Circuit Analysis Revision
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Parallel combination (1/Rp); (I = V/Rp)
Equivalent reciprocal resistance, where the potential difference across the every single resistor is the same but the current flowing through them vary.
Serial combination (Rs); (V = I * Rs)
Equivalent resistance; Current flowing through each resistor is the same but they have different potential differences across them.
P = I * (R^2)
Formula to calculate the power dissipated by resistors in a serial arrangement.
P = (V^2)/R
Formula to calculate the power dissipated by resistors in a parallel arrangement.
P = I * V(terminal)
Formula to calculate the power supplies to the resistor or circuit by the voltage source.
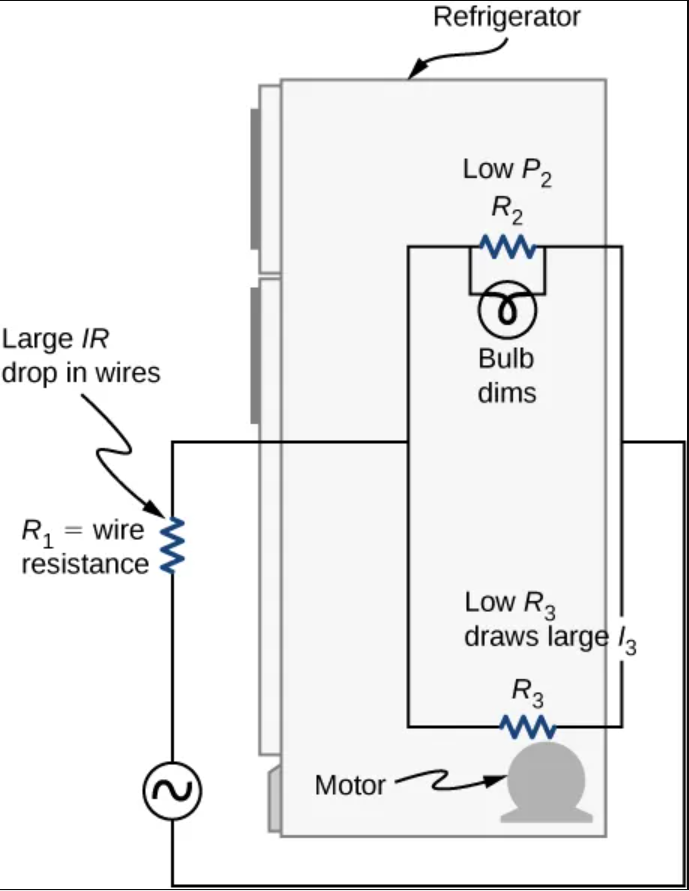
low, large, increased, IR drop, voltage
Device represented by R3 have very ___ resistance, so when it is switched on, a _____ current flows. This _________ current causes a larger ______ in the wires represented by R1, reducing the ______ across the light bulb, (which is R2), which then dims noticeably.
voltage, current
In the parallel arrangement of the resistors, their _______ is the same across all of the resistors however the _______ varies depending on the resistors value.
current, voltage
When the resistors are arranged in a serial manner, their _______ is the same through all of them, however now the _______ varies depending on the value of their resistors
larger
In series, ______ resistors will dissipate more power
smaller
In parallel, _______ resistors will dissipate more power.
Gustav Kirchhoff
A German physicist after whom the Kirchhoff’s rules are named
ΣI(in) = ΣI(out)
Kirchhoff’s junction rule
ΣV = 0
Kirchhoff‘s loop rule
U = qV
Potential energy formula
ΔV = Vb - Va = -IR or +V
In the ab resistor, where a is the lhs and b is rhs,
When the direction of travel is in the same direction of the current then
[end point arrow’s voltage - start arrow voltage] (of current)
For a battery: (higher potential - lower potential) [agar travel me negative pehle aa jaaye]
ΔV = Va - Vb = IR or -V
In the ab resistor, where a is the lhs and b is rhs,
When the direction of travel is in the opposite direction of the current then
[start arrow voltage - end point arrow’s voltage] (of current)
For a battery: (lower potential - higher potential) [agar travel me positive pehle aa jaaye]
internal resistances, emf, same
In series connection of batteries, their ____________________ and their ___ can be added together. Voltage sources in the parallel combination have the ____ emf as the total emf, but their total _________________ will be lesser than the individual one, and in the serial case it will be vice versa.
ε1 - Ir1 + ε2 - Ir2 - IR = 0; [(ε1 + ε2) - I(r1 + r2)] - IR = 0
Kirchhoff’s loop rule on the multiple battery (in series) circuit.
V(terminal) = (ε1 - Ir1) + (ε2 - Ir2) = [(ε1 + ε2) - I(r1 + r2)] = (ε1 + ε2) - Ireq
Terminal voltage formula for multiple cells connected in series
Yes, it is true
Is it true that batteries are connected in series in order to increase the voltage supplied
And in parallel to increase the current to the load
(ε1 - Ir1) + (ε2 - Ir2) = IR; Ir1 + Ir2 + IR = ε1 + ε2; I = (ε1 + ε2)/(r1 + r2 + R)
Formula for finding the current in the load when it is placed across the voltage source in series
together, together, emf
When the batteries are connected in parallel their positive terminals are connected ________ and their negative terminals are connected ________. Their ___ are identical
I = ε/( || req + R)
Formula for finding the current in the load when it is placed across the voltage sources in parallel
internal resistance, current, smaller
When the batteries are connected in parallel, they can reduce the ___________________ and therefore can produce a larger _______. The equivalent internal resistance here is _______ than the individual internal resistance.
V(terminal) = ε - I*(|| req)
Terminal voltage for batteries that are connected in parallel
Photovoltaic generation
The conversion of sunlight directly into electricity, which is based upon photoelectric effect.
Photoelectric effect
Photons are hitting the surface of the solar cell, which then creates an electric current in the cell.
Pure silicon
Element from which the solar cells are made from.
Incident solar radiation or insolation
The current output is a function of the amount of sunlight falling on the cell.
100mA/cm^2
Current density produced by a typical single solar cell under a bright noon.
36, 72, 50W, 140W, unidirectional
A solar cell array usually consists of between __ to __ , with a power output of ___ to ____. Solar cells provide a ______________ current.
IR = (ε/req + R)
Formula to prove that the terminal voltage is equal to the potential drop across the load resistor, and how parallel battery combination produces large by reducing the internal resistance.