Electrolytes
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Hypo meaning
Hyper meaning
Hypo - too low
Hyper - too much
What is potassium used for (K+)
Heart and skeletal muscles.
EKG changes:
Arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythm)
weakness
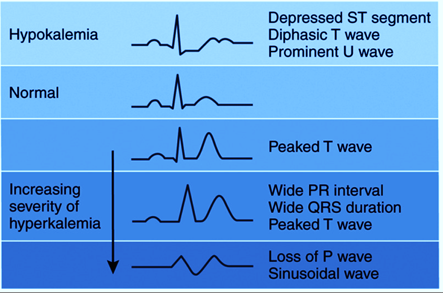
What are the danger zones, caution zones and safe zones for Potassium (K+)
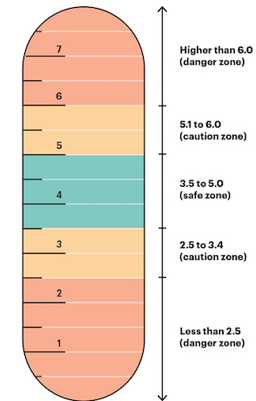
What is Hypokalemia? Signs/symptoms selected causes
Hypokalemia (not enough potassium)
Signs/symptoms: Arrhythmias. Muscle weakness → paralysis (lower extremities) U waves and flattened T waves {EKG}
Causes: Increased renal loss (diuretics). Increased Gi losses (vomiting/diarrhea)
Increased K entry into cells. Hypomagnesemia. Cannot correct K until Mg is corrected.

What is Hyperkalemia? Signs and symptoms and causes.
Hyperkalemia: too much potassium in the body
Signs/symptoms: Heart palpitations, muscle weakness EKG changes. Nausea vomiting.
Causes: Decreased K excretion in urine (acute and chronic kidney disease.) Insulin deficiency. Beta blockers. Lysis of cells.
Beta blockers
any of a class of drugs which prevent the stimulation of the adrenergic receptors responsible for increased cardiac action, used to control heart rhythm, treat angina, and reduce high blood pressure.
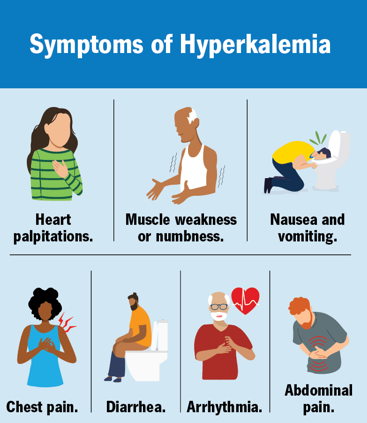
What are the calcium level ranges? (Ca2+)
9-10 normal
10-10.5 need investigation
10.5-12 danger usually require surgery
Hypocalcemia: <8.5 mg/dL
Hypercalcemia > 10.5 mg/dL
What is Hypercalcemia? Symptoms and causes
Hypercalcemia: Too high levels of calcium
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic. Kidney stones. Excessive free water excretion. Loss of ability to concentrate urine. Decreased GFR → acute renal failure.
Causes: Hyperparathyroidism (parathyroid glands create high amounts of parathyroid hormone in the bloodstream.) Malignancy (cancerous cells)
Kidney stones, renal failure, Bone pain. Anxiety, altered mental state.
Hypervitaminoses D. Calcitriol supplements.
What is Hypocalcemia. Symptoms and causes
Hypocalcemia: too little calcium in the body
Symptoms: Tetany (a condition marked by intermittent muscular spasms, caused by malfunction of the parathyroid glands and a consequent deficiency of calcium.) Muscle twitches, Calcium blocks Na channels in neurons
Low Ca ➜easy depolarization ➜spontaneous contractions
•High Ca ➜difficult depolarization➜weakness
•Hyper-excitability of neurons and motorend plates
•Trousseau's sign: Hand spasm with BP cuff inflation
•Chvostek's sign: Facial contraction with tapping on nerve
•Seizures

What is Hypermagnesemia? (Mg2+) levels and Hypomagnesemia levels?
Hypermagnesemia: <1.7mg/dL
Hypomagnesemia: >2.4 mg/dL
Hypermagnesemia symptoms and causes.
Signs: Mg blocks Ca and K channels. Neuromuscular toxicity (decreased reflexes and paralysis). Bradycardia (slow HR) hypotension (low BP) cardiac arrest. Hypocalcemia (inhibit PTH secretion) Hypermagnesemia
Causes: Renal failure (kidney failure). Excessive intake of lots of Mg than the kidneys are able to excrete.
Hypomagnesemia symptoms and causes. (not enough Mg2+)
Symptoms: Tetany/tremor (neuromuscular excitability). Hypocalcemia. Hypokalemia (not enough Calcium and Potassium).
Causes: Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreases) Renal loss. Alcohol abuse. Drugs.
Hypomagnesemia/Parathyroid Gland
Low Mg
•↑ PTH release (same effect as calcium)
•↑ GI and renal magensium along with calcium
Very low Mg ➜inhibits PTH release
•Some Mg required for normal CaSR function
•Abnormal function ➜suppression of PTH release
•Hypocalcemia often seen in severe hypomagenesemia
What is Hyperphosphatemia? (PO43-) Causes and symptoms.
Too much phosphate.
Causes: Acute and chronic kidney disease. Hypoparathyroidism (too much parathyroid hormone in the blood). Tumor lysis syndrome. Most patients asymptomatic.
Metastatic calcifications: excess phosphate taken up by vascular smooth muscle. Increased systolic BP. Small vessel thrombosis and painful nodules, skin necrosis.
Safe phosphate levels?
Adult: 3.0-4.5 mg/dL or 0.97-1.45 mmol/L (SI units)
Elderly: values slightly lower than adult.
Child: 4.5-6.5 mg/dL or 1.45-2.1 mmol/L (SI units)
Newborn: 4.3-9.3 mg/dL or 1.4-3 mmol/L (SI units
Hypophosphatemia symptoms and causes.
Hypophosphatemia: too little phosphate in the body
Causes: Weakness, ATP depletion. Respiratory muscle weakness. Bone loss osteomalacia (bone weakness)
Causes: Primary hyperparathyroidism. Low po4 from poor nutrition. Antacids. DKA - diabetic ketoacidosis
Hyponatremia (Na+) Symptoms
Symptoms: Coma, Anorexia, Lethargy, decreased tendon reflexes, limp muscles, seizures and stomach cramping.
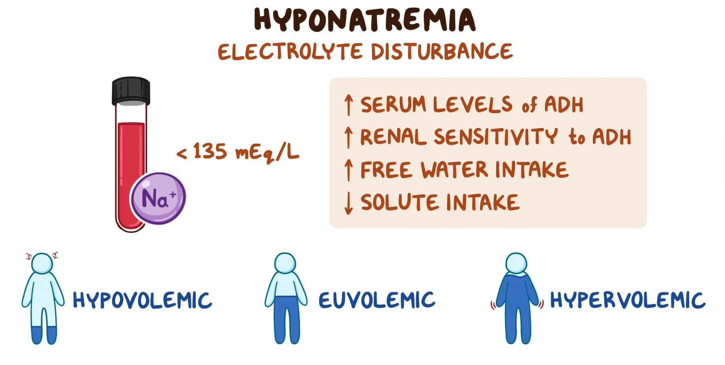
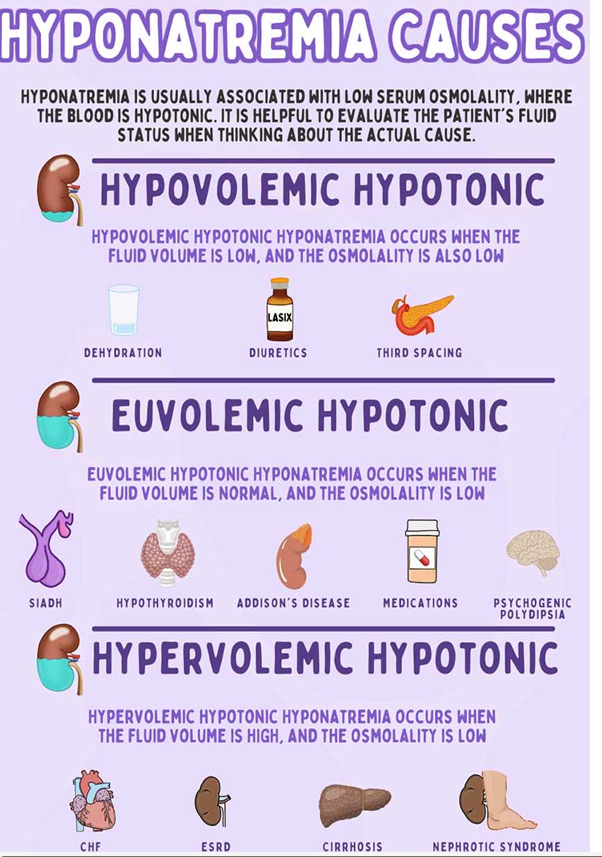
Hyponatremia causes
Hypernatremia causes and symptoms
Symptoms: excessive thirst. Extreme fatigue. Muscle twitches and spasms
Causes: fluid loss
Links between different deficiencies.
Can’t correct K until Mg is corrected. Cause of Hypokalemia is Hypomagnesemia
Causes of Hypocalcemia is hyper/hypomagnesemia