Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 4
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Cell Junctions
Contact points between the plasma membranes of tissue cells
Types of Cell junctions(5)
Tight Junctions, Adherens Junctions, Desmosomes, Herhidemosomes, and Gap Junctions
Gap Junction
Connexons connect neighboring cells to rapidly move energy or electricity to other cells. "Tunnels"
Tissue
Group of similar cells that predom specific functions
Types of tissues
Epithelial, Connective, Nervous, and muscular
Epithelium Tissue
Closely packed cells arranger in continuous sheets that form the outer covering of body, line body cavities and cover some internal organs. Avascular, and reproduce readily.
Apical Surface
Surfaces faces body surface- internally or externally.
Basal Surface
Opposite of Apical surface- adheres to basement membrane
Basement membrane
Basal lamina and reticular lamina
Vascular/Avascular
Not own nerve supply/Own nerve supply
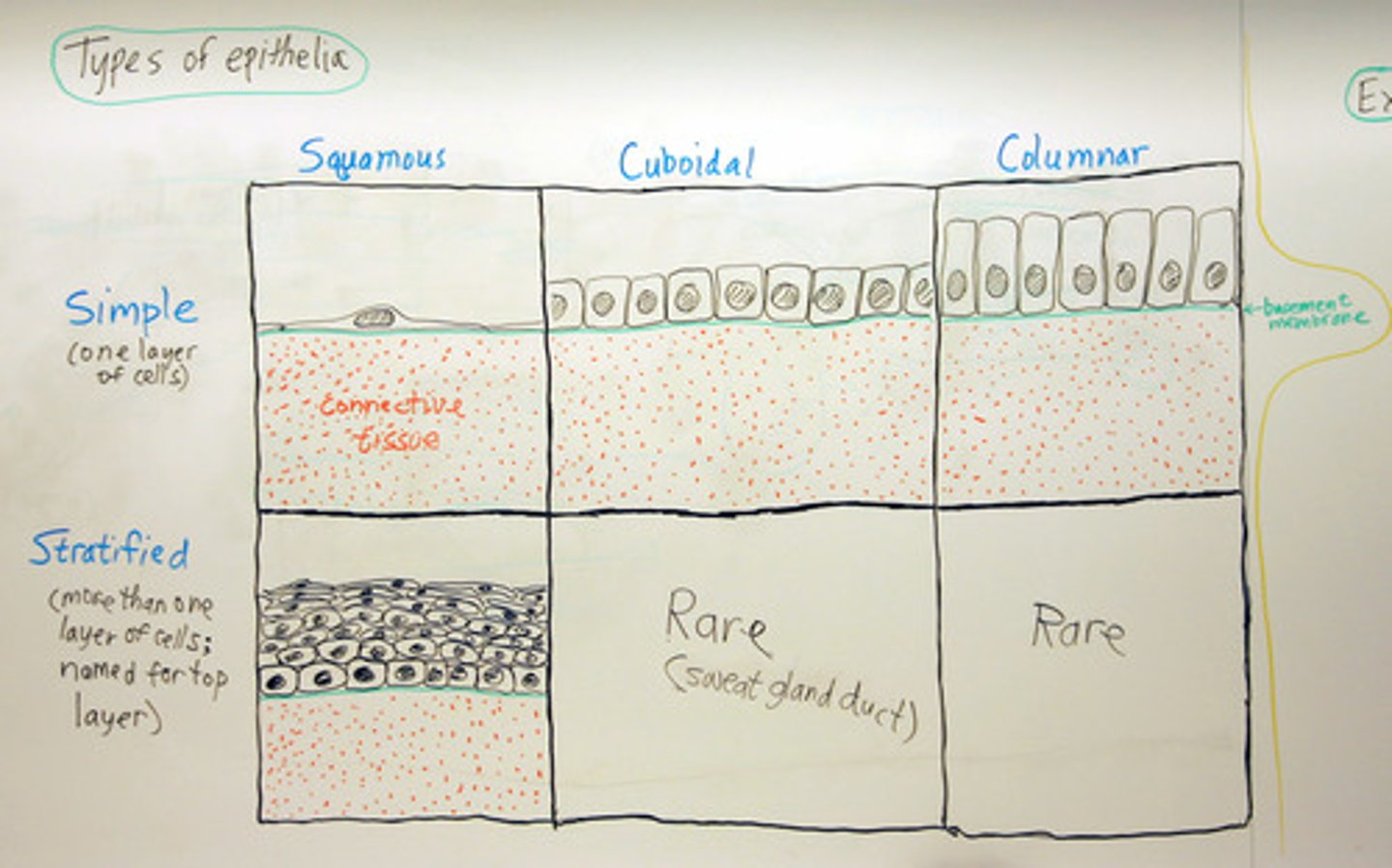
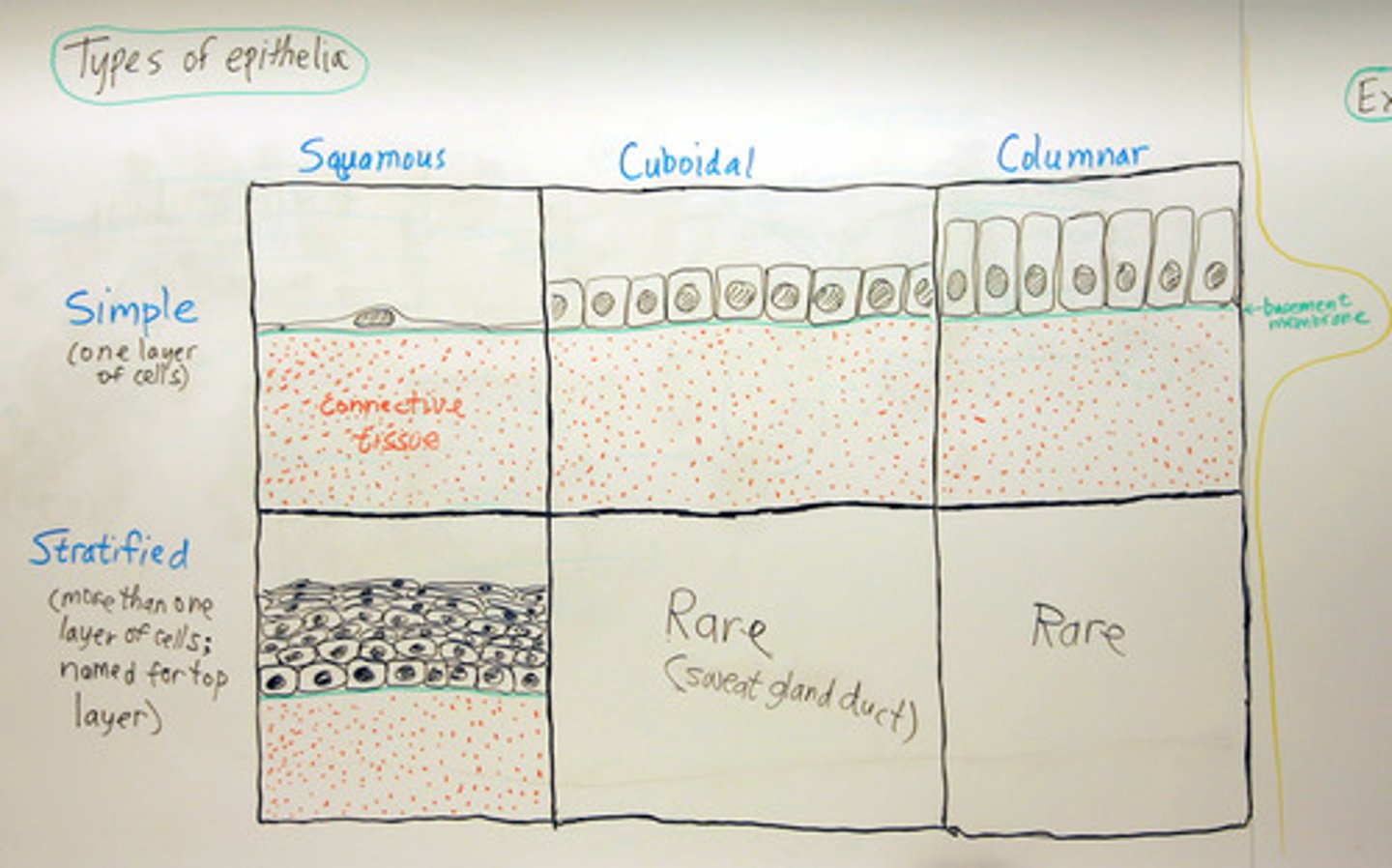
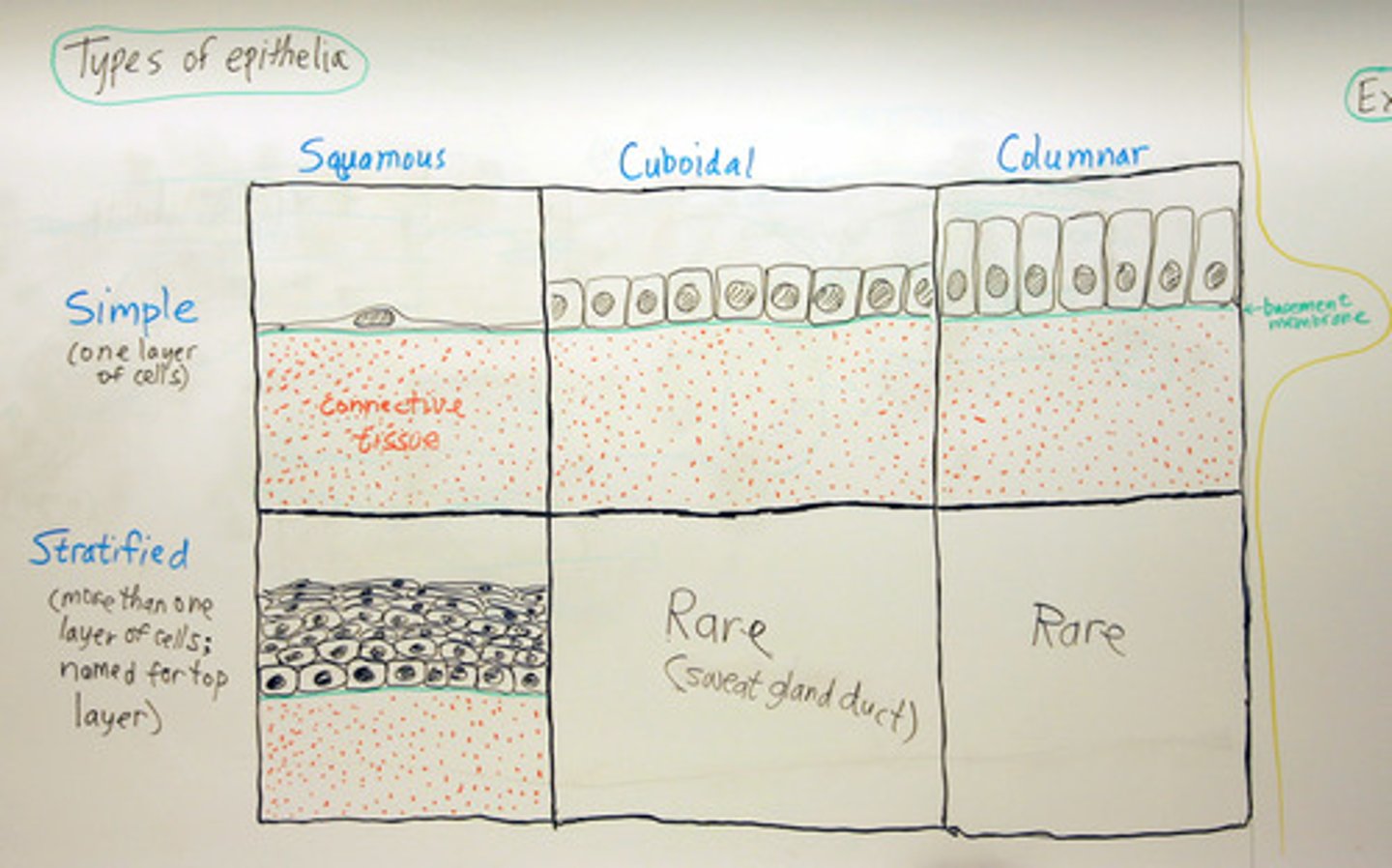
Epithelial classification
Number of layers(Simple Vs. Stratified) and shape (Squamous Vs. Cuboidal Vs. Columnar)
Simple
Single layer of cells. Allow for diffusion, osmosis, secretion, excretion, absorption, filtration.
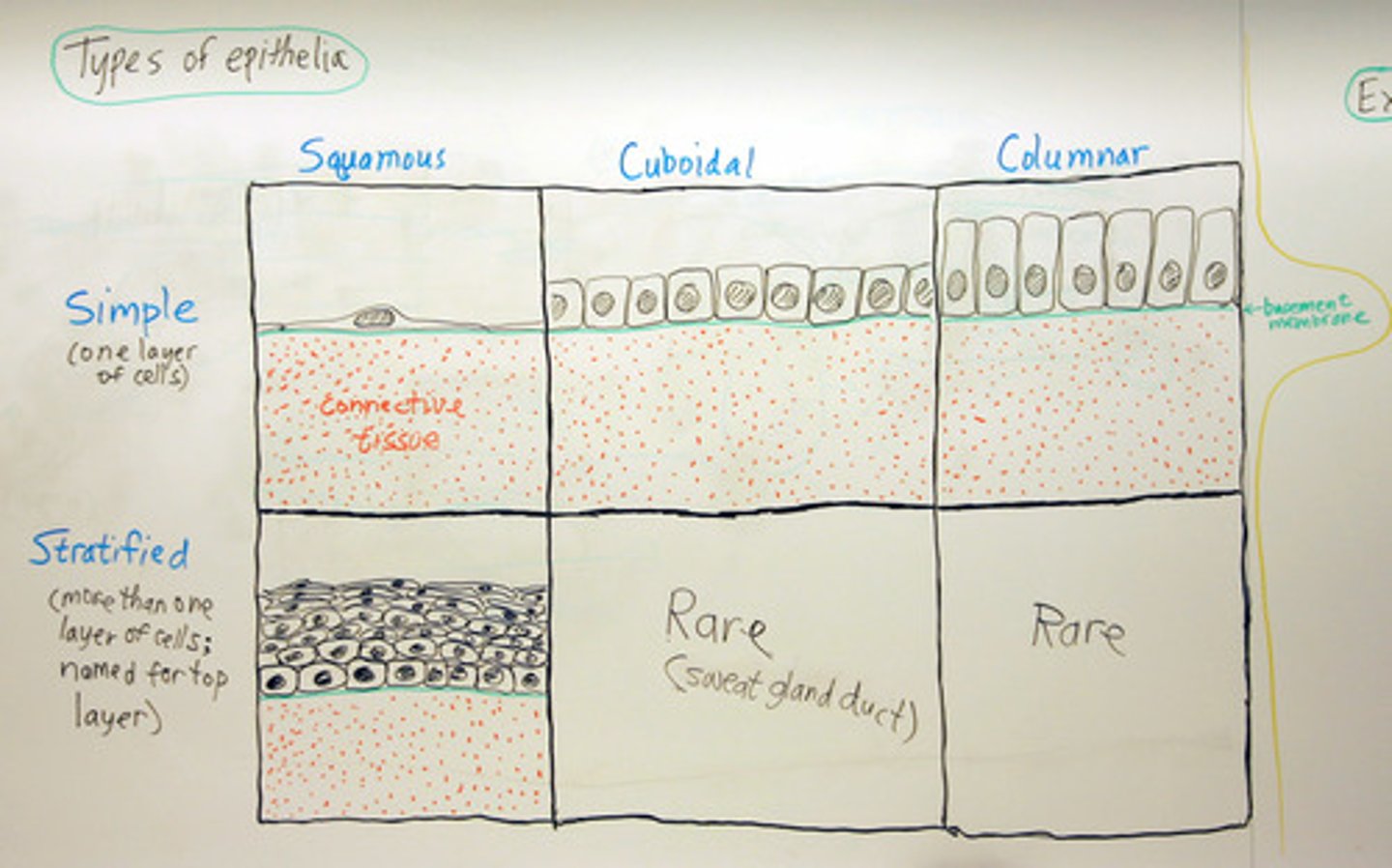
Stratified
For protection (skin), multiple layers on top of each other
Pseudostratified
Pseudo-false. Looks like multiple layers but all cells are touching basal surface.

Squamous
Thin and flat
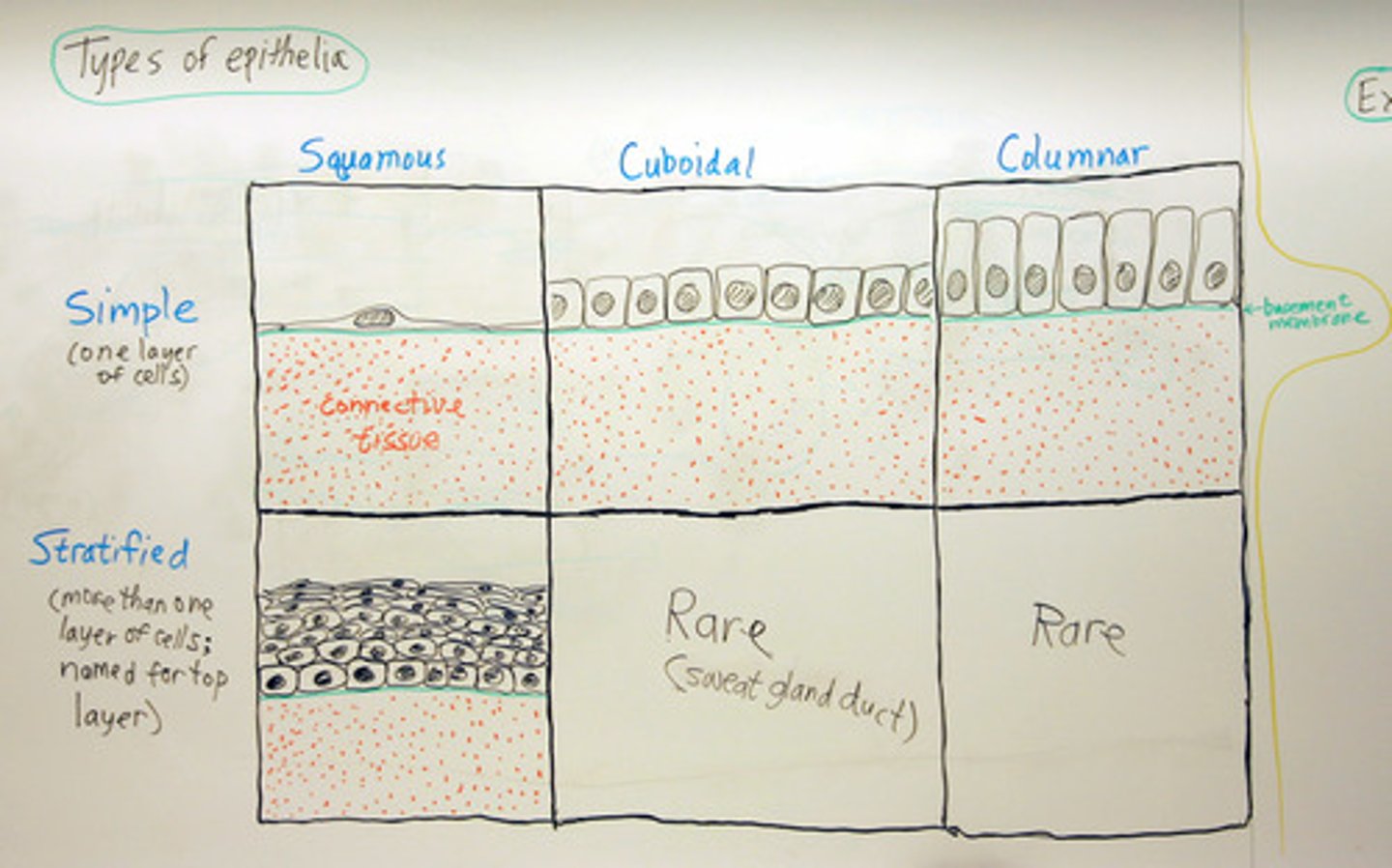
Cuboidal
Cube shaped
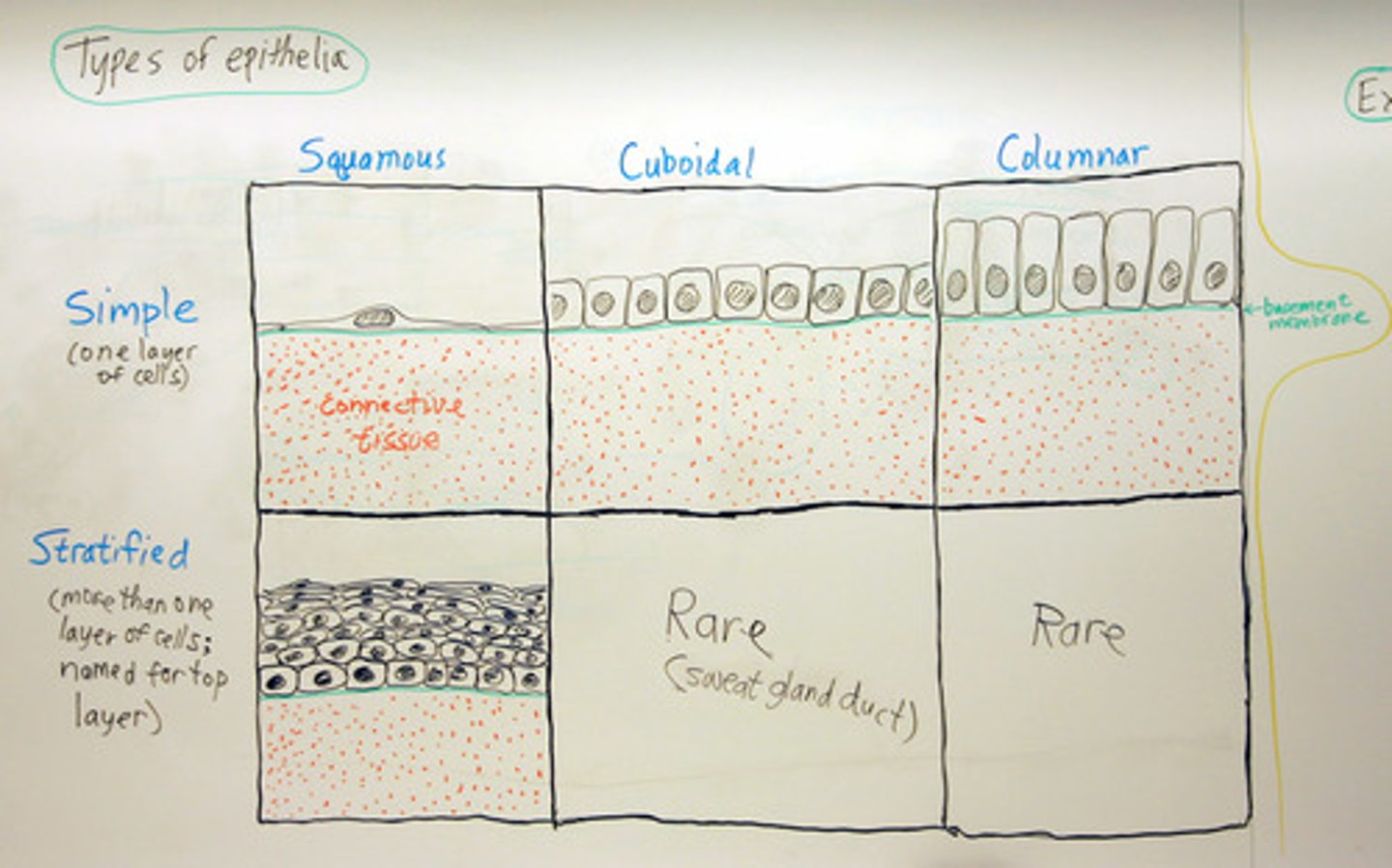
Columnar
Cells in columns
Transitional
Cells appear one way, but change shape under different conditions
Glandular Epithelium
Cells lie in clusters deep to covering and lining epithelium, produce secretions. (Glands)
Endocrine Glands
Secretions(Hormones) enter the interstitial fluid and diffuses directly into blood stream with out flowing into a duct
Exocrine Glands
Cells produce a secretion into duct system that empties directly on surface of body or into a cavity (Sweat). Unicellular Vs. Multicellular. Simple Vs. Compound. Tubular Vs. Acinar Vs. tubuloacinar.
Tubular Vs Acinar Vs Tubuloacinar
Tube like Vs. Round Vs. Both
Merocrine
Most glands, excretes by vesicle- burst off and out of vesicle. Made in Endoplasmic Reticulum, move to golgi complex and then are released.
Apocrine
Separates off. Made in Endoplasmic Reticulum, move to golgi complex and then are released.
Holocrine
Excretes by bursting cell completely. Made in Endoplasmic Reticulum, move to golgi complex and then are released.
Connective Tissue
Most abundant in body, derived from mesenchyme, vascular, deep to epithelium
Functions of connective tissue
Protection, support, binding, insulation and transportation.
Composition of connective tissue
Cells Vs. Extracellular Matrix-> Ground substance Vs. Fibers
"___"Blast
Immature cell
"____"Cyte
Mature cell
Osteo
Bone
Chondro
Cartialge
Fibroblasts
Secrete substances of extra cellular matrix
defensive cells
macrophages, White blood cells, Mast cells, and plasma cells
Adipocytes
Store energy though triglycerides
Extracellular Matrix
Contain Ground substance and fibers
Ground substance
Supports cell and binds together- stores water
Fibers (Connective)
Strengthen and support matrix. Types- Collagen, elastic, and reticular
Collagen Fibers
Strength
Elastic fibers
Elasticity or stretch
Reticular fibers
Support
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
Efficient in collagen- stretchy skin- no collagen between joints
Loose connective tissue (3)
Areolar, Reticular, Adipose->Adipocytes
Dense connective tissue(3)
Regular, irregular, Elastic
Regular connective tissue
all parallel
Irregular connective tissue
fibers in all different directions
Elastic connective tissue
Lungs and arteries
Cartilage
Avascular. Hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage, bone, blood and lymph.
Hyaline cartilage
Most abundant. Flexible, support, reduces friction, absorbs shock. The weakest of cartilage.
Elastic Cartialge
Strong and elastic
Fibrocartilage
Strongest cartilage- very thick. Lacks perichondrium.
Muscle tissue(3)
Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth
Skeletal muscle
Attaches to bone. Voluntary, striated, multinucleated.
Voluntary Vs. involuntary
You control the contraction Vs. Body does the contraction without your knowledge.
Multinucleated Vs. uninucleated
multiple nucleons Vs. One nucleus
Striated Vs. Smooth
Striped looking Vs. no striations
Cardiac tissue
Involuntary, striated, uninucleated. Heart
Smooth Tissue
Involuntary, no striations, uninucleated. Spindle shaped cells found in the walls of hollow structures.
Nerve Tissue
Tissue in the nervous system
cell types of nerve tissue(2)
Neurons, Neuroglia
Neurons
Nerve cells. Structure: Cell body, Axon, Dendrites

Neuroglia
Protective and supporting cells