13- Magnetic fields due to currents
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
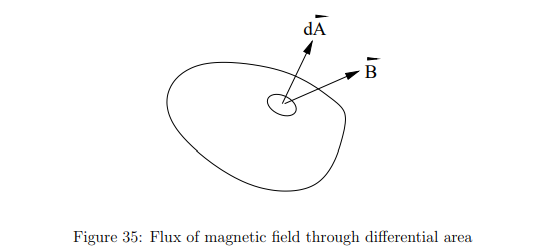
What does Gauss’s Law for magnetism state?
The net magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero
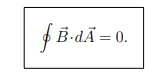
What is the physical interpretation of Gauss’s Law for magnetism?
Magnetic field lines always form closed loops; there are no magnetic monopoles.
How do electric and magnetic field lines differ?
Electric field lines start on positive charges and end on negative charges.
Magnetic field lines do not have a beginning or end—they always form loops or extend to infinity.
Why is there no magnetic equivalent of Coulomb’s Law?
Because there are no magnetic monopoles, only magnetic dipoles.
What is required to produce and feel a magnetic field?
Moving electric charges
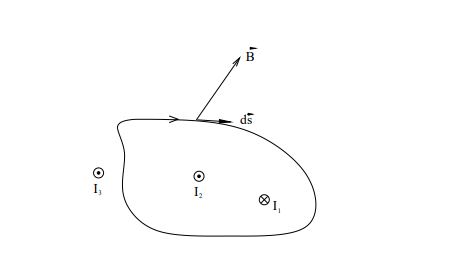
What does Ampere’s Law state?
The circulation of the magnetic field around a closed loop is proportional to the net enclosed current:
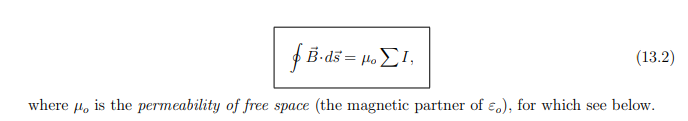
What is μ0 in Ampere’s Law?
It is the permeability of free space
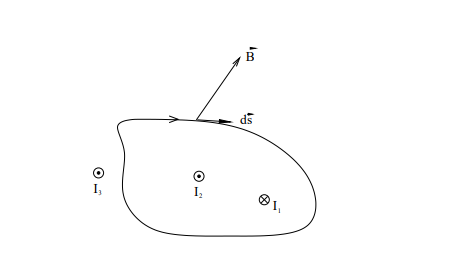
What is an Amperian loop?
An imaginary closed path used to calculate the circulation of B.
How do you determine the sign of the enclosed current?
Use the right-hand rule:
Curl your fingers in the direction of integration.
If the current flows along your thumb’s direction, it's positive.
If it flows opposite, it's negative.
What happens if a current is outside the Amperian loop?
It does not contribute to the integral ∮B⋅ds.
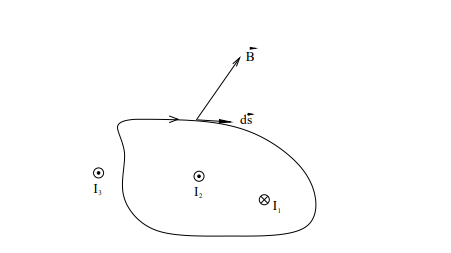
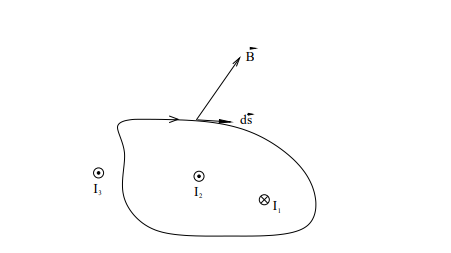
Why is ∮B⋅ds≠0?
Because the magnetic field does not originate from a scalar potential like E=−dV/dr
What is the magnetic field B at a distance r from a long straight wire carrying current I?
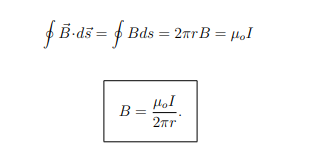
What do the magnetic field lines around a long straight wire look like?
They form concentric circles around the wire.
How can Ampere’s Law be used to derive the field around a straight wire?
By using a circular Amperian loop of radius r centered on the wire:
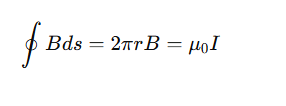
What is the force per unit length f between two long parallel wires carrying currents I1 and I2?
r is the distance between the wires.
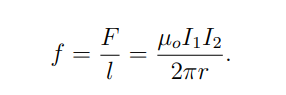
When do two parallel wires attract each other?
When their currents flow in the same direction.
What is the Biot-Savart Law?
It describe the magnetic field dB generated by a current element ds
ˆr is a unit vector in the ⃗r direction.
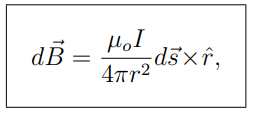
What does the cross product r^×ds represent in the Biot-Savart Law?
It gives the direction of the magnetic field generated by the current element, following the right-hand rule.
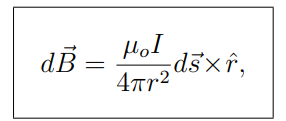
What is the magnetic field B generated by a current loop?
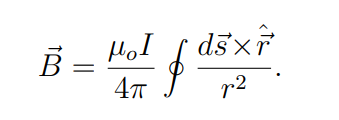
What is a solenoid?
A coil of insulated wire tightly wound into a cylindrical shape, often used to generate a uniform magnetic field.
What is the magnetic field inside a long solenoid?
The magnetic field inside a long solenoid is uniform and parallel to the axis of the solenoid.
How does the magnetic field inside a solenoid arise?
The magnetic field inside the solenoid is the sum of the fields generated by the currents flowing in the loops.
The fields from current loops going in opposite directions add up inside, but cancel out outside.
What is the formula for the magnetic field B inside a long solenoid?
n is the number of turns per unit length
I is the current.
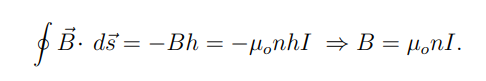
What happens to the magnetic field outside an infinite solenoid?
The magnetic field outside an infinite solenoid is zero.
What is the magnetic field inside a solenoid analogous to in electrostatics?
Its analogous to the uniform electric field between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor.