Intro Plate Tectonics Ruggiero 24-25
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Alfred Wegener
A German meteorologist who proposed a hypothesis in 1915 that stated that all the continents were once joined together in a single land mass in the past and they have moved apart since.
Vine and Matthews
two graduate students who used the pattern of geomagnetic reversals from the ocean floor support ideas of seafloor spreading.
Harry Hess
Princton geologist who proposed Sea Floor Spreading in 1962 as the mechanism for Pangea's break-up
Tharp and Heezen
Creators of the first world ocean floor map & discovered the central rift valley (runs through the Mid-Atlantic Ridge)
Lithosphere
A mechanical layer of earth which is rigid and brittle and breaks into segments. It includes the crust and very top of mantle.
Asthenosphere
A mechanical layer of earth located within the mantle below the lithosphere, that has the ability to flow, so is called a plastic-solid.
continental crust
part of outermost compositional layer of earth. Usually made of granite (mostly quartz and feldspar minerals)
oceanic crust
part of outermost compositional layer of earth, usually made of basalt (magnesium and iron-rich igneous rock).
Continental Drift Hypothesis
hypothesis states that at one point in time, all the continents on Earth were together in a large land mass called Pangaea and have since moved apart.
Plate Tectonic Theory
States that the earth's surface is broken into rigid tectonic plates that are in constant motion driven by convection
Volcanic Island Arc
chain of volcanic islands that form on oceanic crust, caused by partial melting of mantle due to the subduction of an oceanic plate beneath another oceanic one.
Continental Volcanic Arc
chain of volcanic mountains that form on continental crust, caused by partial melting of mantle due to the subduction of an oceanic plate beneath a continental one.
convection current
A rising and sinking loop of slow flowing mantle below and lithosphere above due to differences in density, temperature and pressure
Convergent Boundary
When plates move toward each other: sub-types are O-C subduction, O-O subduction, or C-C collision.
Transform Boundary
two plates slide past each other
Divergent Boundary
Plates that are moving away from each other.
Folded Mountain Ranges
Mountains formed when two plates carrying continental crust collide, deforming the rocks and earth with great force.
hot spots
plumes of very warm mantle material that rise up in essentially fixed locations not necissarily caused or associated with plate boundaries
Paleomagnetism
The alignment of magnetic minerals in rock that form a historical record of the location and polarity of Earth's magnetic poles
Pangea
The name of the most recent supercontinent. Means "all land". Existed about 250-200 million years ago.
rift valley
A shallow valley formed through extensional forces as magma swells the lithosphere and lithosphere pulls apart.
Seafloor Spreading Hypothesis
The hypothesis proposed by Harry Hess in 1962. Convection currents in the asthenosphere allows lithosphere on top to separate and new sea floor to form, in other places the lithosphere crashes together and subduction takes lithosphere back into mantle. Continents ride along as part of the lithosphere as it separates.
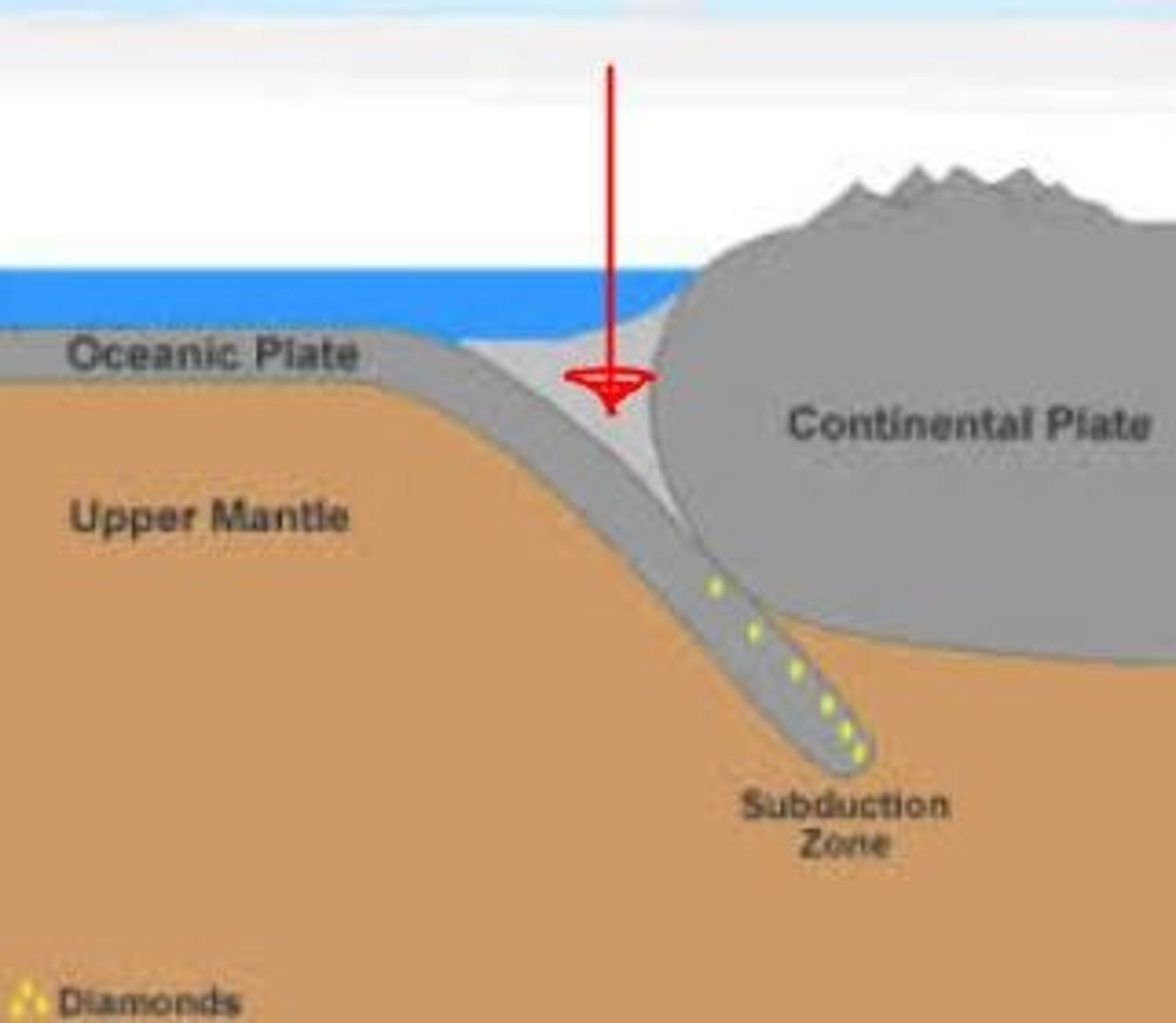
subduction
Denser oceanic crust sinks down into the mantle beneath the less dense plate
Tectonic Plate
A block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle
Trench
Deep, steep valley on the ocean floor created by bending down top plate during subduction of two converging plates.
lower mantle
The dense, slow flowing lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core
outer core
the hot, dense, liquid layer of the Earth's core that lies beneath the mantle and surrounds the inner core
inner core
A hot, dense sphere of solid iron and nickel at the center of Earth
continental-continental convergent boundary
when two continental plates collide, with no subduction
oceanic-continental convergent boundary
When a more dense oceanic plate subducts under a less dense continental plate. Creates trenches and continental volcanic arcs.
oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary
When 2 oceanic plates converge against one another, causing the colder, denser, older plate to subduct. Creates trenches and volcanic island arcs.
Paleoclimate
climate in the geologic past