Chromatography: Elements compounds and mixtures: Chemistry: (9:1)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
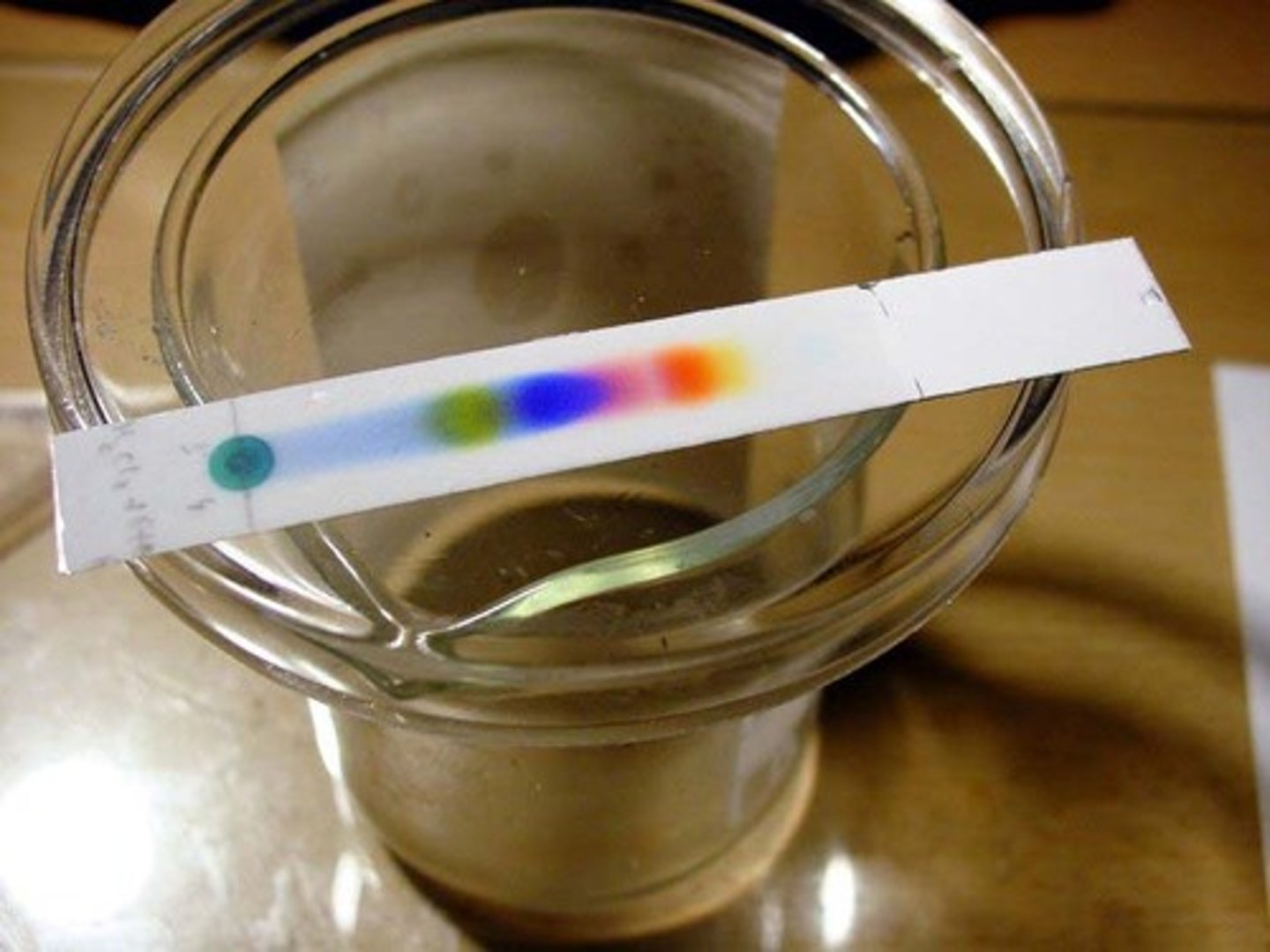
Chromatography
Separates the components of a mixture based on their solubility
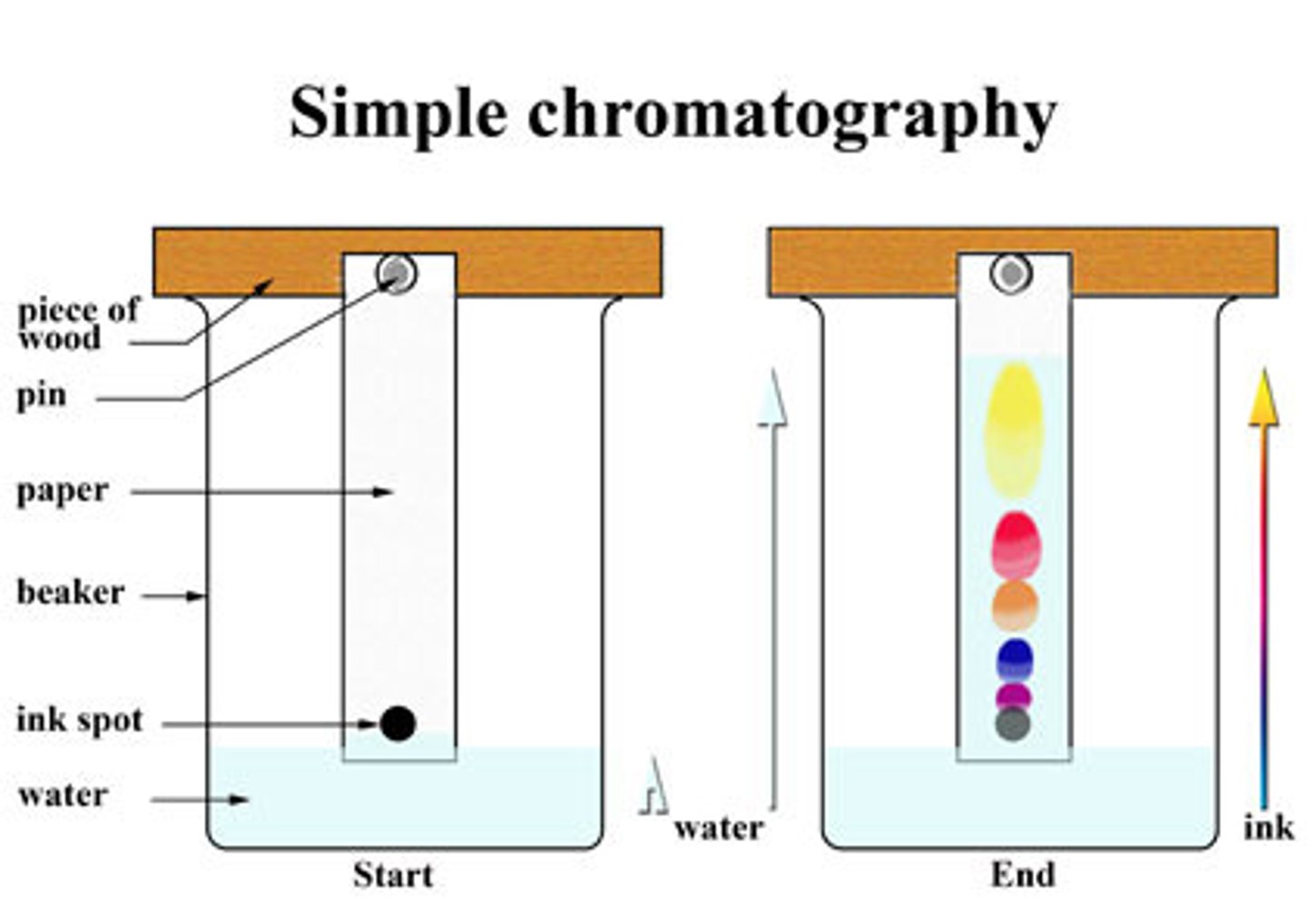
Mobile phase of chromatography
Solvent, which moves up the stationary phase
Stationary phase of chromatography
The substances the mobile phase moves through, usually paper
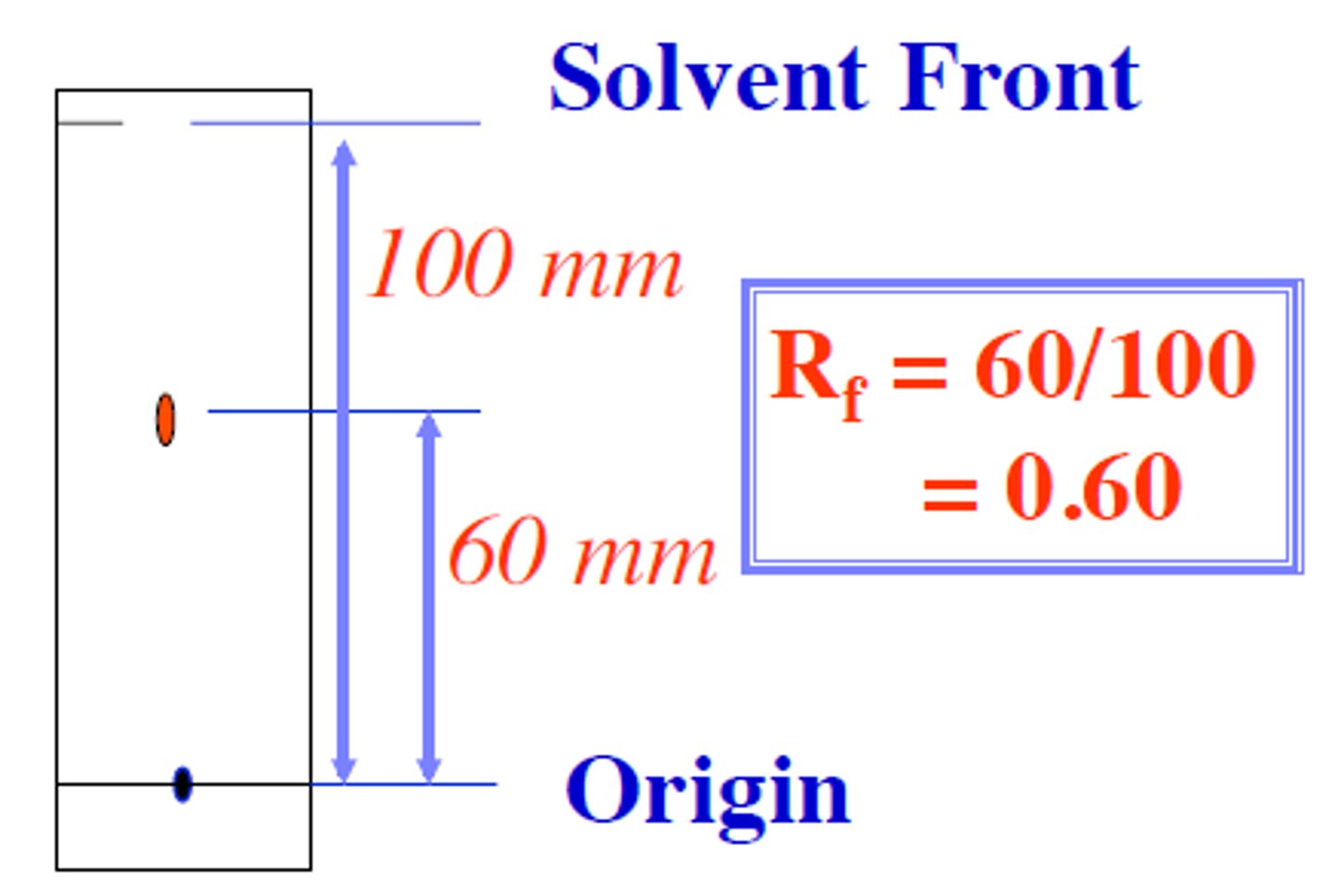
Rf factor
A measurement of how far components of a mixture moves up a chromatogram
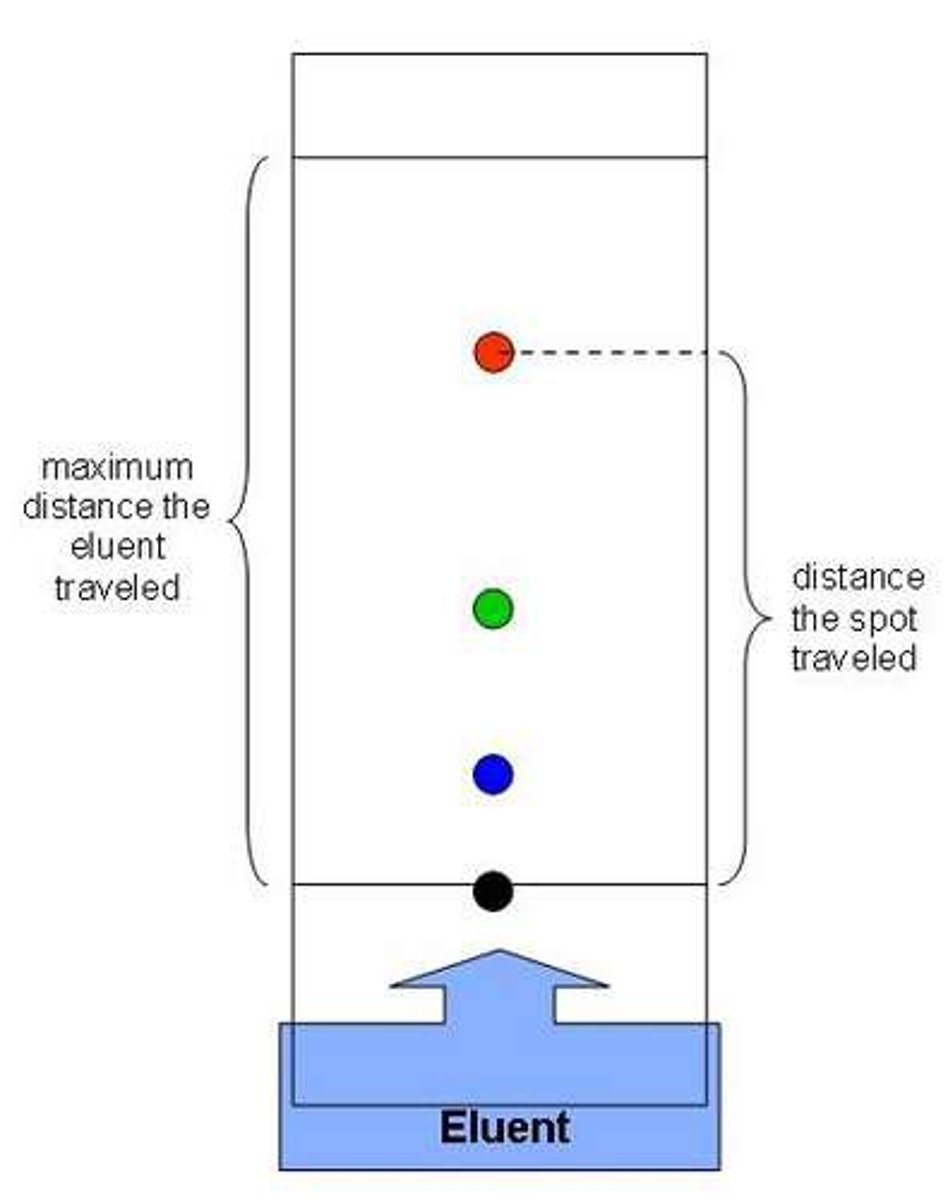
Chromatogram
The chromatography strip at the end of the experiment
Rf formula
distance traveled by spot ÷ distance traveled by solvent

Solvent front
The furthest point reached by the solvent
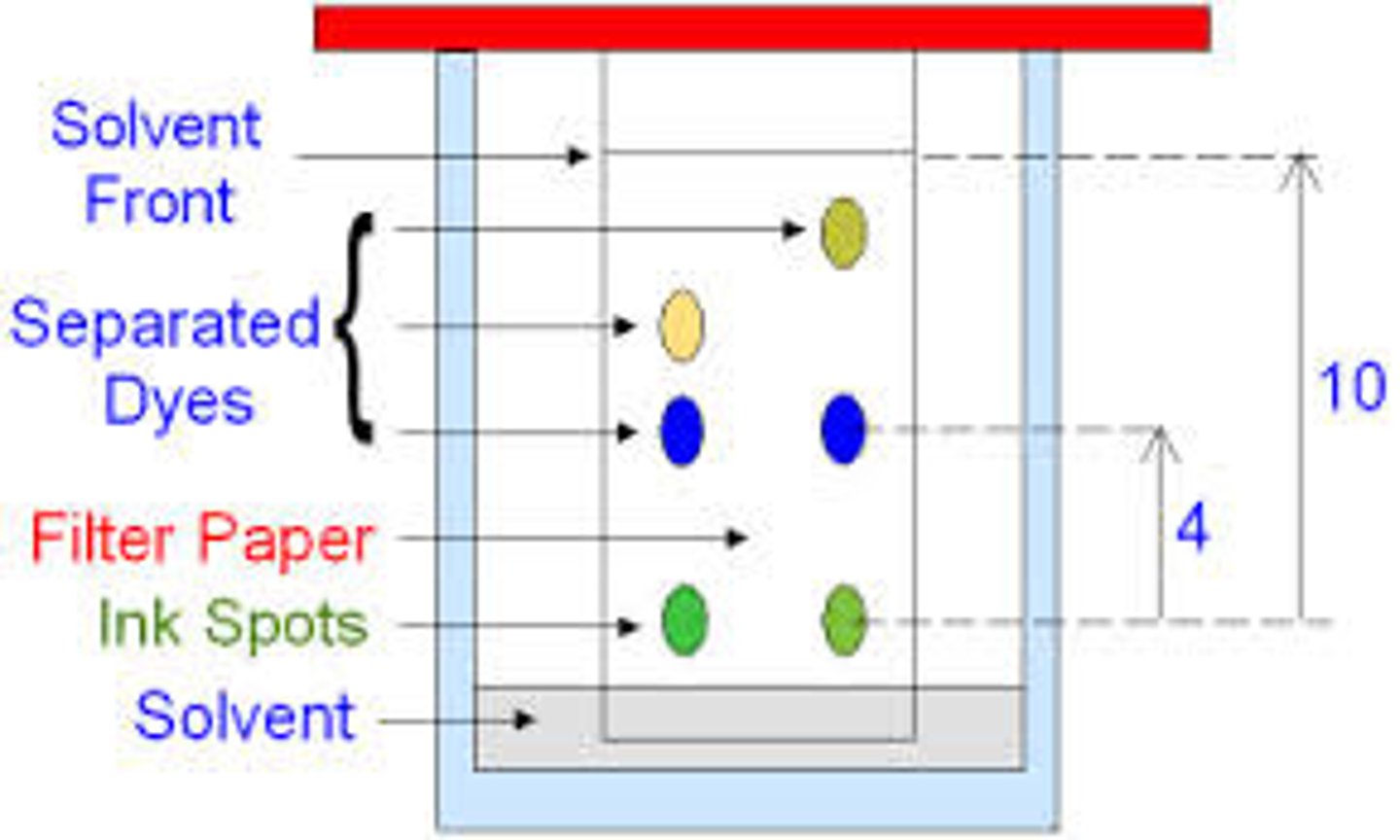
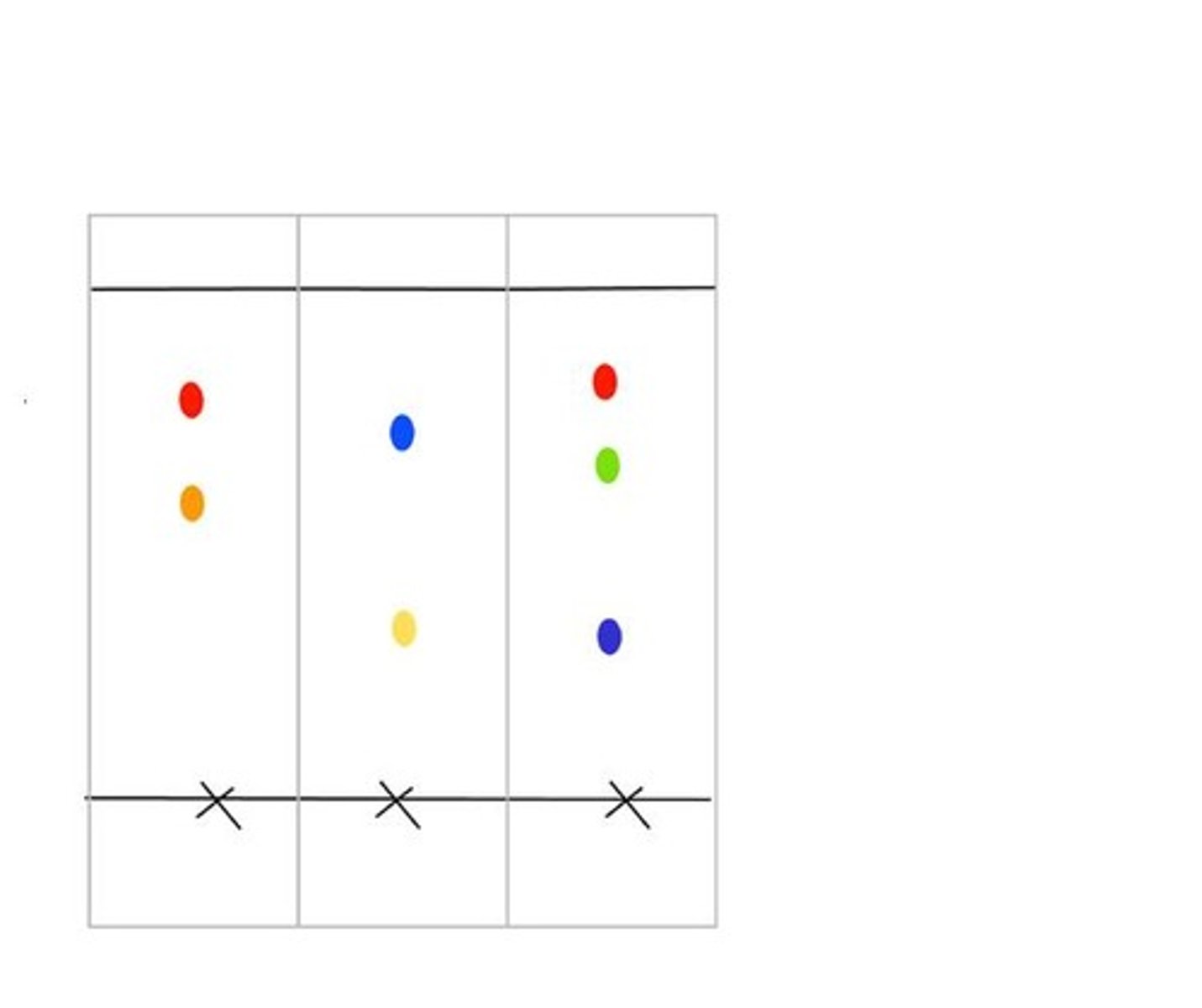
Rf of the same chemical
Is always the same in the same solvent
Pure substance on chromatogram
Will produce one spot in the same vertical column
Mixtures on a chromatogram
Will produce more than one spot in the same vertical column
A substance moves at different speeds
depending on how attarcted it is to the stationary/mobile phase
Identification of chemicals using chromatography
Compare Rf to known substances in a database
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
A type of chromatography that uses a thin layer of powder on a plate as the stationary phase
