Household Wiring
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Thermal and Shock hazard
Name the two hazards presented by the electricity.
Thermal hazard
Hazard in which an excessive electric current causes undesired thermal effects. (Like starting a fire in the wall of a house)
Shock hazard
Hazard that occurs when an electric current passes through a person
Short-circuit
A low resistance path between terminals of a voltage source.
Overloaded
Term used to refer to a condition where the current exceeds the rated maximum current.
Yes, it is true
Is it true that the wires overheat if either the current or the resistance of the wires is too large?
Electric shock
The physiological reaction or injury caused by an external electric current passing through the body.
300 mA
The magnitude of the current which may cause death when it passes through the heart.
Causes the heart and diaphragm of the lung to contract for the duration of the shock. Resulting in both the heart and respiration to stop.
Ventricular fibrillation
A massively irregular and often fatal, beating of the heart. This is the reason why most electrical shock fatalities occur.
Defibrillator
Used to save heart attack victims whose heart is in fibrillation, by giving them an electric shock through the device.
Voluntary muscle control
The ability of consciously controlling the skeletal muscles. Its loss causes the victim to not be able to let go of the source of current.
Amount of current, Path taken by the current, Duration of the shock, and Frequency of the current.
Four major factors upon which the severity of the effects of the electrical shock depend.
Water content
Feature of the human bodies that makes it a good electric conductor
Ground
Term that refers to the large sink or source of electrons.
When the body is in contact with a voltage source and ground.
A dangerous condition of the shock hazard that occurs
lowest resistance
When there is a direct path to the ground, a large amount of currents will pass through the parts of body with the _______________ and a direct path to ground.
Wearing insulated shoes
A safety precaution used by many professionals in the dangerous condition of the shock hazard
large resistance
Insulated shoes prohibit a pathway to ground for electrons through the feet by providing a large resistance.
Working with one hand.
A common safety precaution to reduce the possibility of providing a current path through the heart.
1 mA
Magnitude of current that is the threshold of sensation.
5 mA
Magnitude of the current after which it becomes harmful for the human body
5 to 30 mA and above
Range of the current magnitude that can stimulate the sustained muscular contractions, much as regular nerve impulses do.
Current
The major factor that determines the shock severity
I = V/R
Formula that states that the severity of the shock depends on the combination of voltage and resistance
200 kΩ
Approximate amount of resistance that a person with a dry skin has.
10.0 kΩ
The approximate amount of resistance that a person who is soaking wet would have
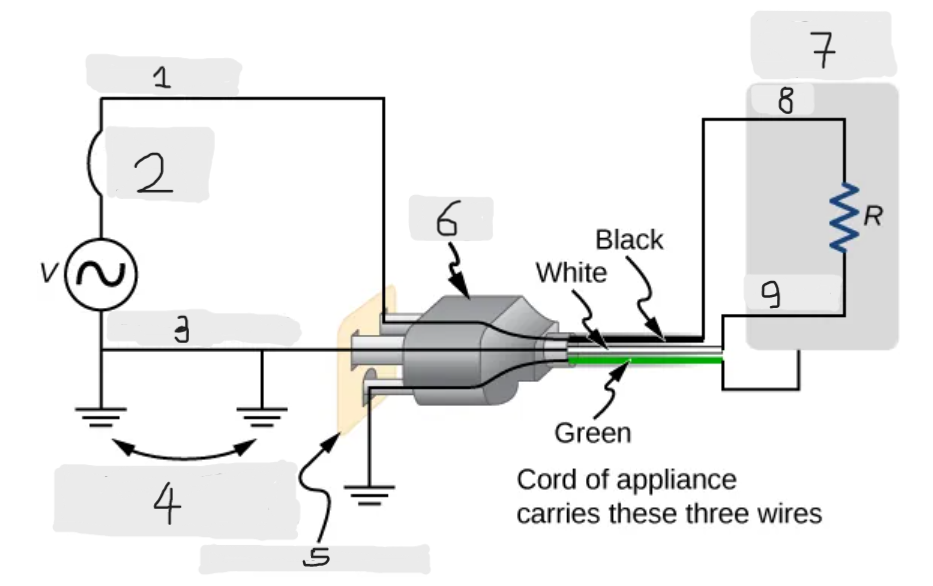
Three wire system
The modern household and industrial wiring, which has the safety feature of preventing the person from touching exposed wires and coming into electrical contact with the circuit, preventing shocks.
Black(hot)
(1)
Circuit breaker
(2)
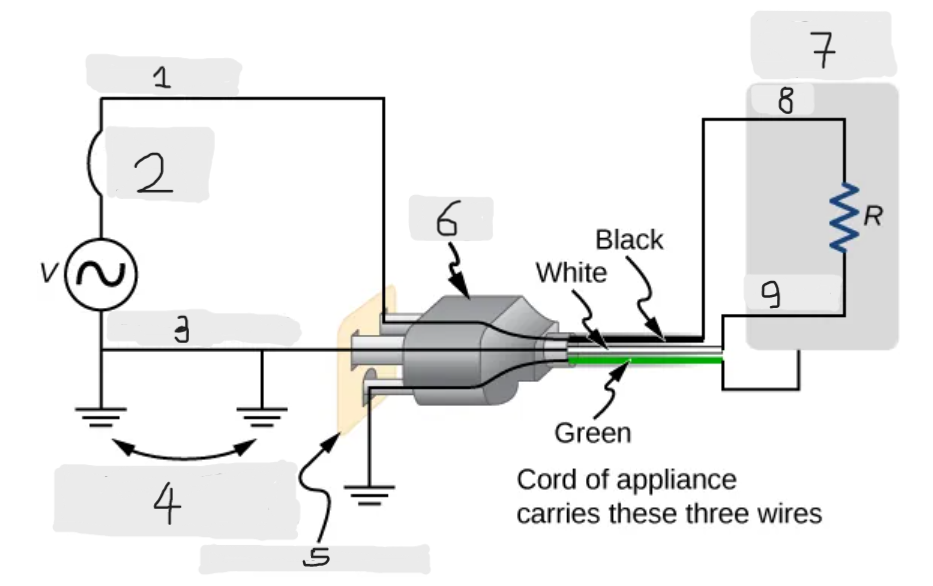
White(neutral)
(3)
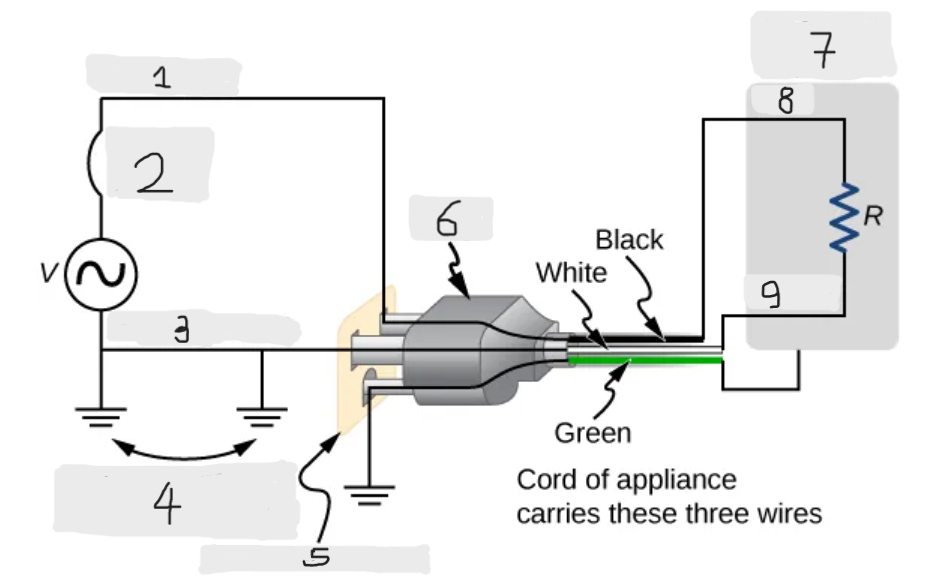
Alternate return path through earth
(4)
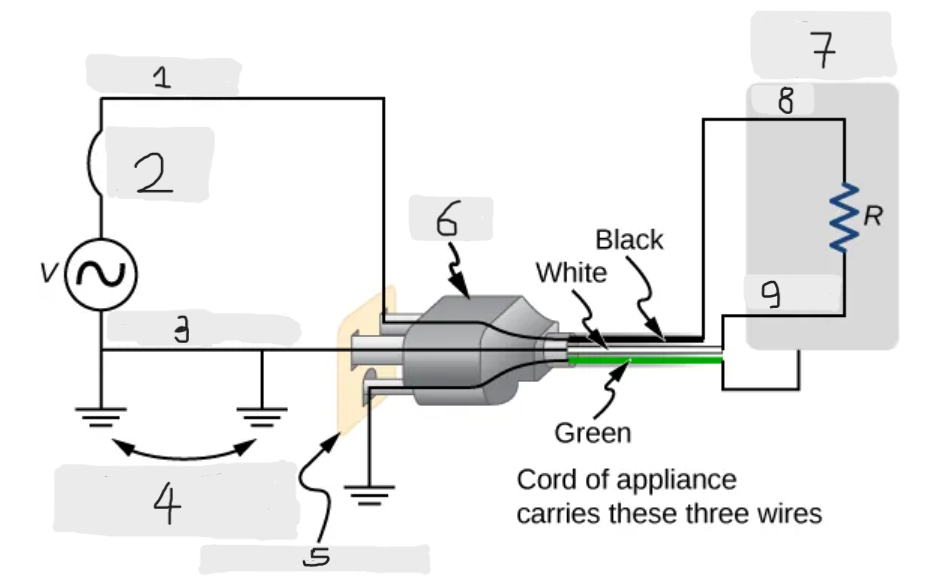
Three-hole outlet
(5)
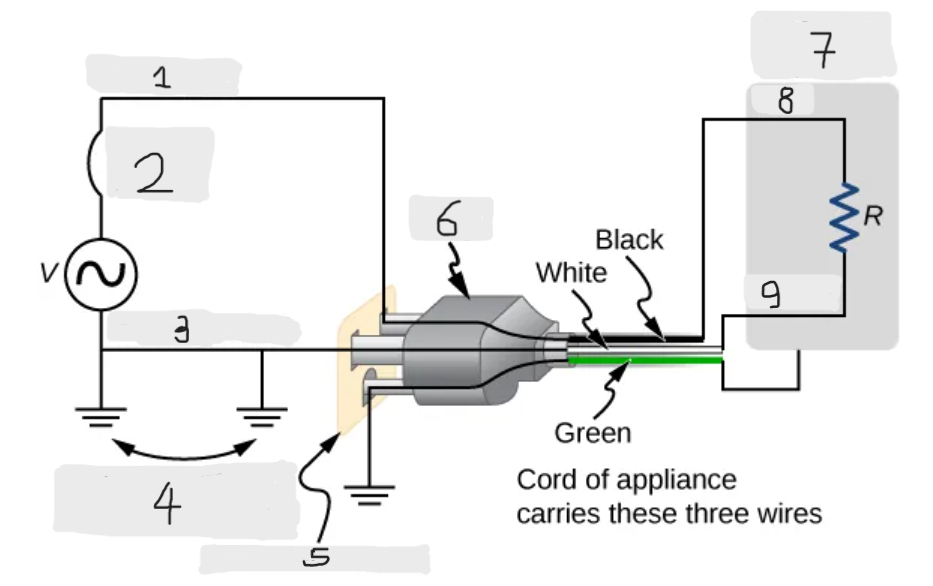
Plug
(6)
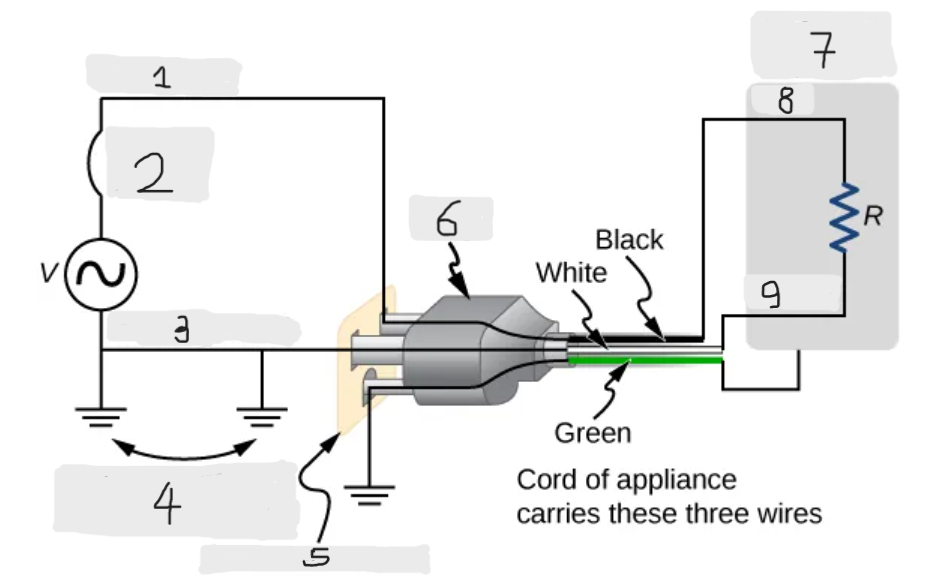
Case of appliance
(7)
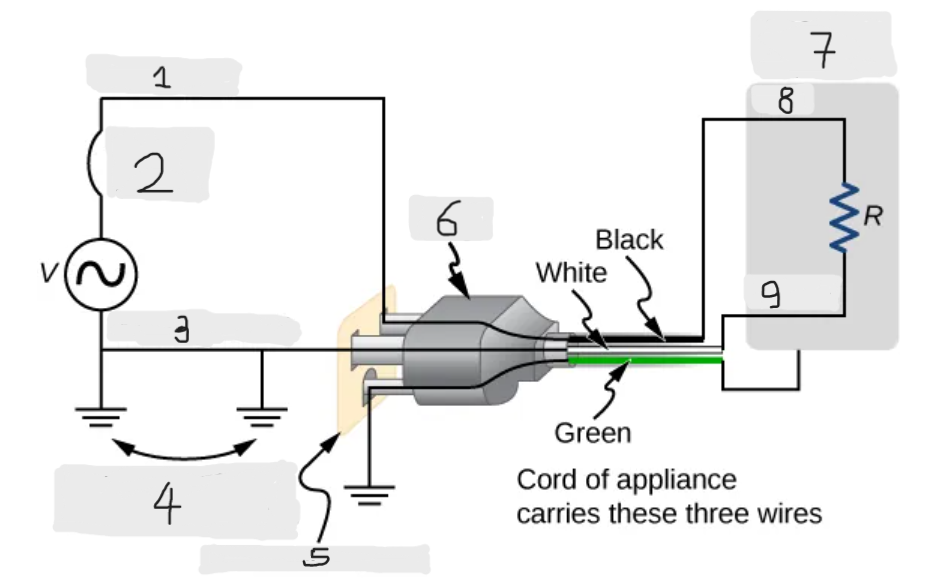
Hot
(8)
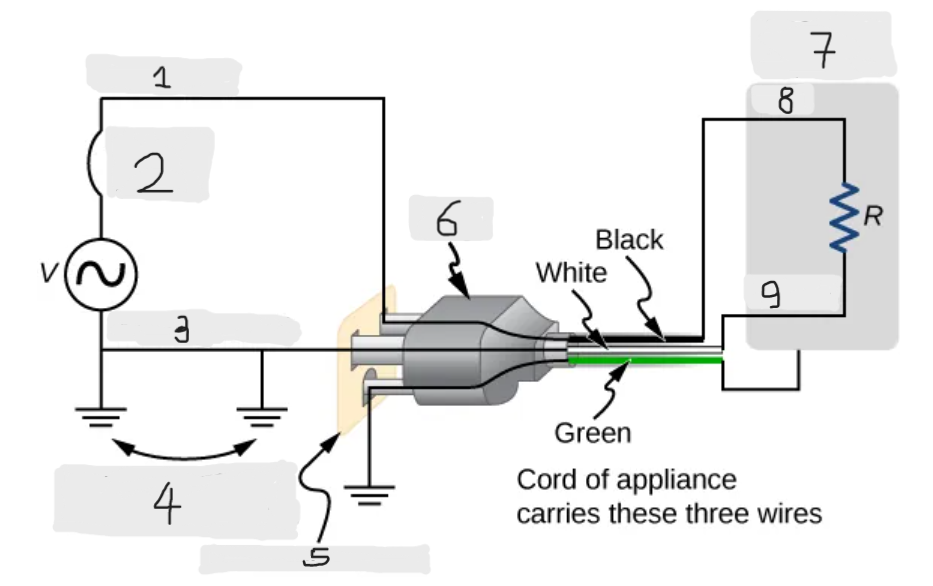
Neutral
(9)
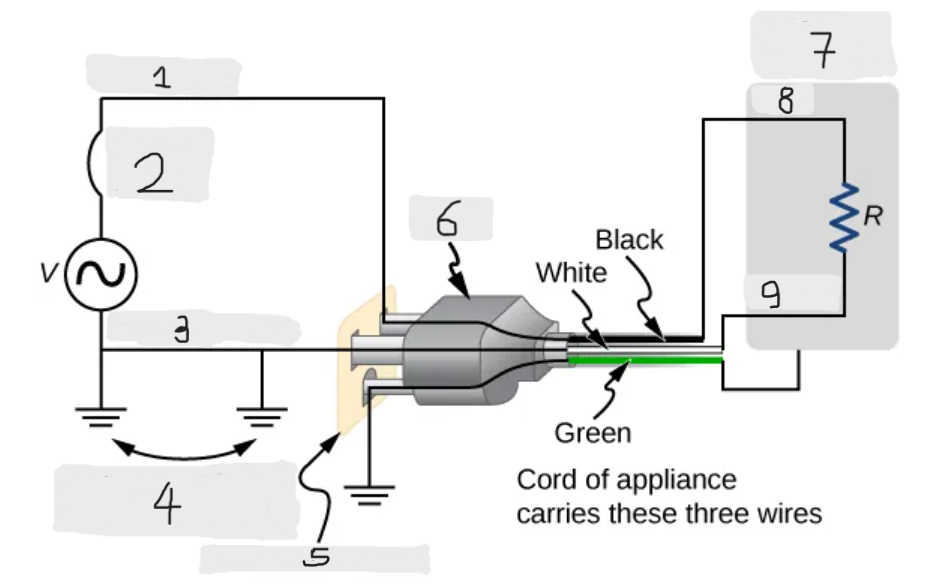
Neutral wire
The wire in the three wire system that acts as the return path for the current to follow to complete the circuit.
generating plant, user’s location
The ground connection closest to the power source could be at the ________________, whereas the other is at the _______________
Live/Hot wire
The wire in the three-wire system that supplies the current to operate the appliance.
Worn insulation
Allows the Live/Hot wire to come into direct contact with the metal case of the appliance
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter
A safety device found in kitchen and bathroom wiring that works based on the Electromagnetic induction
Compares the currents in the Live/Hot and the neutral wires
less
Live/Hot wire and neutral currents aren’t equal, it’s almost always because the current in the neutral is ____ than in the Live/Hot wire.
Leakage current
Some of the current, which is returning to the voltage source by path other than through the neutral wire.
The path which it travels is assumed that it is hazardous.
trip, leakage
Even if the leakage current goes safely to ground through an intact ground wire, the GFCI will ____ forcing repair of the _______.