Lecture 9 Neurodivergence in development and Autism
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Required:
– Chapter 15: pp. 532-541
– Gernsbacher & Yergeau (2019)
• Recommended:
– Jaswal & Akhtar (2019)
– Sheppard et al (2016)
What are developmental conditions/differences?
Condition manifesting before adulthood that alters typical development
– Motor, cognitive, socio-emotional
– One (specific) or more (pervasive) of these areas affected
– Can manifest in delay or deficit or difference
• CAVEAT!
– Language matters (and is always changing)!
– Diagnostic manuals and some practitioners will refer to “neurodevelopmental disorders”
(Reserved to those with a functional impairment in day-to-day life
Causes of Developmental Conditions
Chromosomal abnormalities
– Genetic mutation
• Down syndrome (extra copy of chromosome 21)
• Prenatal factors
– Damage while in womb (oxygen deprivation, maternal infection, structural
differences in brain)
• Ex: Cerebral Palsy
• Unknown combination
– Genetic, environmental, psychological, neurologica
CAVEAT
We are exploring the history of autism to better understand where we are
today and how we can move forward
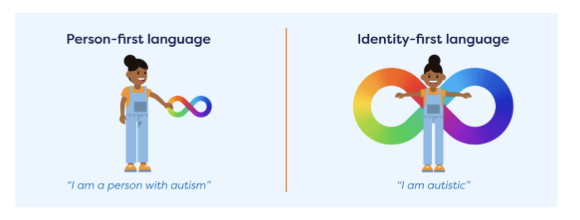
• Person-first (person with autism) vs. identity-first (autistic person)
Taboas A, Doepke K, Zimmerman C. Preferences for identity-first versus person-first language in a US sample of
autism stakeholders. Autism. 2023 Feb;27(2):565-570. doi: 10.1177/13623613221130845. Epub 2022 Oct 13.
PMID: 36237135.