IB Bio - Genetics
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
In garden peas, the pairs of alleles coding for seed shape and seed colour are unlinked. The allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). The allele for yellow seeds (Y) is dominant over the allele for green seeds (y). If a plant of genotype Ssyy is crossed with a plant of genotype ssYy, which offspring are recombinants?
if it is the exactly the same as Ssyy and ssYy its not a recombinate.
What constitutes a linkage group?
All the genes found on the same chromosome
A parent organism of unknown genotype is mated in a test cross. Half of the offspring have the same phenotype as the parent. What can be concluded from this result?
The unknown parent is heterozygous (a test cross of Aa × aa → 1:1 phenotypes).
The allele for red flower colour (R) in a certain plant is co-dominant with the allele for white flowers (R’). Thus a plant with the genotype RR’ has pink flowers. Tall (D) is dominant to dwarf (d). What would be the expected phenotypic ratio from a cross of RR’dd plants with R’R’Dd plants?
1:1:1:1 (RR’Dd:RR’dd:R’R’Dd:R’R’dd)
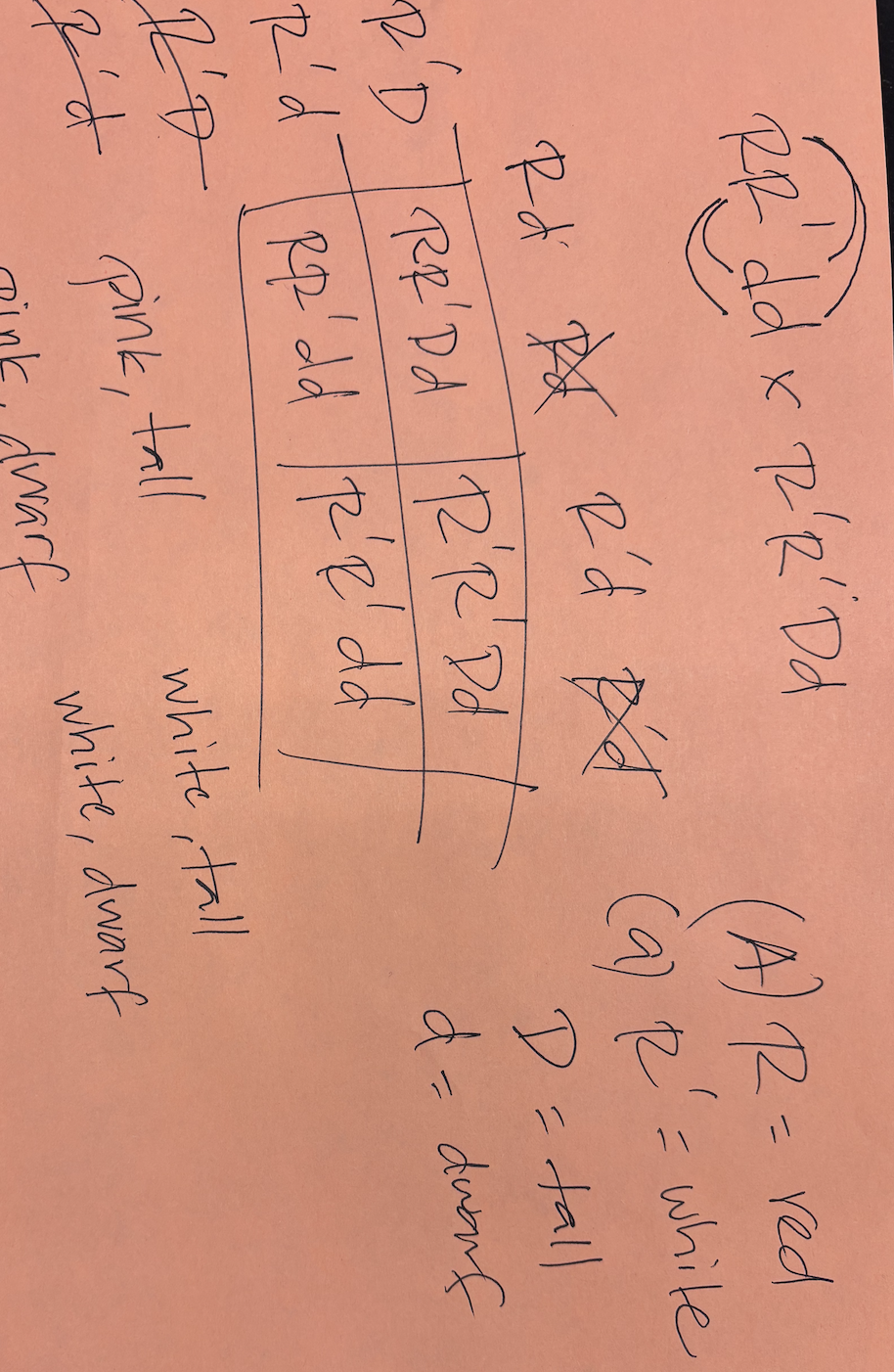
Two genes A and B are linked together as shown below.
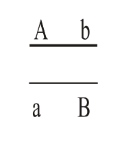
If the genes are far enough apart such that crossing over between the alleles occurs occasionally, which statement is true of the gametes?
The number of Ab gametes will be greater than the number of ab gametes
A polygenic character is controlled by two genes each with two alleles. How many different possible genotypes are there for this character?
there are 9
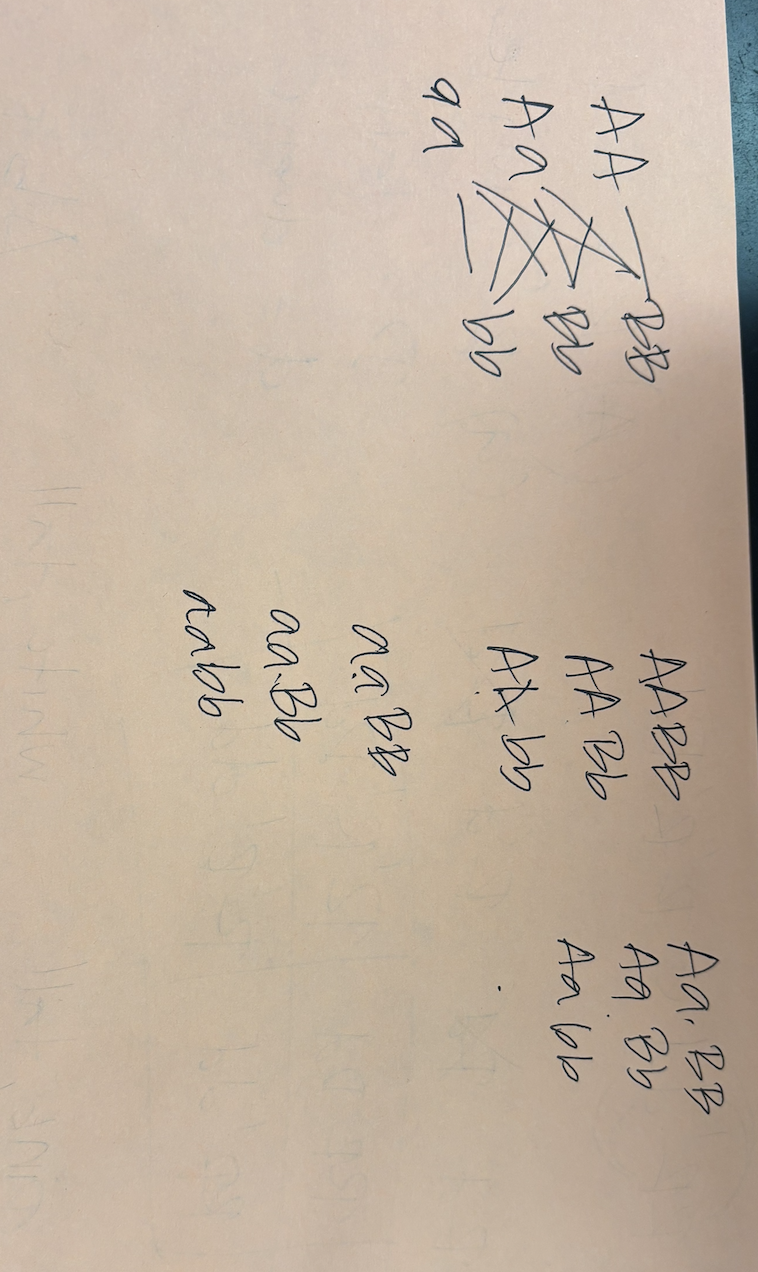
A cross is performed between two organisms with the genotypes AaBb and aabb.
What genotypes in the offspring are the result of recombination?
Test-cross logic: offspring possibilities → AaBb, Aabb, aaBb, aabb.
Recombinants: Aabb and aaBb (non-parental allele combinations).
The pedigree below shows which members of a family were Rhesus positive (■ and •) and Rhesus negative (□ and O). The allele for Rhesus positive blood (Rh+) is dominant over the allele for Rhesus negative blood (R-).
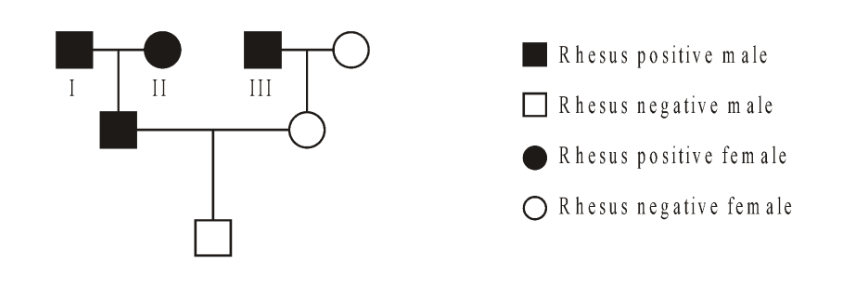
Which are possible genotypes of the individuals numbered I, II and III?
I and II could be homozygous or heterozygous, but 3 is definitely heterozygous.
Rh+R- or Rh+Rh+
In peas the allele for round seed (R) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seed (r). The allele for yellow seed (Y) is dominant over the allele for green seed (y).
If two pea plants with the genotypes YyRr and Yyrr are crossed together, what ratio of phenotypes is expected in the offspring?
3 yellow round, 3 yellow wrinkled 1 green round, 1 green wrinkled
If red (RR) is crossed with white (rr) and produces a pink flower (Rr), and tall (D) is dominant to dwarf (d), what is the phenotypic ratio from a cross of Rr dd and rr Dd?
Color: Rr × rr → 1/2 pink, 1/2 white.
Height: dd × Dd → 1/2 tall, 1/2 dwarf.
Overall: 1:1:1:1 (pink tall : pink dwarf : white tall : white dwarf).
Hemophilia is caused by an X-linked recessive allele. In the pedigree shown below which two individuals in the pedigree must be carriers of hemophilia?
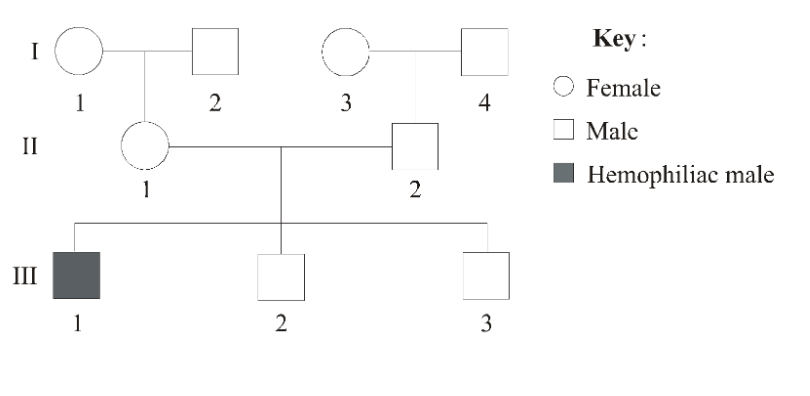
(III has a bad X = got from mom, so II 1is a carrier, and so is I 1.
Ans: II1 and I1.
A single gene in humans causes blood to be either rhesus positive (dominant allele) or rhesus negative (recessive allele). A woman with rhesus negative blood has already had a child with rhesus positive blood. There could be complications during pregnancy if she has another child with rhesus positive blood.
What is the probability of this, if the father is the same, and if his mother is known to have rhesus negative blood?
Mother is rr (Rh–). father must be Rr.
Cross rr × Rr → ½ Rr (Rh⁺), ½ rr (Rh–) → 50% chance Rh⁺.
What is the locus of a gene?
The specific position of a gene on a chromosome
Mendel crossed pure breeding (homozygous) tall pea plants that had coloured flowers with pure breeding dwarf pea plants that had white flowers. All of the resulting F1 plants were tall and had coloured flowers.
If Mendel had crossed these F1 plants with a pure breeding strain of dwarf pea plants with coloured flowers, what proportion of tall coloured plants would be expected in the offspring?
TtCC, TtCc, ttCC, ttCc
50%
What is a sex-linked gene?
A gene whose locus is on a sex chromosome (usually the X), so its inheritance depends on sex.
The pedigree chart below shows the inheritance of a genetic disease in a family. What is the nature of the allele that causes this disease?
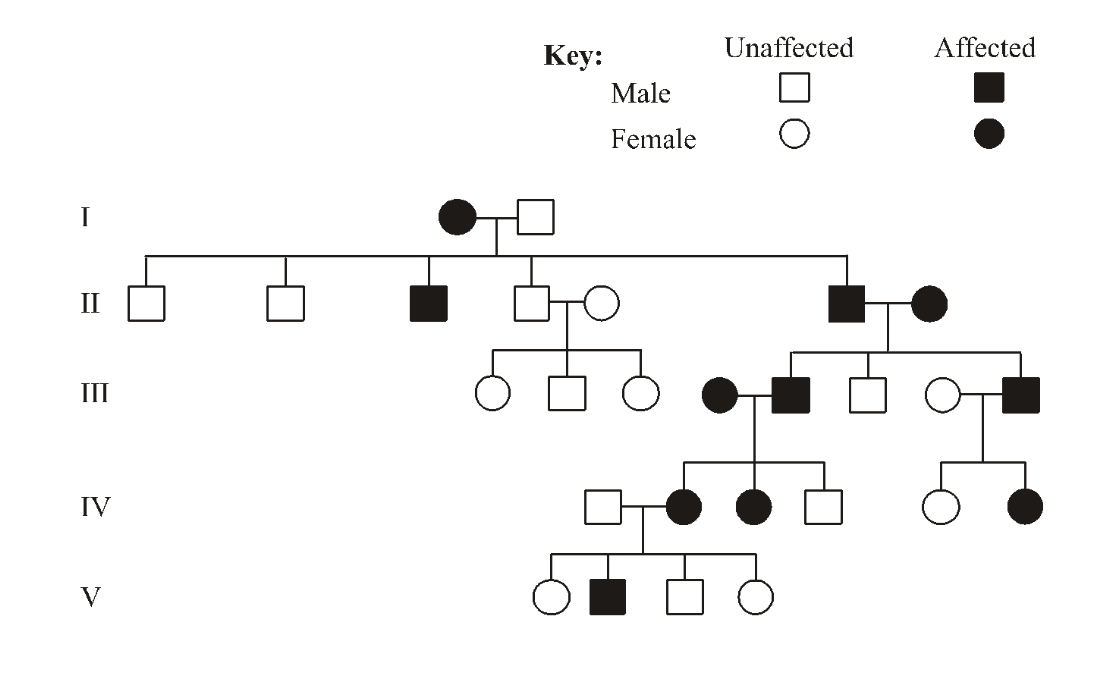
Affected genders are almost same = autosomal
So the disease can be hidden so it’s recessive.
Not recessive because healthy parents have healthy kids
If recessive, the far right of second gen should both parents be healthy.
Ans: Autosomal dominant
What is always a difference between the alleles of a gene?
Their DNA base sequence (they differ by one or more nucleotides)
Ans: Sequence of DNA.
Hypophosphataemia is a disorder involving poor re-absorption of phosphate from glomerular filtrate in humans. It shows a sex-linked dominant pattern of inheritance as illustrated in the following pedigree.
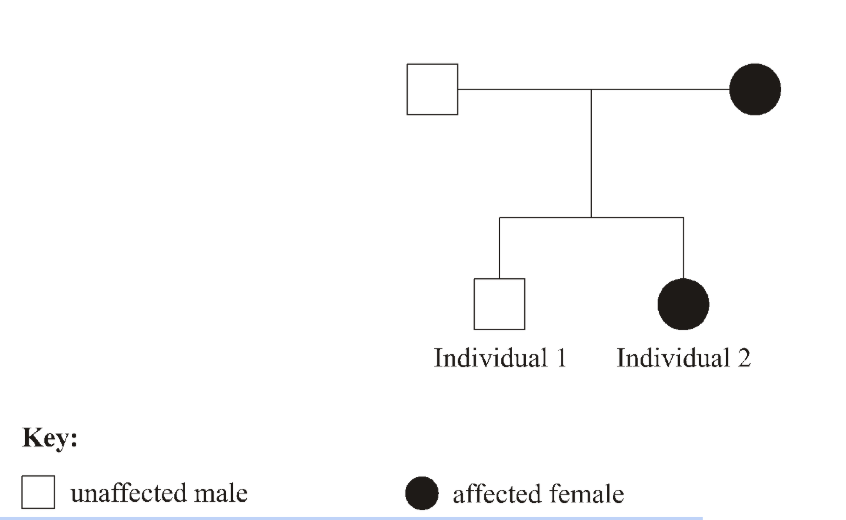
Which row in the table correctly identifies the genotypes of individuals 1 and 2?
(Males don’t get their xs from their fathers)
Mom is heterozygous
Individual 1 is X^hY
Individual 2 is X^HX^h
A gene has three alleles. How many different genotypes can be found for this gene?
A, B, O
AB, AO, BO, BB, AA, OO = 6
A cross is carried out between two heterozygous individuals (AaBb) where the genes A and B are not linked genes. What would be the proportions of genotypic recombinants amongst the offspring of this cross?
Recombinant = different genes than the parents.
¾ of the offspring would be recombinants
What is the genetic cross called between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual who is homozygous recessive for a particular trait?
A test cross
Which human trait shows a pattern of polygenic inheritance?
Skin color ( also height, hair type)
What is a karyotype?
The number and appearance/arrangement of chromosomes of an individual (usually shown as a karyogram).
What is the relationship between Mendel’s law of segregation and meiosis?
Segregation = separation of allele pairs during meiosis (primarily when homologs separate in meiosis I), so each gamete gets one allele.
Which fluid is sampled to try to detect chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus?
Amniotic fluid (via amniocentesis).
How does the X chromosome differ from the Y chromosome in humans?
X is much larger and carries many more genes; Y is smaller and carries few genes (including SRY). This difference underlies X-linked inheritance.
How does recombination normally occur for unlinked genes?
By independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis (not by linkage-based crossing over).
Why is it sometimes difficult to identify how certain characteristics are inherited in humans?
Because a lot of them is polygenic.
Which of the following represents a test cross to determine if phenotype T is homozygous or heterozygous? (Note: allele T is dominant to allele t.)
Cross the individual with unknown genotype to tt (homozygous recessive). Format: T? × tt.
Which of the following blood group phenotypes always has a homozygous genotype?
O HAS to be homozygous
In the pedigree shown below, the female, labelled I-2, is a carrier for colour blindness, however neither male (I-1 or II-1) is colour blind
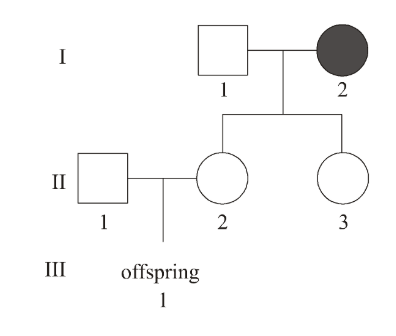
What is the probability that offspring III-1 will be colour blind?
Color blindess = sex linked
Hemophilia = sex linked (for example)
Dad = X^HY
Mom = X^HX^h
Daughter 2 = X^HX^H or X^HX^h
Daughter 3 = X^H…
Male 1 = X^HY
Offspring = X^hY (1/4 chance) if Daughter 2 is X^HX^h = ¼ + ¼ = 1/8
So X^hY = ¼ chance color blind
? 12.5%
Why is amniotic fluid collected during prenatal testing for abnormal chromosomes?
It contains fetal cells and molecules used to karyotype/analyze chromosomes and test for abnormalities.
What procedure is used to determine whether a chromosome is in excess or missing in an organism?
Karyotyping (creating a karyogram to count and inspect chromosomes)
What feature demonstrates codominance in the inheritance of ABO blood groups?
In AB individuals, both A and B antigens are fully expressed on red blood cells.
Alleles S and T are both dominant. In the theoretical cross ttSs × Ttss, which of the following offspring would show recombination?
Recombinant is anything not of the parent genotypes.
Parental gamete combinations are tS and Ts; recombinants unite T with S together or t with s together.
Recombinant offspring genotypes: TtSs and ttss.
What is a test cross?
A cross between an individual with unknown genotype and a homozygous recessive individual to reveal the genotype.
What is the aim of the Human Genome Project?
Scientists that tried to map out al the genes in humans, so they could tell you exactly where your genes are located.
What does a karyotype show?
The number, size, and types of chromosomes (including sex chromosomes) in a cell.
A woman has a heterozygous genotype for blood group B. She is expecting a baby with a man who is homozygous Group A. What are the possible blood groups for their baby?
A or AB (genotypes IAi or IAIB).
Colour blindness in humans is caused by an X chromosome linked recessive allele. In the pedigree chart below which two individuals must, for certain, be carriers of colour blindness?
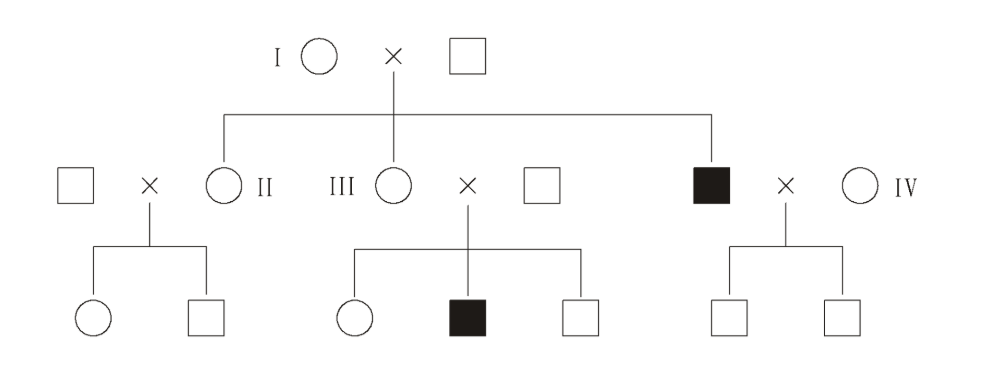
Not male because males can’t be carriers
I & III
A pure breeding tall plant with smooth seeds was crossed with a pure breeding short plant with wrinkled seeds. All the F1 plants were tall with smooth seeds. Two of these F1 plants were crossed and four different phenotypes were obtained in the 320 plants produced.
How many tall plants with wrinkled seeds would you expect to find?
Anytime crossing F1 plants together = Dihybrid 9:3:3:1 → tall wrinkled = 3/16.
Tall and smooth are both dominant.
320×3/16=60320 × 3/16 = 60320×3/16=60. Answer: 60.
What can be concluded on the basis of the following karyotype?
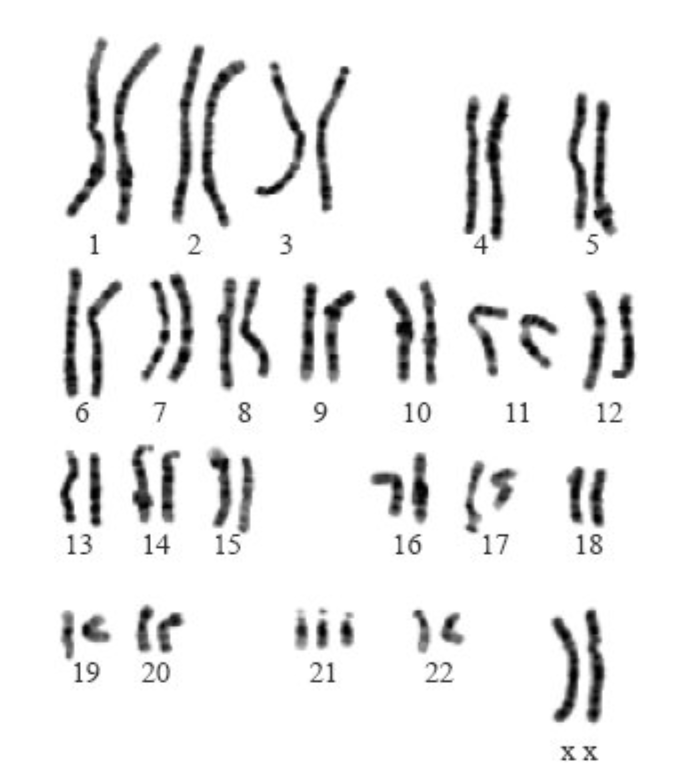
Female because two x chromosomes.
21 has 3 chromosomes
When you have an extra chromosome = down syndrome
Shows a karyotype of a female with down syndrome.
What are homologous chromosomes?
A pair of chromosomes (one from each parent) with the same genes in the same order, which pair during meiosis. One from mom one from dad.
Which feature of a genetic pedigree chart demonstrates that a characteristic is sex linked?
Affects one gender more than the other.
What does the genotype XH Xh indicate?
A female carrier of an X-linked recessive trait (phenotypically normal).
If a purple flowered (Pp) and a white flowered pea plant (pp) are crossed, what will the offspring be?
Offspring: ½ Pp (purple), ½ pp (white) → 1:1
Hemophilia is sex-linked and is caused by a recessive allele. A woman’s father has hemophilia, but her husband does not.
What is the probability of the women and her husband having a child with hemophilia?
No daughters will have it. 50% of sons will have it because they are getting the x from the mom, and the mom has one bad and one good x.
Brachydactyly, abnormal shortness of the fingers, was the first human genetic disorder found to be caused by a dominant allele.
The pedigree below shows a family with affected males ■, unaffected males □, affected females ● and unaffected females ○.
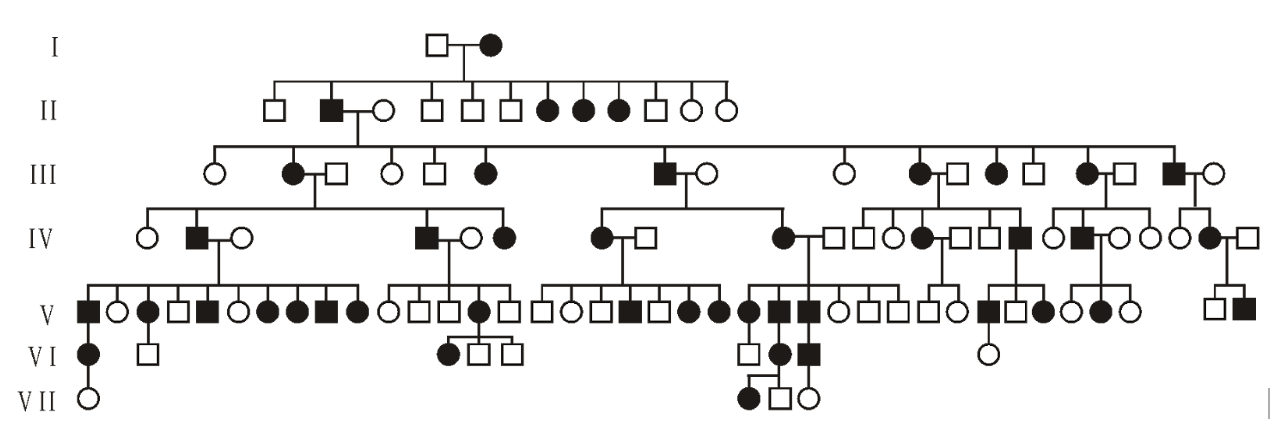
What are the genotypes of the father and mother in the first generation, using the symbol B for the dominant alleles and symbol b for recessive allele?
Dad = bb
Mom is heterozygous = Bb
In Drosophila the allele for normal wings (W) is dominant over the allele for vestigal wings (w) and the allele for normal body (G) is dominant over the allele for ebony body (g). If two Drosophila with the genotypes Wwgg and wwGg are crossed together, what ratio of phenotypes is expected in the offspring?
Test cross result = WwGg, wwGg, Wwgg, wwgg
Combine → 1:1:1:1 across the four phenotypes.
What constitutes a linkage group?
All genes located on the same chromosome (tend to be inherited together unless crossing over occurs).
A gene in cattle controls whether horns develop or not. When cattle without horns are mated together, none of the offspring ever has horns. A male with horns is mated with females without horns. If half of the offspring have horns and half do not, what is the conclusion?
Horns are dominant and the horned male is heterozygous (Hh); hornless is recessive (hh).
Humans are in blood group M, N or MN. The alleles for blood group M (M) and blood group N (N) are co-dominant. Humans are also in blood group A, B, AB or O. The alleles controlling these blood groups are IA, IB and i.
If two parents have the genotypes ii MM and IA i MN what is the ratio of possible phenotypes of their offspring?
OO MM x AO MN = OM x (AM, AN, OM, ON)
= AOMM, AOMN, OOMM, OOMN
= AM, AMN, OM, OMN
= 1:1:1:1
A parent organism of unknown genotype is mated in a test cross. Half of the offspring have the same phenotype as the parent. What can be concluded from this result?
That result means the parent is heterozygous.
If a man has blood group O and a woman has blood group AB, what is the probability that their child will be blood group O?
Cross: ii × IᴬIᴮ → offspring genotypes Iᴬi (type A) or Iᴮi (type B).
No ii offspring possible.
Probability child = group O = 0%.
Define the term sex-linkage.
Sex-linkage means genes located on a sex chromosome, causing traits to be inherited differently in males and females.
The diagram below shows the pedigree of a family with red green colour-blindness, a sex-linked condition.
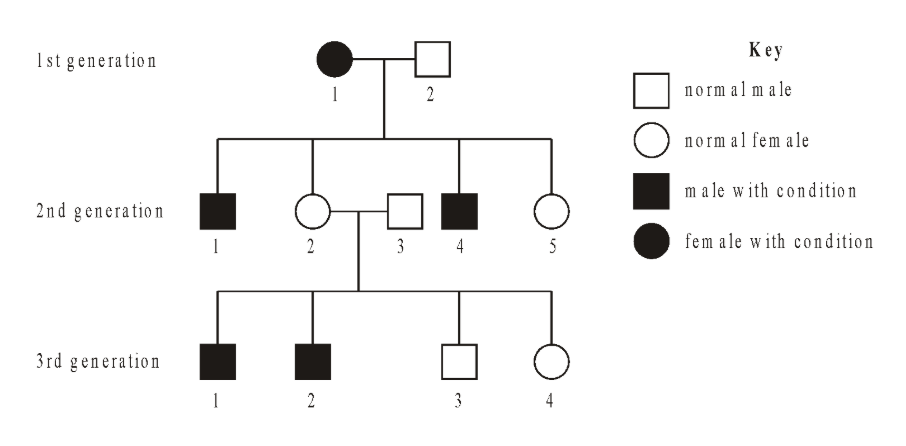
Deduce, with a reason, whether the allele producing the condition is dominant or recessive.
Recessive (analyzed by putting genotypes in place of all of the males and females)

The diagram below shows the pedigree of a family with red green colour-blindness, a sex-linked condition.

Determine all the possible genotypes of the individuals in the pedigree above.
Define the term co-dominant alleles.
Co-dominant alleles are a pair of alleles that are both expressed equally in the phenotype when present together in a heterozygote.
The following diagram represents a two generation pedigree showing the blood groups of the individuals. The female has been married to two different individuals.
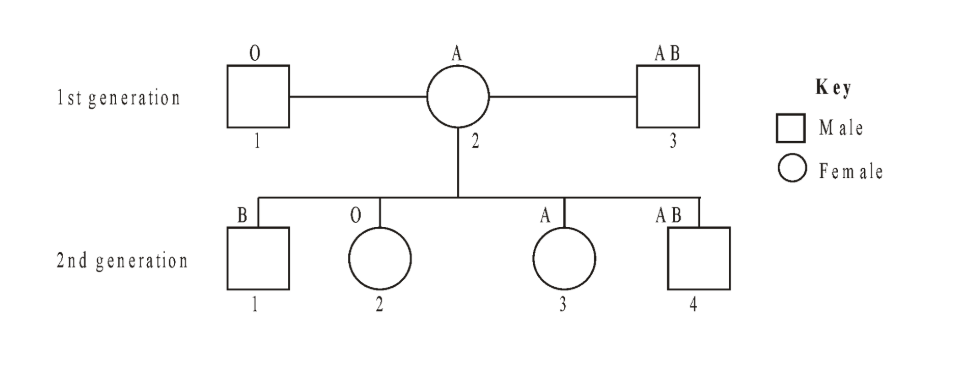
Deduce with a reason the probable father of 2nd generation–1.
the father of 2nd gen 1 is father AB
The following diagram represents a two generation pedigree showing the blood groups of the individuals. The female has been married to two different individuals.

If 2nd generation–3 marries a man with blood group AB, predict the possible genotypes of the children.
AO, BO, or AB
A farmer has rabbits with two particular traits, each controlled by a separate gene. Coat colour brown is completely dominant to white. Tailed is completely dominant to tail-less. A brown, tailed male rabbit that is heterozygous at both loci is crossed with a white, tail-less female rabbit. A large number of offspring is produced with only two phenotypes: brown and tailed, white and tail-less, and the two types are in equal numbers.
Deduce the pattern of inheritance of these traits.
Let brown BBB > white bbb; tailed TTT > tail-less ttt.
Male: BbTtBbTtBbTt in coupling (cis) (BT/bt)(BT/bt)(BT/bt); female: bbttbbttbbtt.
If independent, a testcross gives 1:1:1:1. But only two parental phenotypes in a 1:1 ratio were seen → only BTBTBT and btbtbt gametes formed.
A farmer has rabbits with two particular traits, each controlled by a separate gene. Coat colour brown is completely dominant to white. Tailed is completely dominant to tail-less. A brown, tailed male rabbit that is heterozygous at both loci is crossed with a white, tail-less female rabbit. A large number of offspring is produced with only two phenotypes: brown and tailed, white and tail-less, and the two types are in equal numbers.
State both parents’ genotypes and the gametes that are produced by each during the process of meiosis.
Parents:
Male: BbTt (linked: BT/bt)
Female: bbtt
Gametes:
Male → BT,bt
Female → bt
Offspring: 1:1 → brown-tailed : white-tail-less
A farmer has rabbits with two particular traits, each controlled by a separate gene. Coat colour brown is completely dominant to white. Tailed is completely dominant to tail-less. A brown, tailed male rabbit that is heterozygous at both loci is crossed with a white, tail-less female rabbit. A large number of offspring is produced with only two phenotypes: brown and tailed, white and tail-less, and the two types are in equal numbers.
Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the F2 generation. Show your working.
The F2 generation will have a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1 and a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 for two unlinked genes with complete dominance
A man of blood type AB and a woman of blood type B are expecting a baby. The woman’s mother had blood type O. Deduce the possible phenotypes of the offspring.
State the two classes of compounds that compose chromosomes in animal cells.
The possible phenotypes for the offspring are blood types A, B, and AB. The two classes of compounds that compose chromosomes in animal cells are DNA (a nucleic acid) and proteins.
A man of blood type AB and a woman of blood type B are expecting a baby. The woman’s mother had blood type O. Deduce the possible phenotypes of the offspring.
Outline how meiotic division results in almost an infinite genetic variation in the gametes produced.
The possible blood type phenotypes for the offspring are A, B, and AB. Meiotic division produces almost infinite genetic variation through independent assortment, crossing over, and random fertilization
A man of blood type AB and a woman of blood type B are expecting a baby. The woman’s mother had blood type O. Deduce the possible phenotypes of the offspring.
In a species of plant, tall is dominant to short and the production of round seeds is dominant to that of wrinkled seeds. The alleles are unlinked. A plant heterozygous for both characteristics is crossed with a plant homozygous for tall with wrinkled seeds. Determine the phenotypes and genotypes of the offspring of this cross.
Human cross (AB × B with O parent): A : B : AB = 1 : 2 : 1
Plant cross (TtRr × TTrr): Tall Round : Tall Wrinkled = 1 : 1
A man of blood type AB and a woman of blood type B are expecting a baby. The woman’s mother had blood type O. Deduce the possible phenotypes of the offspring.
State how chromosome number can increase in human beings.
ERQ
In Zea mays, the allele for coloured seed (C) is dominant over the allele for colourless seed (c). The allele for starchy endosperm (W) is dominant over the allele for waxy endosperm (w). Pure breeding plants with coloured seeds and starchy endosperm were crossed with pure breeding plants with colourless seeds and waxy endosperm.
State the genotype and the phenotype of the F1 individuals produced as a result of this cross.
CCWW x ccww = CcWw heterozygus for both traits and the phenotype are going to be all colored and starchy
In Zea mays, the allele for coloured seed (C) is dominant over the allele for colourless seed (c). The allele for starchy endosperm (W) is dominant over the allele for waxy endosperm (w). Pure breeding plants with coloured seeds and starchy endosperm were crossed with pure breeding plants with colourless seeds and waxy endosperm.
The F1 plants were crossed with plants that had the genotype c c w w. Calculate the expected ratio of phenotypes in the F2 generation, assuming that there is independent assortment. Use the space below to show your working.
ccww x CcWw = CcWc, Ccww, ccWww, ccww = 1:1:1:1
In Zea mays, the allele for coloured seed (C) is dominant over the allele for colourless seed (c). The allele for starchy endosperm (W) is dominant over the allele for waxy endosperm (w). Pure breeding plants with coloured seeds and starchy endosperm were crossed with pure breeding plants with colourless seeds and waxy endosperm.
The observed percentages of phenotypes in the F2 generation are shown below.
coloured starchy 37% colourless starchy 14%
coloured waxy 16% colourless waxy 33%
The observed results differ significantly from the results expected on the basis of independent assortment.
State the genotype and the phenotype of the F1 individuals produced as a result of this cross.
Chi-square test
In Zea mays, the allele for coloured seed (C) is dominant over the allele for colourless seed (c). The allele for starchy endosperm (W) is dominant over the allele for waxy endosperm (w). Pure breeding plants with coloured seeds and starchy endosperm were crossed with pure breeding plants with colourless seeds and waxy endosperm.
The observed percentages of phenotypes in the F2 generation are shown below.
coloured starchy 37% colourless starchy 14%
coloured waxy 16% colourless waxy 33%
The observed results differ significantly from the results expected on the basis of independent assortment.
The F1 plants were crossed with plants that had the genotype c c w w. Calculate the expected ratio of phenotypes in the F2 generation, assuming that there is independent assortment. Use the space below to show your working.
Answer for question 6d = chances are they are linked.
A male and female with normal colour vision each have a father who is colour blind. They are planning to have children. Predict, showing your working, the possible phenotypes and genotypes of male and female children.
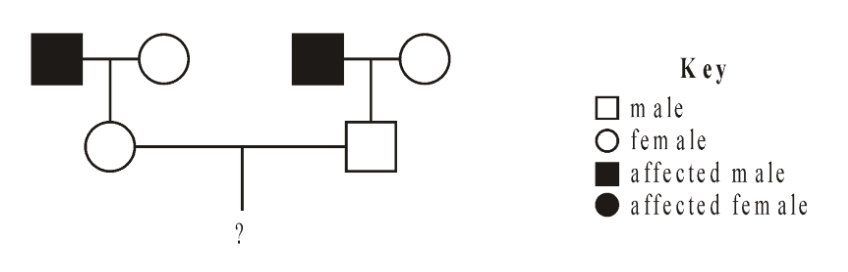
ERQ
Explain the relationship between Mendel’s law of segregation and meiosis.
ERQ
Outline one example of inheritance involving multiple alleles.
Blood type. Three alleles A, B, and O. Possible combinations are AO, BO, OO, AA, BB, and AB.