physics p6 molecules and matter
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:03 PM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
mass
amount of matter in something, measured in kg
2
New cards
volume
amount of space something takes up. measured in m squared
\
volume of an irregular object can be found using a displacement can
\
volume of an irregular object can be found using a displacement can
3
New cards
density
mass per unit volume, measured in kg/m squared
4
New cards
floating
an object with a lower density than the liquid will float
5
New cards
sinking
an object with a higher density than the liquid will sink
6
New cards
evaporation
happens at any temp
7
New cards
sublimation
solid turns straight into gas
8
New cards
solid
particles held together in fixed positions by strong forces, least energetic
9
New cards
liquid
particles move at random but are in contact with each other. medium energy
10
New cards
gas
particles move randomly and are far apart from each other. weak forces of attraction, most energetic
11
New cards
melting point
temperature where solid turns to liquid, same as freexing point
12
New cards
boiling point
temperature where liquid turns to gas, same as condensation point
13
New cards
latent heat
energy transferred when a substance changes state but temperature doesnt change
14
New cards
specific latent heat of fusion
energy needed to melt 1kg of solid into liquid
15
New cards
specific latent heat of vaporisation
energy needed to boil 1kg of liquid into gas
16
New cards
At state changes
temperature and kinetic energy of particles stays constant, internal energy increases due to an increase of potential energy as particles move further apart
17
New cards
Heating and cooling curves
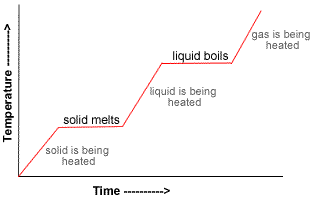
18
New cards
gas pressure
caused by particles hitting surfaces. increases when temperature increases