10. Dementia
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What happens at the presynaptic neuron when an AP reaches it?
Activation of voltage-gated Ca channels
Ca influx
Ca mediated vesicle docking and NT release
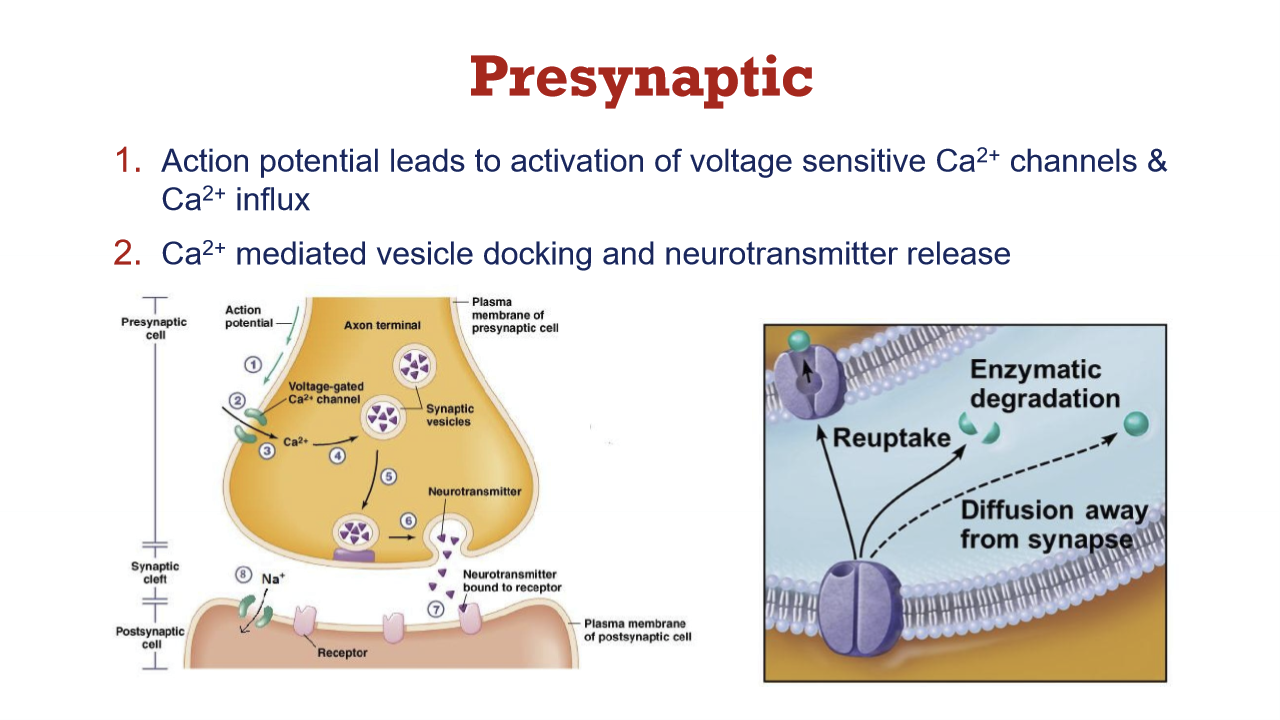
What is glutamate responsible for?
Learning, working memory, cognitive processing
What is GABA responsible for?
Learning, working memory, anxiety
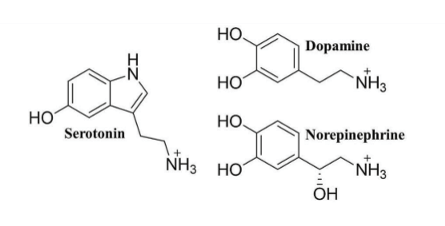
What is Dopamine responsible for?
Motor control, cognition, judgement, impulsivity, attention/ Alertness: working mem, motivation, clarity
What is serotonin used for?
Moodiness, anxiety/ Satisfaction: learning memory, pleasure/pain, relaxation
What is Norepinephrine used for?
Moodiness, anxiety/ concentration: execution, perseverance, recall memory.
What is Acetylcholine used for?
Cognitive functions
What is glycine used for?
Cognition, mood
What NT are considered Monoamine NT?
Serotonin
Dopamine
Norepinephrine
What can low dopamine levels result in?
Parkinson’s disease, decreased ability to move properly; resulting in stiffness, tremors or shaking
How can low dopamine or problems using dopamine affect the thinking and feeling regions of the brain?
May contribute to schizophrenia or ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder)
What NT is released during stress?
Norepinephrine
What neurotransmitter is involved in emotional arousal, attention, stress, anxiety, and mood disorders?
Norepinephrine
What role does norepinephrine play in drug dependence?
It contributes to anxiety and stress responses associated with drug dependence.
Which disorders are associated with norepinephrine imbalance?
Depression and ADHD
What functions doe4s serotonin control?
Mood, appetite, and sleep
What levels of serotonin are correlated with depression?
Lower levels of serotonin is correlated with depression
How do most depression medications work?
They aim to block reuptake of serotonin.
What type of neurotransmitter is glutamate?
Excitatory neurotransmitter
What does an excitatory neurotransmitter do?
Increases the chance that a neuron will fire
How abundant is glutamate in the brain?
It is among the most abundant neurotransmitters
What role does glutamate play in brain function?
Enhances electrical flow required for normal function. It is important for early brain development. Also involved in learning and memory.
What mental disorders are linked to low glutamate levels?
Autism
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Schizophrenia
Alzheimer's disease
Depression
What is the most significant inhibitory NT?
GABA
What does GABA do?
It opens Cl ion channels to hyperpolarize the synapse.
Why would drugs target GABA?
To treat epilepsy.
What drugs affect GABA?
Barbiturates
Tranquilizers (Valium, Xanax)
Alcohol
What is Glycine involved in?
Immune response
Mood, cognition, and pain perception
What does glycine do?
It activates Cl channesl and produces hyperpolarization.
What does ACh bind to?
Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.
What is ACh used in?
Sensory processing, attention, and memory.
What is Low ACh associated with?
Dementia/Alzheimer’s
What is dementai?
An umbrella term that describes a set of symptoms causing a person to have changes in brain function that interfere with ability to function and do everyday activities.
What are the symptoms of dementia?
Cognition: memory, language, orientation, judgment, and planning
Behavior: depression, anxiety, agitation, hallucinations, paranoia, and aggressiveness
Other: Weight loss, incontinence, gait disturbances, sleep disturbances
What are the goals of treatment in dementia?
Improve or preserve activities of daily living (ADL) function
Reduce caregiver durgen
Enhance quality of life
What are the treatment strategies of dementia?
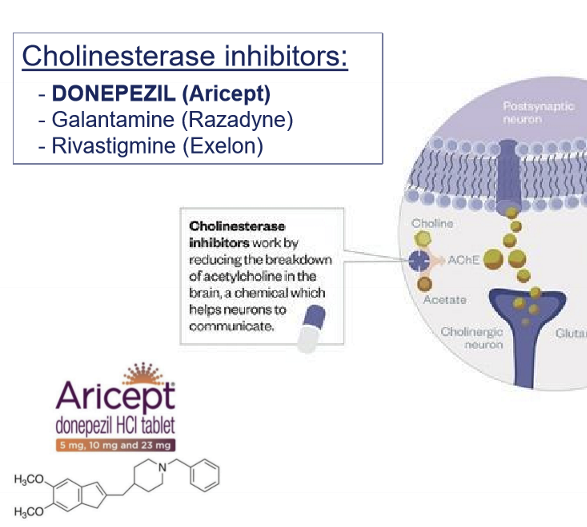
Increase ACh signaling via AChEsterase inhibitors
Decease glutamate signaling via inhibiting NMDA receptors
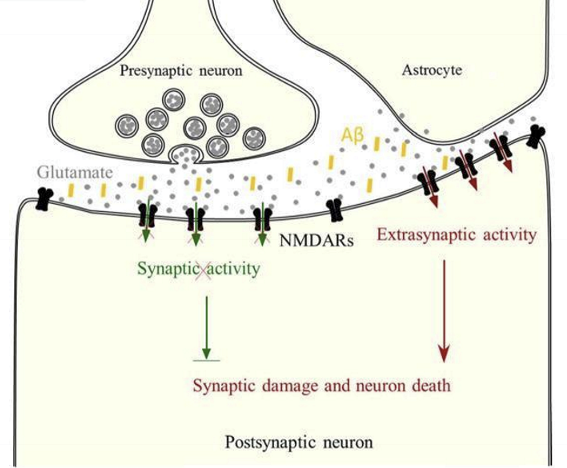
How does glutamate contribute to dementia?
Excess glutamate causes overstimulation of NMDA receptors, reducing synaptic NMDA receptor activity and activating extrasynaptic NMDA receptors, which promotes neuronal apoptosis.
What is Donepezil (Aricept)?
A cholinesterase inhibitor used in dementia treatment.
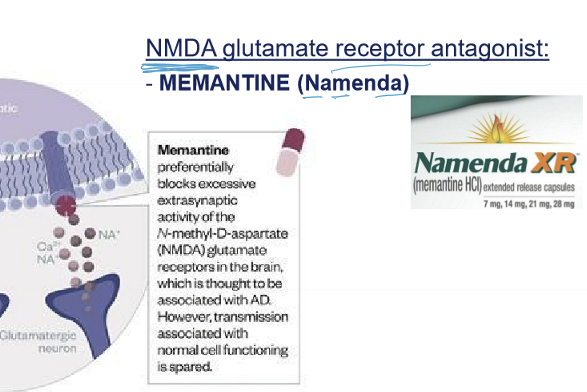
What is Memantine (Namenda)?
A NMDA glutamate receptor agonist used in dementia treatment.
What other agents are used to treat associated symptoms of dementia?
Depression via SSRIs
Psychosis via anti-psychotics
Sleep disturbances via benzodiazepines etc.