Earth's Physical Systems and Geology Overview
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
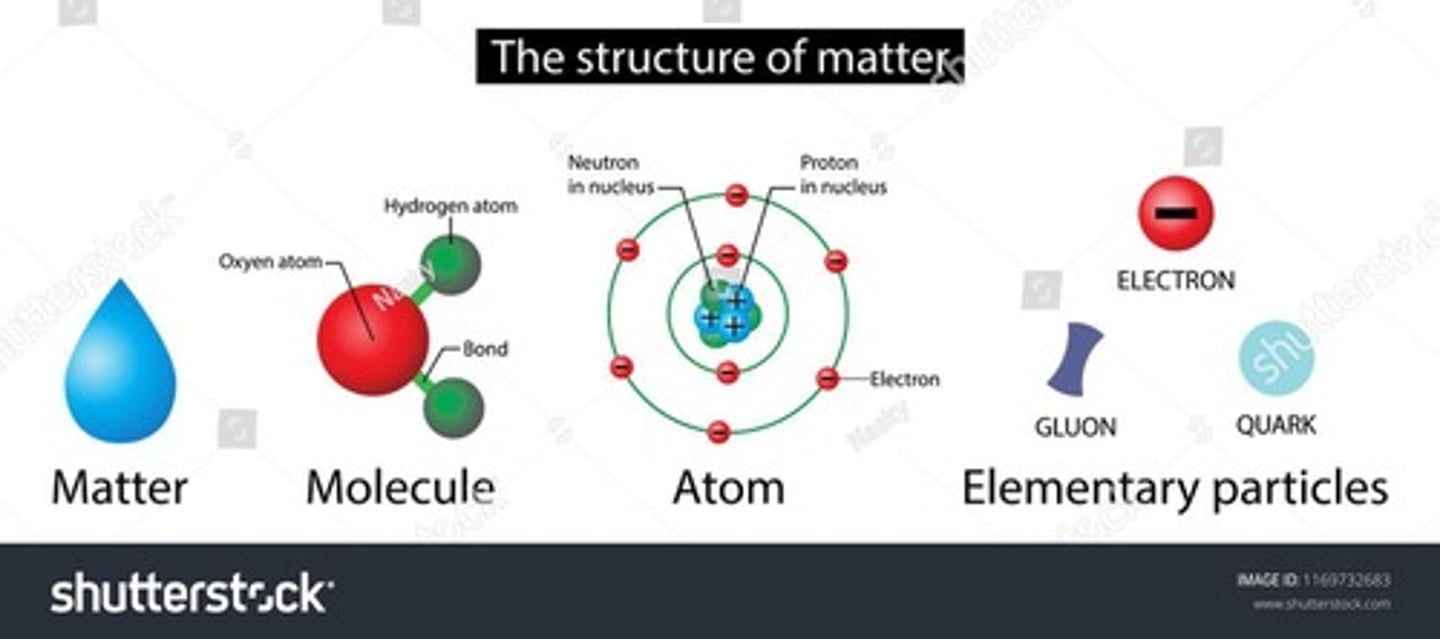
Matter
Material with mass and occupies space.
Energy
Capacity to change position or composition.
Geology
Study of Earth's physical structure and processes.
Chemistry
Study of matter and its interactions.
Atoms
Smallest units of matter, building blocks of molecules.
Elements
Substances made of atoms with specific properties.
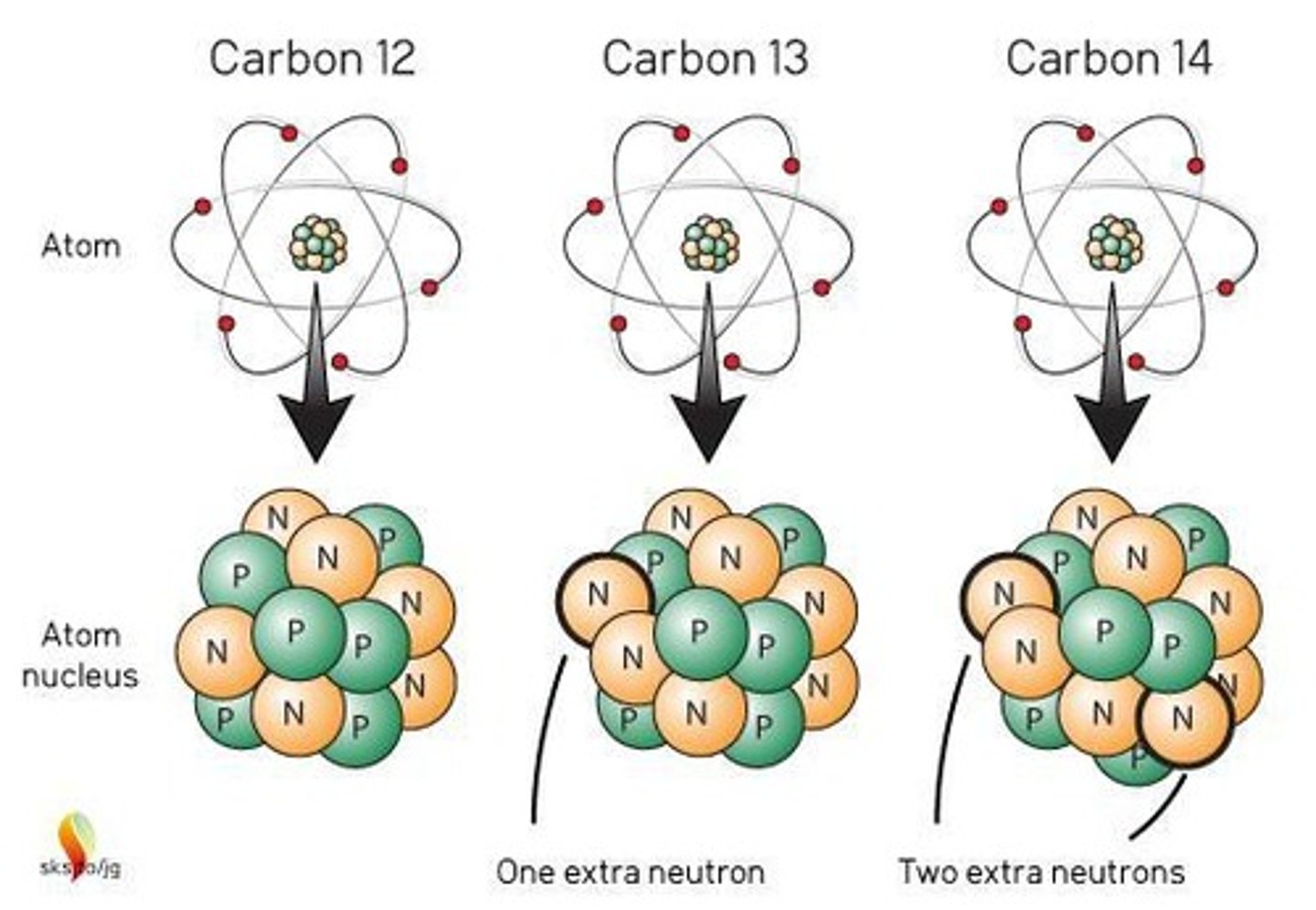
Isotopes
Atoms with same protons, different neutrons.
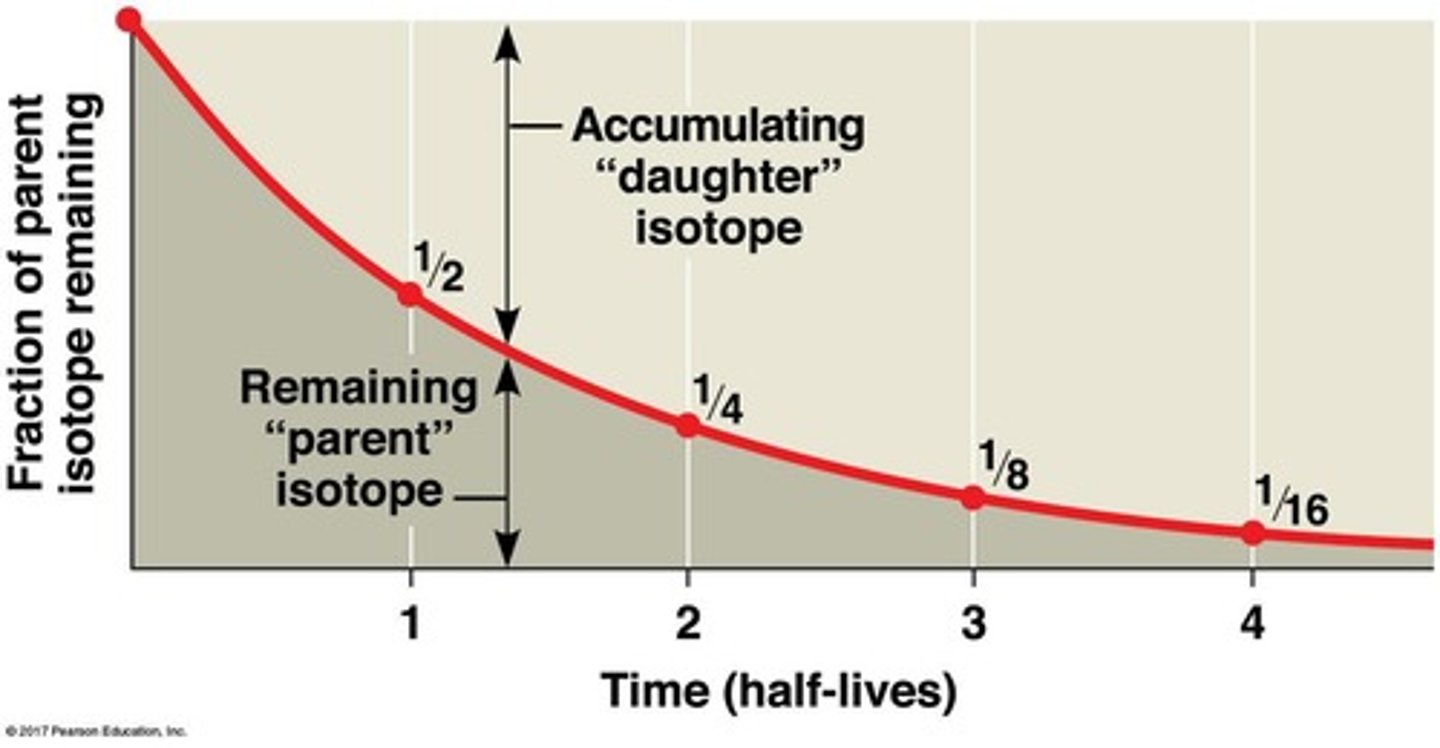
Radioactive isotopes
Isotopes that decay, releasing radiation.
Half-life
Time for half of a radioactive sample to decay.
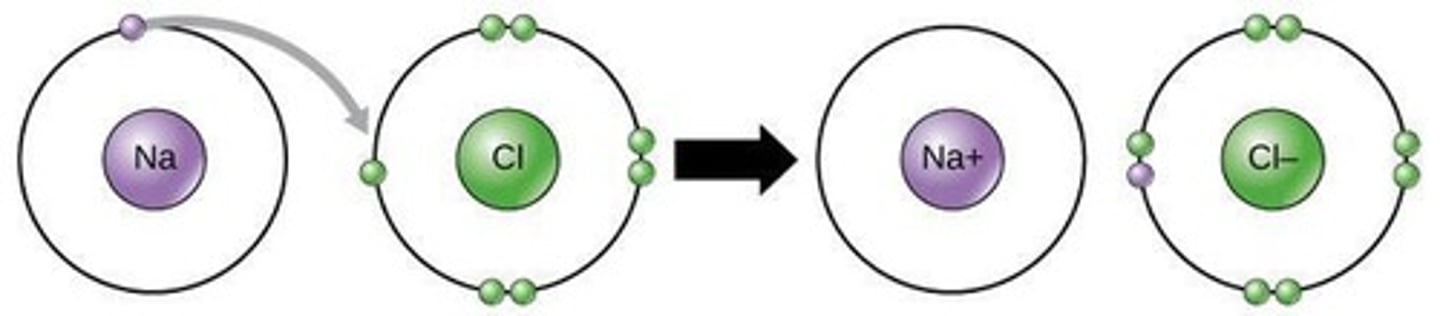
Ions
Atoms with unequal protons and electrons.
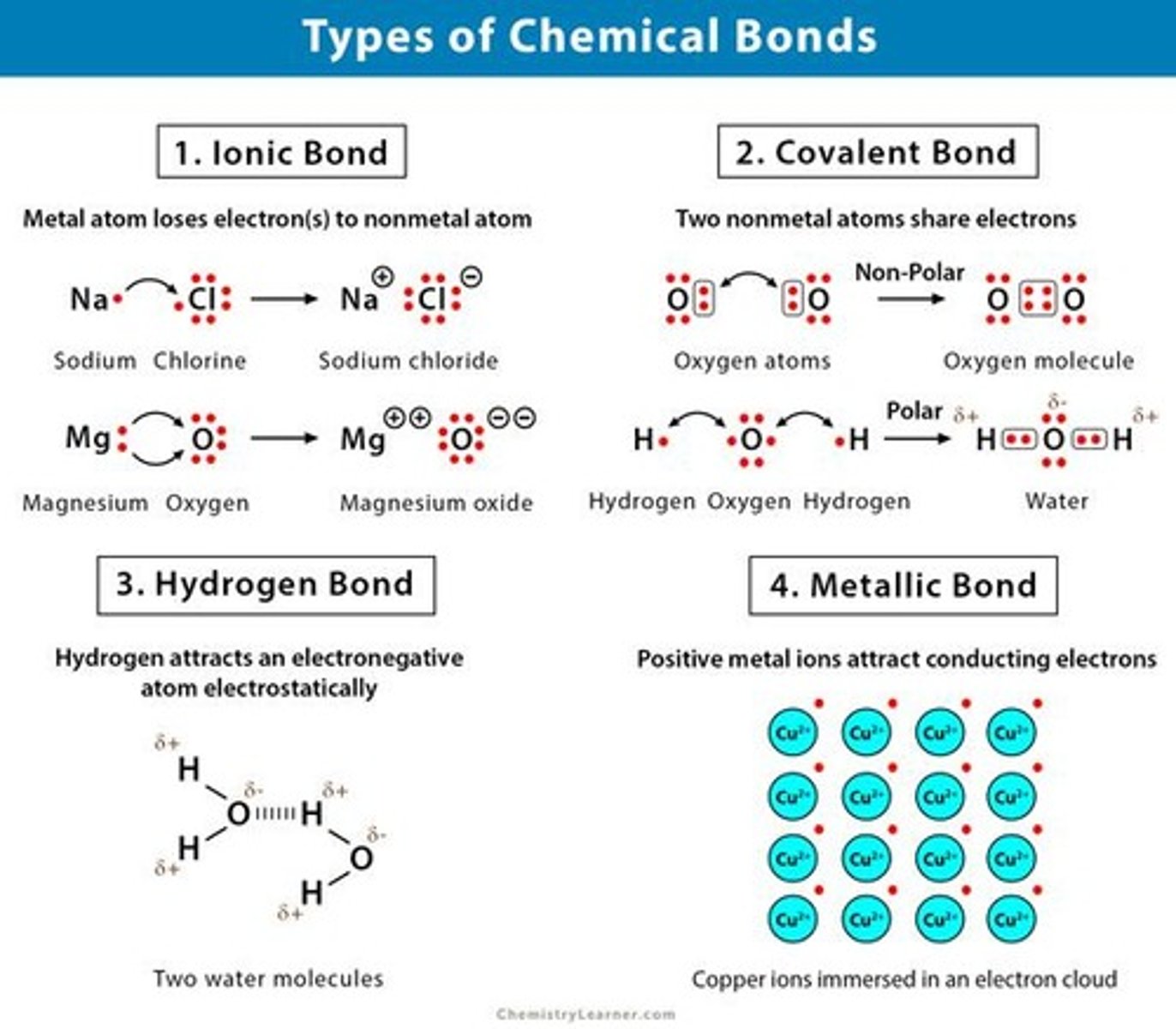
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds between hydrogen and electronegative atoms.
Ionic bonds
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Covalent bonds
Chemical bonds formed by sharing electrons.
Water's specific heat
Water requires significant energy for temperature change.
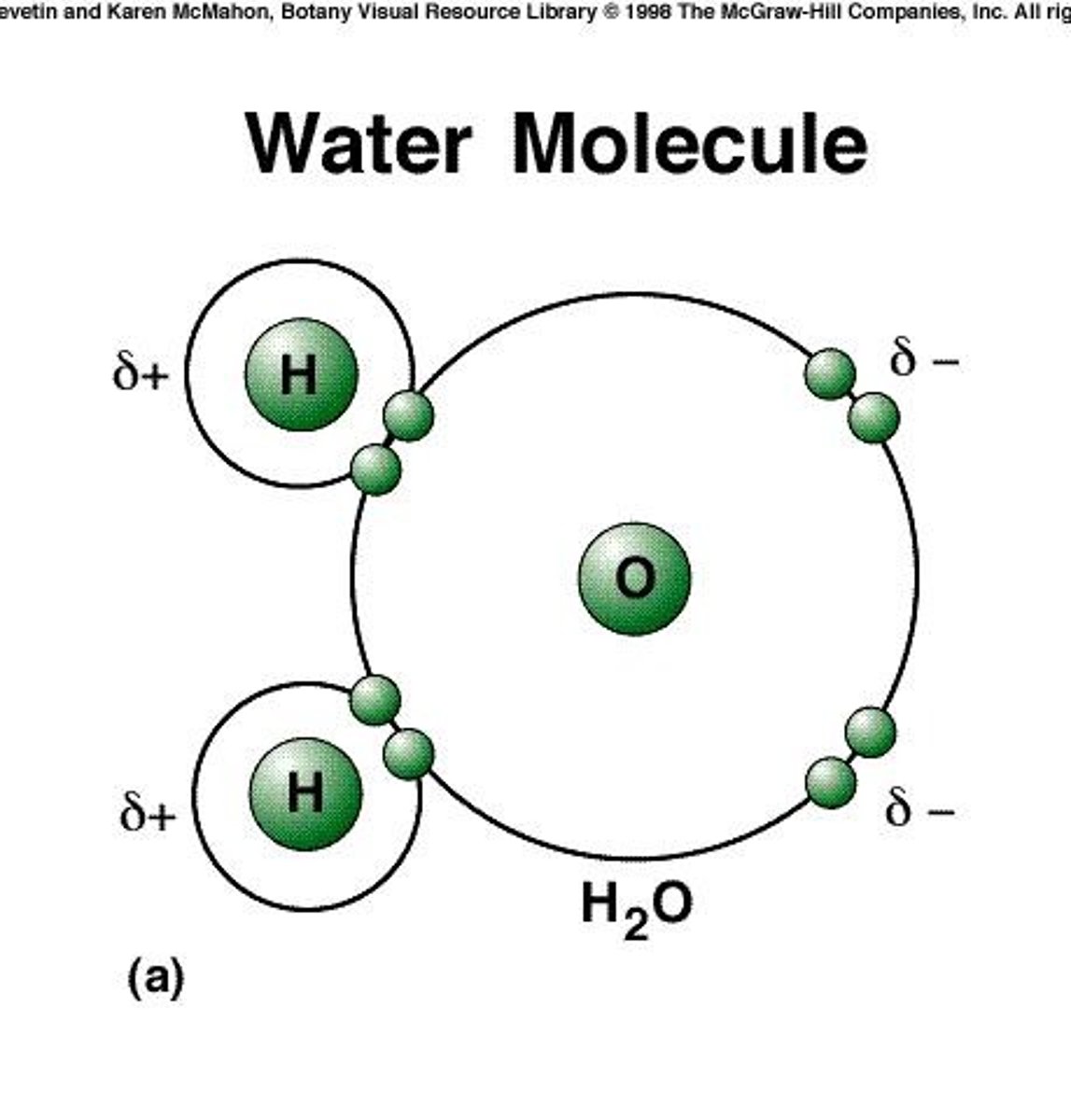
Polarity of water
Unequal distribution of charge, making it a solvent.
pH scale
Measures acidity or basicity of a solution.
Organic compounds
Compounds primarily consisting of carbon.
Macromolecules
Large molecules essential for life functions.
Proteins
Molecules that perform various functions in cells.
Nucleic acids
Biomolecules that carry genetic information.
Nucleotides
Subunits of nucleic acids, forming polymers.
Phospholipids
Key components of cell membranes.
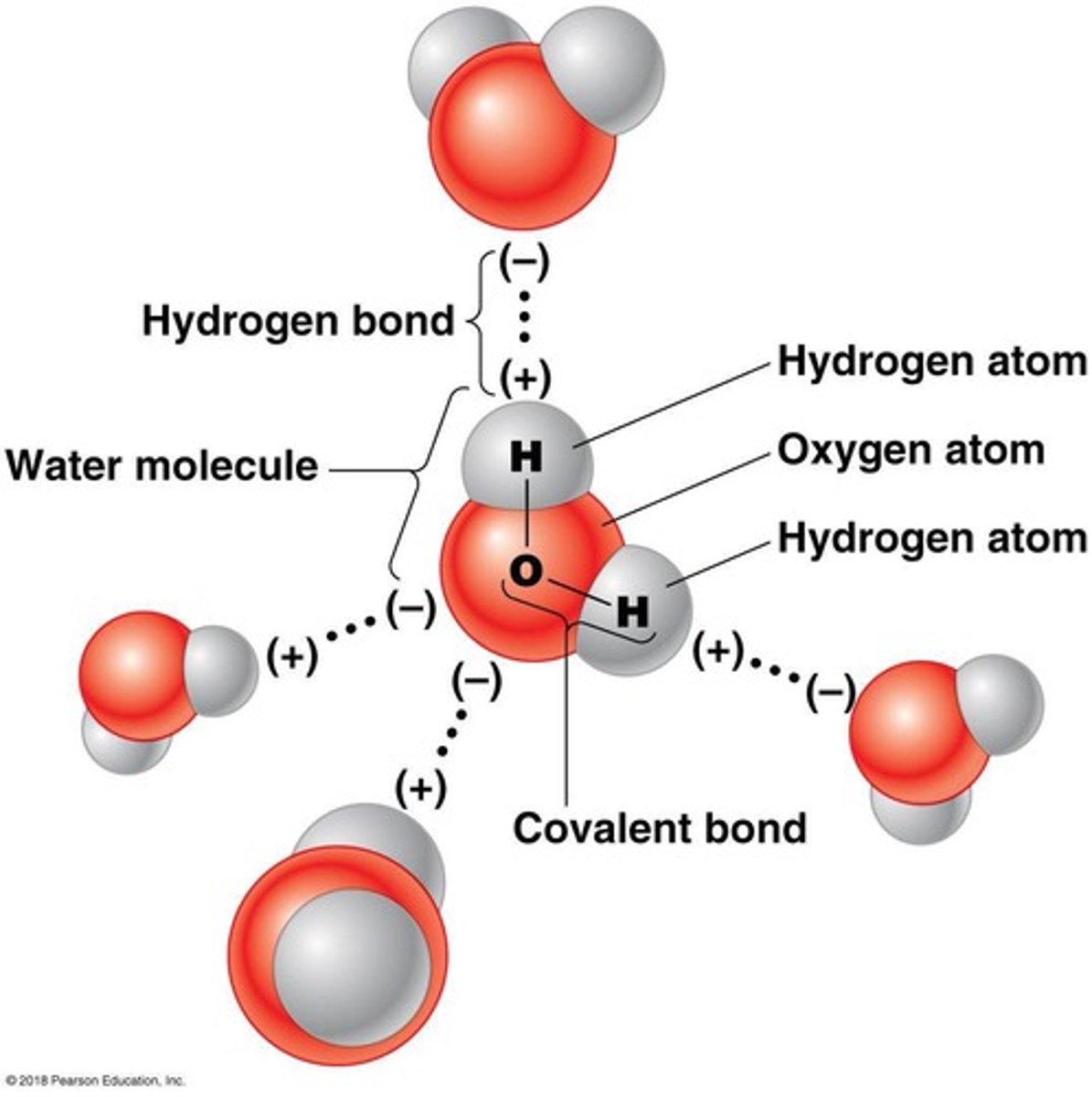
Plate tectonics
Theory explaining movement of Earth's crustal plates.
Earth's crust
Outer layer of Earth, composed of tectonic plates.
Transform boundary
Plate boundary where plates slide past each other.
Convergent boundary
Boundary where one plate dives beneath another.