Chapter 18: Emotion
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
studying emotion and neuroscience
Affective neuroscience
2
New cards
Brain mechanisms of emotion derived from these 3 things
* Animal models
* Human studies
* Brain lesions
* Human studies
* Brain lesions
3
New cards
emo system is dif than sensory system because
* Diversity of emotions and brain activity
* Many structures involved in emotion
* No one-to-one relationship between structure and function
* Many structures involved in emotion
* No one-to-one relationship between structure and function
4
New cards
def 2 Early Theories of Emotion
The James–Lange theory: emotion experienced in response to physiological changes in body
The Cannon–Bard theory: emotions occur independent of emotional expression—no correlation with physiological state
The Cannon–Bard theory: emotions occur independent of emotional expression—no correlation with physiological state
5
New cards
Can stimulus have emotional impact without conscious
awareness.
awareness.
yes
* Aversive conditioning to masked stimulus results in increased skin conductance (ex. sweating)
* Increased activity in the amygdala
Many possible ways for the brain to process emotional information
* Aversive conditioning to masked stimulus results in increased skin conductance (ex. sweating)
* Increased activity in the amygdala
Many possible ways for the brain to process emotional information
6
New cards
def Broca’s limbic lobe structures
Areas of brain forming a ring around corpus callosum:
* cingulate gyrus
* medial surface temporal lobe
* hippocampus
* cingulate gyrus
* medial surface temporal lobe
* hippocampus
7
New cards
def Broca’s limbic lobe funct
high cog functioning
8
New cards
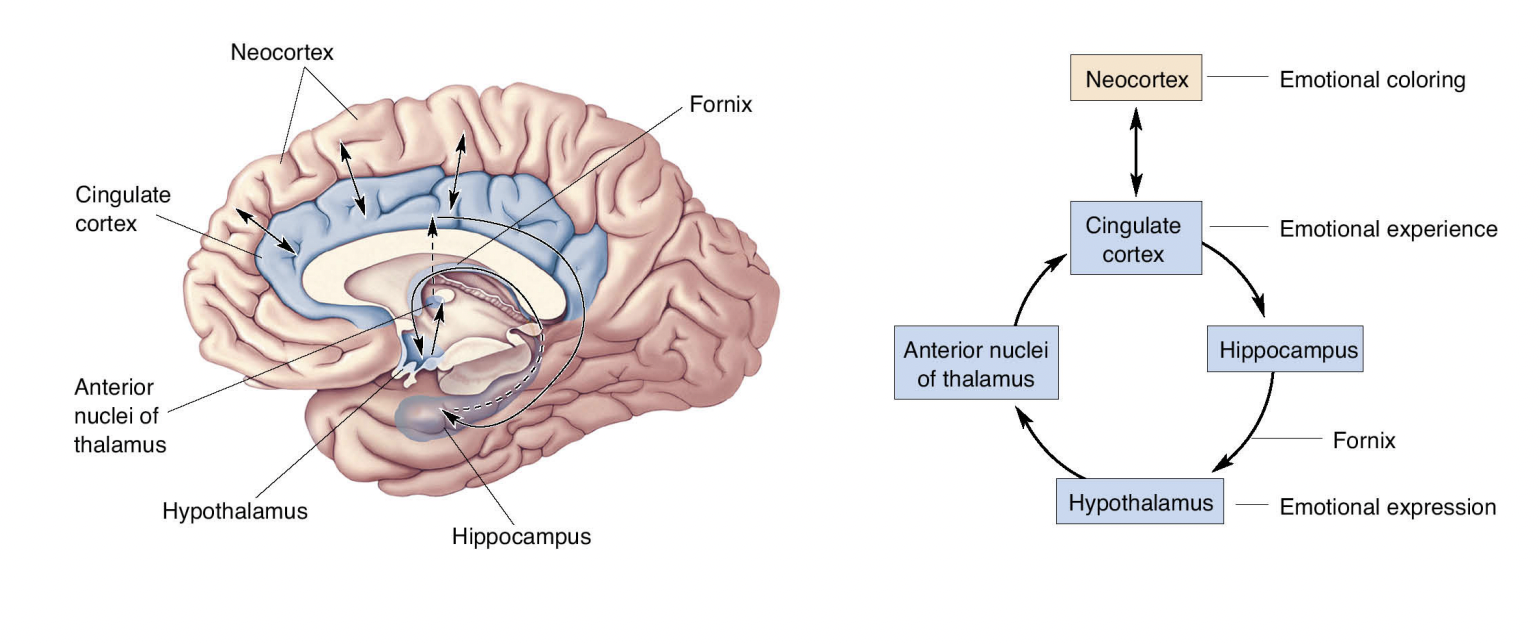
The Papez Circuit
Limbic structures, including cortex, involved in emotion
* hippocampus
* hypothalamus
* thalamus
* cingulate cortex
* neocortex
* fornix
* hippocampus
* hypothalamus
* thalamus
* cingulate cortex
* neocortex
* fornix
9
New cards
def Papez Circuit funct
__Emotional__ __system__ on the medial wall of the brain linking cortex with hypothalamus
10
New cards
what strengthens memory
cortosol
11
New cards
what governs behavioral expression of emotion
hippocampus
* evidence: Rabies infection implicates hippocampus in emotion -> hyperemotional responses
* evidence: Rabies infection implicates hippocampus in emotion -> hyperemotional responses
12
New cards
Lesions to what lead to spontaneous laughing or crying
thalamus
13
New cards
Evolution of limbic system allows animals to…
experience and express emotions beyond stereotyped brain stem behaviors
14
New cards
Early theories of emotion and limbic system built on…
introspection and inference from brain injury and disease
15
New cards
Studies of disease and consequences of lesions not ideal for revealing…
normal funct
\
\*This is a drawback
\
\*This is a drawback
16
New cards
def 2 more recent theories of emotion
* Basic emotion theories
* Dimension emotion theories
* Dimension emotion theories
17
New cards
Certain emotions thought… experiences.
unique, indivisible, universal experiences
18
New cards
hypothesis for basic emo theories
basic emotions have distinct representations or circuits in brain
Analogous to distinct representations for sensory experiences
Analogous to distinct representations for sensory experiences
19
New cards
def 6 basic emotions
Anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, surprise
20
New cards
fMRI shows _____ activation with the basic emotions.
different
21
New cards
not single areas but…may represent emotions.
Patterns of activity
22
New cards
Emotions can be…. into…. fundamental elements. Combined in… ways and… amounts
broken down, smaller, different, differing
23
New cards
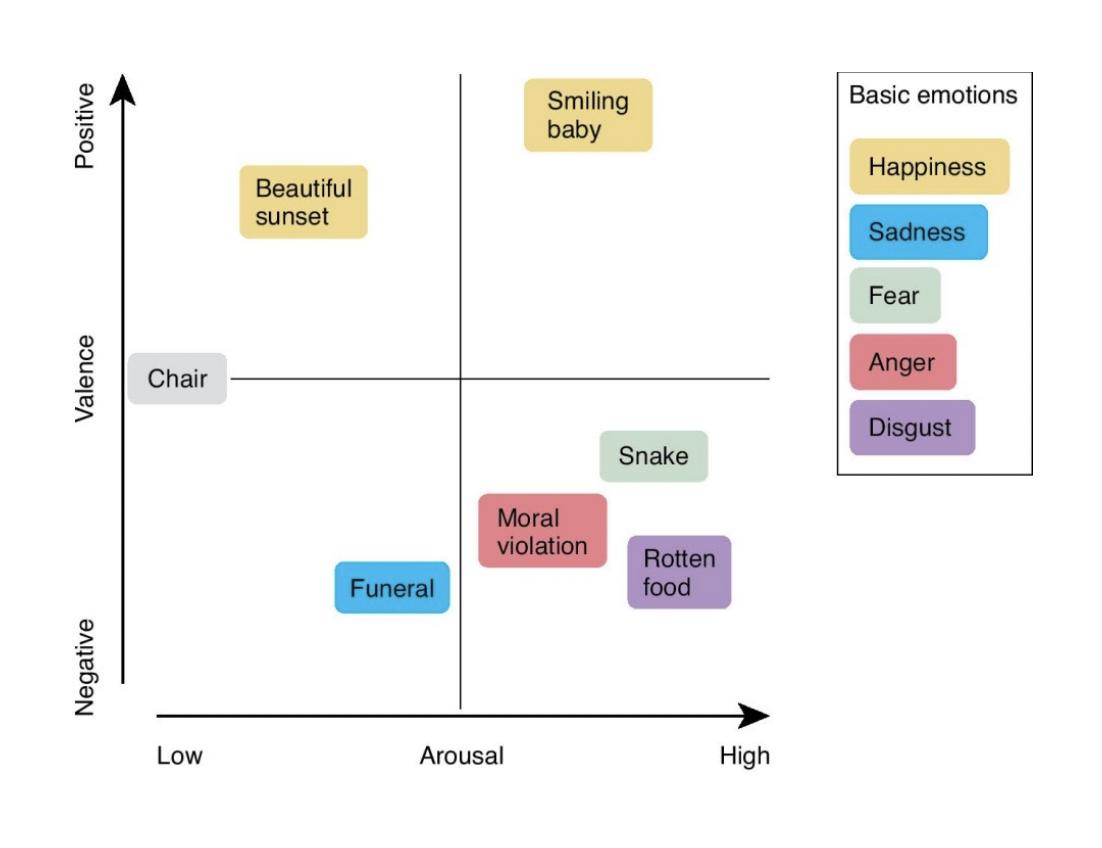
Emotions correspond to brain activation along dimensions such as…
valence and arousal
24
New cards
• Psychological constructionist theories of emotion
* Variation on dimensional theories
* Includes nonemotional psychological components
* Emotion an emergent consequence of combined components
* Includes nonemotional psychological components
* Emotion an emergent consequence of combined components
25
New cards
• Unknown whether each emotion is represented by:
Activity in a specialized area of the brain – A network of areas – A more diffuse network of neurons
26
New cards
def 3 Study approaches for defining emo
Behavioral observations – Physiological recordings – Studies of effects of lesions and disease
27
New cards
ex of studying emo
studying fear and anger
28
New cards
def 2 things that produced the Klüver–Bucy Syndrome
* temporal lobectomy in rhesus monkeys
* Temporal lobe lesions in humans—particularly lesions in amygdala
* Temporal lobe lesions in humans—particularly lesions in amygdala
29
New cards
what are the symptoms of Klüver–Bucy Syndrome
Decreased fear and aggression – Decreased vocalizations and facial expressions of fear– Flattened emotions
30
New cards
what does Bilateral amygdalectomy lead to
reduced fear and aggression in all animals tested
Anger, sadness, and disgust may also be affected
Anger, sadness, and disgust may also be affected
31
New cards
what is the S.M. case study
inability to recognize fear in facial expressions
32
New cards
how does anxiety and fear in humans arise
Electrical stimulation of amygdala → increased vigilance or attention
33
New cards
what does fMRI imaging show about fearful faces
Fearful faces evoke greater amygdala activity than happy or neutral faces.
34
New cards
what is involved in forming memories of emotional and painful events
amygdala - learned fear
35
New cards
what are Intertwined in Animals
anger and agression
36
New cards
predatory aggression vs affective aggression
attack
* Against different species for food – Few vocalizations, attack head or neck – No activity in sympathetic division of ANS.
for show
* Used for show, not kill for food – High levels of sympathetic activity – Makes vocalizations, threatening posture
* Against different species for food – Few vocalizations, attack head or neck – No activity in sympathetic division of ANS.
for show
* Used for show, not kill for food – High levels of sympathetic activity – Makes vocalizations, threatening posture
37
New cards
what operation leads to less aggression in animals
Amygdala lesions in animals
38
New cards
what operation leads to less aggression in humans/treats medical aggression
Amygdalectomy →
* Reduced aggressive behavior
* Relief from anxiety
* Profound, unpleasant side effects
Psychosurgery—now treatment of last resort
* Reduced aggressive behavior
* Relief from anxiety
* Profound, unpleasant side effects
Psychosurgery—now treatment of last resort
39
New cards
Removal of cerebral hemispheres but not hypothalamus →
rage beh
* Behavior reversed with additional lesions in hypothalamus
* Behavior reversed with additional lesions in hypothalamus
40
New cards
Hypothalamus may normally be inhibited by…
telencephalon
41
New cards
• Flynn’s research on affective and predatory aggression
* Elicited affective aggression by stimulating __medial__ hypothalamus
* Predatory aggression elicited by stimulating __lateral__ hypothalamus
* Predatory aggression elicited by stimulating __lateral__ hypothalamus
42
New cards
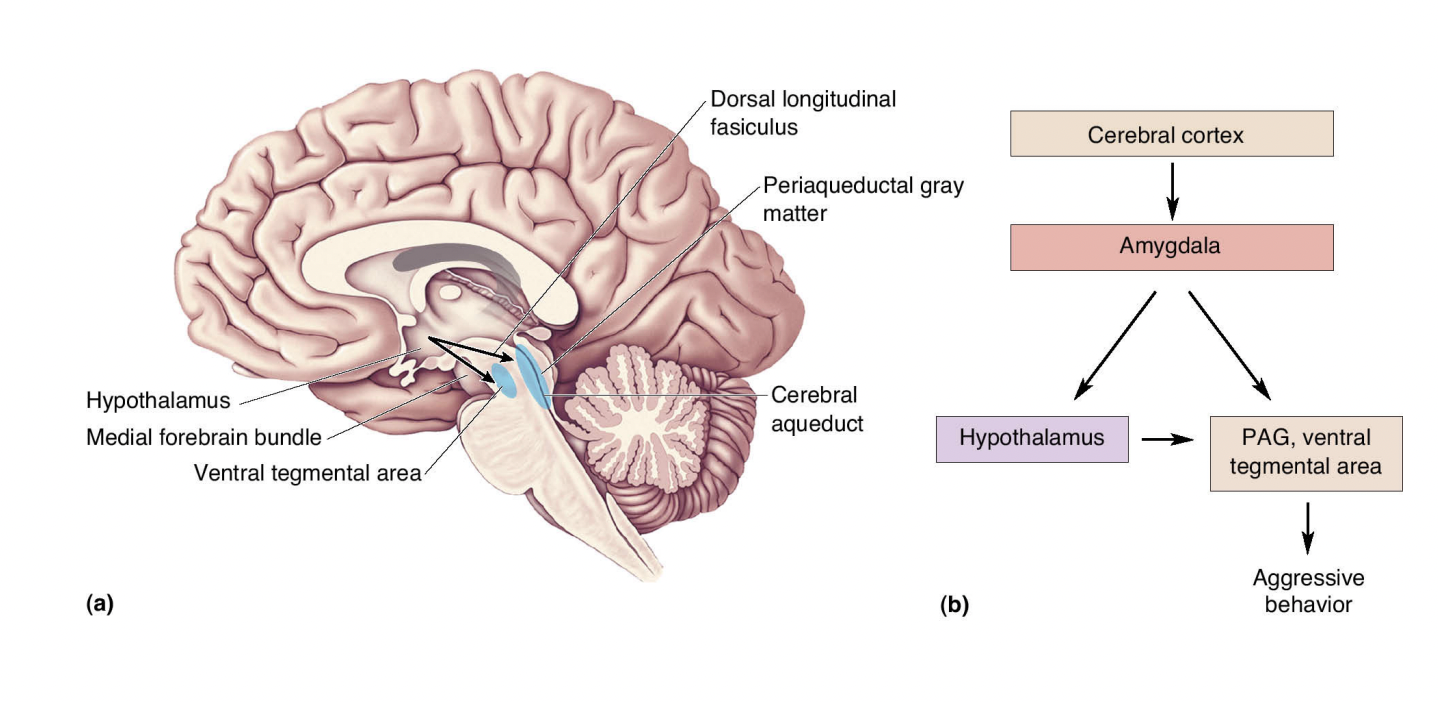
Midbrain and Aggression
Two hypothalamic pathways to brain stem involving autonomic function
* Medial forebrain bundle → ventral tegmental area; predatory aggression
* Dorsal longitudinal fasciculus → periaqueductal gray matter; affective aggression
* Medial forebrain bundle → ventral tegmental area; predatory aggression
* Dorsal longitudinal fasciculus → periaqueductal gray matter; affective aggression
43
New cards
A Neural Circuit for Anger and Aggression
44
New cards
what NT Regulates Anger and Aggression
Serotonin
45
New cards
what is the Serotonin deficiency hypothesis
Aggression is inversely related to serotonergic activity.
46
New cards
Serotonergic raphe neurons project to the hypothalamus and limbic structures via the medial forebrain bundle
47
New cards
dec in Serotonin turnover →
inc of aggression in rodents
48
New cards
Drug PCPA blocks serotonin synthesis →
inc in aggression
49
New cards
humans: _______ correlation between
serotonin activity and aggression
serotonin activity and aggression