Anatomy - other kinds of pressure
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
urine, kidney, nephron, you know the deal! (mod. 17)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is capillary exchange influenced by
Osmotic/hydrostatic pressure
Hydrostatic pressure
pressure of fluid against container
Osmotic pressure
forced needed prevent water movement
High osmolarity =
high osmotic pressure
nephron part that helps w/water/glucose/sodium reabsorption
Proximal tubule
What kind of pressure should be LOWER on capsule side
osmotic
What kind of pressure should be GREATER on capsule side
Hydrostatic
Water recovery happens in
Collecting ducts
BP decrease. Blood vessels in kidney ___ for steady filtration
RELAX
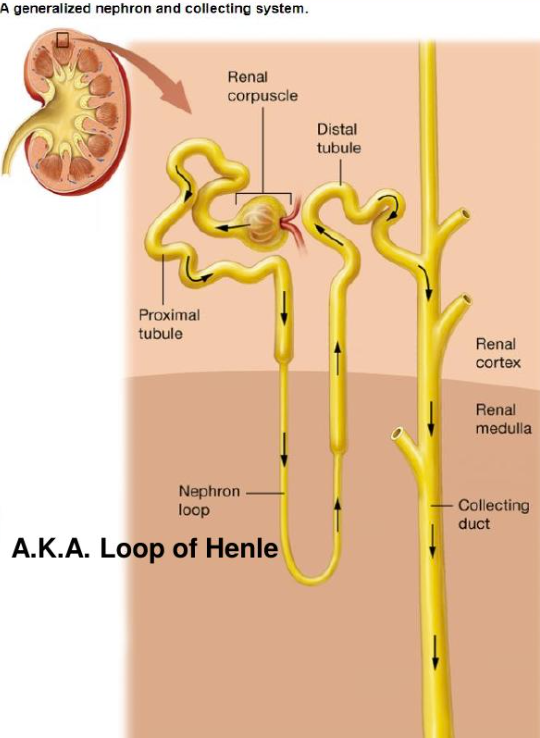
look over
looked.
when is ONLY CASE red blood cells present in filtrate (urine)
Kidney damage present
What helps w/protein metabolism
Urea/ammonium
Nucleic acid metabolism?
Uric acid
Kidneys filter entire blood plasma (___ L) through capillaries to ____ 60 times a day! OVER _____
3 Liters, proximal tubule, 180 LITERS
WHAT ELSE does proximal tubule do
remove nitrogenous waste
JGA (juxtaglomerular) influences arteriole diameter based on ____
filtrate concentration
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System
helps with BP and GFR
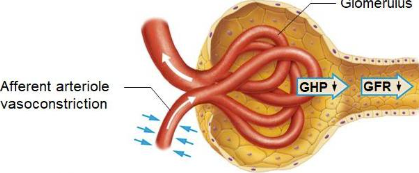
Afferent arteriole vasoconstriction
GHP decreases, GFR decreases
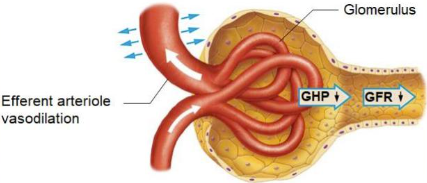
Efferent arteriole vasodilation
GHP DECREASES, GFR DECREASES
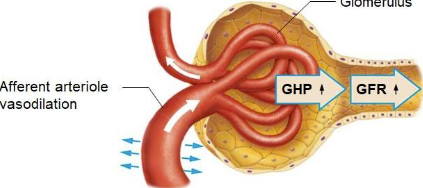
Afferent arteriole vasodilation
GHP INCREASES, GFR INCREASES
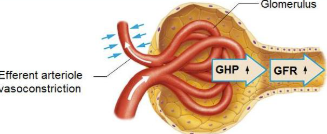
Efferent arteriole vasoconstriction
GHP increases, GFR increases
What blood vessel connects glomerulus to peritubular capillaries (aka capsule)
efferent arteriole
What vessel associated with cortical radiate artery (Hint: coming INTO glomerulus)
Afferent arteriole
WHERE do hydrogen ions leave (hint: nephron)
Distal convoluted tubule/collecting duct
What do JG cells do
Change vessel diameter AND renin release for BP
What does renin do
INCREASE filtration rate through RAAS