Private Pilot Theory Exam 3
1/138
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HW ?'s #16, #17, #18, #19, #20, #21, #23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
What is the FAA definition of "crewmember" and in what FAR can it be found?
A person assigned to perform duty in an aircraft during flight time, 14 CFR 1.1
What is the meaning of the FAR abbreviation “MEL” and in what FAR is it found?
Minimum equipment list, 14 CFR 1.2
Who can change the oil in your airplane, and in what FAR is that information found?
owners, mechanics, repairmen
14 CFR 43.3
In what FAR can your doctor find the specific requirements for a FAA 3rd Class medical physical?
14 CFR 67.301
How long is a Student Pilot Certificate valid for, and in what FAR is it found?
After April 1, 2016, it never expires, 14 CFR 61.21
How long is a Class 3 medical certificate valid for when someone is younger than 40 and in what FAR is that found?
60 calendar months after date of examination, 14 CFR 61.19
Can a Private Pilot be hired to fly someone’s pets from Omaha to Green Bay, and in what FAR is that found?
no, 14 CFR 61.113
How and where do you log training time given by your flight instructor, in what FAR is it found?
in logbook with date and total flight time, 14 CFR 61.51
You have a beer at lunch and want to fly that night. What restrictions are you held to and in what FAR is it found?
within 8 hours after last drink, 14 CFR 91.17
Which FAR describes aircraft Right-of-Way rules?
14 CFR 91.113
Which FAR describes aircraft ATC light signals?
14 CFR 91.125
Which FAR describes VFR cruising altitude rules?
14 CFR 91.159
What equipment is required for VFR day flight and in what FAR is this found?
14 CFR 91.205
A - airspeed indicator
T - Tachometer for each engine
O - oil pressure
M - manifold pressure gauge
A - altimeter
T - temperature gauge for each liquid-cooled engine
O - oil temperature gauge
F - fuel gauge indicating quantity in each tank
L - landing gear position indicator
A - anti-collision light system
M - magnetic direction indicator
E - emergency locator transmitter
S - seat belts
What additional equipment is required for VFR night flight and in what FAR is this found?
14 CFR 91.205
F - fuses
L - electric landing light
A - anti-collision light
P - position lights
S - source of electrical energy for all installed electrical and radio equipment
Which Title and Part describes what to do in case you are involved in an accident?
FAA order 8020.11
For Class "A" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums.
visibility: None
Distance from clouds: none
For Class "B" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums.
visibility: 3 statute miles
Distance from clouds: clear of clouds
For Class "C" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums.
visibility: 3 statute miles
Distance from clouds: 1000 above, 500 below, 2000 horizontal
For Class "D" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums.
visibility: 3 statute miles
distance from clouds: 500 below, 1000 above, 2000 horizontal
For Class "E" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums at or above 10,000 MSL
visibility: 5 Statue miles
Distance from clouds: 1000 above, 1000 below, 1 SM horizontal
For Class "E" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums at less than 10,000 MSL
visibility: 3 Statute miles
distance from Clouds: 1000 above, 500 below, 2000 horizontal
For Class "G" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums at 1,200 AGL or less during the day
visibility: 1 statute miles
distance from clouds: clear of clouds
For Class "G" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums at 1,200 ft AGL or less at night
visibility: 3 statute miles
distance from clouds: 1000 above, 500 below, 2000 horizontal
For Class "G" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums from more than 1,200 but less than 10,000 at day
visibility: 1 statute mile
distance from clouds: clear of clouds
For Class "G" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums more than 1,200 but less than 10,000 at night
visibility: 3 statute miles
distance from clouds: 1000 above, 500 below, 2000 horizontal
For Class "G" Airspace, state the basic VFR visibility and distance from clouds minimums more than 1,200 and at/above 10,000
visibility: 5 statute mile
distance from clouds: 1000 above, 1000 below, 1 SM horizontal
the prime meridian is how many degrees latitude or longitude?
0 degrees of longitude
the prime meridian runs through?
Greenwich, England
Where would a pilot find information about a Military Operations Area (MOA) such as Altitude of Use, Time of Use, and Controlling Agency?
back of sectional charts
Unless otherwise specified, Federal Airways include that Class E airspace extending upward from
1,200 feet above the surface up to and including 17,999 feet MSL
A blue segmented circle on a Sectional Chart depicts which class airspace?
class D
In which type of airspace are VFR flights prohibited?
Class A
what hazards to aircraft may exist in restricted areas that have a solid blue line around with dashes on the inside?
Unusual, often invisible, hazards such as aerial gunnery or guided missiles
What are the differences between civilian and military airport beacons?
civilian is green and white
military is green and 2 white
What is the minimum altitude over a congested area
1000 ft
what is the minimum altitude over an uncongested area
500 ft
What actions do we take if we're converging head-to-head with another aircraft?
turn to the right
What actions do we take if we're converging at an angle with another aircraft that is the same category?
aircraft on the right has the right of way
What actions do we take if we're converging at an angle with another aircraft that is a different category?
less maneuverable aircraft has right of way
What actions do we take if we're overtaking another aircraft from the rear?
Pass on the right
What does it mean if a runway is designated 32L or 32C?
parallel runways (L is left) (C is center)
What is the rule for VFR cruising altitudes regarding direction of flight for 000-179?
odd thousands + 500’
What is the rule for VFR cruising altitudes regarding direction of flight for 180-359?
even thousands + 500’
When approaching to land on a runway served by a visual approach slope indicator (VASI), the pilot shall
maintain an altitude at or above the glide slope
Which is the correct traffic pattern departure procedure to use at a noncontrolled airport?
comply with any FAA traffic pattern established for the airport
The recommended entry position to an airport traffic pattern is
to enter at 45 degree at the midpoint of the downwind leg at traffic pattern altitude
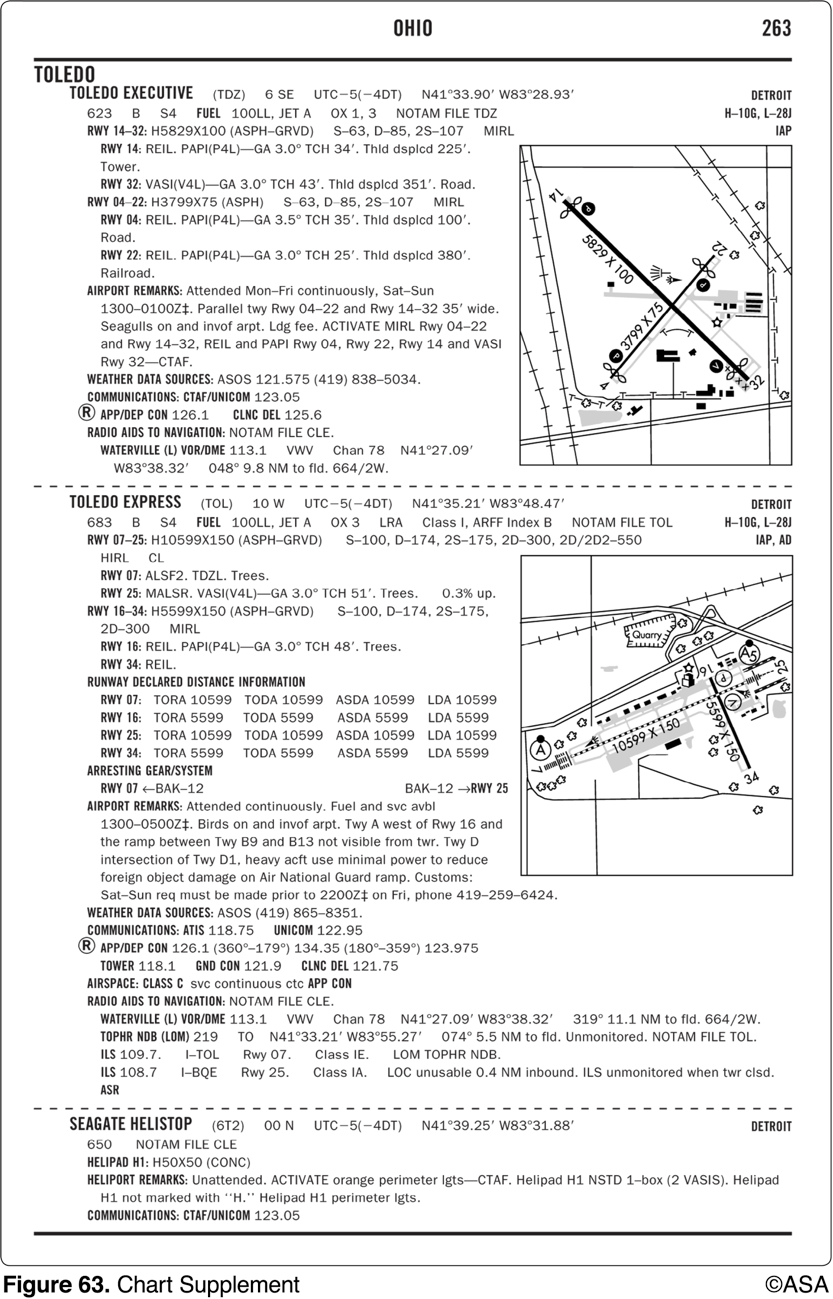
What is the length of the displaced threshold for runway 22 at Toledo (TDZ)?
380 ft
An airport's rotating beacon operated during daylight hours indicates
that weather at the airport located in Class D airspace is below basic VFR weather minimums.
The numbers 9 and 27 on a runway indicate that the runway is oriented approximately
090° and 270° magnetic.
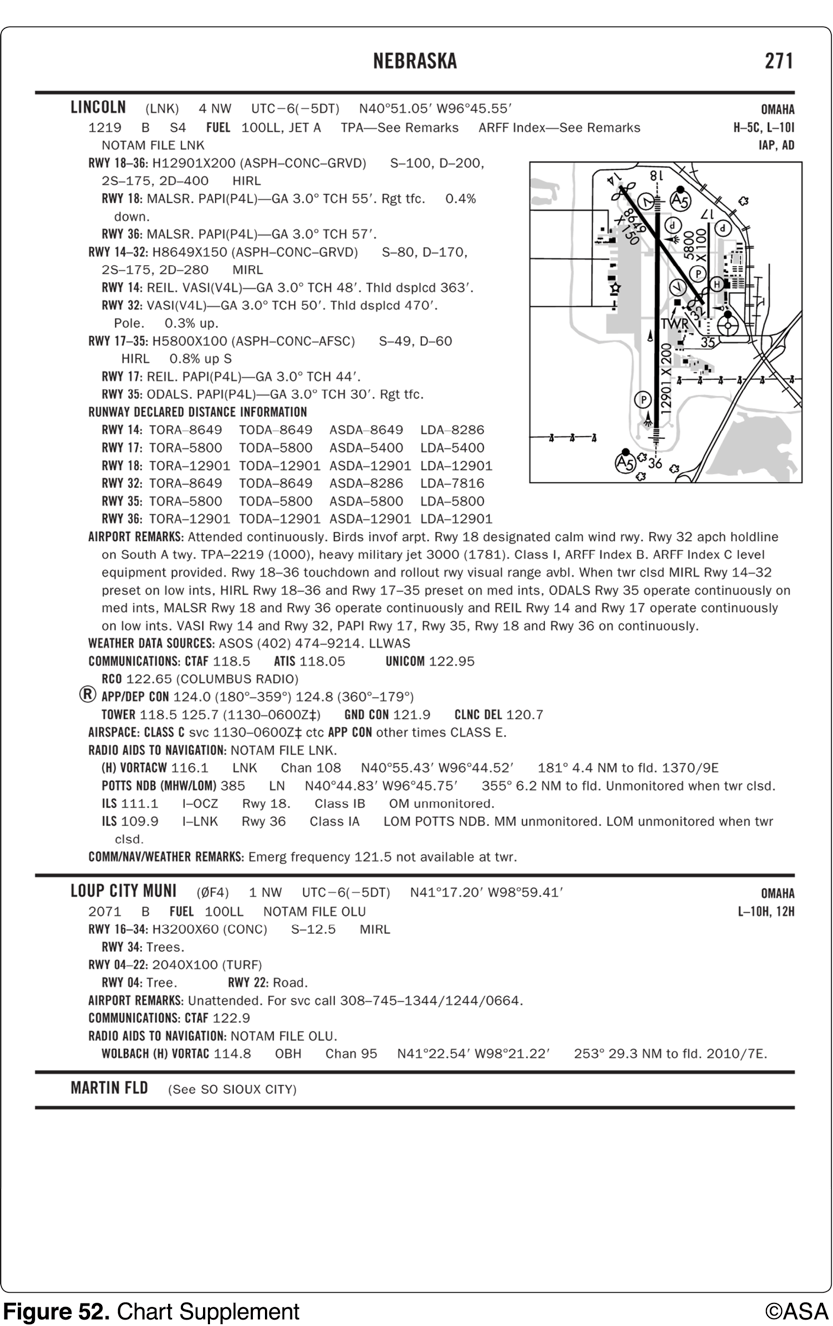
When approaching Lincoln Municipal from the west at noon for the purpose of landing, initial communications should be with
Lincoln Approach Control on 124.0 MHz
Who should not participate in the Land and Hold Short Operations (LAHSO) program?
Student pilots
What does the outbound destination sign identify?
Identifies direction to take-off runways
While operating in Class D airspace, each pilot of an aircraft approaching to land on a runway served by a visual approach slope indicator (VASI) shall
maintain an altitude at or above the glide slope until a lower altitude is necessary for a safe landing
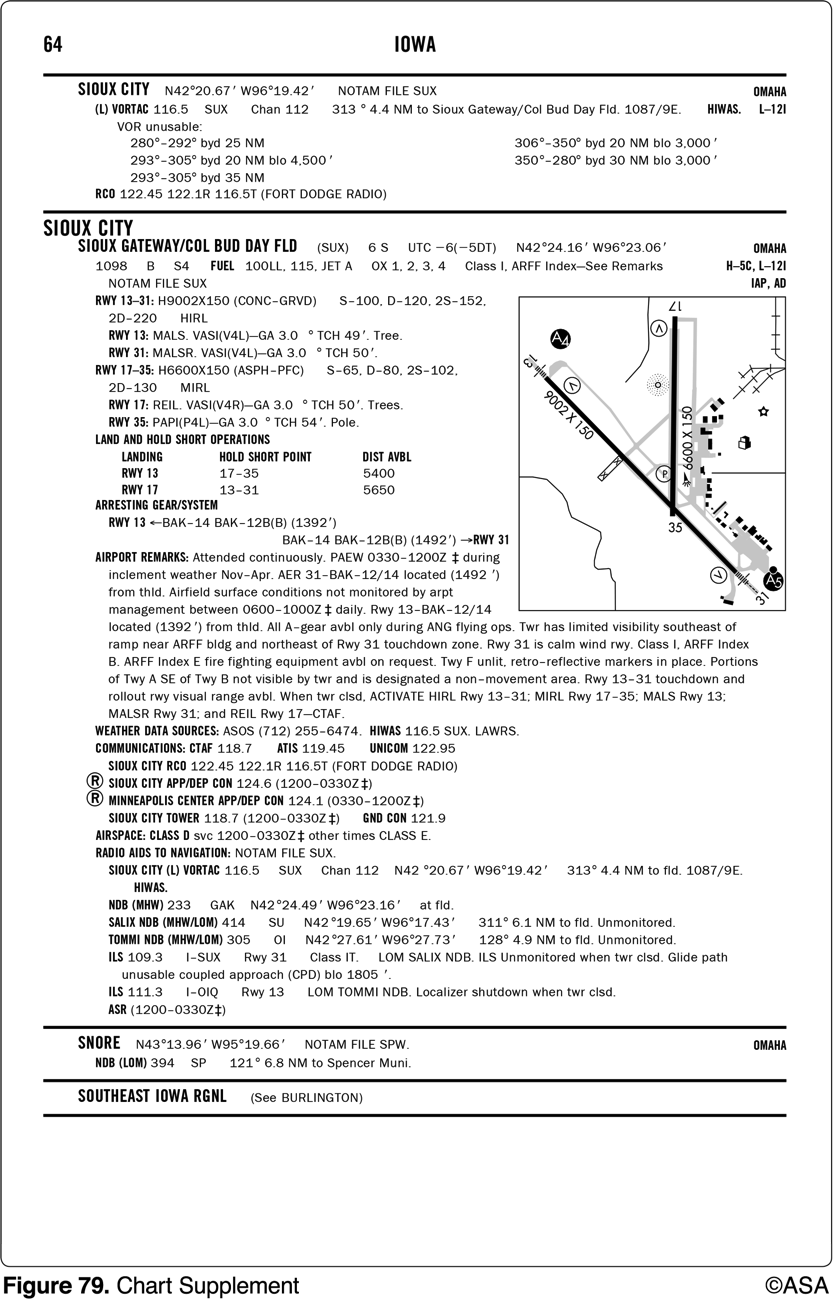
Where in relation to the airfield is the airport beacon located for Sioux City (SUX) airport?
East of runway 17-35.
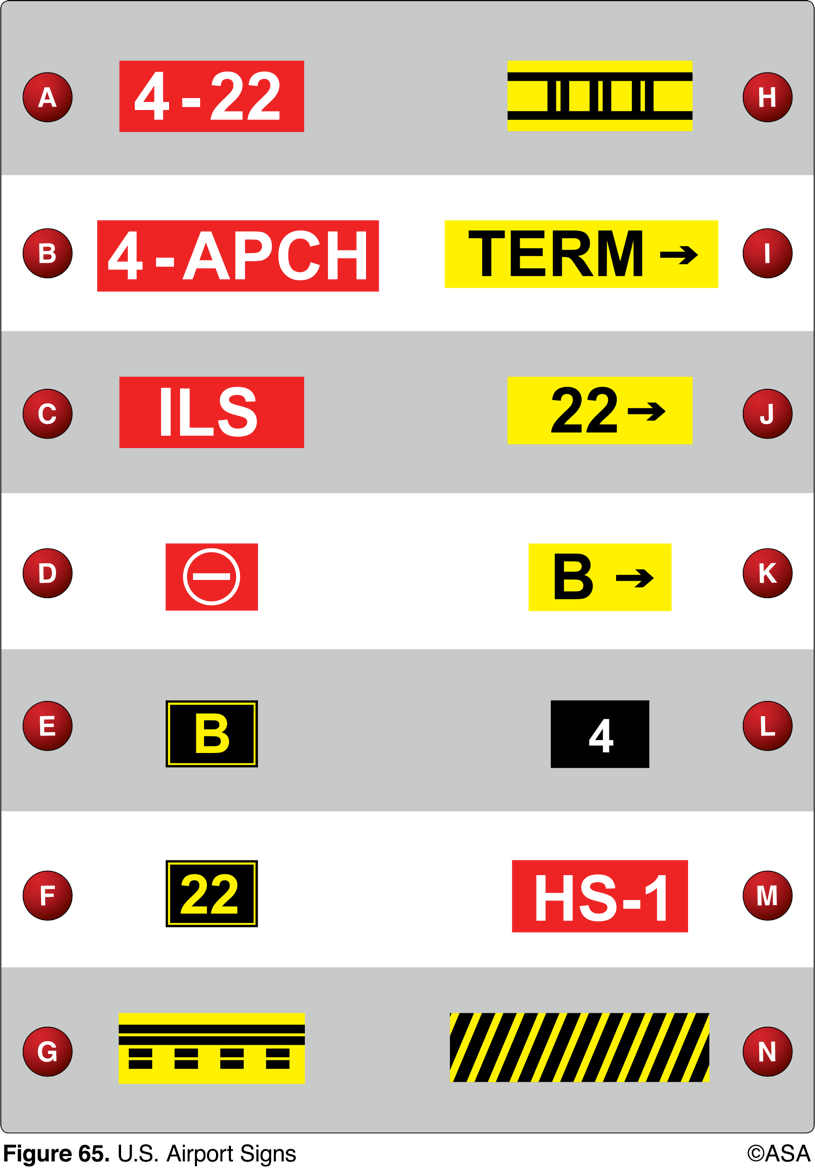
From the cockpit, marking G confirms the aircraft to be
on a runway, about to clear
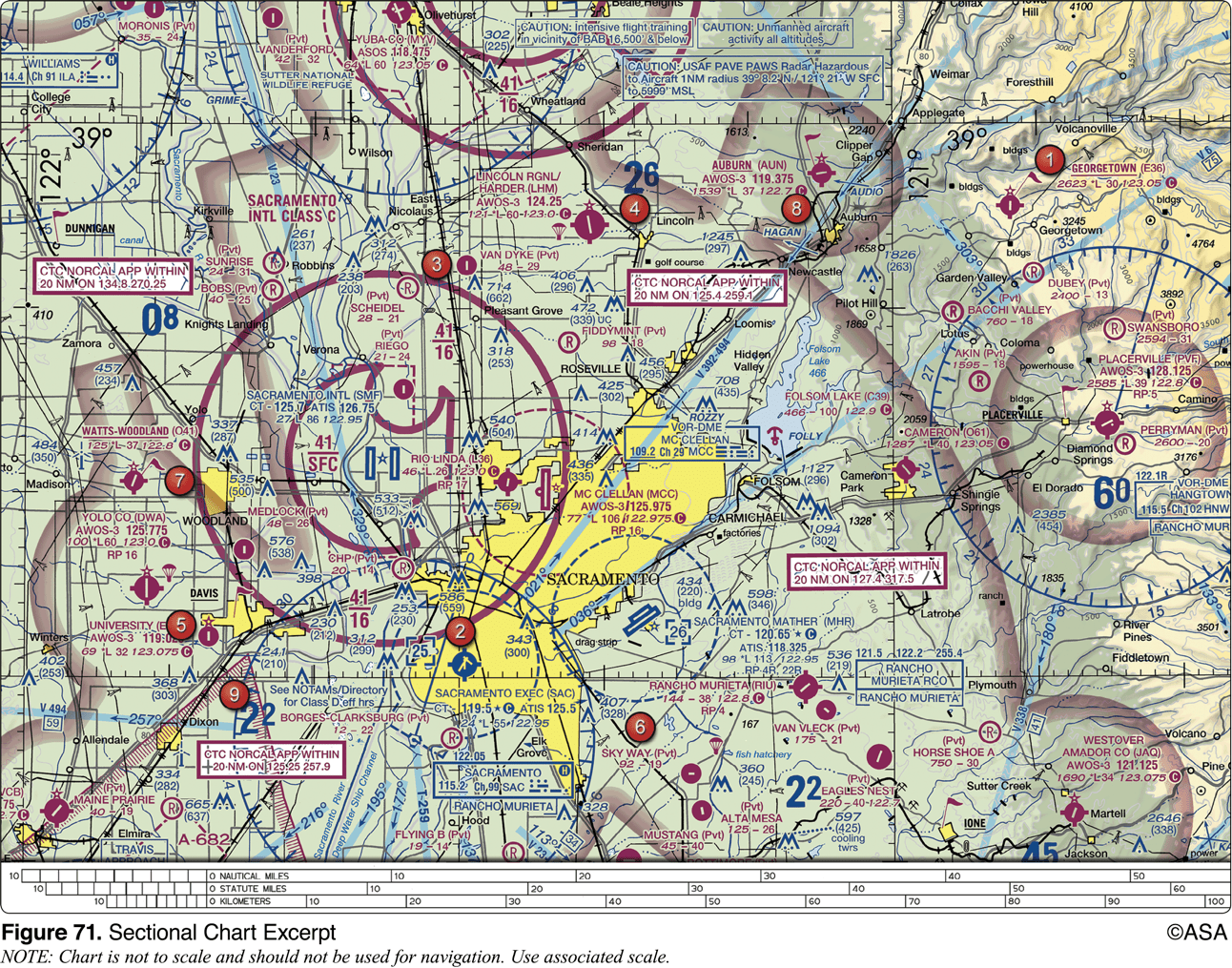
For information about the parachute jumping operations at Lincoln Regional/ Harder (LHM) Airport, refer to
the Chart Supplements U.S. (formerly Airport/Facility Directory)
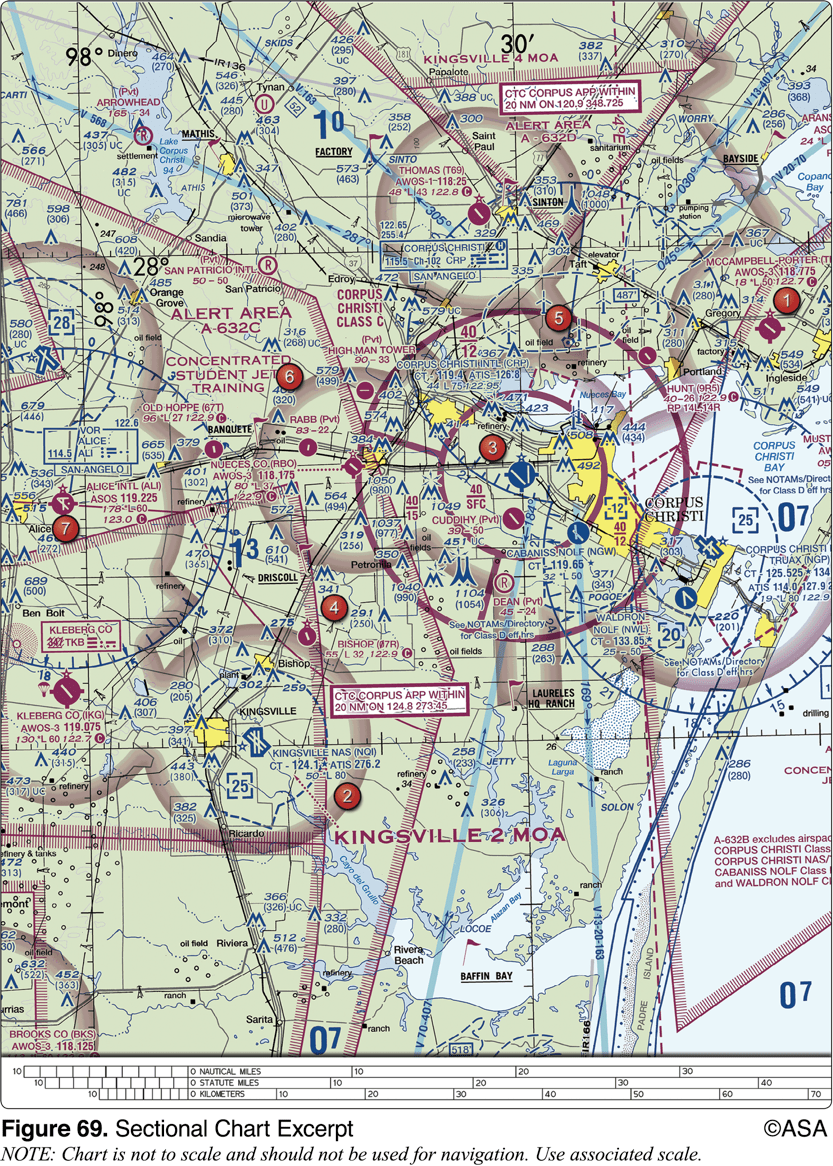
What minimum equipment is required for a flight from Kleberg Co. Airport (area 7) to Corpus Christi Intl. Airport (area 3)?
Two-way radio and Mode C transponder with altitude reporting equipment
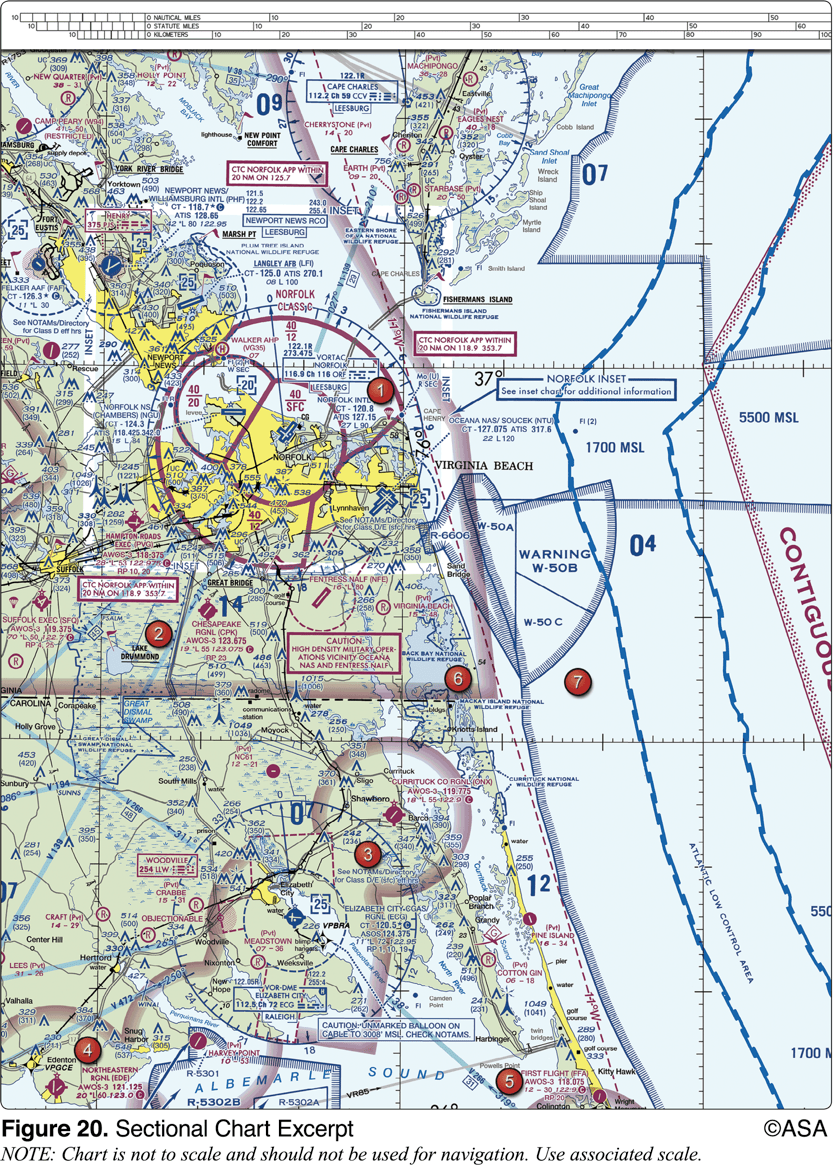
The NALF Fentress (NFE) Airport is in what type of airspace?
class E
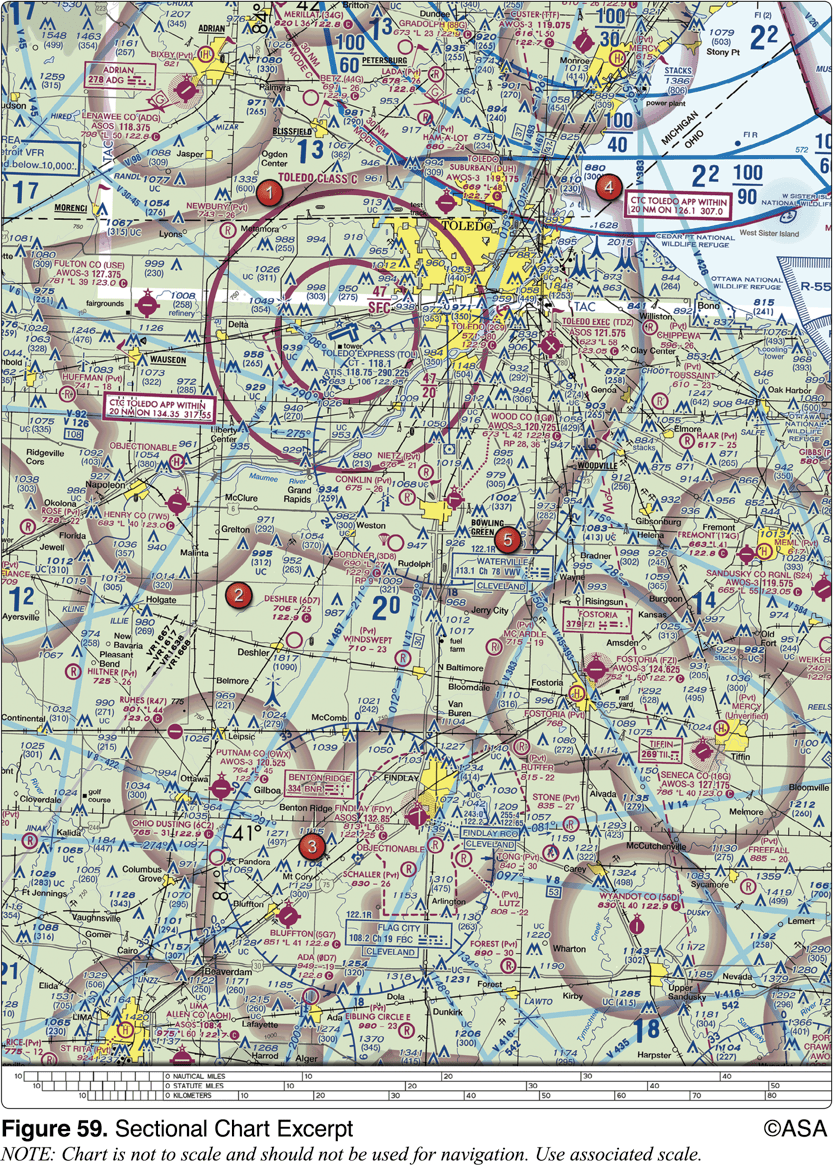
The airspace directly overlying the town of Findlay is
surface area Class E airspace
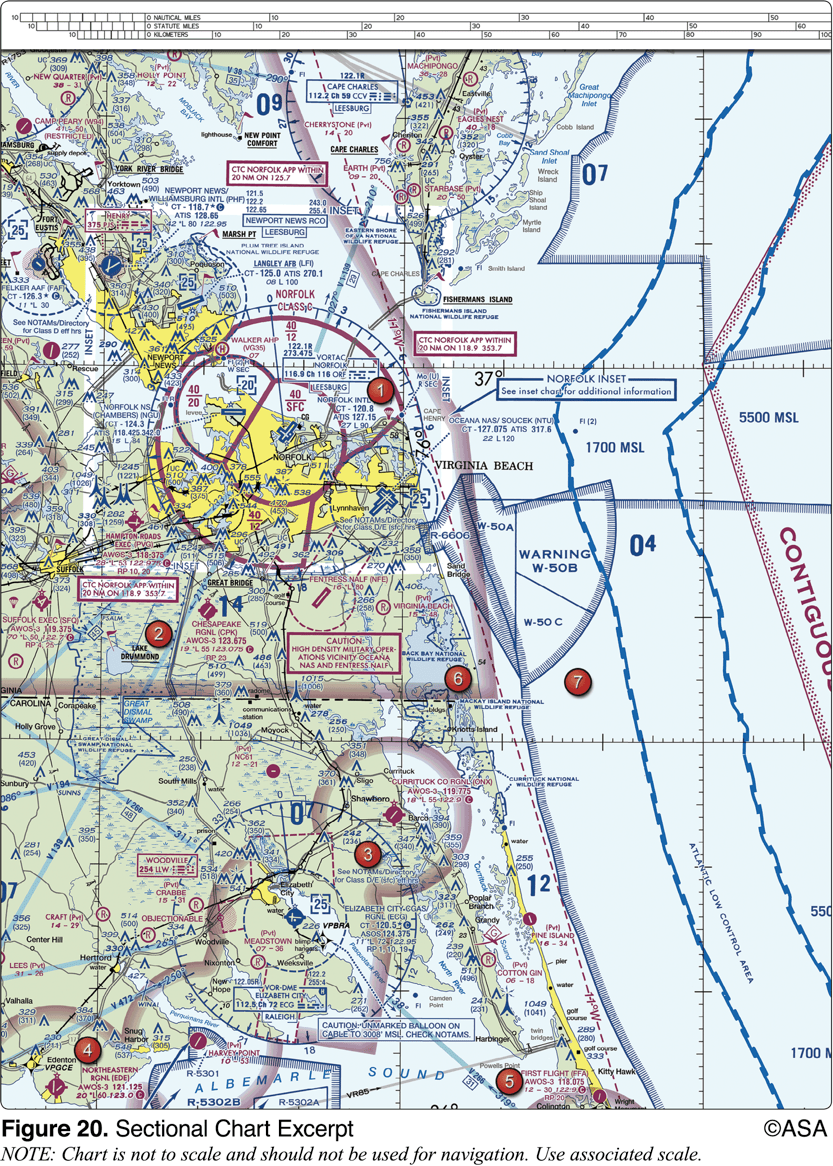
What hazards to aircraft may exist in restricted areas such as R-5302B?
Unusual, often invisible, hazards such as aerial gunnery or guided missiles
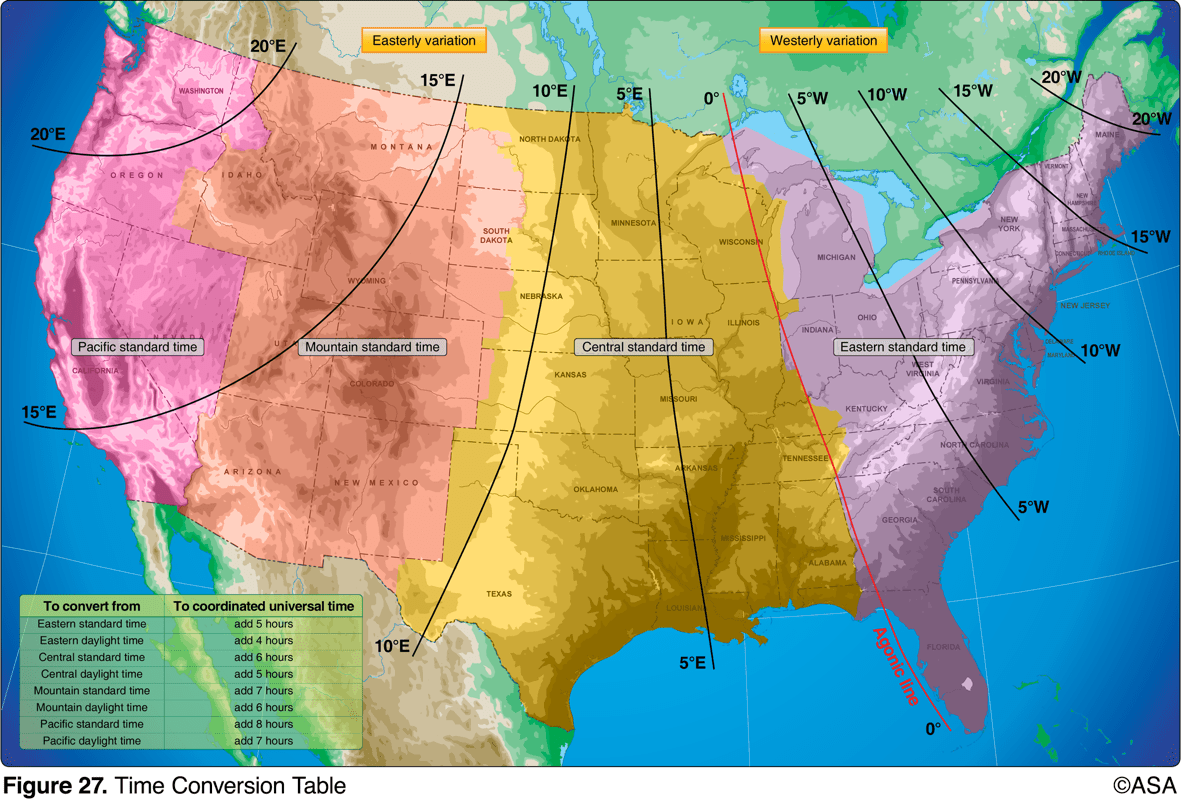
An aircraft departs an airport in the central standard time zone at 0930 CST for a 2-hour flight to an airport located in the mountain standard time zone. The landing should be at what time?
1030 MST
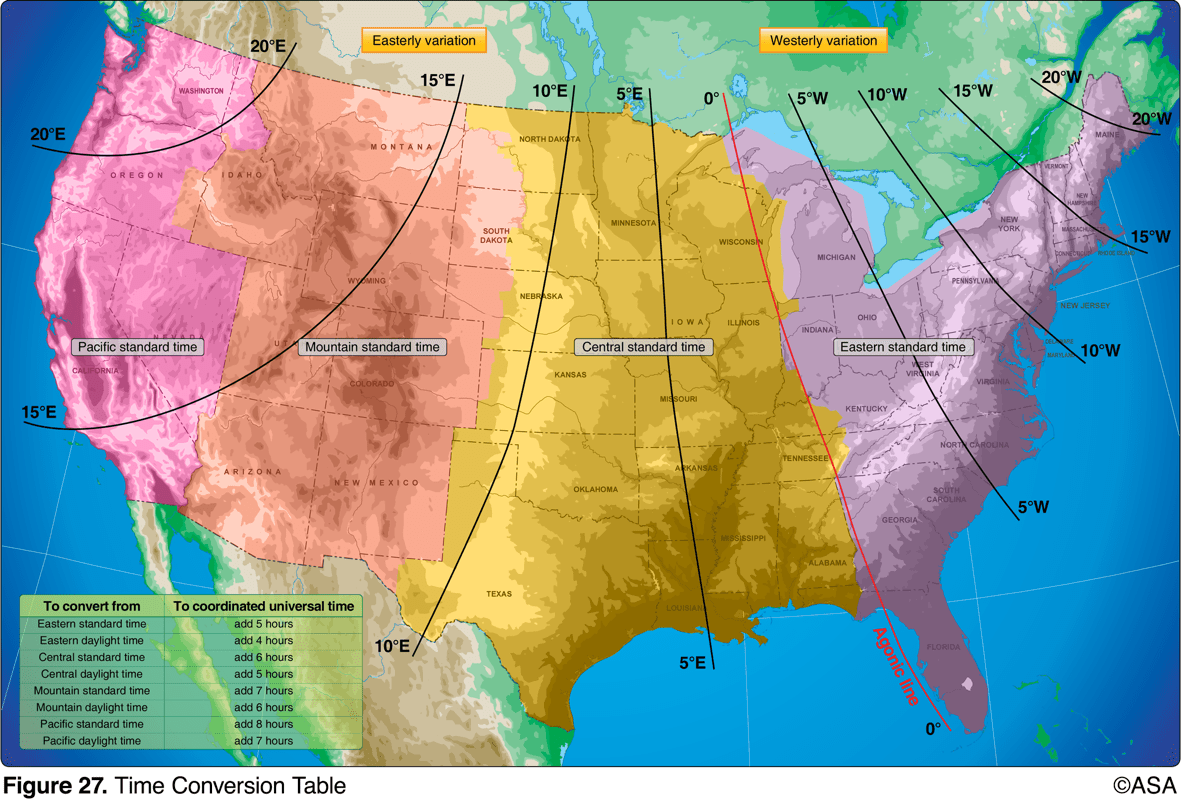
An aircraft departs an airport in the Pacific standard time zone at 1030 PST for a 4-hour flight to an airport located in the central standard time zone. The landing should be at what coordinated universal time?
2230Z
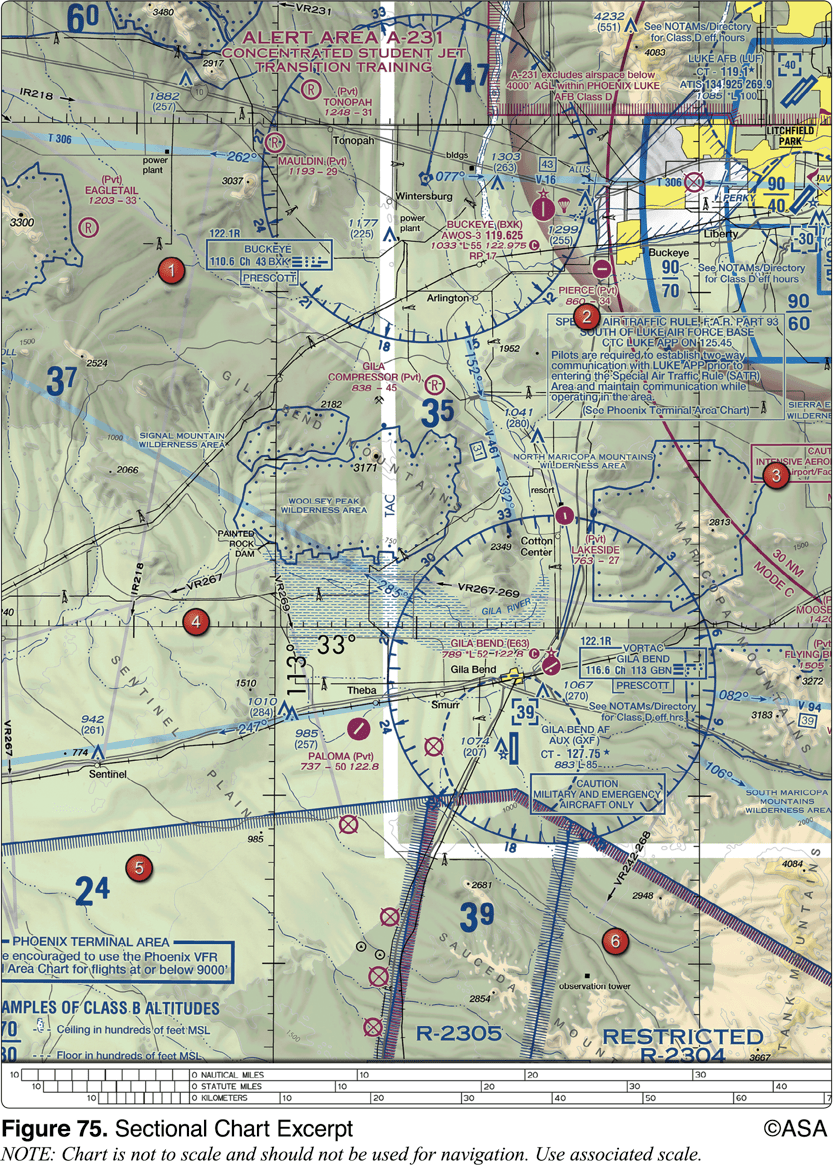
During preflight planning, your course is plotted to fly through R-2305. Where would you find additional information regarding this airspace?
On the Sectional Chart in the Special Use Airspace area
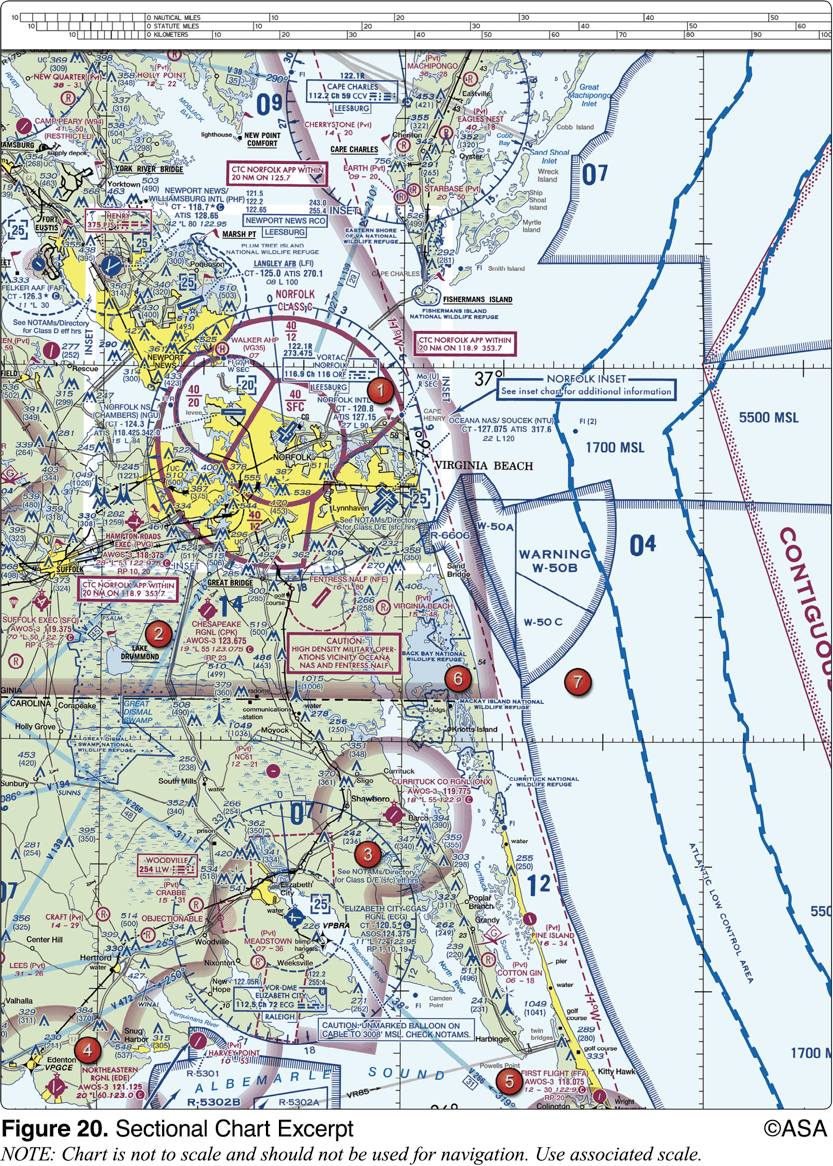
The CAUTION box denotes what hazard to aircraft?
Unmarked balloon on cable to 3,008 feet MSL
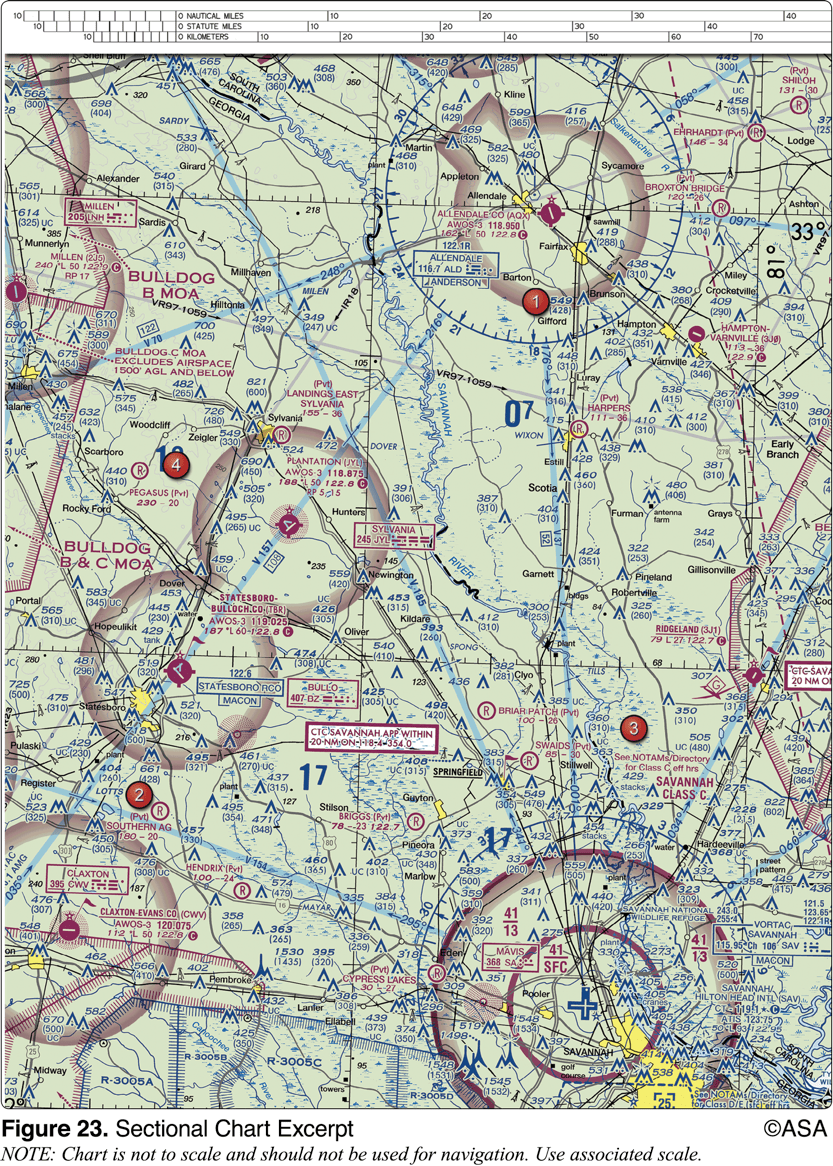
What is the height of the lighted obstacle approximately 6 nautical miles southwest of Savannah International?
1,548 feet MSL
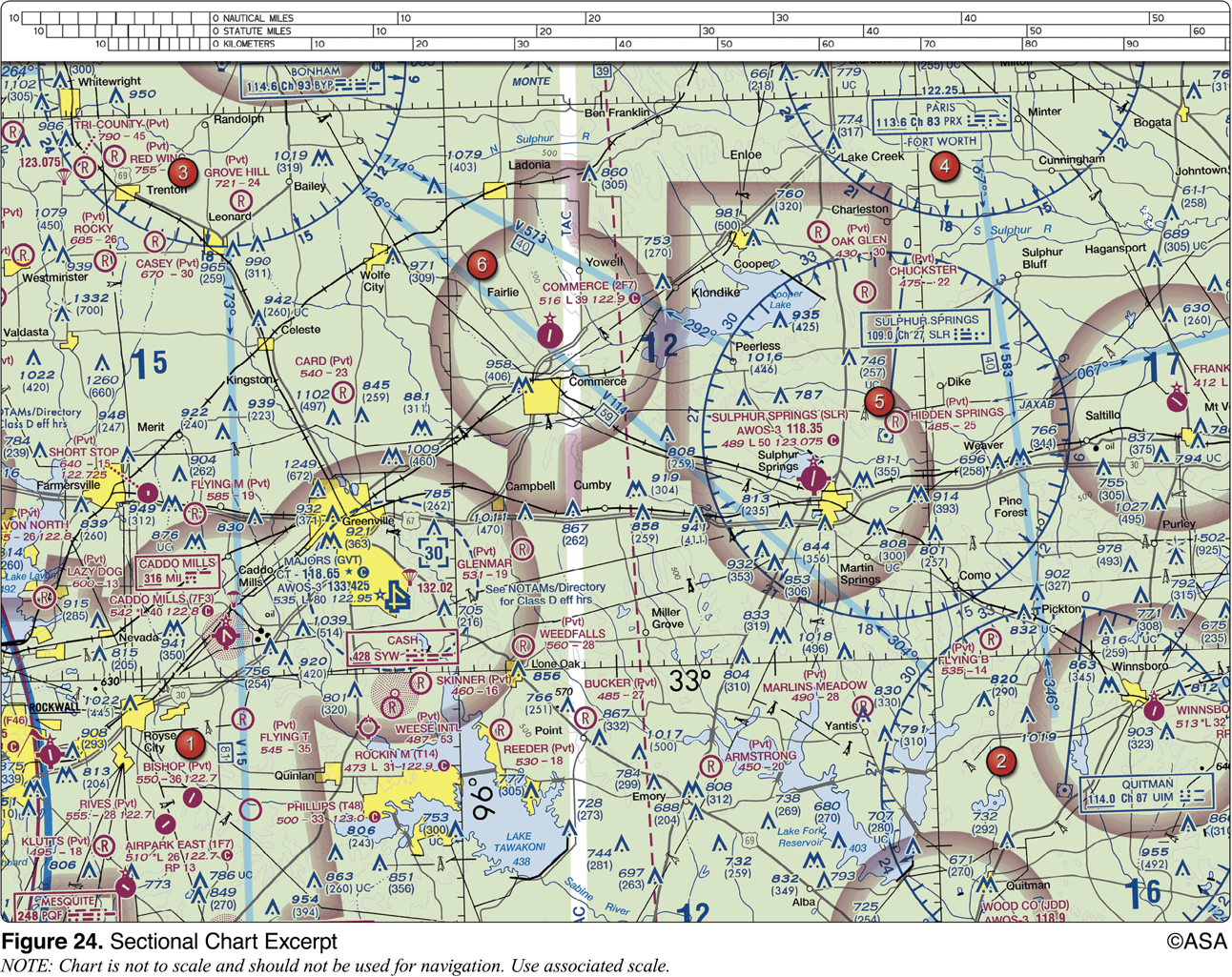
What minimum altitude is necessary to vertically clear the obstacle on the southeast side of Winnsboro Airport by 500 feet?
1,403 feet MSL
Pilots flying over a national wildlife refuge are requested to fly no lower than
2,000 feet AGL
Define "true airspeed"
speed at which a plane travels through the air
Which statement about longitude and latitude is true?
Lines of longitude cross the Equator at right angles
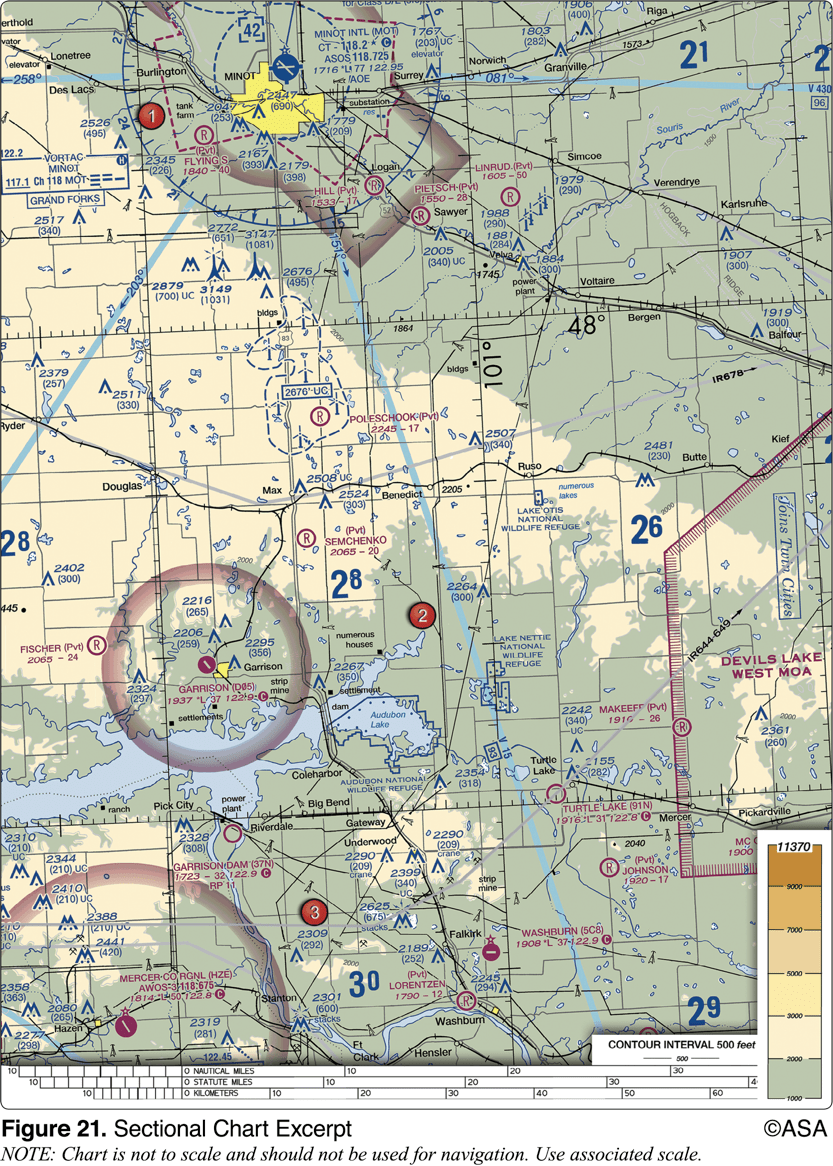
Which public use airports depicted are indicated as having fuel?
Minot Intl. (area 1)
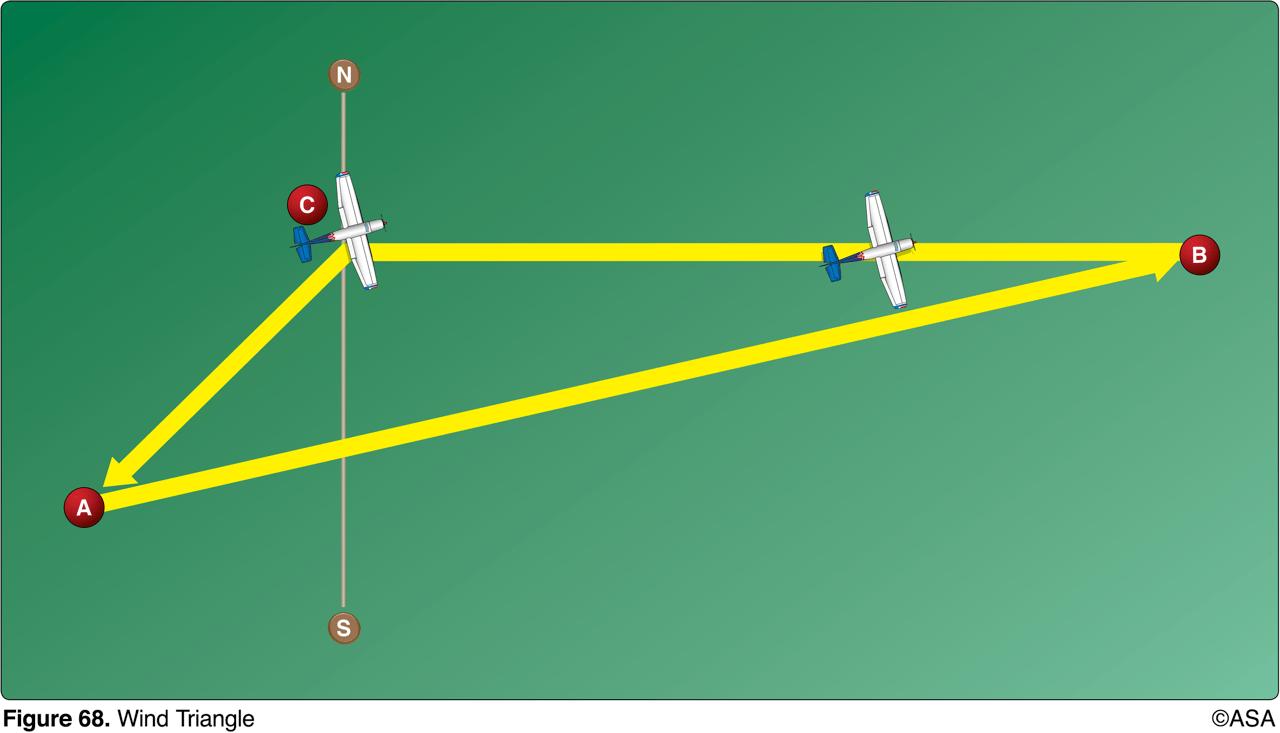
The line from point C to point A of the wind triangle represents
wind direction and velocity
Traveling eastward across the dateline from Hong Kong to Hawaii, you would expect to gain 1 day
false
The VFR cruising altitude rules are based on ___________ heading of the route of flight and state_________________________.
magnetic, 000° - 179° odd thousands plus 500 feet
An ATC radar facility issues the following advisory to a pilot flying on a heading of 090°:
'TRAFFIC 3 O'CLOCK, 2 MILES, WESTBOUND...'
Where should the pilot look for this traffic?
south
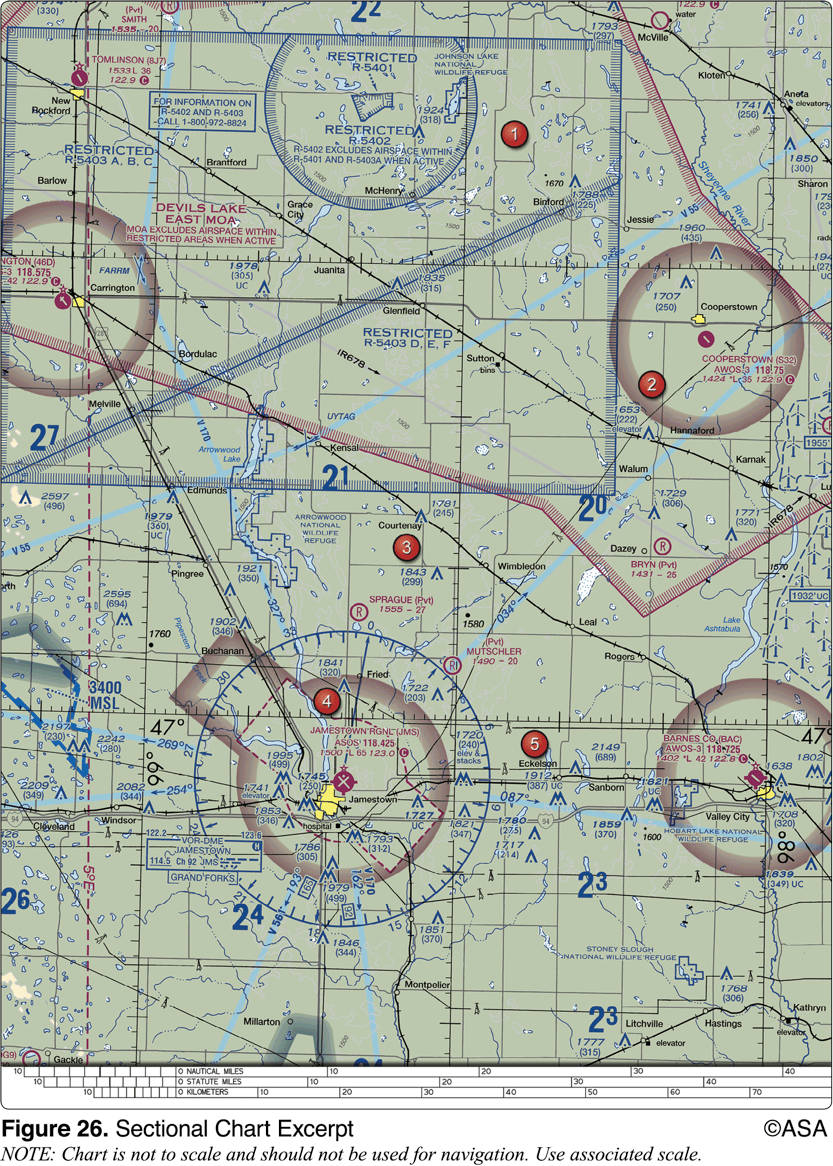
Identify the airspace over Tomlinson Airport.
Class G airspace - surface up to but not including 1,200 feet AGL, Class E airspace - 1,200 feet AGL up to but not including 18,000 feet MSL.
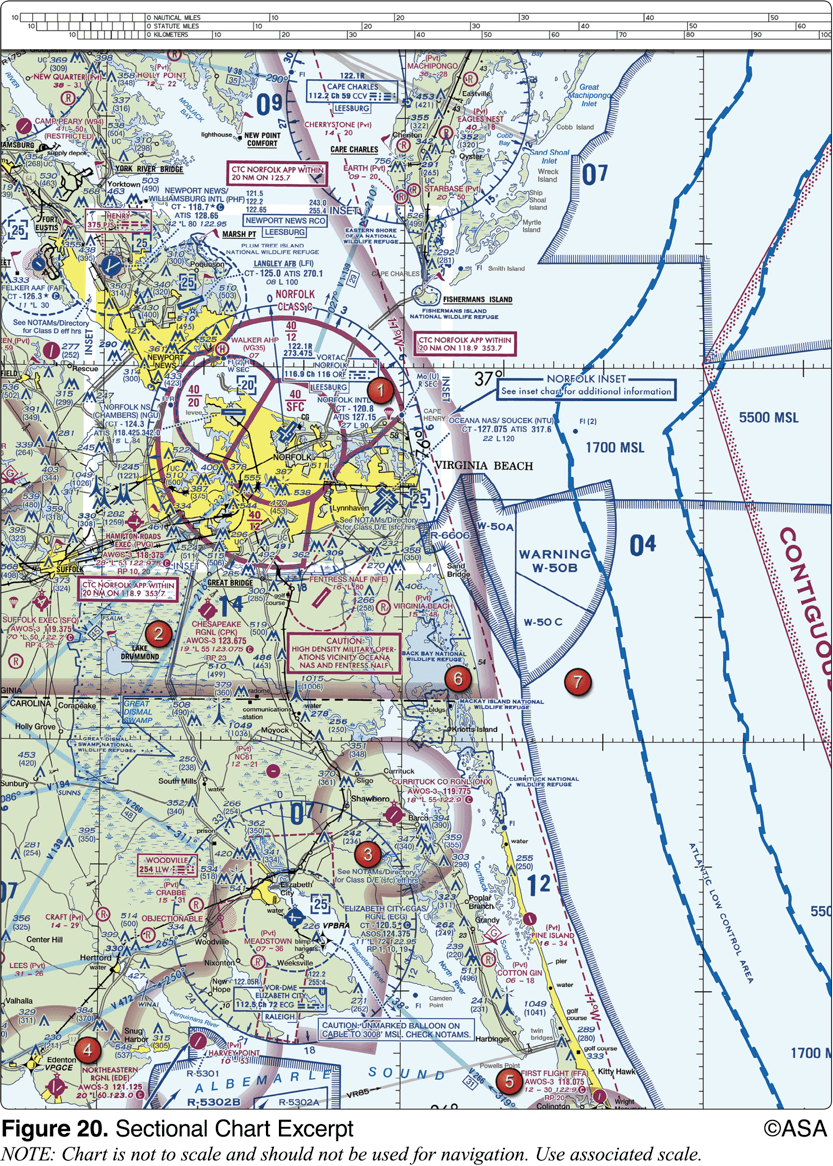
The elevation of the Chesapeake Regional Airport is
19 feet
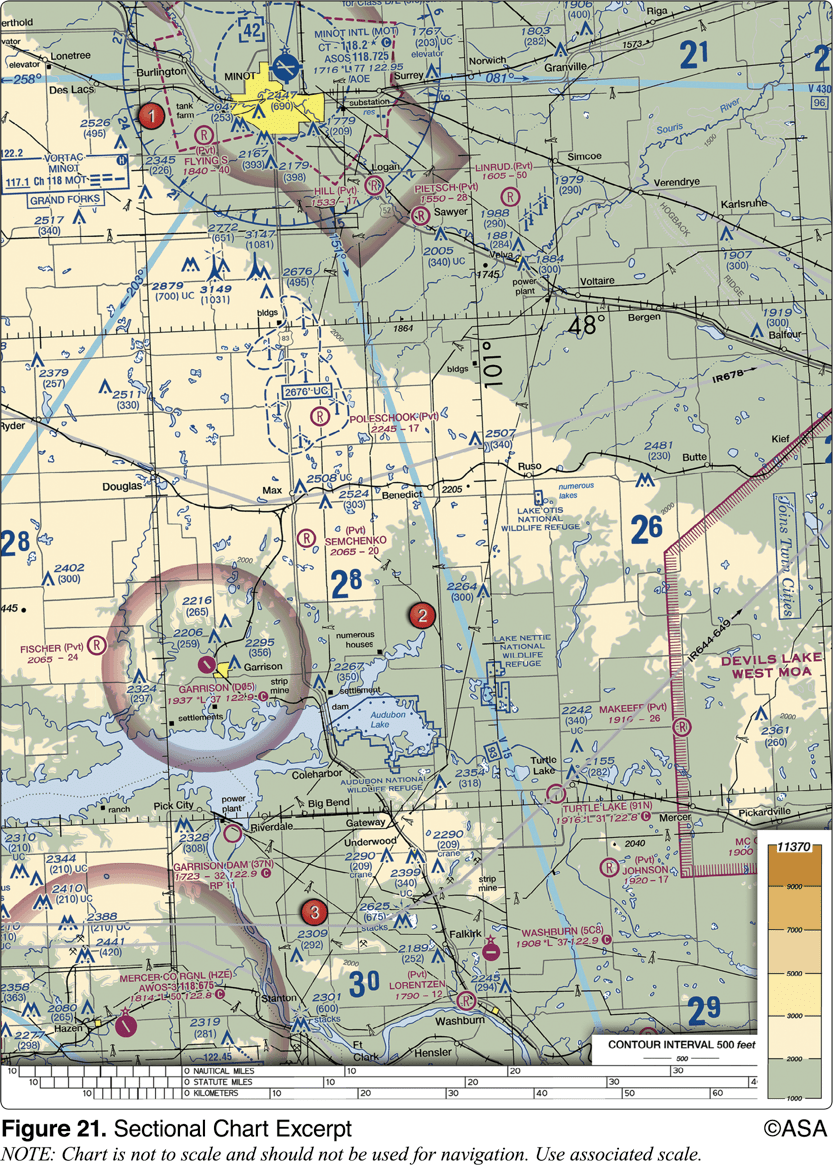
The terrain elevation of the light tan area between Minot (area 1) and Audubon Lake (area 2) varies from
2,000 feet to 2,500 feet MSL
How many feet are in a nautical mile
6067
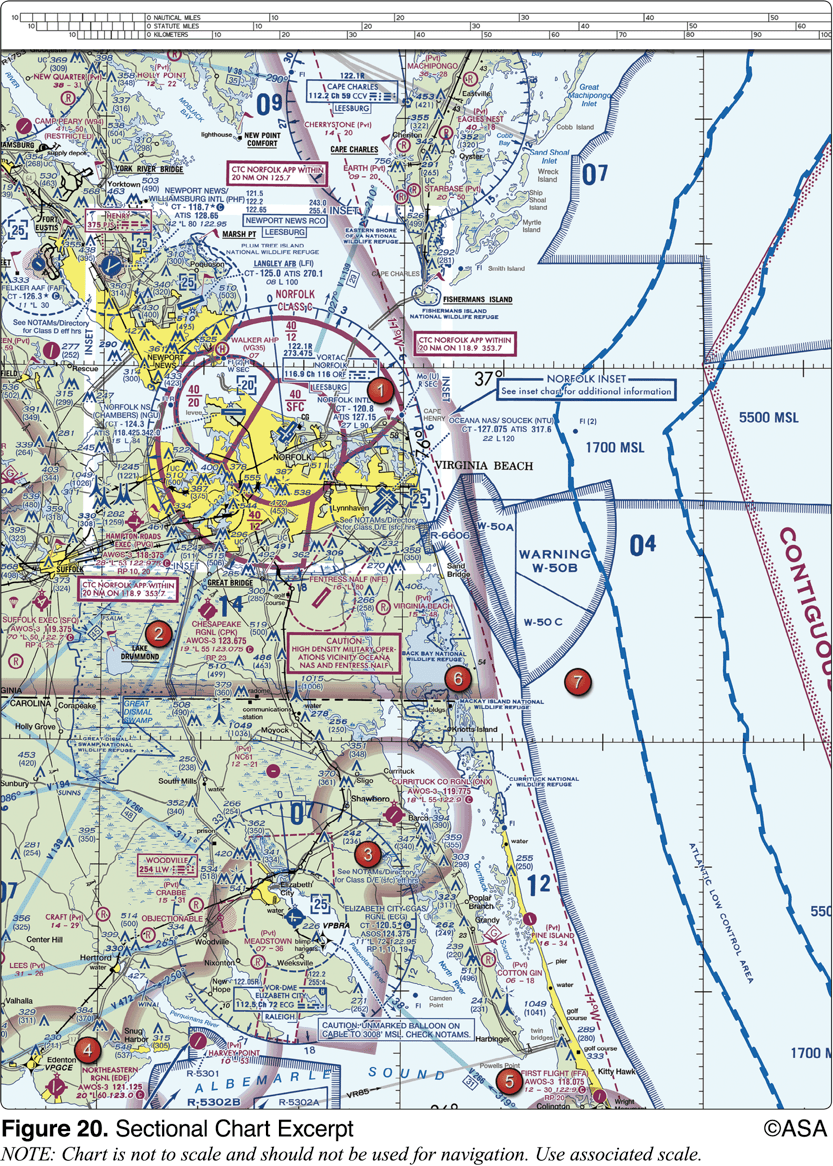
What hazards to aircraft may exist in restricted areas such as R-5302B?
unusual, often invisible, hazards such as aerial gunnery or guided missiles
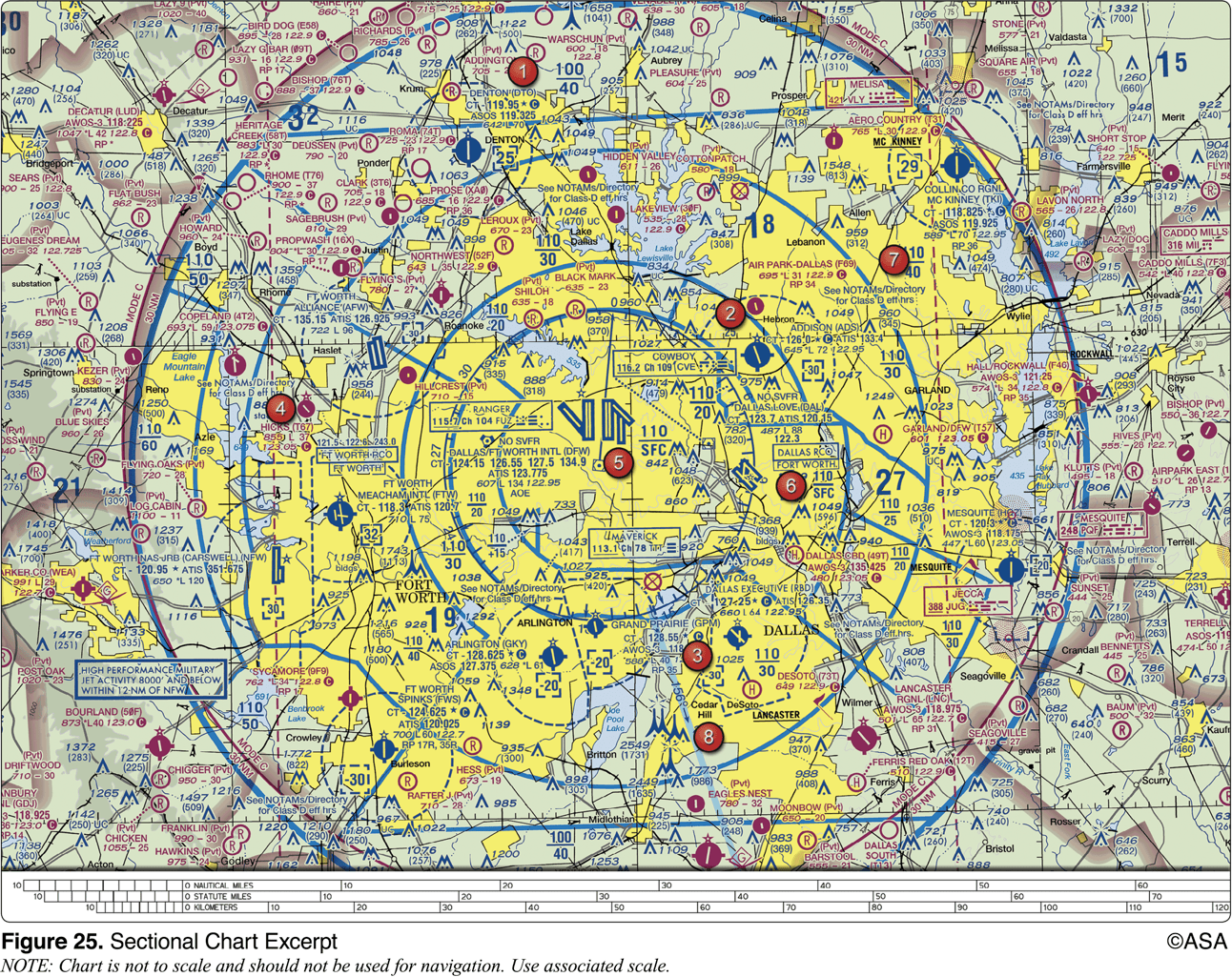
What minimum altitude is required to fly over the Cedar Hill TV towers in the congested area south of Dallas Executive (RBD)?
3549
Using the E6-B find the density altitude given:
Pressure altitude: 3000’
Temp: 20 C
4000
Using the E6-B find the density altitude given:
Pressure altitude: 10,000’
Temp: -20 C
8000
Using the E6-B find the density altitude given:
Pressure altitude: 4000’
Temp: -25 C
0
Using E6-B find the time it takes to fly 240 NM at 180 kts
80 minutes
Using E6-B find time it takes to fly 33 NM at 110 kts
18 minutes
Using E6-B if you fly for 2 hours at a speed of 110 kts how far did you go in NM?
220
Using E6-B if you fly for 1:30 at 100 kts how far did you go in NM
150
Using E6-B if it takes 43 minutes to travel 90 NM how fast are you flying?
125 kts
Using E6-B if it takes 19 minutes to fly 35 NM how fast were you flying?
111 kts
Using E6-B if your plane burns 12 GPH and it burns 30 gallons how long were you flying
150 minutes
Using E6-B if your plane burns 11 GPH and it burns 24 gallons how long were you flying
131 minutes
Using E6-B if you fly for 40 minutes and burn 7 gallons of fuel what is your rate in GPH
10.5
Using E6-B if you fly for 4 hours and 11 minutes and burn 36 gallons of fuel what is your rate in GPH
8.4
Using E6-B if you fly for 15 minutes and your fuel burns at 14 GPH how much fuel did you use
3.5
Using E6-B if you fly for 28 minutes and your fuel burns at 11 GPH how much fuel did you use
5.15
Using E6-B what’s your true airspeed if
CAS: 125
temp: 15
press. alt: 5000
137 kts
Using E6-B whats your true airspeed if
CAS: 110
temp: 0
press. alt: 8000
124 kts
Using E6-B what’s your true airspeed if
CAS: 149
temp: -5
press. alt: 12,000
180 kts
Using E6-B find your true heading and groundspeed
TC: 30
TAS: 170
Wind: 080/20kt
TH: 35
GS: 156
Using E6-B find your true heading and groundspeed.
TC: 310
TAS: 120
Wind: 180/16kt
TH: 304
GS: 130