Ch. 3; Energy
Index
- 3.1 - Energy Sources
- 3.2 - Heating
- 3.4 - Efficiency
3.1; Energy Sources
Learning objectives
- [ ] You can explain what an energy source is
- [ ] You can name the features of the new energy system (energy transition)
- [ ] You can name advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
- [ ] You know the different forms of energy
What is an energy source?
Anything that can provide a usable form of energy is called an energy source. Sometimes it is used directly, such as when you let the sun heat your house, but usually a device is used to convert the energy form of the source into another form of energy, for example;
- A solar cell converts radiant sunlight into electrical energy
- A wind turbine converts kinetic energy of (flowing) air into electrical energy
- A stove converts chemical energy of natural gas into heat
Energy sources
In the Netherlands there are six energy sources used, these are listed below.
Fossil fuels (91.4%)
Fossil fuels such as natural gasses and coal contain chemical energy. Natural gas is used to heat buildings and in power stations. Some power stations also use coal
Biomass (4.5%)
Biomass is material that is originated from plants and animals, this can be prunings (branches etc.) and waste wood, as well as crops and plant remains. Biomass provides chemical energy, some types can be burned directly. Plant remains can be fermented in a biogas plant, which produces biogas.
Wind (1.7%)
Wind, as an energy source, is becoming more and more important. The blades of a windmill or turbine drive a generator that’s built into it. This converts kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy.
Nuclear Fission (1.4%)
Some atomic nuclei, can be split. Splitting an atomic nucleus releases a lot of energy in the form of heat. In a nuclear power station, this heat is used to create steam. The steam is forced past the blades of a turbine that connects to a generator. The generator converts that kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Solar (0.6%)
The sun is a source of radiant energy. A solar collector converts the radiant energy into heat that’s used to heat water, and solar cells convert irradiation into electrical energy.
Geothermal heat (0.25)
The deeper you go in the ground, the higher the temperature. It’s possible to bring heat from the deep layers of the ground up to the surface. Two wells are used to bring this heat up. The first well is for pumping hot groundwater up, which is then passed trough a heat exchanger where it transfers parts of its heat to cold water. The second well is used for pumping this back to the ground
The energy transition
The ideal energy source is inexhaustible, always available, environmentally friendly and cheap. These don’t exist. Natural gas used to be seen as the ideal energy source, but it wasn’t until later that people realized carbon dioxide is harmful to the climate. The dutch energy want to ‘get rid of gas’ and switch to other ‘climate neutral’ energy sources. This is called the Energy transition. A new energy system needs to have the following four characteristics;
Sustainable energy sources
fossil fuels must have almost entirely be replaced by renewable energy sources, like wind.
Efficient energy management
use of energy must be limited as much as possible.
Large scale energy storage
there are possibilities for storing large quantities of energy efficiently
Local production of energy
energy supplies have to be arranged more locally.
3.2; Heating
Learning objectives
- [ ] You can show energy conversions in an energy flow diagram
- [ ] You know the law of conservation of energy (energy never disappears, it can just be converted into different forms of energy)
- [ ] You can explain the difference between heat and temperature
- [ ] You can explain what “specific heat” means (you know the definition)
- [ ] You can calculate the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance, using Q = m・c・ΔT
- [ ] You know the specific heat of water is 4.2 J/(g·℃)
Heat sources
Around your home, you can find various heat sources. A central heating boiler or heat pump supplies the heat that heats the house up, other forms of heat sources are a cooker, oven, an electric kettle etc.
An electric boiler has a heating element, an electric current passes through the heating element and that makes it warm up. This turns electrical energy into heat. Such an energy conversion can be represented in an energy flow diagram. The arrow on the left represents the total energy being used, and the arrow on the right represents the energy that the heat source releases (provides). 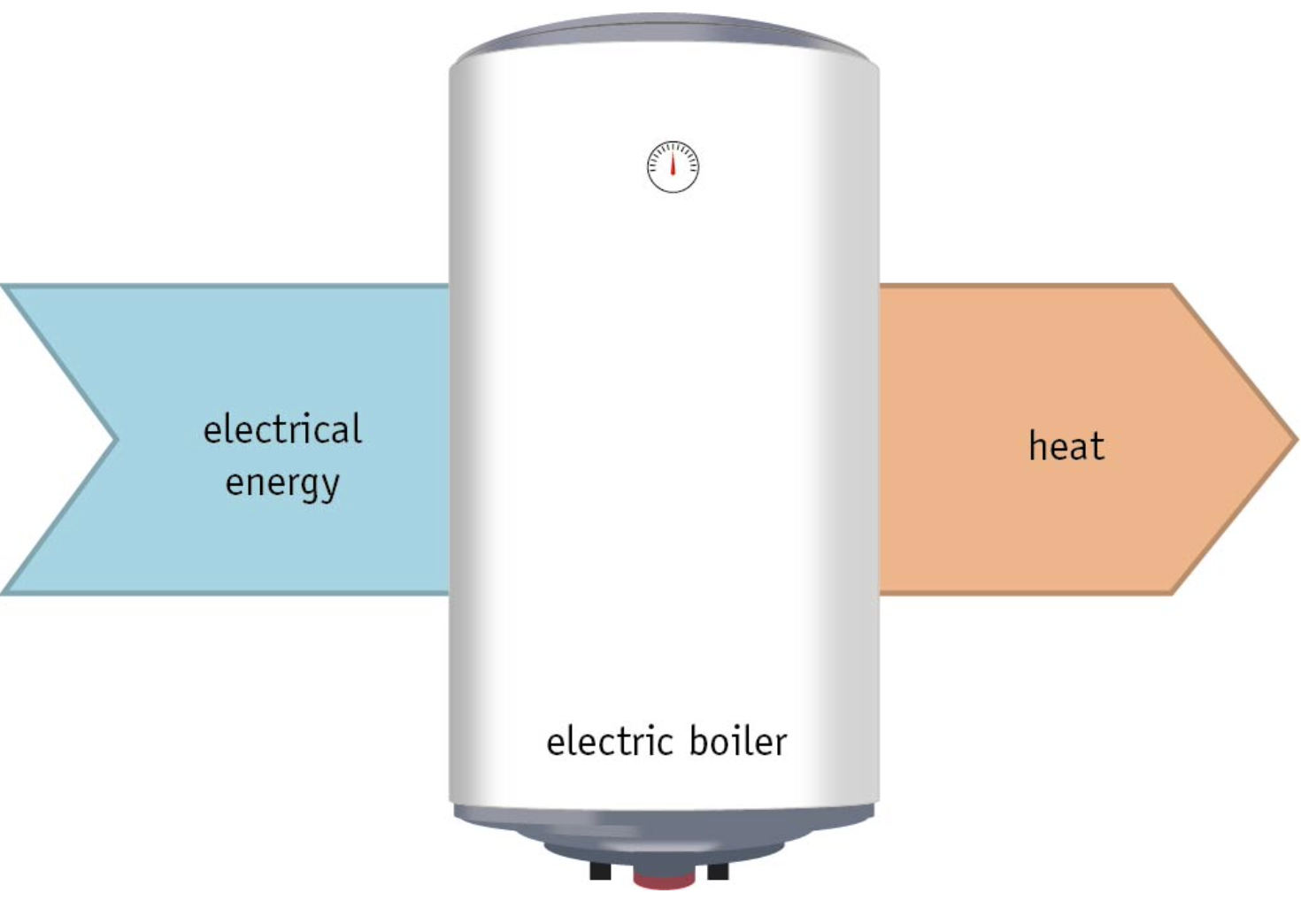
The quantity of energy never changes during an energy conversion
\n