Ocular W1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/348
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:45 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
349 Terms
1
New cards
(orbital) fat
substance that serves as cushioning in the orbit and wraps around the EOMs, nerves, and blood vessels
2
New cards
displacement from normal position
Since there is a small amount of space between orbital walls and the eyeball, tumors or masses expanding in the orbit would have what effect on the eyeball?
3
New cards
frontal, zygomatic, maxillary, ethmoid, sphenoid, lacrimal, palatine
What are the seven bones that form the walls of the orbit?
4
New cards
2, 2, 3, 4, all have the sphenoid except the floor
How can you remember how many bones make up each wall of the orbit? (Hint: start at the top, then lateral, etc.)
5
New cards
frontal
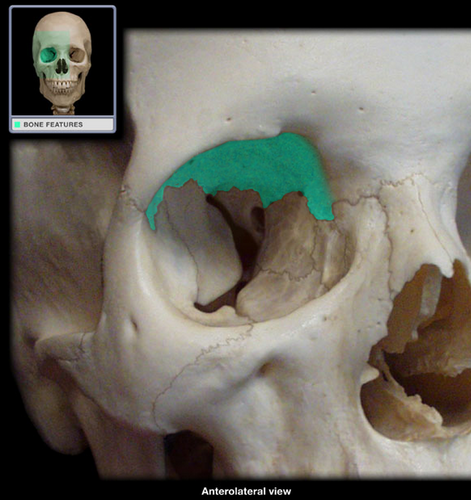
6
New cards
zygomatic
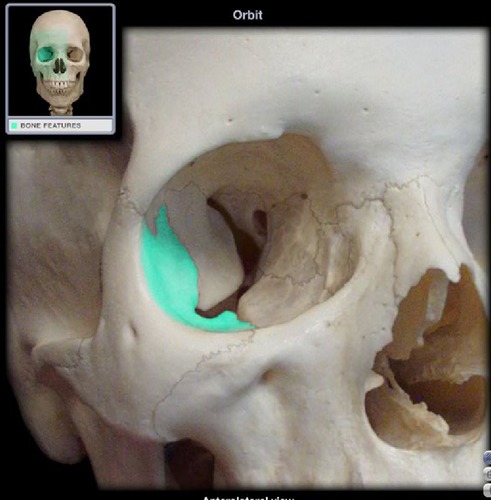
7
New cards
maxillary
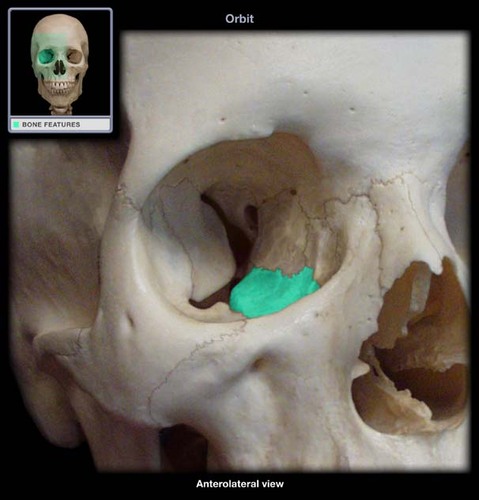
8
New cards
ethmoid
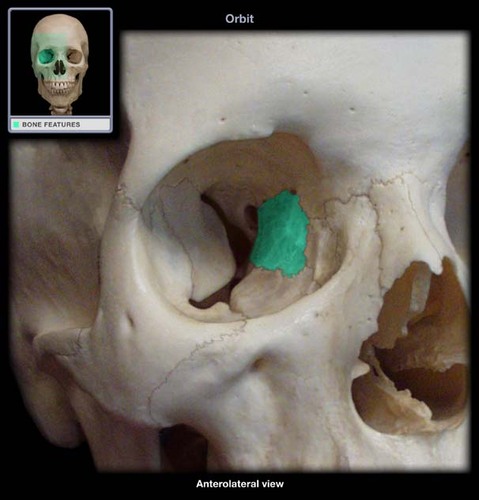
9
New cards
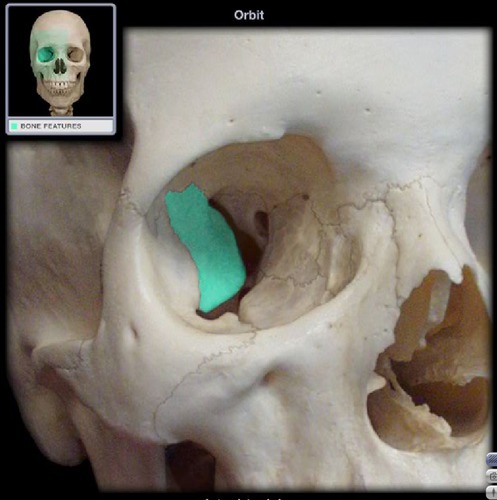
sphenoid
10
New cards
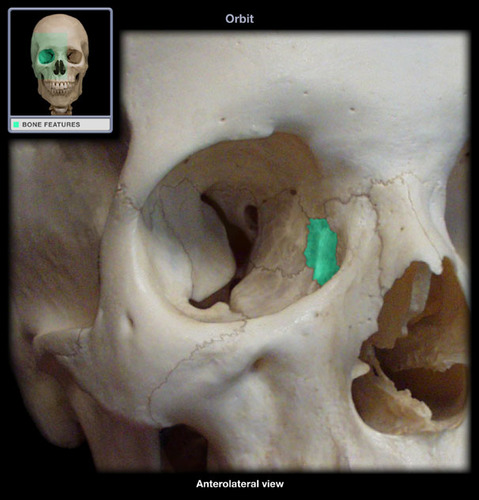
lacrimal
11
New cards
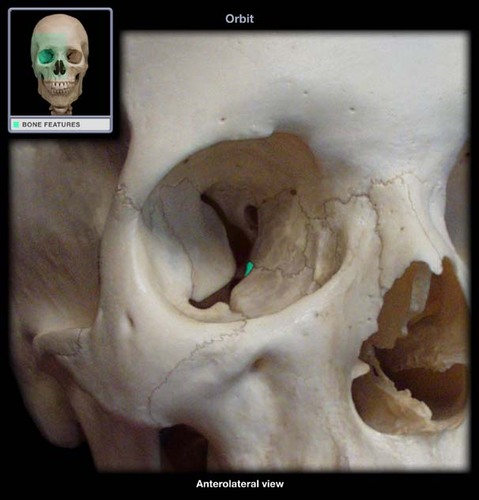
palatine
12
New cards
90
The lateral walls of the orbit are roughly how many degrees apart?
13
New cards
45
What is the value of the angle where the lateral and medial walls meet at the orbital apex? (resembles a pyramid, about 18 mm apart)
14
New cards
lateral, roof, floor
Which walls of the orbit are roughly triangular in shape?
15
New cards
medial
Which wall of the orbit is roughly rectangular in shape?
16
New cards
15 mm behind the margin
Where is the widest point of the orbit? (Hint: NOT at margin)
**approximately lines up with equator of the orbit
**approximately lines up with equator of the orbit
17
New cards
45 mm
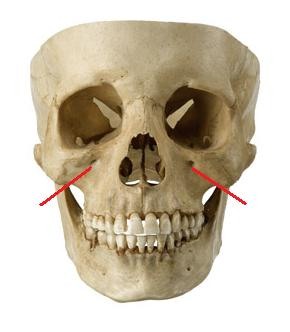
What is the depth of the orbit?
18
New cards
frontal, lesser wing of sphenoid
What bones form the roof of the orbit?
19
New cards
frontal
Which bone forms the MAJORITY of the orbital roof?
20
New cards
lesser wing of sphenoid
Which bone forms the SMALLER posterior portion of the roof?
21
New cards
frontal
Which bone of the orbital roof is much thinner and is therefore subject to "blow-in fractures" as well as penetrating injuries: frontal or sphenoid?
22
New cards
roof (specifically in the frontal bone)
Where do blow-in fractures most commonly occur?
23
New cards
anterior cranial fossa
Which division of the skull lies directly superior to the orbit?
**except for anterior part, where the frontal sinus is above the orbit
**except for anterior part, where the frontal sinus is above the orbit
24
New cards
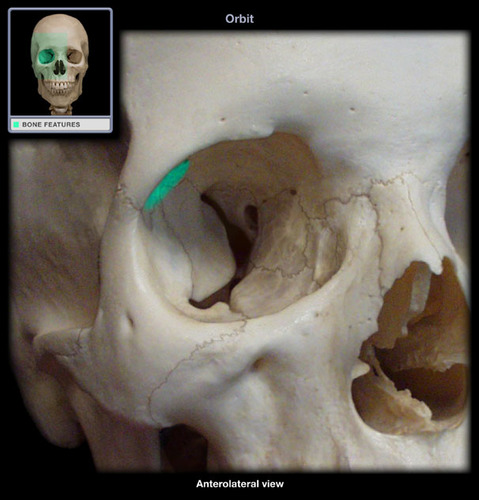
lacrimal fossa
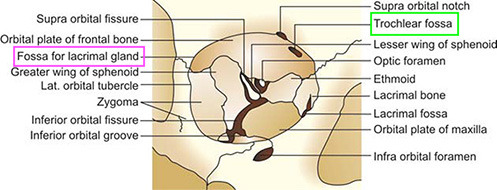
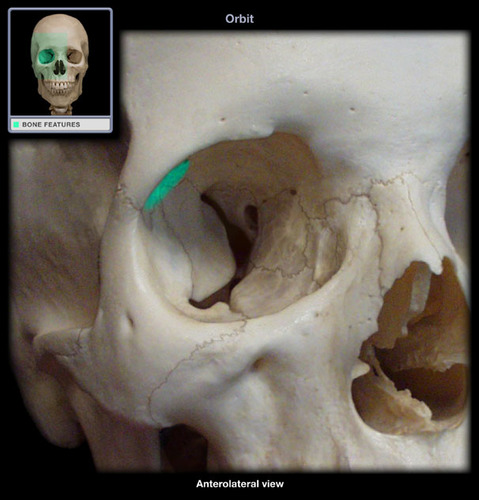
depression which lies in the superior temporal position on the frontal bone, just behind the superior orbital margin; the lacrimal gland is found here!
25
New cards
fovea trochlearis, trochlear fossa
two names for the small medial depression on the frontal bone behind the medial aspect of the superior orbital margin; the cartilaginous pulley for the tendon of the superior oblique muscle lies here in the anterior-medial portion of the orbital roof
26
New cards
frontal
On which bone are both the lacrimal fossa (for the lacrimal gland) and the fovea trochlearis found?
27
New cards
true
True or false: The fovea trochlearis is located more medially, and the fossa for the lacrimal gland is temporal.
28
New cards
fovea trochlearis
29
New cards
lacrimal fossa
30
New cards
superior oblique
If the roof of the orbit were damaged in such a way that affected the cartilage pulley in the fovea trochlearis, what muscle would be affected?
31
New cards
dura mater
Parts of the orbital roof can actually be absorbed in old age, bringing what specific part of the frontal lobe into contact with the periosteum of the orbit?
32
New cards
frontal sinus
Anteriorly, the orbital plate of the frontal bone may contain a portion of what structure?
**an enlarging mucocele in this could expand into the orbit through the thin roof, causing an infection to potentially spread superiorly to the frontal lobes and their meninges or inferiorly to the orbit
**an enlarging mucocele in this could expand into the orbit through the thin roof, causing an infection to potentially spread superiorly to the frontal lobes and their meninges or inferiorly to the orbit
33
New cards
zygomatic, greater wing of sphenoid
What bones form the lateral wall of the orbit?
34
New cards
zygomatic
Which bone forms the anterior third of the lateral wall of the orbit?
35
New cards
greater wing of sphenoid
Which bone forms the posterior two-thirds of the lateral wall of the orbit?
36
New cards
lateral wall
Which orbital wall is the thickest?
37
New cards
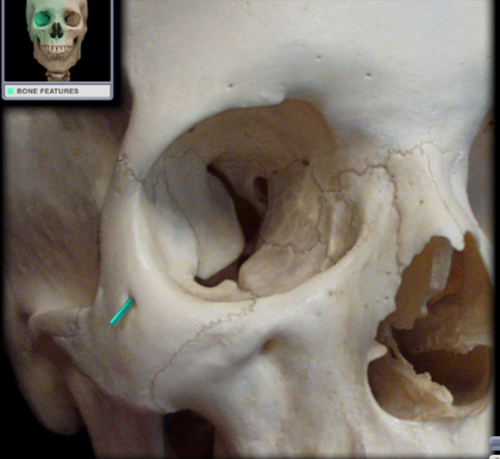
lateral orbital tubercle
small elevation/bump on the orbital surface of the zygomatic bone, located just within the lateral orbital margin at its midpoint; serves as the attachment site for several structures

38
New cards
zygomatic
On which bone is the lateral orbital tubercle found?
39
New cards
zygomaticoorbital foramen
opening in the zygomatic bone that carries the zygomatic nerve and blood vessels
**some people have 1, some have 2 (each one opens up into either the zygomaticofacial or zygomaticotemporal)
**some people have 1, some have 2 (each one opens up into either the zygomaticofacial or zygomaticotemporal)
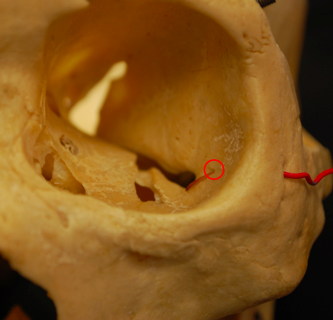
40
New cards
zygomaticoorbital foramen
transmits zygomatic nerve
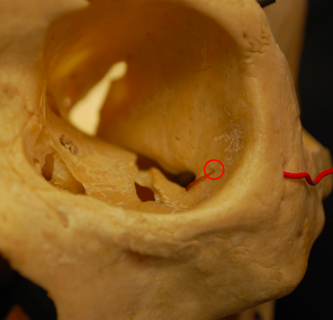
41
New cards
zygomaticofacial foramen
transmits namesake nerve
42
New cards
zygomaticotemporal foramen
transmits namesake nerve
43
New cards
temporal
Anteriorly, the lateral wall separates the orbit from what region of the skull? (Hint: contains the temporalis muscle)
44
New cards
middle cranial fossa
Posteriorly, the greater wing of the sphenoid separates the lateral wall of the orbit from what division of the skull?
45
New cards
superior orbital fissure
What separates the lateral wall of the orbit from the roof?
46
New cards
maxillary, lacrimal, ethmoid, body of sphenoid
What bones form the medial wall of the orbit? (from anterior to posterior)
47
New cards
medial
Which orbital wall is the thinnest?
48
New cards
mostly consists of the very thin lamina papyracea (of the ethmoid)
Why is the medial wall of the orbit the thinnest wall?
49
New cards
orbital cellulitis
Infections in both ethmoid air cells and the sphenoid sinus can easily spread to the orbit via the lamina papyracea, causing what condition?
50
New cards
fossa for the lacrimal sac
depression formed by the maxillary & lacrimal bones the is bounded by the anterior & posterior lacrimal crests; contains the lacrimal sac
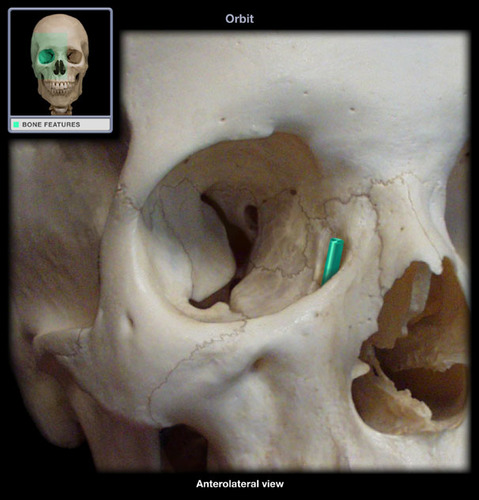
51
New cards
maxillary, lacrimal
What two bones form the fossa for the lacrimal sac?
52
New cards
maxillary
Which bone contains the ANTERIOR lacrimal crest?
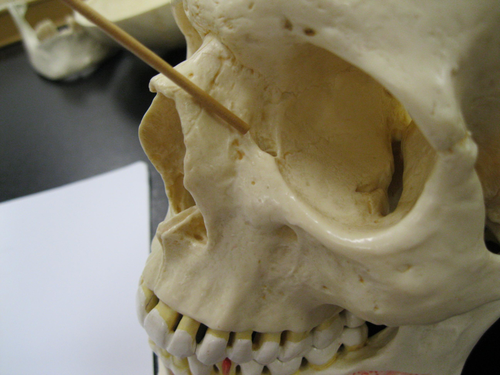
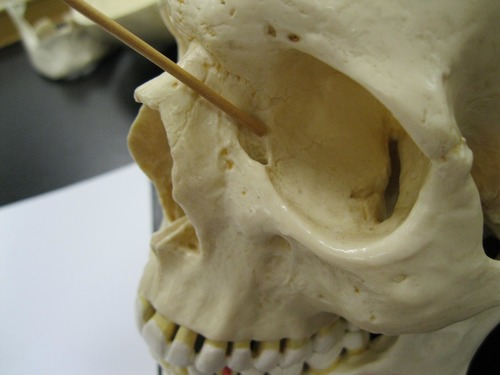
53
New cards
lacrimal
Which bone contains the POSTERIOR lacrimal crest?
54
New cards
nasolacrimal canal
bony canal within the maxilla that is continuous superiorly with the fossa for the lacrimal sac; lies below the orbital floor and leads inferior into the inferior meatus of the nasal cavity, which contains the nasolacrimal duct
lies anterior-medial on the floor
lies anterior-medial on the floor
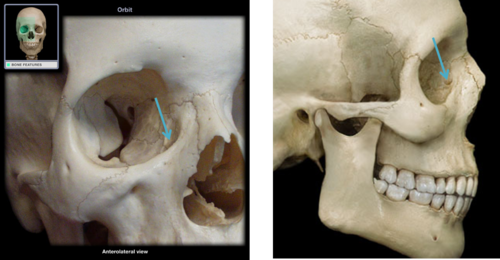
55
New cards
true
True or false: Both the lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct are considered "soft tissue" and are lined by an epithelium.
56
New cards
lamina papyracea
specific part of the ethmoid that makes up the medial wall
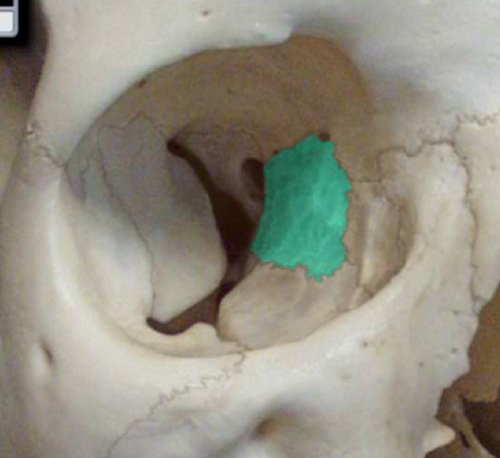
57
New cards
fossa for the lacrimal sac
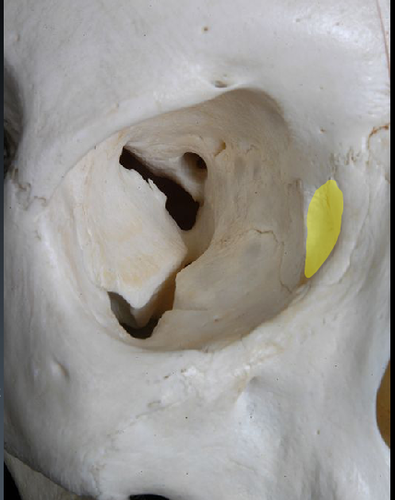
58
New cards
anterior lacrimal crest, maxillary
structure, what bone it's found on
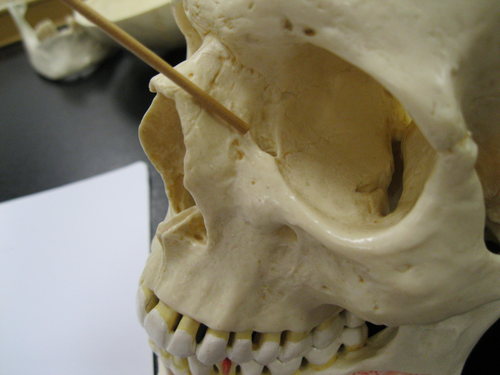
59
New cards
posterior lacrimal crest, lacrimal
structure, what bone it's found on
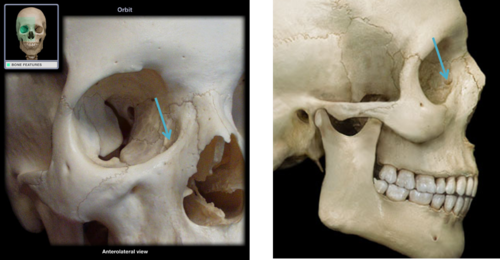
60
New cards
nasolacrimal canal
61
New cards
maxillary, zygomatic, palatine
What bones form the floor of the orbit?
62
New cards
maxillary
What bone forms the LARGEST portion of the orbital floor?
63
New cards
palatine
What bone forms the SMALLEST portion of the orbital floor?
64
New cards
inferior orbital fissure
leads into the infraorbital groove
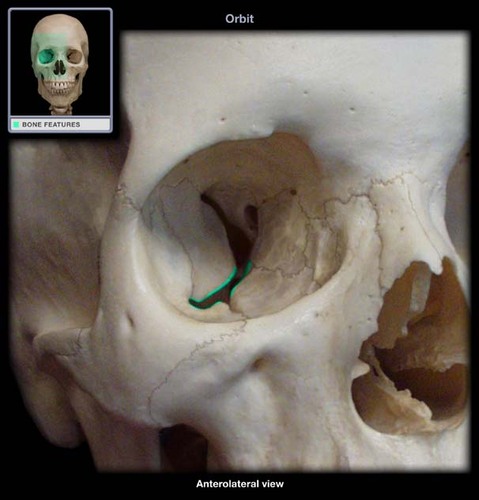
65
New cards
infraorbital groove
leads into the infraorbital canal
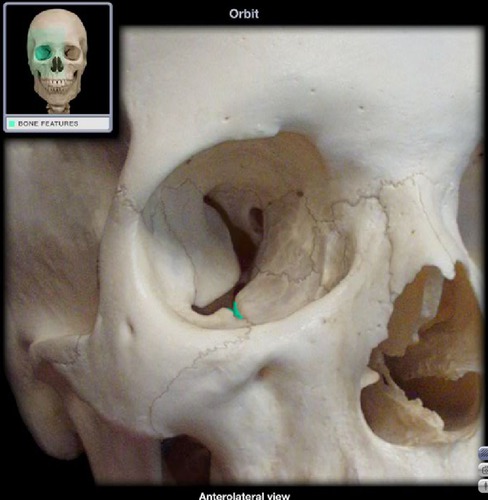
66
New cards
infraorbital canal
leads to the infraorbital foramen
**transmits namesake nerve, artery, & vein
**transmits namesake nerve, artery, & vein
67
New cards
maxillary
The infraorbital canal is located within which bone?
68
New cards
maxillary sinus
What lies beneath most of the orbital floor?
69
New cards
orbital cellulitis
Maxillary sinus infections can easily invade the orbit, leading to what condition?
70
New cards
proptosis
A maxillary sinus tumor could extend superiorly into the orbit causing what condition if the tumor ends up in the orbit behind the eyeball?
71
New cards
inferior orbital fissure
The nasolacrimal canal lies anterior-medial on the floor, which is separated from the lateral wall by what?
72
New cards
inferior orbital fissure
Where is the orbital floor the thinnest? (i.e. Where is a fracture most likely to occur in the floor?)
73
New cards
horizontal
Does the orbit have a greater horizontal or vertical diameter?
74
New cards
frontal, maxillary, zygomatic
What three bones make up the orbital margin (rim)?
75
New cards
frontal
What comprises the superior orbital margin?
76
New cards
supraorbital notch (or foramen)
structure located just medial to the center of the superior orbital margin that transmits its namesake nerve, artery, & vein
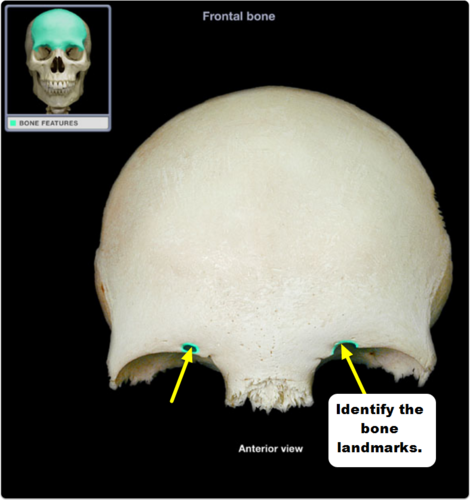
77
New cards
frontal, zygomatic
What comprises the lateral orbital margin?
78
New cards
zygomatic, maxillary
What comprises the inferior orbital margin?
79
New cards
maxillary, frontal
What comprises the medial orbital margin?
80
New cards
lateral
(though its weakest part is at the suture between the frontal and zygomatic bones)
(though its weakest part is at the suture between the frontal and zygomatic bones)
Which part of the orbital margin is the strongest?
81
New cards
blow out fracture
Even though the orbital margin is very thick, when someone receives a heavy blow to the margin, the bones of the orbit may fracture "away" from the margin. What is this called?
**refers to the rupture of the orbital bones
**refers to the rupture of the orbital bones
82
New cards
floor
Where do blow-out fractures most commonly occur? (i.e. which wall)
83
New cards
groove part of maxilla, lamina papyracea of ethmoid
What are the two most common sites for orbital fractures?
84
New cards
B
The most common site for a blow-out fracture following trauma involves which of the following orbital bones?
A. zygomatic
B. maxillary
C. ethmoid
D. lacrimal
E. sphenoid
F. frontal
G. palatine
A. zygomatic
B. maxillary
C. ethmoid
D. lacrimal
E. sphenoid
F. frontal
G. palatine
85
New cards
IOP
Ultimately, the orbital walls may experience a blow-out fracture due to a sudden increase (and resulting shockwave) in what value?
86
New cards
black eye (ecchymosis), loss of sensation, diplopia, enophthalmos
What are four symptoms of a blow-out fracture?
87
New cards
restriction of ocular motility
(due to EOM damage by medial wall or floor and entrapment of EOMs within fracture site)
(due to EOM damage by medial wall or floor and entrapment of EOMs within fracture site)
Why does diplopia occur from a blow-out fracture?
88
New cards
posterior displacement of eye in orbit
Why does enophthalmos occur from a blow-out fracture?
89
New cards
lesser wing of sphenoid (therefore the roof)
Where is the optic canal located? (What bone?)
90
New cards
orbit, middle cranial fossa
What two larger spaces does the optic canal connect?
91
New cards
optic nerve, ophthalmic artery
What two things does the optic canal transmit?
92
New cards
roof, lateral
What two walls of the orbit does the superior orbital fissure separate?
93
New cards
lesser and greater wings of sphenoid
What two bones of the orbit does the superior orbital fissure separate?
94
New cards
orbit, middle cranial fossa
What two larger spaces does the superior orbital fissure connect?
95
New cards
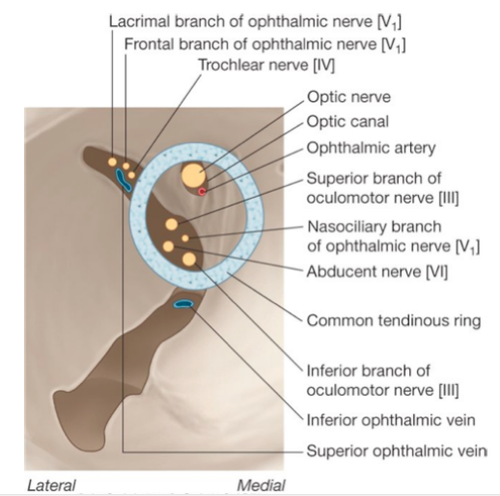
lacrimal (from V1), frontal (from V1), nasociliary (from V1), trochlear (IV), oculomotor (III), abducens (VI)
What six NERVES does the superior orbital fissure transmit?
96
New cards
superior and inferior ophthalmic veins
What two VESSELS does the superior orbital fissure transmit?
97
New cards
common tendinous ring
fibrous structure that the rectus muscles arise from
98
New cards
lacrimal nerve, frontal nerve, superior ophthalmic vein, trochlear nerve
What passes ABOVE the common tendinous ring? (that also goes through the SOF)
99
New cards
upper branch of oculomotor nerve, nasociliary nerve, abducens nerve, lower branch of oculomotor nerve
What passes THROUGH the common tendinous ring? (that also goes through the SOF)
100
New cards
inferior ophthalmic vein
What passes BELOW the common tendinous ring? (that also goes through the SOF)