Carbon Chemistry and Functional Groups in Organic Molecules
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the significance of carbon atoms in organic molecules?
Carbon atoms are the base of every organic molecule and form the backbone of large, complex molecules.
What types of structures can carbon molecules form?
Carbon can form a huge variety of chain and ring structures, including branched and unbranched chains.
What are hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons are carbon molecules that only contain carbon and hydrogen, commonly used as fuels.
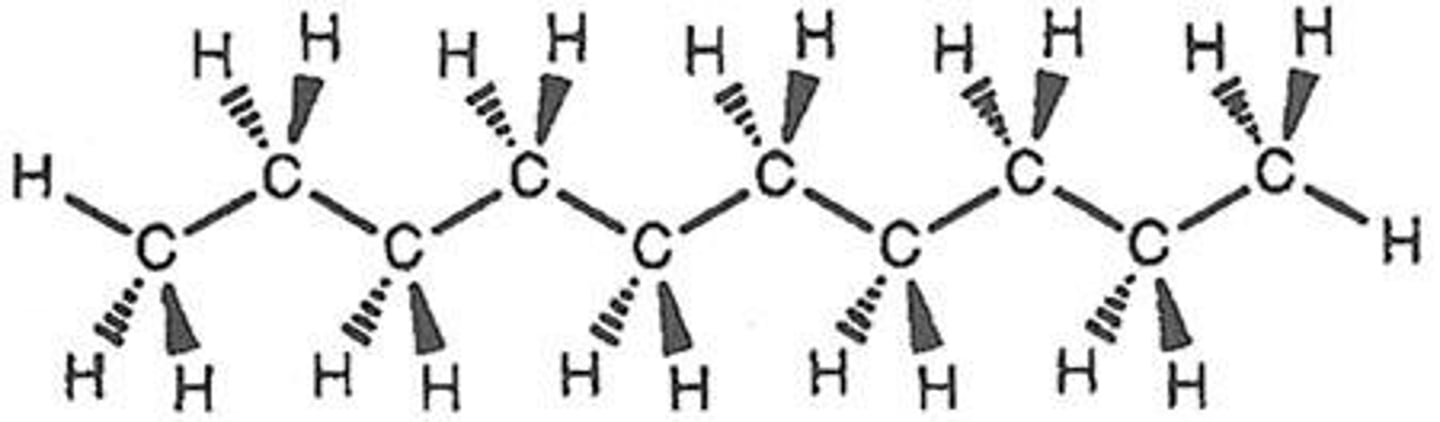
What types of bonds can carbon form?
Carbon can bond with four other molecules and can form single, double, and triple bonds.
What is a functional group?
A functional group is a group of atoms that affects the function of a molecule by participating in chemical reactions.
How do functional groups affect carbon structures?
Functional groups attach to carbon structures and give them specific chemical characteristics, often making them ionic or strongly polar.
What is the role of functional groups in making molecules water soluble?
Functional groups make molecules available for cell use by making them water soluble.
Why can ethanol be metabolized by cells while ethane cannot?
Ethanol contains a functional group that makes it water soluble, whereas ethane lacks such a group.
What are the characteristics of the carboxyl functional group (COOH)?
The carboxyl group can release protons (H+).
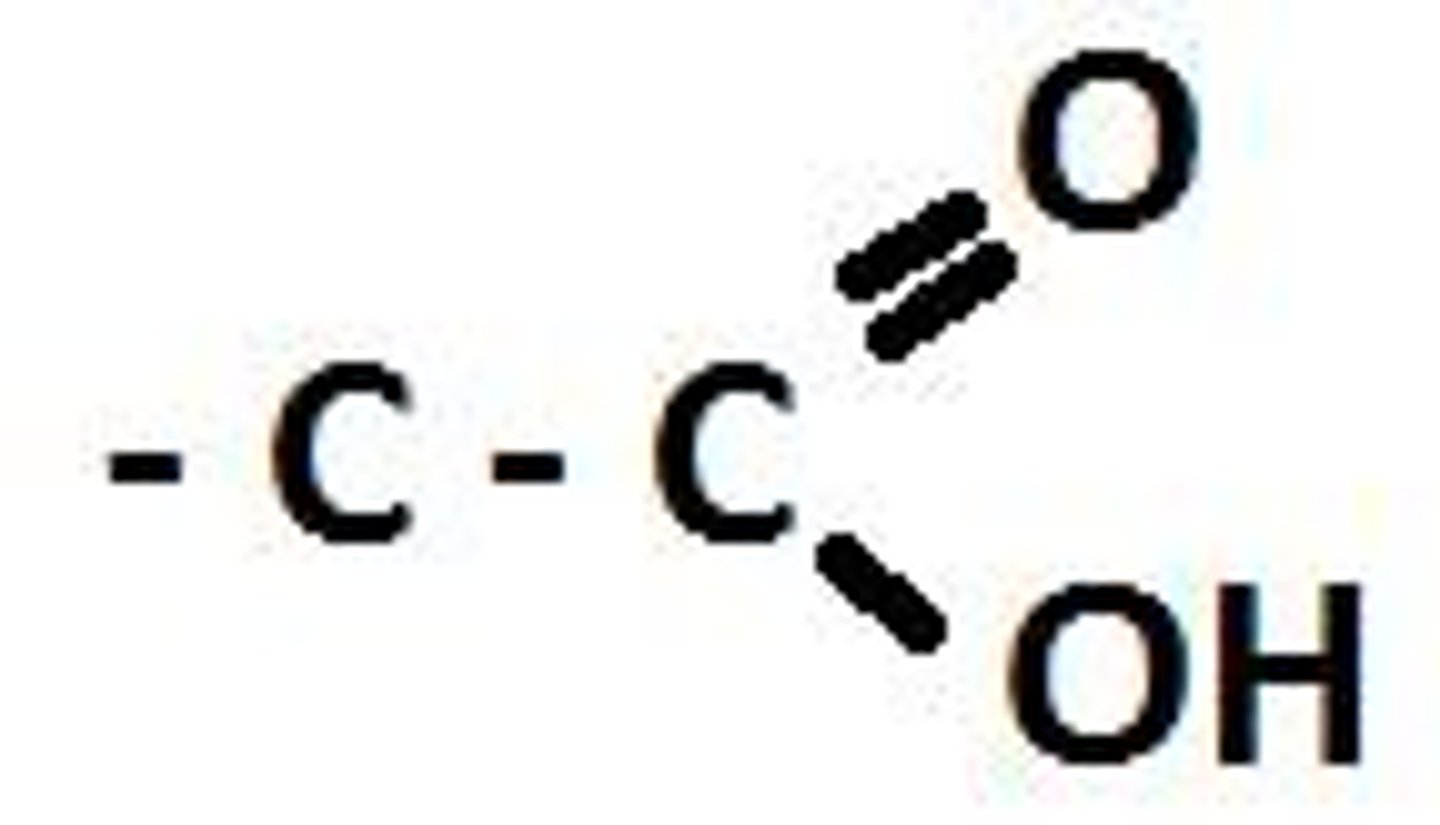
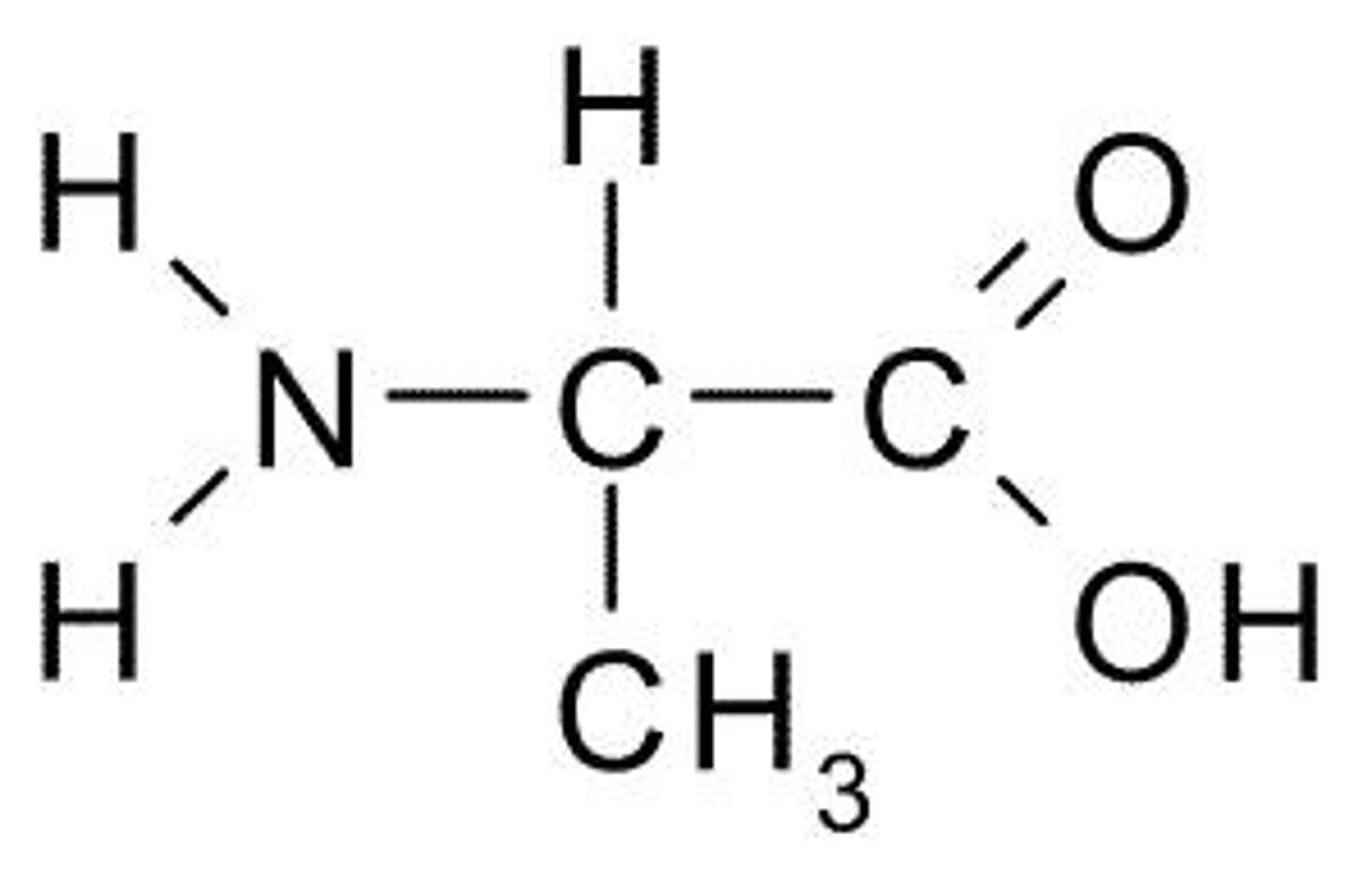
What is the function of the amino functional group (NH2)?
The amino group can accept protons (H+) to become NH3+.
What happens to the phosphate functional group (H2PO4) in reactions?
The phosphate group loses hydrogen atoms to become PO4^2-.
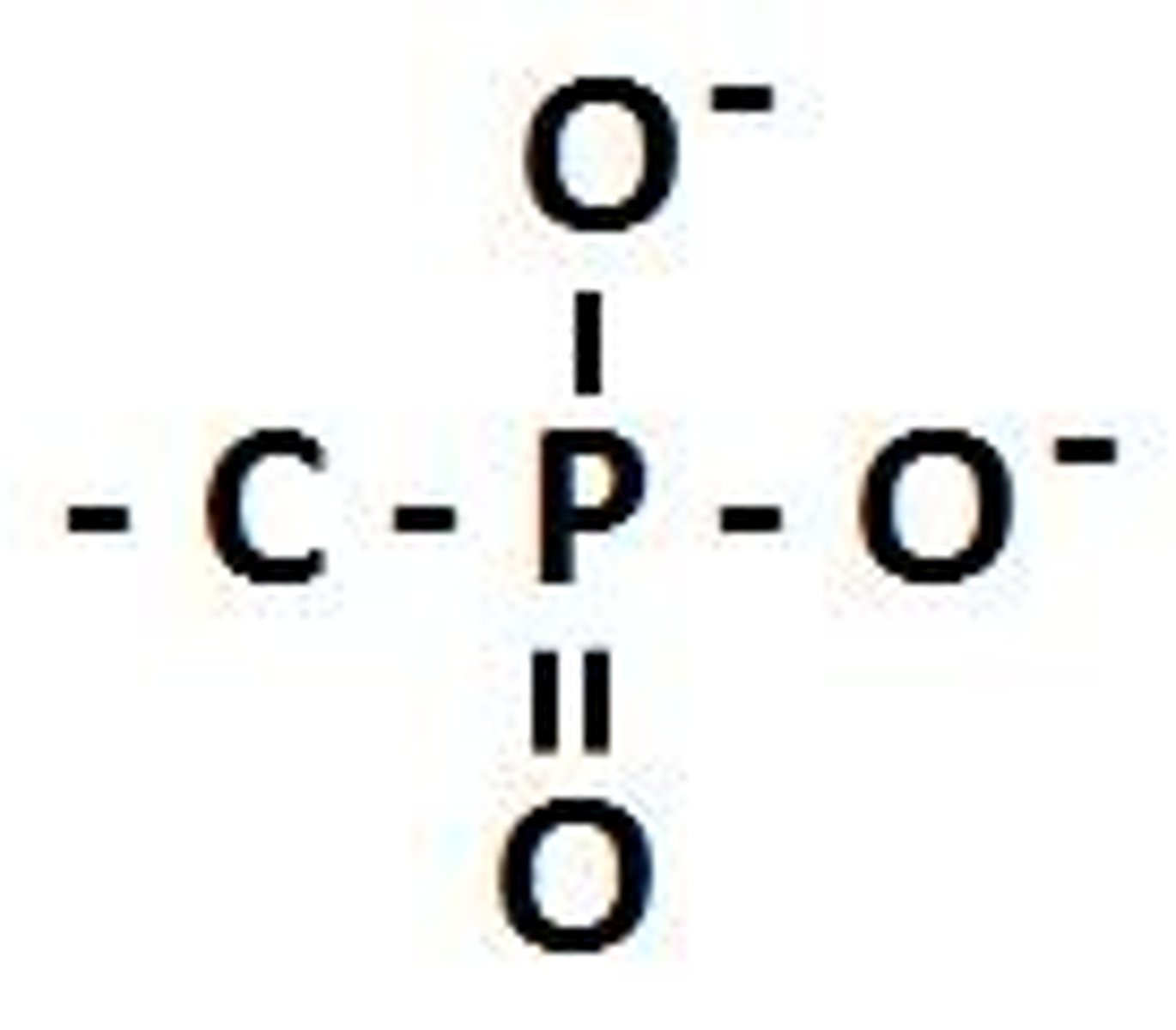
What is the relationship between amino acids and functional groups?
Amino acids contain both amino groups and acidic carboxyl groups.
Why are DNA molecules negatively charged?
DNA molecules are negative because they contain phosphate groups.
What are the basic shapes that carbon molecules can make?
Carbon molecules can form chains, rings, and more complicated three-dimensional structures.
What are the two main types of carbon structures mentioned?
Branched and unbranched chains, as well as rings.
What is the importance of carbon's ability to form multiple bonds?
It allows for the creation of diverse and complex organic molecules.
How do functional groups participate in chemical reactions?
They often engage in chemical reactions due to their ionic or polar nature.
What is the impact of non-polar parts of molecules in reactions?
Non-polar parts do not interact in chemical reactions.
What is the primary use of hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons are primarily used as fuels.
How do carbon rings contribute to molecular complexity?
Carbon rings can join to form chains and create more complicated three-dimensional structures.
What is the role of functional groups in organic chemistry?
They determine the chemical reactivity and properties of organic molecules.