
* Trustworthiness
* Emotional intelligence
* Needs for power and achievement
* A sense of humour
* Self-confidence
* Trustworthiness
* Emotional intelligence
* Needs for power and achievement
* A sense of humour
9
New cards
Limitations of “Trait” Approach (Trait Theory)
* Failure to take into account the situation in which leadership occurs
* Traits alone are not sufficient for successful leadership
* Traits are only a pre-condition for certain actions that a leader must take in order to be successful
* Certain traits may enhance the perception that somebody is a leader
* Traits alone are not sufficient for successful leadership
* Traits are only a pre-condition for certain actions that a leader must take in order to be successful
* Certain traits may enhance the perception that somebody is a leader
10
New cards
Behavioural Theories can be defined as _______
* These are theories proposing that @@**specific behaviours**@@ differentiate leaders from non-leaders
* The behaviour of the leader rather than specific personality traits determines a leader’s effectiveness
* Recognizes that some leaders modify their leadership style as the situation requires
* The behaviour of the leader rather than specific personality traits determines a leader’s effectiveness
* Recognizes that some leaders modify their leadership style as the situation requires
11
New cards
“Behavioural Theories” examples are:
1. Ohio State Studies
2. Michigan Studies
3. Leadership Grid
4. Leader-Member Exchange Model
5. Servant Leadership
12
New cards
The “**Ohio State Studies**” measured _______
specific leader behaviours
13
New cards
The “**Ohio State Studies**” identified **two** dimensions:
–**Consideration-** the extent to which a leader is sensitive to subordinates, respect their ideas and feelings and establishes mutual trust
\
–**Initiating Structure-** describes the extent to which leader is task oriented and directs subordinates work toward achieving goals
\
–**Initiating Structure-** describes the extent to which leader is task oriented and directs subordinates work toward achieving goals
14
New cards
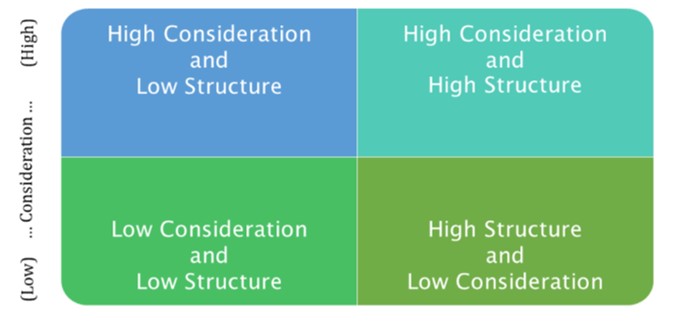
The “**Ohio State Studies”** states a relative mixture of _______
“Initiating structure and Consideration” a leader could possess.
15
New cards
The “**Ohio State Studies**” research findings are:
* A leader could possess varying amounts of both dimensions (consideration/ initiating structure)
* Consideration→ satisfaction with leader, overall job satisfaction
* Initiating structure→ job performance
* Attention must be paid to both dimensions in order to attain job satisfaction and production
* Consideration→ satisfaction with leader, overall job satisfaction
* Initiating structure→ job performance
* Attention must be paid to both dimensions in order to attain job satisfaction and production
16
New cards
The “**Michigan Studies**” compared the behaviour of _______
effective and ineffective supervisors
17
New cards
The “**Michigan Studies”** identified two basic leadership styles:
–Employee-centred managers (humanistic)
–Production-centred managers (scientific)
–Production-centred managers (scientific)
18
New cards
The research findings of the “**Michigan Studies**” are:
* Employee-centred managers had the most productive work groups
* The most effective leaders had supportive relationships with employees, used group decision-making, and encouraged employee goal setting
* The most effective leaders had supportive relationships with employees, used group decision-making, and encouraged employee goal setting
19
New cards
**“Leadership Grid”** Describes leadership style in terms of _______
concerns for production and people. These concerns reflect attitudes rather than actual behaviour.
* @@**Concern for production** @@includes results, bottom-line performance, profits, and mission
* @@**Concern for people** @@includes group members and co-workers
* @@**Concern for production** @@includes results, bottom-line performance, profits, and mission
* @@**Concern for people** @@includes group members and co-workers
20
New cards
(Leadership Grid) Grid assumes that an _______
opportunistic leader shifts to any Grid style to achieve personal gain and self-promotion.
* Best style is team management — at 9,9 on the Grid (high concern for both production and people)
* Best style is team management — at 9,9 on the Grid (high concern for both production and people)
21
New cards
In the **“Leader-Member Exchange Model”** Leaders do not ________
relate to each group member in the same manner
* Leaders develop unique working relationships with each group member
* Two groups: @@**in-group & out-group**@@
* The quality of relationship a group member has with a leader has a big impact on the individual’s job behaviour and performance.
* Leaders develop unique working relationships with each group member
* Two groups: @@**in-group & out-group**@@
* The quality of relationship a group member has with a leader has a big impact on the individual’s job behaviour and performance.
22
New cards
Servant Leadership style proposes that leaders _______
@@serve@@ the needs of their group members (constituents)
* Leaders measure their own effectiveness in terms of their ability to help others
* Servant leaders use a humanistic approach
\-Self-sacrificing
\-Humble
\-Helping others to develop
* Leaders measure their own effectiveness in terms of their ability to help others
* Servant leaders use a humanistic approach
\-Self-sacrificing
\-Humble
\-Helping others to develop
23
New cards
Contingency Theories are a group of theories that suggest that leadership effectiveness is _______
@@**contingent on** @@(depends on) the @@**situation**@@ **or** @@**setting**@@
* Contingent or flexible leadership can be thought of in terms of doing the right thing at the right time (as the situation evolves)
* Contingent or flexible leadership can be thought of in terms of doing the right thing at the right time (as the situation evolves)
24
New cards
Examples of “**Contingency Theories**”
* Fielder’s Contingency Theory
* Path-Goal Theory
* Normative Decision Model
* Path-Goal Theory
* Normative Decision Model
25
New cards
“**Fielder’s Contingency Theory**” Assumes that the best style of leadership is _______
Assumes that the best style of leadership is determined by the situation in which the leader is working
26
New cards
Fielder’s Contingency Theory Uses the **________** scale to measure the leader’s style
least-preferred co-worker (LPC)
27
New cards
(Fielder’s Contingency Theory) LPC is a measure of how _______
a manager describes his or her relationship to a referent (least preferred) co-worker.
28
New cards
(Fielder’s Contingency Theory, LPC) Positive LPC descriptions indicate _______
relationship-oriented management styles (e.g. I believe s/he does his/her best)
29
New cards
(Fielder’s Contingency Theory, LPC) Negative LPC descriptions indicate _______
task-oriented management styles (e.g. s/he is not meeting my expectations)
30
New cards
“**Fielder’s Contingency Theory**” Situational control is _______
the degree to which the leader can control and influence the outcomes of group effort.
31
New cards
“**Fielder’s Contingency Theory**” Situational control measurements are based on:
–Leader-member relations (good to bad)
–Task structure (well to ill-defined)
–Position power (leader’s ability to reward and control)
\
*There is not one best style of leadership*
–Task structure (well to ill-defined)
–Position power (leader’s ability to reward and control)
\
*There is not one best style of leadership*
32
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” specifies what a leader must do to _______
achieve high morale and productivity in a given situation
33
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” Focuses on helping employees find _______
the **right path** to **goal attainment**
34
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” assumes that the leader will choose the _______
right leadership style to match the contingencies of a particular situation.
35
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” Is based on Expectancy Theory in that its _______
key propositions relate to motivation, satisfaction, and performance.
36
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” choices for adjusting leadership styles to meet situational contingency demands:
* Directive
* Supportive
* Participative
* Achievement-oriented
* Supportive
* Participative
* Achievement-oriented
37
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” The “***Directive***” leadership style to meet situational contingency demands can be described as:
Initiating structure, setting guidelines and standards, and conveying expectations.
38
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” The “***Supportive***” leadership style to meet situational contingency demands can be described as:
Emphasizes showing concern for the wellbeing of group members and developing mutually satisfying relationships.
39
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” The “***Participative***” leadership style to meet situational contingency demands can be described as:
Involves consulting with group members and using their input into the decision-making process.
40
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory**” The “***Participative***” leadership style to meet situational contingency demands can be described as:
Leader sets challenging goals, promotes work improvement, sets high expectations and expects group members to act responsibly.
41
New cards
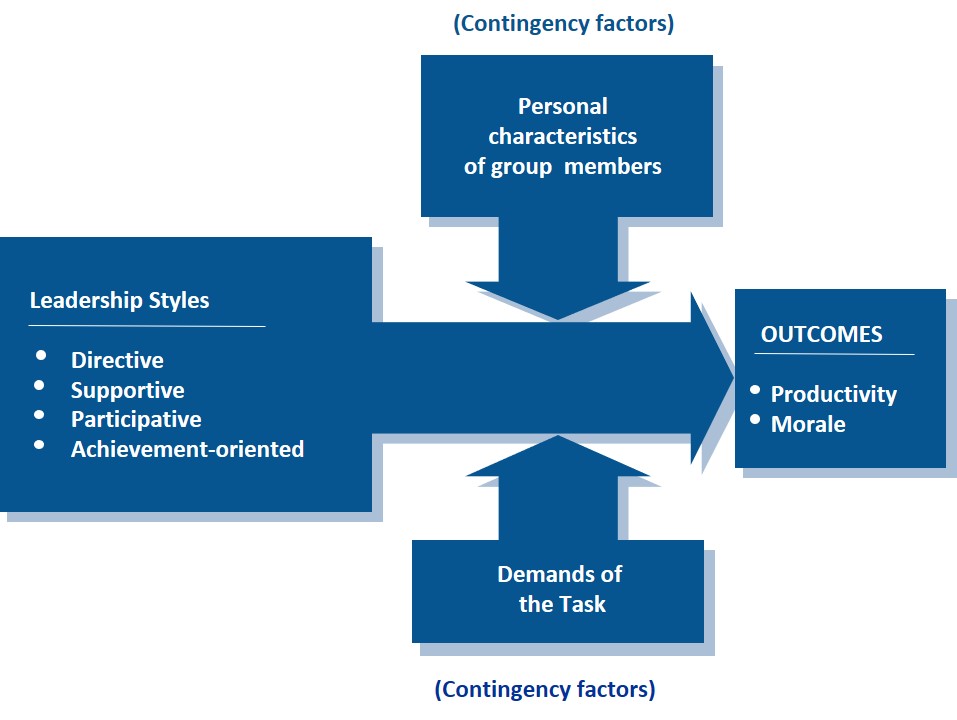
What is the above diagram?
Path Goal Theory
42
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory”** Leadership style “***Directive”*** the situation in which appropriate to deploy _______
\-Positively affects satisfaction and expectancies of subordinates working on ambiguous tasks.
\-Negatively affects satisfaction and expectancies of subordinates working on clearly defined tasks
\-Negatively affects satisfaction and expectancies of subordinates working on clearly defined tasks
43
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory”** Leadership style “***Supportive*****”** the situation in which appropriate to deploy _______
Positively affects satisfaction of subordinates working on dissatisfying, stressful, or frustrating tasks
44
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory”** Leadership style “***Paricipative*****”** the situation in which appropriate to deploy _______
Positively affects satisfaction of subordinates who are ego-involved with nonrepetitive tasks
45
New cards
“**Path-Goal Theory”** Leadership style “***Participative***” the situation in which appropriate to deploy _______
Positively affects confidence that effort will lead to effective performance of subordinates working on ambiguous and nonrepetitive tasks.
46
New cards
“Normative Decision Model” **leadership** is a decision-making process in which the
leader examines the situation and chooses the most effective decision-making style for the situation
47
New cards
**“Normative Decision Model”** five styles of decision making they are
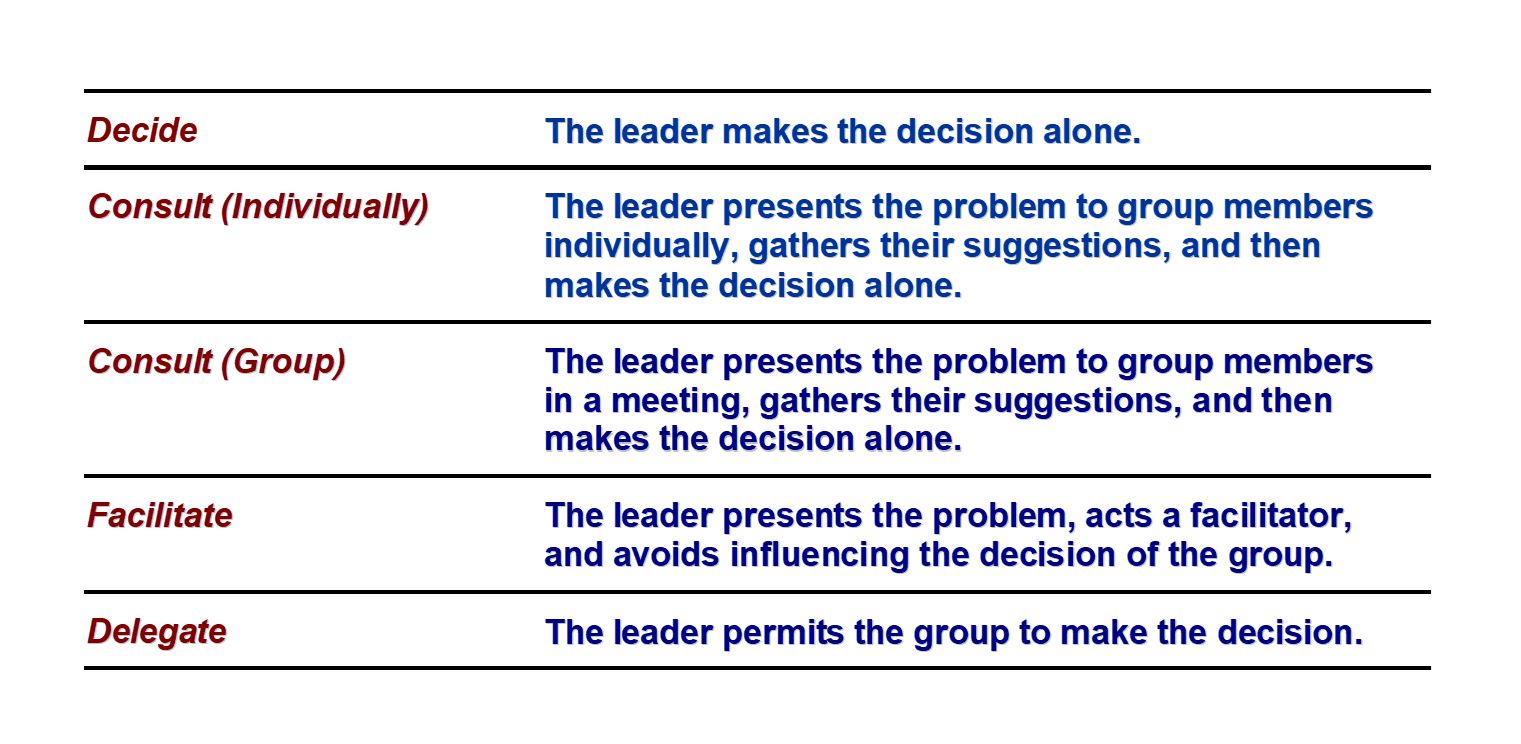
48
New cards
“***Contemporary Theories***” are a group of theories that provide _______
more recent approaches to leadership
49
New cards
__Examples__ of “***Contemporary Theories***” are:
Transformational Leadership and Charismatic Leadership
50
New cards
Transactional Leadership
–Focuses on results and structures
–Tends to conform to the existing structure of an organization
–Measures success through the formal system of rewards and penalties.
–Works within formal authority structures
–Depends on responsibility structures.
–Focuses on delivery through individual and group performance
–Optimizes performance
–Tends to conform to the existing structure of an organization
–Measures success through the formal system of rewards and penalties.
–Works within formal authority structures
–Depends on responsibility structures.
–Focuses on delivery through individual and group performance
–Optimizes performance
51
New cards
Transformational Leader
–Helps organizations and people make positive changes in the way they conduct their activities
–Is closely linked to strategic leadership
–Is involved in sweeping positive changes
–Is closely linked to strategic leadership
–Is involved in sweeping positive changes
52
New cards
Transformations:
– Raising people’s level of consciousness
– Getting people to transcend their self-interests
– Focusing people on the quest for self-fulfillment
– Helping to develop a long-range perspective
– Helping people understand the need for change
– Investing managers with a sense of urgency
\- Committing to greatness
– Getting people to transcend their self-interests
– Focusing people on the quest for self-fulfillment
– Helping to develop a long-range perspective
– Helping people understand the need for change
– Investing managers with a sense of urgency
\- Committing to greatness
53
New cards
(**Charismatic Leadership**) Charisma
Is the ability to lead others based on personal charm, magnetism, inspiration, and emotion.
54
New cards
(**Charismatic Leadership**) Key characteristics of Charismatics:
– They have vision
– They are masterful communicators
– They inspire trust
– They are energetic
– They manage their impressions
– They are masterful communicators
– They inspire trust
– They are energetic
– They manage their impressions
55
New cards
Substitutes for Leadership
**•Group member characteristics**
* Highly capable persons or groups (followers) can function with less leadership
* Effective followers are self-managers, are committed, have competence and focus, and possess courage
\
**•Task Characteristics**
* Highly standardized tasks that provide feedback and are intrinsically satisfying can substitute for leadership
\
**•Organizational factors**
* Explicit plans with well-defined goals that are carried out by cohesive groups reduce the need for leadership
* Highly capable persons or groups (followers) can function with less leadership
* Effective followers are self-managers, are committed, have competence and focus, and possess courage
\
**•Task Characteristics**
* Highly standardized tasks that provide feedback and are intrinsically satisfying can substitute for leadership
\
**•Organizational factors**
* Explicit plans with well-defined goals that are carried out by cohesive groups reduce the need for leadership