lines, tubes, drains, & devices
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
under what conditions should you NOT apply a BP cuff to an extremity?
1. A-line (CAC) or central venous catheter (CVC)
2. lymphedema
3. ipsilateral to mastectomy
4. AV fistula or graft
5. blood clot
2
New cards
what is an arteriovenous (AV) fistula?
* access for long-term hemodialysis
* fistula is the surgical joining of an artery & vein, allowing for arterial blood to flow directly to a vein (anastomosis)
* fistula is the surgical joining of an artery & vein, allowing for arterial blood to flow directly to a vein (anastomosis)
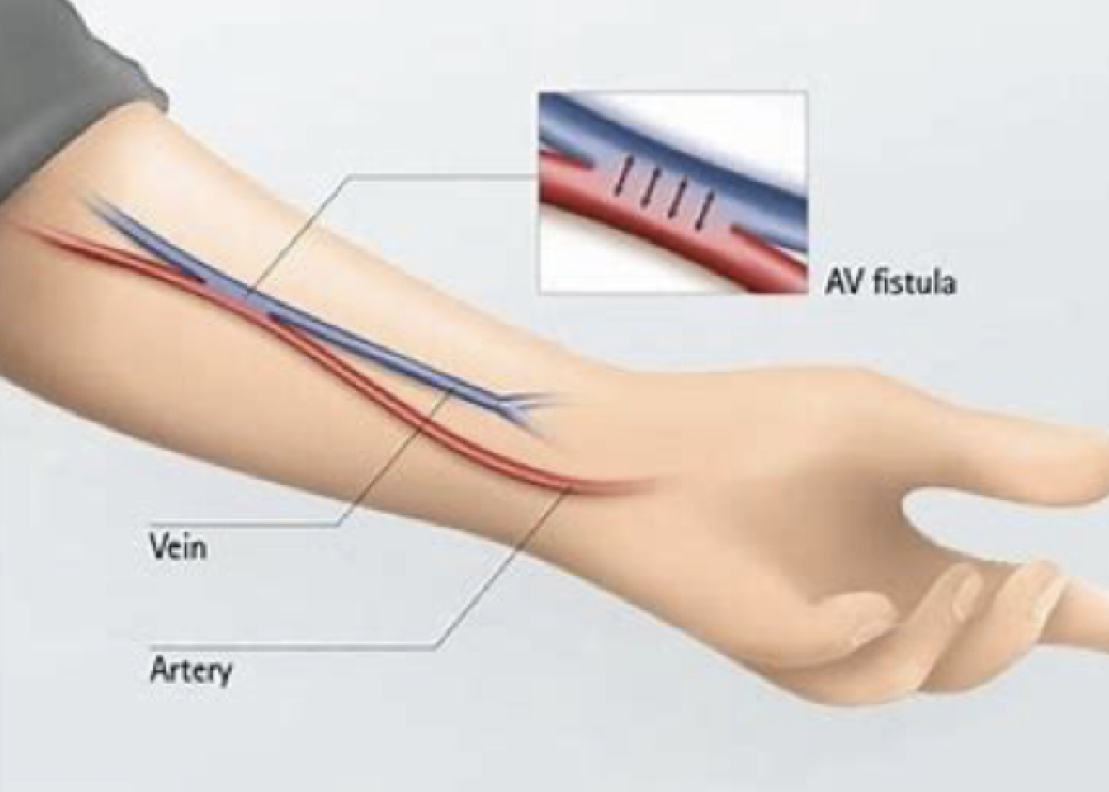
3
New cards
arteriovenous (AV) fistula
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
* no BP cuff on involved UE (will also not be used for IV or blood draw)
* elevate & avoid WB on the involved extremity for 24 hrs after procedure
* elevate & avoid WB on the involved extremity for 24 hrs after procedure
4
New cards
vascular access port (VAP)
* for long-term use (> 6 mos) for chemotherapy or other intermittent infusion therapy
* typically placed via surgery in the subclavian or jugular vein & terminates in SVC
* typically placed via surgery in the subclavian or jugular vein & terminates in SVC
5
New cards
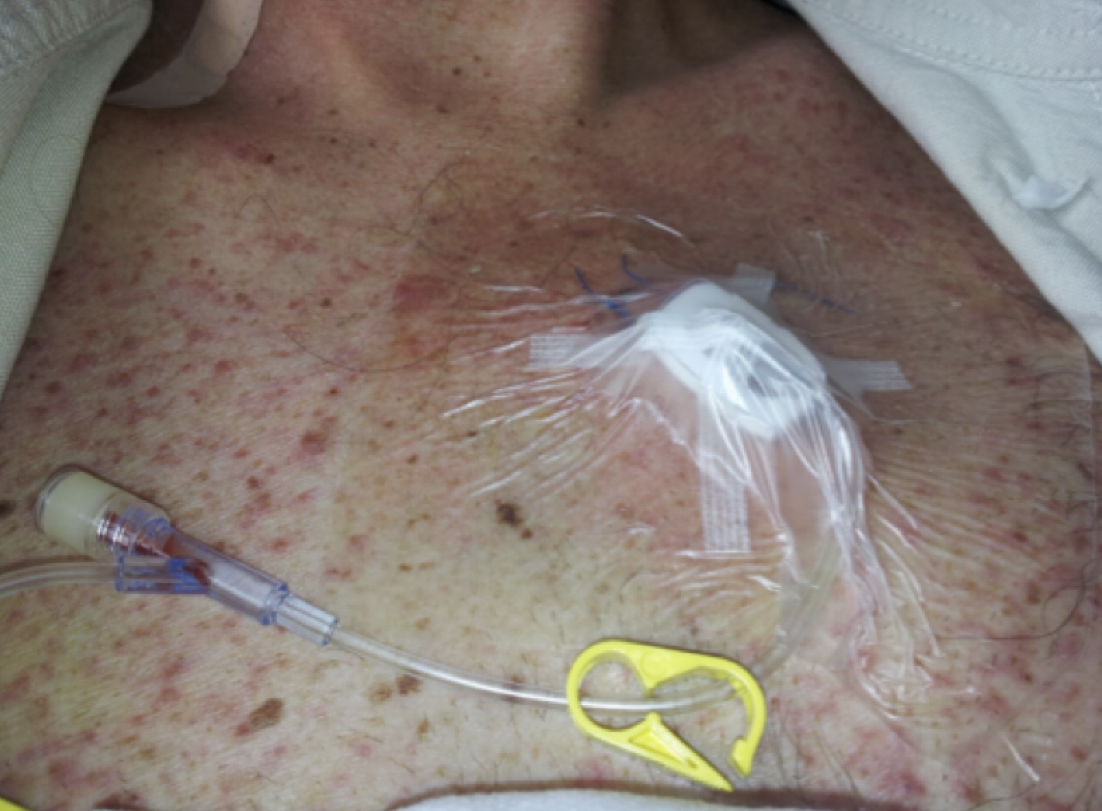
appears as a protrusion under the skin
vascular access port (VAP)
6
New cards
catheter
(indications)
(indications)
1. urine retention
2. incontinence
3. urinary output monitoring
4. SCI
5. imaging
6. surgery
2. incontinence
3. urinary output monitoring
4. SCI
5. imaging
6. surgery
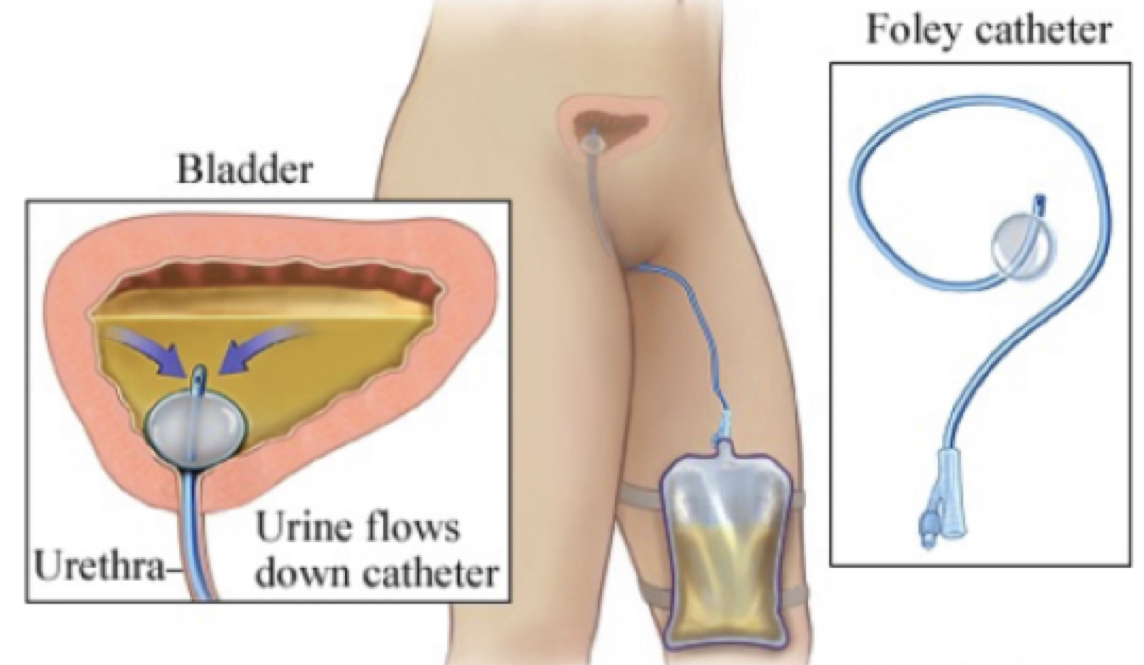
7
New cards
catheter
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. keep collecting bag below bladder
2. may need to empty prior to movement (unless intake & output are being monitored)
3. S&S of ==infection==
4. ==autonomic dysreflexia==
8
New cards
signs of infection in catheter
1. pain
2. fever
3. foul smelling urine
4. hematuria
2. fever
3. foul smelling urine
4. hematuria
9
New cards
autonomia dysreflexia
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. signal emergency
2. sit pt upright
3. empty collecting bag or correct tube blockage
2. sit pt upright
3. empty collecting bag or correct tube blockage
10
New cards
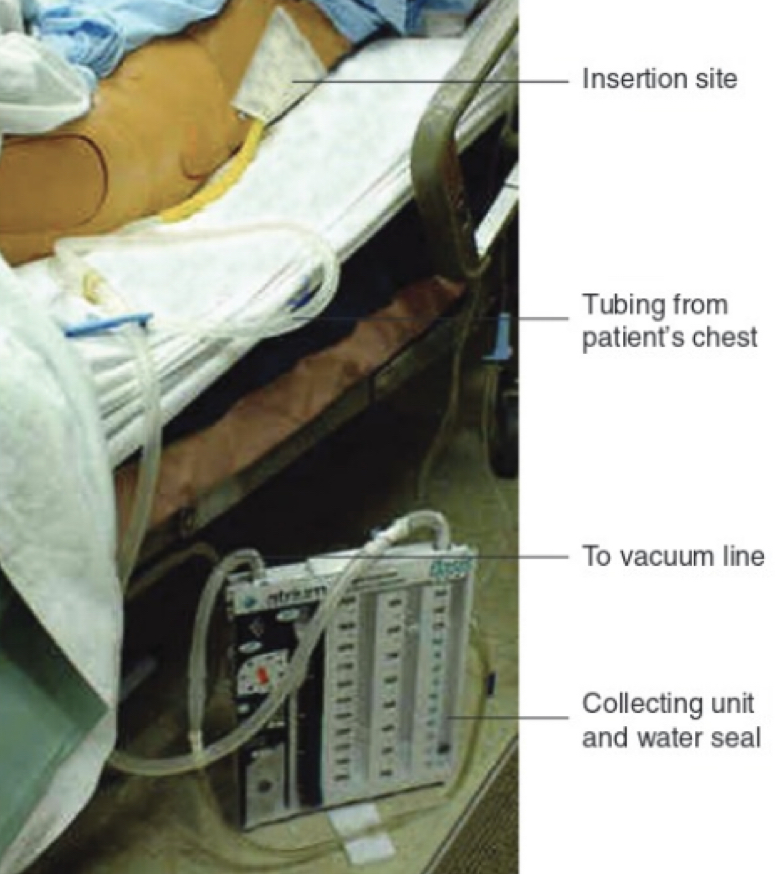
chest tube
11
New cards
chest tube
* surgically inserted into intrapleural space (chest wall). attached to vacuum line and water seal to prevent any air from entering tube
* removes air, blood, fluid or pus following __pneumothorax__, __cardiothoracic surgery__, __pleural effusion__, __emphysema__, or other conditions
* removes air, blood, fluid or pus following __pneumothorax__, __cardiothoracic surgery__, __pleural effusion__, __emphysema__, or other conditions
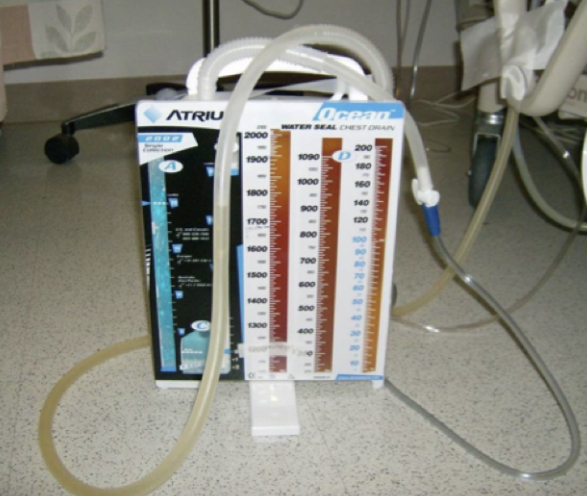
12
New cards
chest tube
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. keep below chest (water seal is often on floor)
2. can utilize portable suction deveice on a moveable platform / trolley for ambulation
3. ==contraindications==: positive pressure devices
4. @@wait at least an hour@@ before working w/ a pt who has just had a chest tube removed (to allow healing & avoid tension pneumothorax)
13
New cards
what do you do if a chest tube is dislodged?
1. ask pt to exhale fully
2. at end of exhalation, place gauze or gloved hand over defect
3. call for medical assistance ASAP
2. at end of exhalation, place gauze or gloved hand over defect
3. call for medical assistance ASAP
14
New cards
what interventions are permissible w/ chest tube (to patient tolerance)?
1. breathing maneuvers
2. relaxation techniques
3. postural drainage positioning
4. percussion & vibration
5. ROM exercises
2. relaxation techniques
3. postural drainage positioning
4. percussion & vibration
5. ROM exercises
15
New cards
what intervention(s) are contraindicated w/ chest tube?
positive pressure devices
16
New cards
peripheral IV (PIV)
- provides short-term access for delivery of meds, fluids, electrolytes, nutrients, or blood product transfusions into a peripheral vein
- usually placed in UE
- usually placed in UE
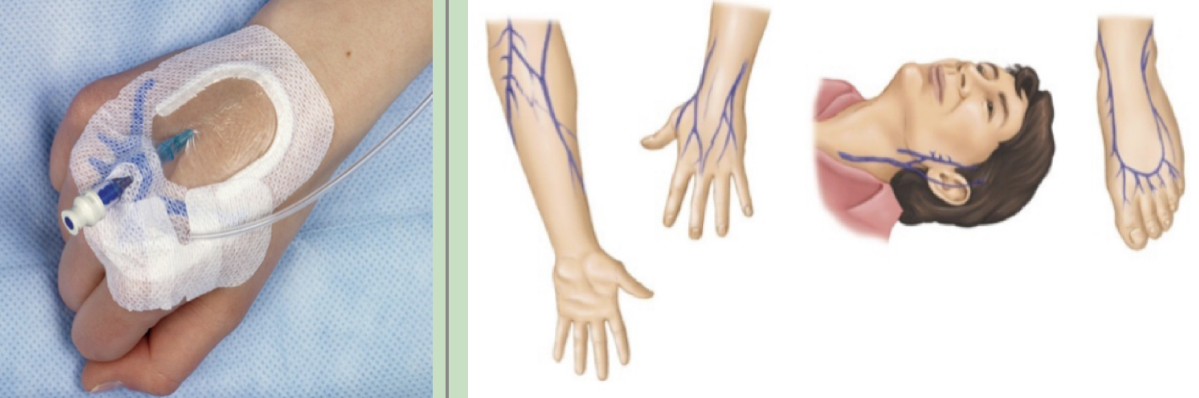
17
New cards
peripheral IV (PIV)
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. avoid raising UE above level of IV med for any length of time to prevent backflow
2. watch out if IV solution is dangerously low/close to empty (air embolism)
3. ==complications==: kinks, phlebitis, infiltration (non-vesicant), extravasation (vesicant)
4. no contraindications
18
New cards
phlebitis
localized redness, p!, heat, & swelling
19
New cards
infiltration
p!, swelling, cool skin, tightening skin around insertion
20
New cards
extravasation
p!, swelling, cool skin, tightening skin around insertion + burning, stinging + redness + tissue injury (necrosis, blisters)
21
New cards
infiltration vs. extravasation treatment
* __**infiltration**__ (**non-vesicant** drug leaking into surrounding tissue) may cause mild discomfort and simply require stopping infusion + re-insertion elsewhere
* __**extravasation**__ (**vesicant**) requires stopping infusion + antidote (if necessary) + ice then warm compress
* __**extravasation**__ (**vesicant**) requires stopping infusion + antidote (if necessary) + ice then warm compress
22
New cards
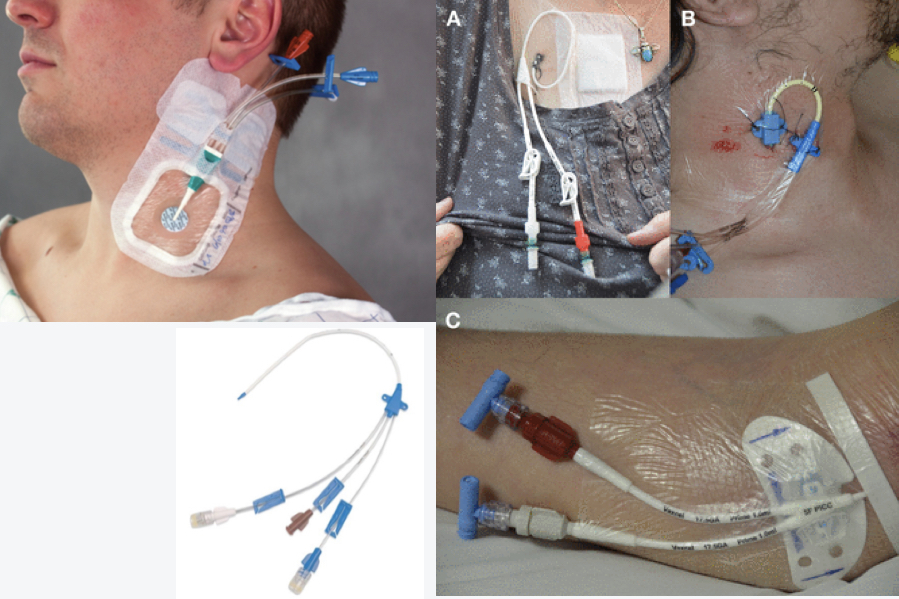
may have 2-3 ports
* central venous catheter (CVC)
* central line
* central line
23
New cards
central venous catheter (CVC / central line)
* allow venous access for 6 days or longer
* %%indications%%: hypovolemic shock, nutrition, repeated blood samples, drug administration, dialysis (temporary access port)
* access to SVC, jugular, subclavian or femoral vein
* %%indications%%: hypovolemic shock, nutrition, repeated blood samples, drug administration, dialysis (temporary access port)
* access to SVC, jugular, subclavian or femoral vein
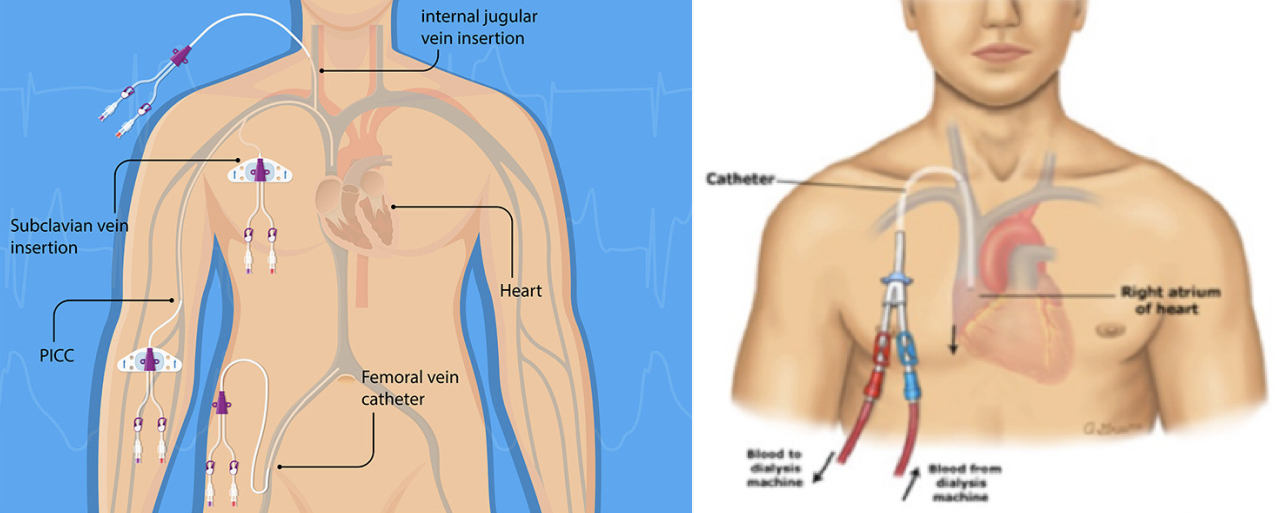
24
New cards
central venous catheter (CVC, central line)
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. ==no BP cuff== on involved UE
2. catheter dislodgement unlikely; little mobility restrictions
3. ==femoral line contraindications==: repetitive hip flexion (cycling), sometimes hip flexion > 45°
25
New cards
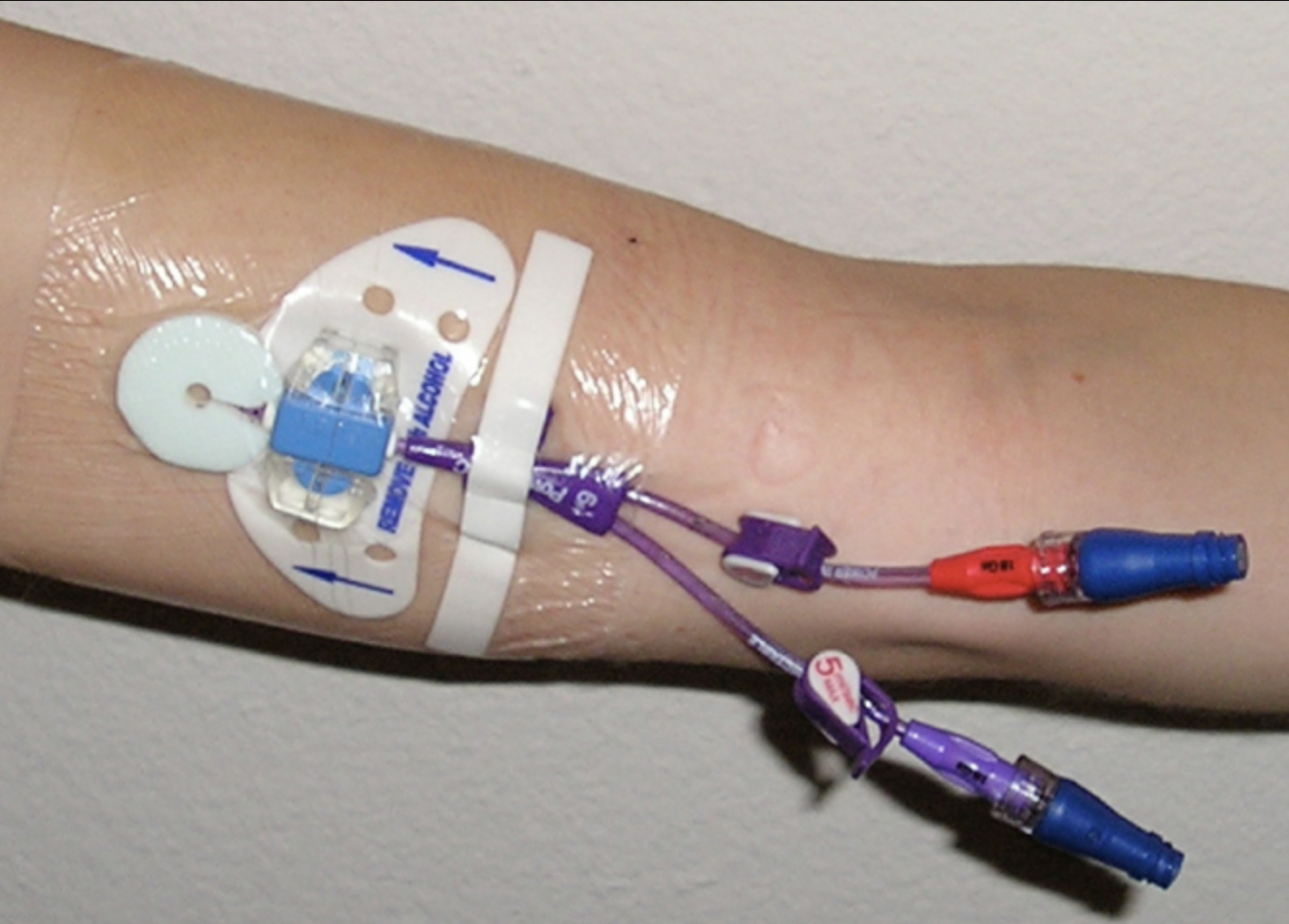
peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC line)
26
New cards
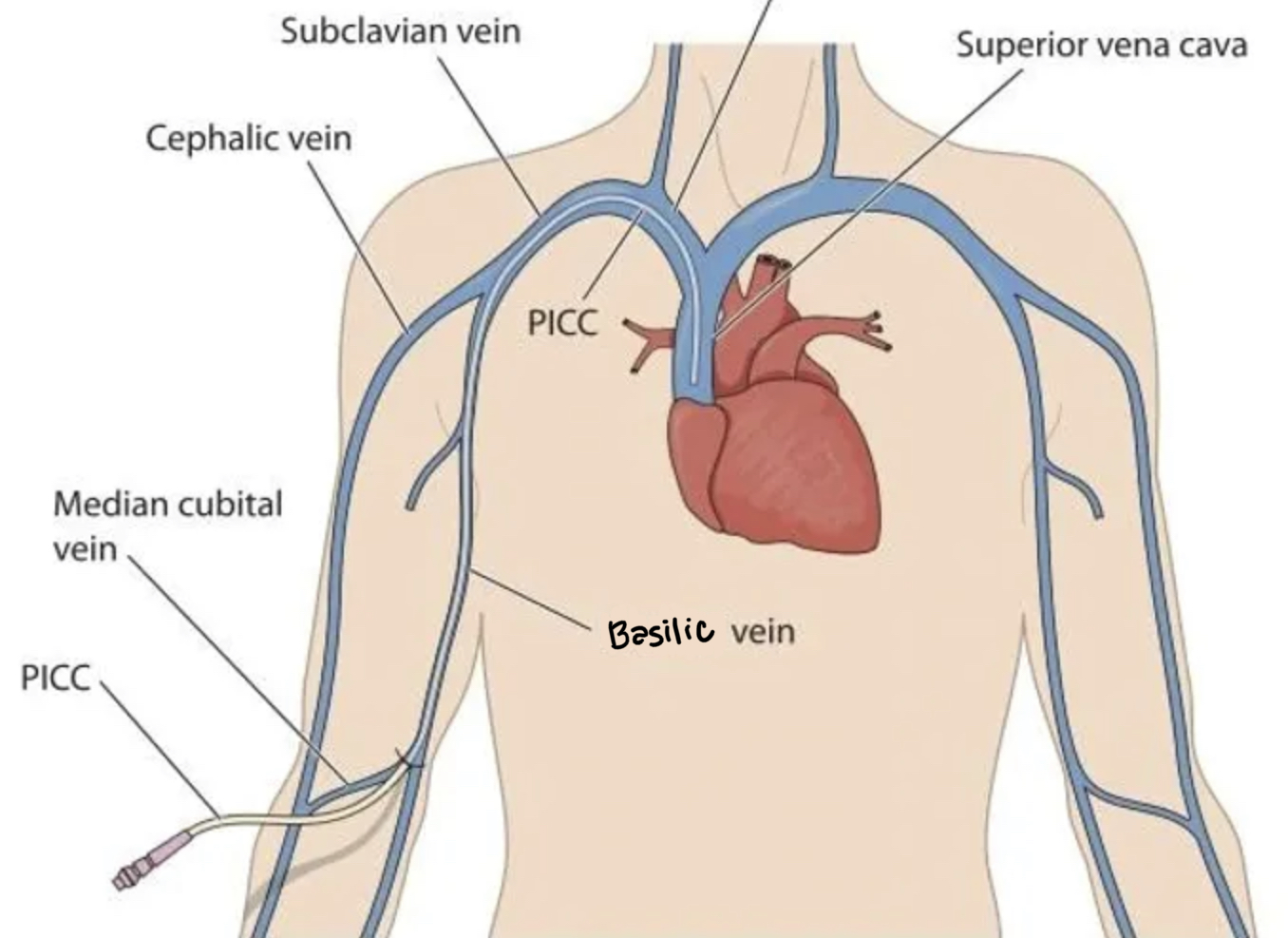
peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC line)
- type of CVC/central line
- placed in UE vein (basilic, medial cubital) w/ direct access to SVC
- placed in UE vein (basilic, medial cubital) w/ direct access to SVC
27
New cards
peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC line)
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. ==no BP cuff== on involved UE
2. ==no axillary crutches== if PICC is in basilic vein
3. activity is not limited; encourage ROM of involved UE
28
New cards
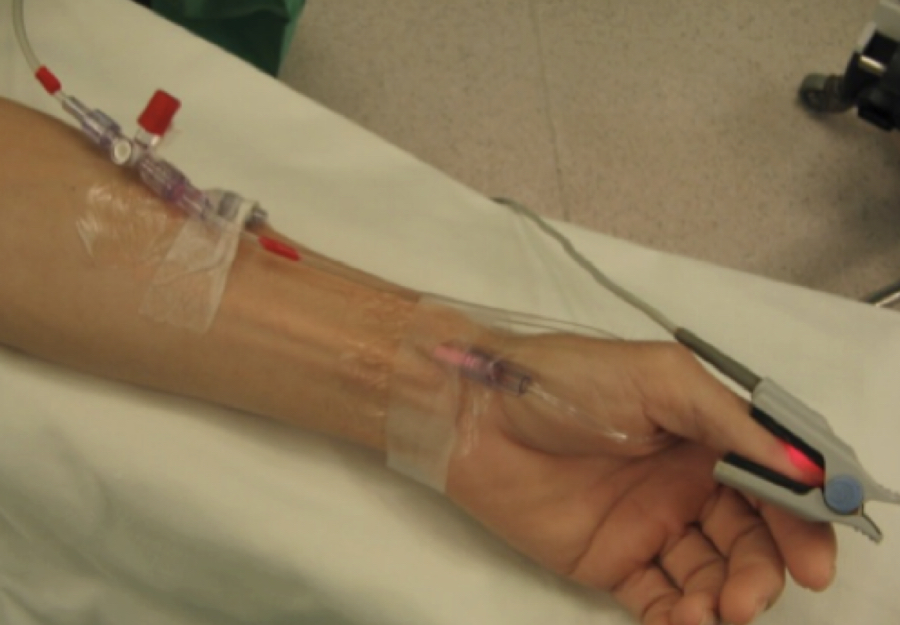
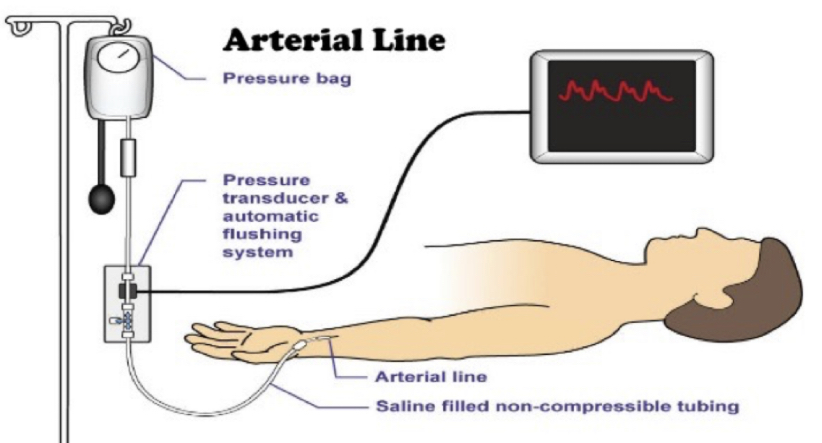
* central arterial catheter (CAC)
* arterial line (A-line)
* arterial line (A-line)
29
New cards
central arterial catheter (A-line)
* monitor intra-arterial BP (SBP, DBP, MAP) or get repeated blood gas samplings
* NOT for med adminstration
* placed in brachial, **radial**, or femoral artery
* NOT for med adminstration
* placed in brachial, **radial**, or femoral artery
30
New cards
central arterial catheter (A-line)
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. early mobilization is safe, though hip flexion may be limited (
31
New cards
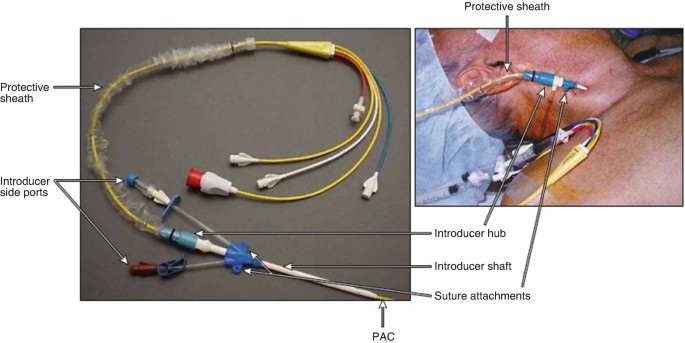
* Swan-Ganz catheter
* pulmonary artery (PA) catheter
* PA line
* pulmonary artery (PA) catheter
* PA line
32
New cards
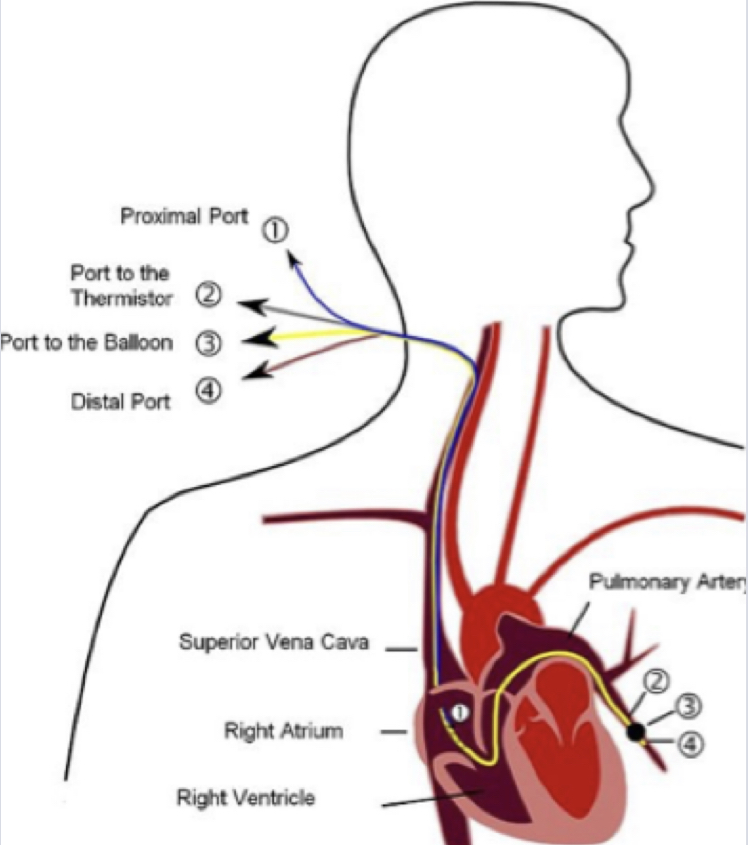
Swan-Ganz catheter (pulmonary artery catheter or PA line)
* type of central arterial catheter
* used to measure pressures of the heart + CO, pulmonary artery pressure, oxyhemoglobin saturation
* usually used w/ VERY ILL pts; be cautious w/ head & neck movements to avoid pulling it out
* used to measure pressures of the heart + CO, pulmonary artery pressure, oxyhemoglobin saturation
* usually used w/ VERY ILL pts; be cautious w/ head & neck movements to avoid pulling it out
33
New cards
what should you do if an arterial line become disloged?
1. immediate firm pressure to or above arterial insertion site to control bleeding
2. seek immediate medical assistance
34
New cards
mobile cardiac telemetry (MCT)
* measures / assesses HR, rhythm, conduction, variability, arrhythmias. can also detect RR
* can monitor ECG for an extended period of time (standard ECG only records a few sec/min at atime)
* can monitor ECG for an extended period of time (standard ECG only records a few sec/min at atime)
35
New cards
what are the types of telemetry?
1. non-portable, standard ECG
1. 12 lead system (most common)
2. 3 lead system (smoke over fire, white on R)
2. portable monitors: mobile cardiac telemetry
1. holter monitor
2. insertable / implantable cardiac monitor
3. zio patch
4. exercise cardiac monitor
36
New cards
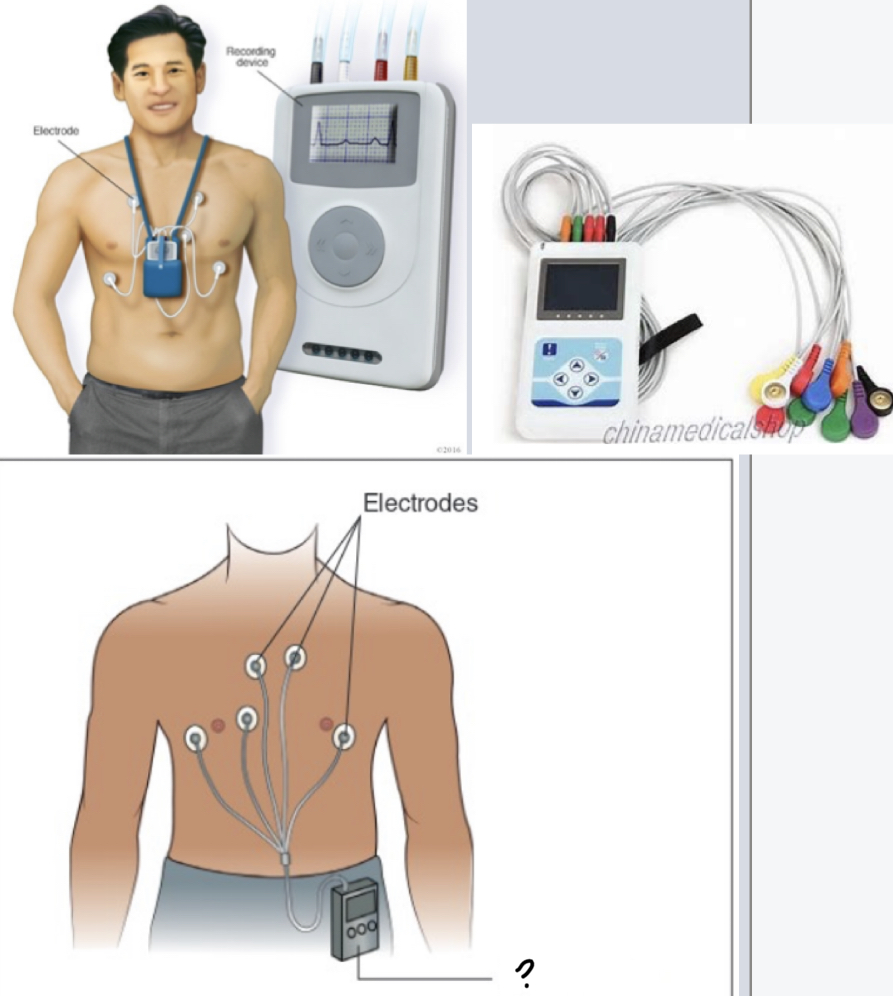
holter monitor
37
New cards
holter monitor
* used at home for up to 14 days
* device is attached by leads & cannot get wet. it records to a chip which is later analyzed at facility
* device is attached by leads & cannot get wet. it records to a chip which is later analyzed at facility
38
New cards
insertable / implantable cardiac monitor
* placed under the skin as a long-term (≥ 1 yr) Holter monitor w/o the bulk & lack of compliance
* not pacemakers; only record info
* will be detected in airport
* not pacemakers; only record info
* will be detected in airport
39
New cards
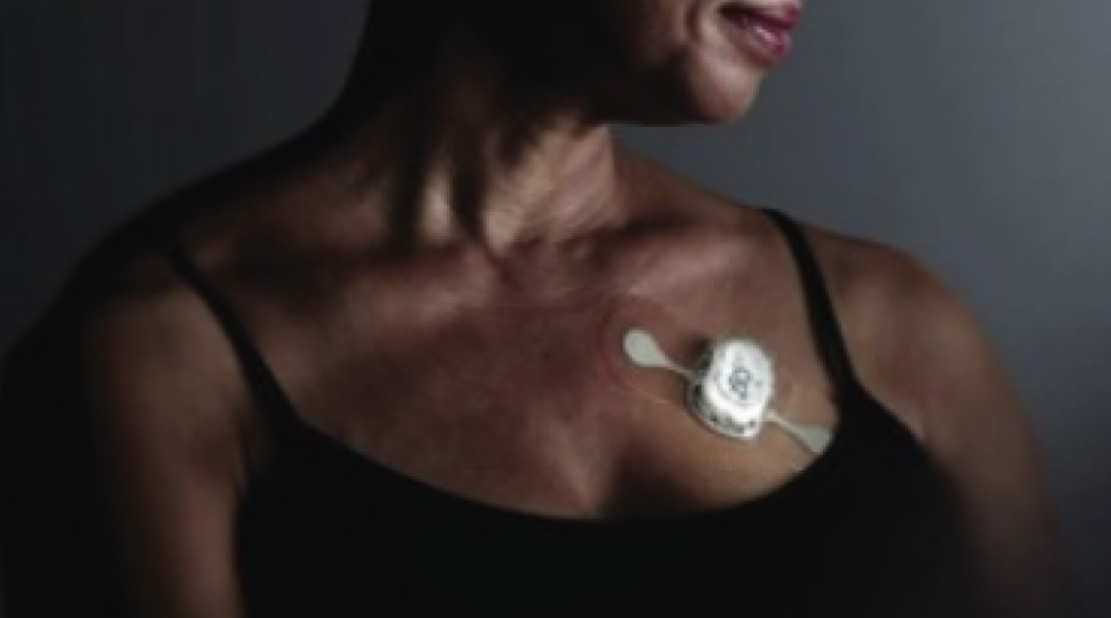
zio patch
40
New cards
zio patch
* small self-contained device that attaches directly to skin on upper L chest
* used for \~2 weeks to store heart activity data that is later analyzed
* no activity restrictions
* used for \~2 weeks to store heart activity data that is later analyzed
* no activity restrictions
41
New cards
exercise cardiac monitor
* data is detected & seen real time on PC, tablet, phone, or smartwatch for analysis of exercise parameters (HR, intensity, calories, workout time, laps, target, HR max, etc)
* ear clip, chest strap, finger sensor, wrist strap
* ear clip, chest strap, finger sensor, wrist strap
42
New cards
what info does telemetry provide PTs?
1. exercise tolerance
2. workload / intensity
3. when to @@take breaks@@ or ==STOP==
43
New cards
when should you stop exercise treatment?
1. irregular heartbeat
1. pt feels weak, dizzy, lightheaded
2. SOB
3. blurry vision
4. SpO2 drops to unacceptable levels
44
New cards
pulse oximetry (SpO2 / SaO2)
* measures % of hemoglobin saturated w/ O2 in arterial blood (%%normal%%: 95-100%)
* can also measure HR
* probe can be placed on a finger, toe, earlobe, or forehead
* can get @@burned@@ if left on too long; switch every **4 hrs**
\
* can also measure HR
* probe can be placed on a finger, toe, earlobe, or forehead
* can get @@burned@@ if left on too long; switch every **4 hrs**
\
45
New cards
what conditions/circumstances may render false SpO2 readings?
1. pt is **movin**g (eg: PD)
2. pt is **cold** (poor BF to digits)
3. **PVD** or **arrhythmia**
4. **dark nail polish**
5. **carbon monoxide intake**
46
New cards
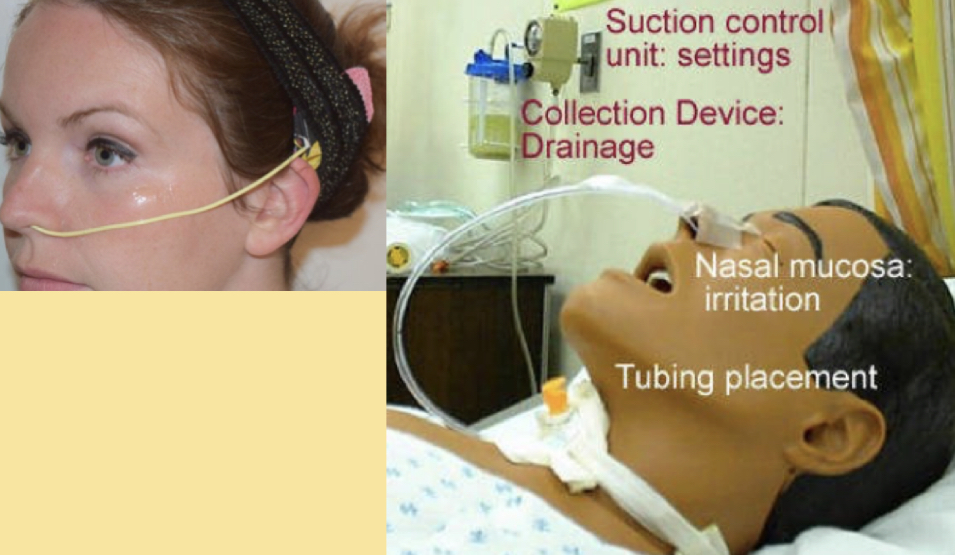
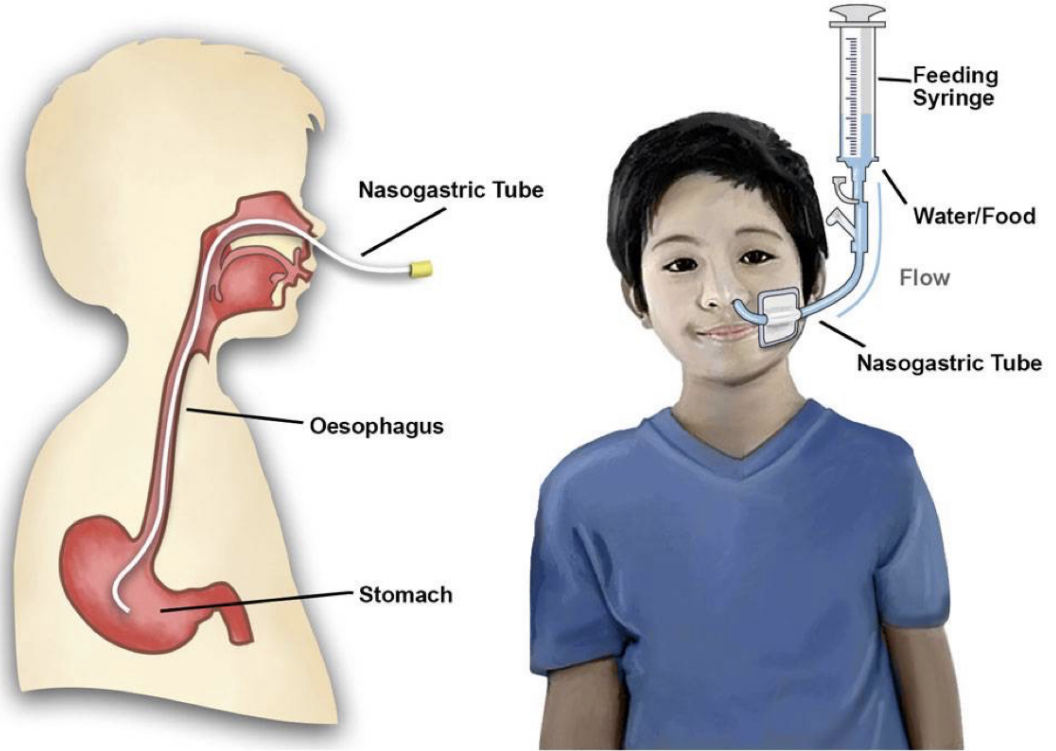
nasogastric tube (NGT)
47
New cards
nasogastric tube (NGT)
* either delivers or removes contents to/from stomach
* short-term: 2-4 wks
* "NGT" used to decribe both the feeding & suctioning system
* feeding: for people who have difficulty swallowing or are sedated and can't physically eat
* "chocolate milk"
* suctioning: pumps stomach; for people w/ gastric disorders
* green, black stuff
* short-term: 2-4 wks
* "NGT" used to decribe both the feeding & suctioning system
* feeding: for people who have difficulty swallowing or are sedated and can't physically eat
* "chocolate milk"
* suctioning: pumps stomach; for people w/ gastric disorders
* green, black stuff
48
New cards
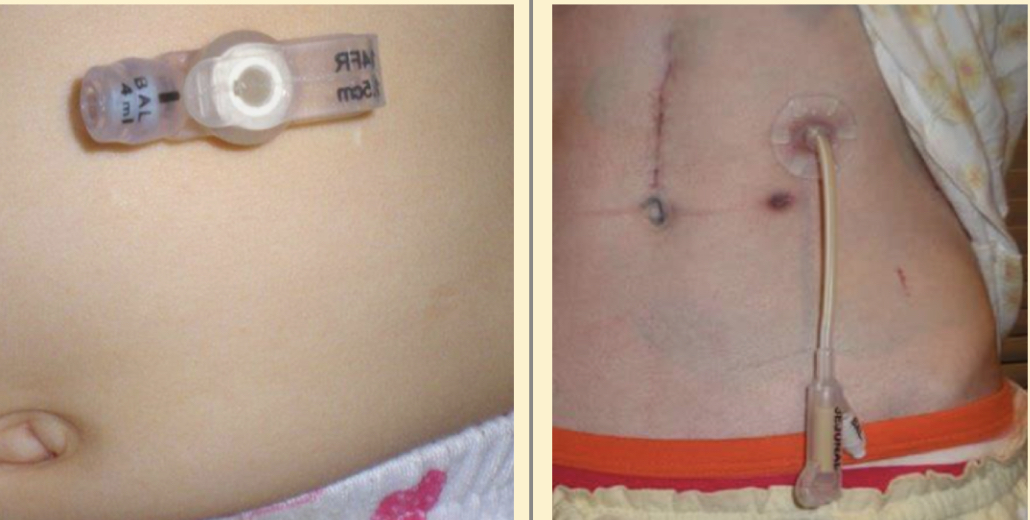
* gastric tube (Gtube)
* PEG tube
* PEG tube
49
New cards
gastric tube / PEG tube
* provides long-term access for nourishment to pts who have:
* dysphagia (TBI, stroke)
* inability to tolerate food by mouth
* nasoenteral obstruction
* %%ok to be prone, crawl, etc%%
* dysphagia (TBI, stroke)
* inability to tolerate food by mouth
* nasoenteral obstruction
* %%ok to be prone, crawl, etc%%
50
New cards
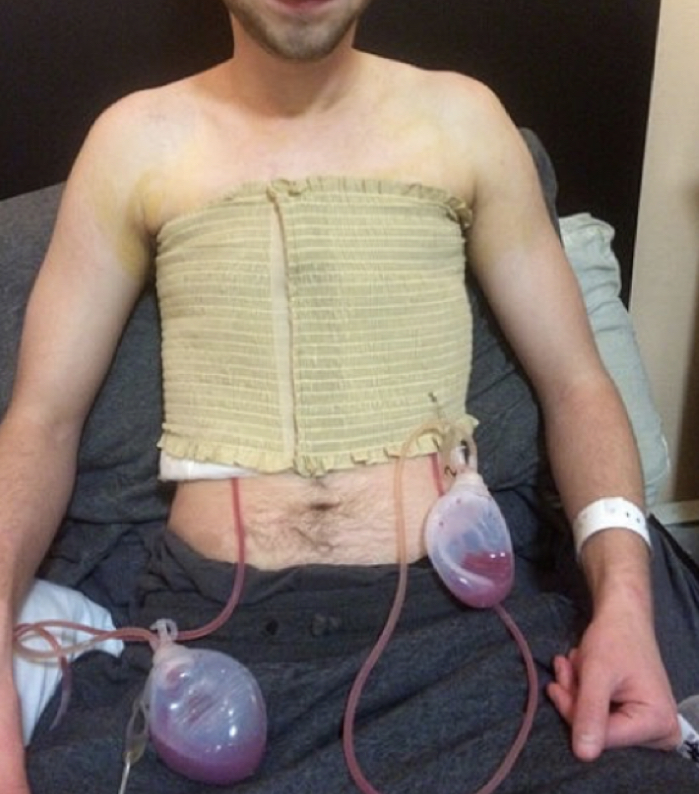
Jackson Pruitt (JP) drain
51
New cards
Jackson Pruitt (JP) drain
* "grenade drain"
* closed suction medical devices that are commonly seen post-op in order to collect fluid from surgical sites
* no suction, just allows fluid to naturally drain out
* hang pretty low w/ long line; may pin to pt’s clothing
* step down from chest tubes
* used when there isn't as much drainage
* closed suction medical devices that are commonly seen post-op in order to collect fluid from surgical sites
* no suction, just allows fluid to naturally drain out
* hang pretty low w/ long line; may pin to pt’s clothing
* step down from chest tubes
* used when there isn't as much drainage
52
New cards
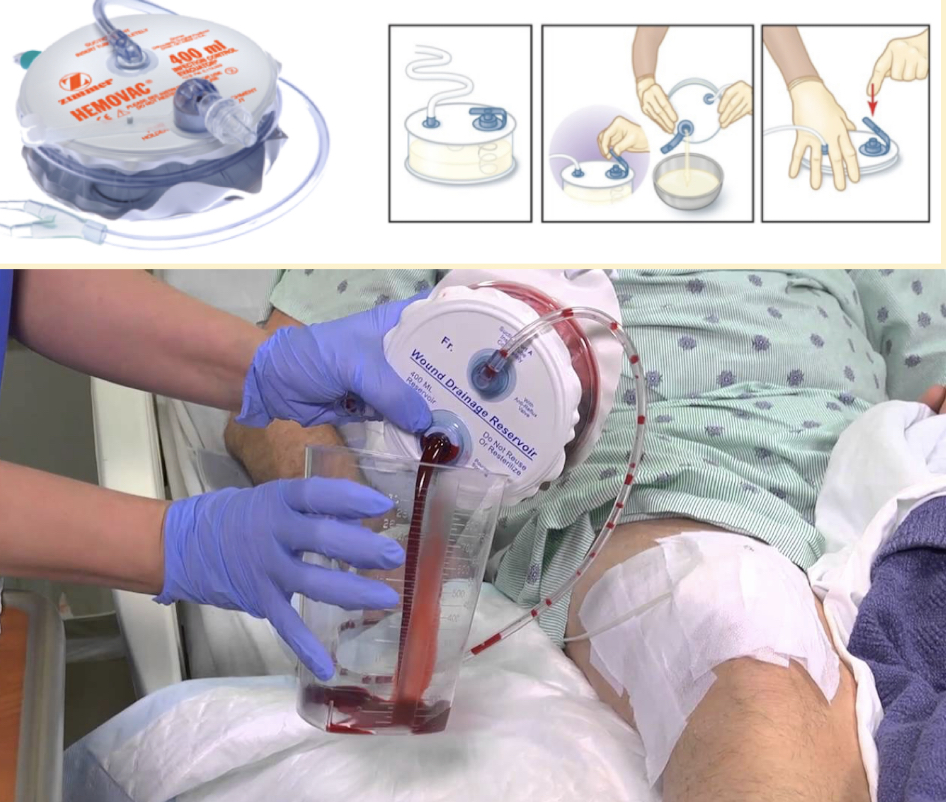
hemovac drain
53
New cards
hemovac drain
* used for a lot of ortho surgeries
* as blood fills, it expands. easy to drain out
* as blood fills, it expands. easy to drain out
54
New cards
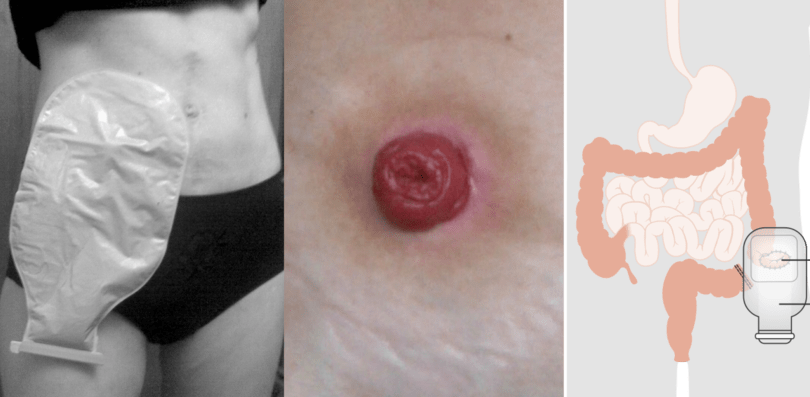
colostomy / ostomy
55
New cards
colostomy / ostomy
* opening in the large intestine that is attached to an ostomy system
* provides an alternative channel for feces to leave the body
* can empty with syringe
* common in pediatrics & geriatrics
* be conscious during @@tummy time@@
* provides an alternative channel for feces to leave the body
* can empty with syringe
* common in pediatrics & geriatrics
* be conscious during @@tummy time@@
56
New cards
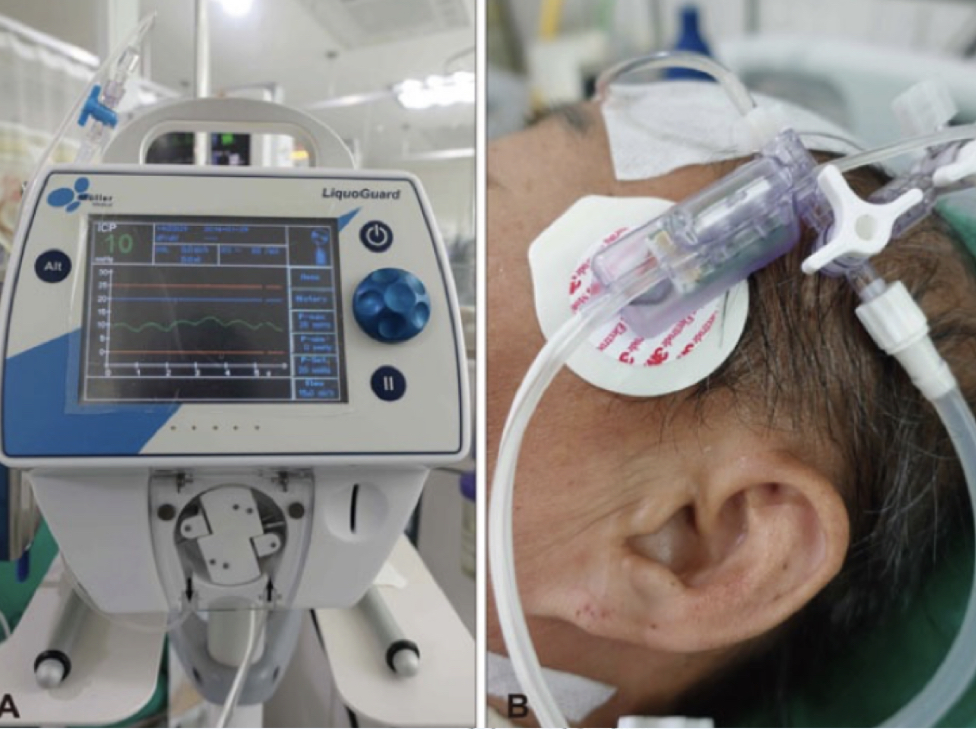
intracanial pressure monitor (ICP)
57
New cards
intracanial pressure monitor (ICP)
* catheter is most common, allows both monitoring & draining
* %%indications%%: neuro insult w/ swelling (MVA, TBI, brain surgery)
* %%indications%%: neuro insult w/ swelling (MVA, TBI, brain surgery)
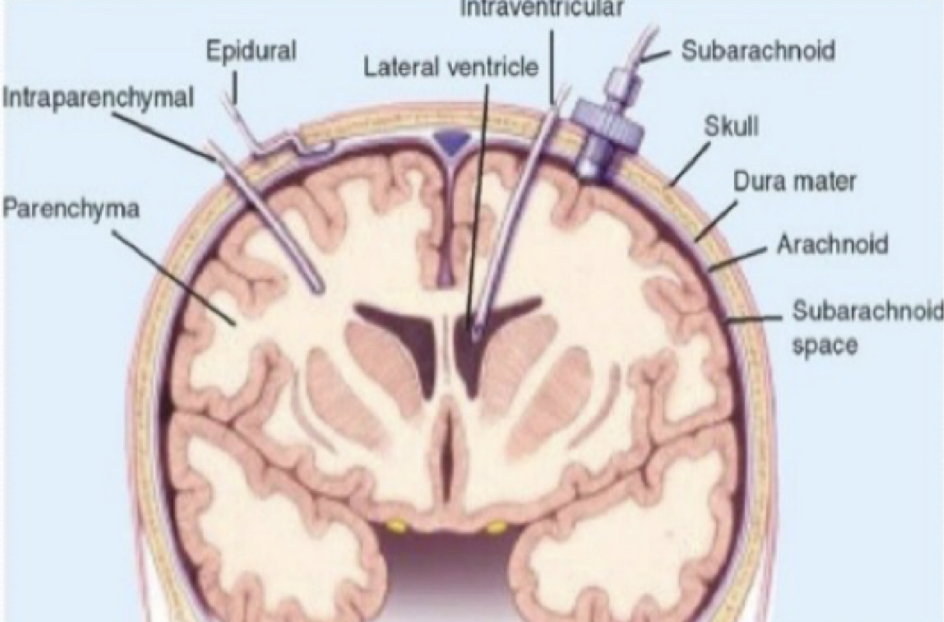
58
New cards
intracranial pressure monitor (ICP)
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
* momentary increases in ICP during movement is normal unless > 5 min in duration
* position w/ elevated HOB (30°) to maximize venous blood flow and decrease ICP
* position w/ elevated HOB (30°) to maximize venous blood flow and decrease ICP
59
New cards
mechanical ventilation
60
New cards
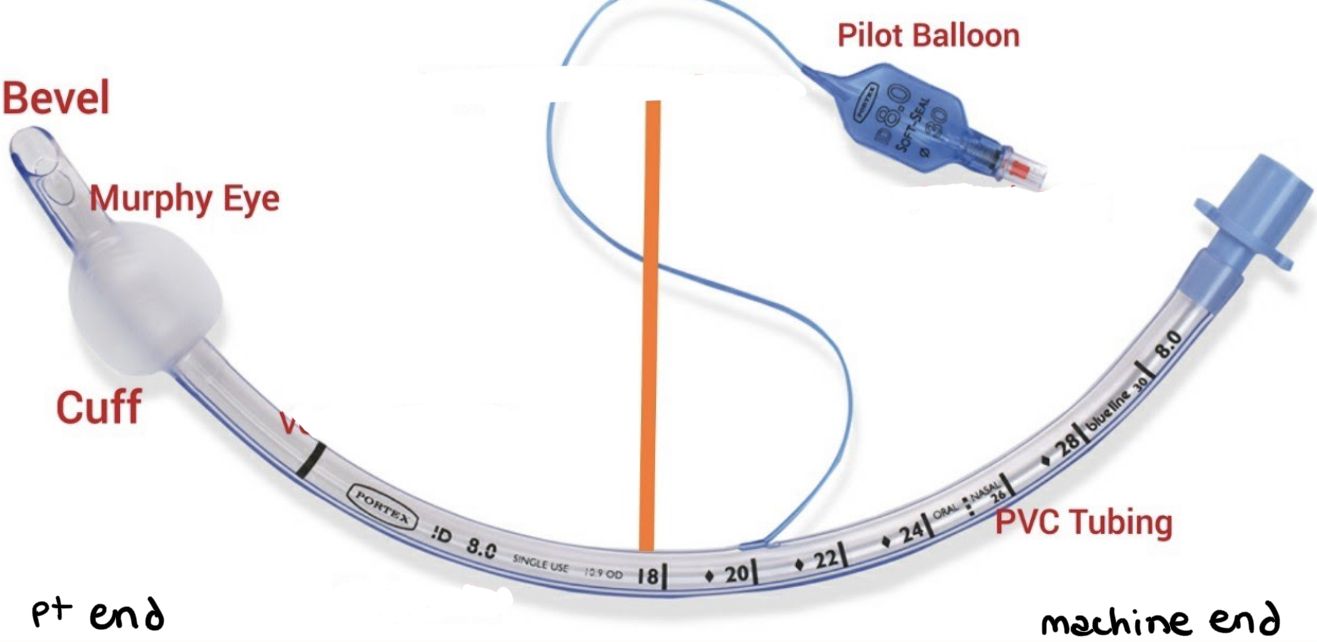
endotracheal tube
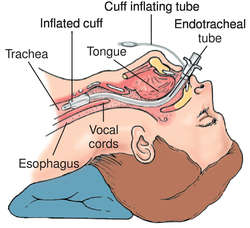
61
New cards
what types of intubation are required for pts receiving mechanical ventilation to connect trachea to ventilator?
1. endotracheal tube (oral - taped)
2. nasotracheal tube (nasal - taped)
3. tracheal or tracheostomy tube (sutured)
1. used for long-term ventilation or if there is an obstruction in the trachea
62
New cards
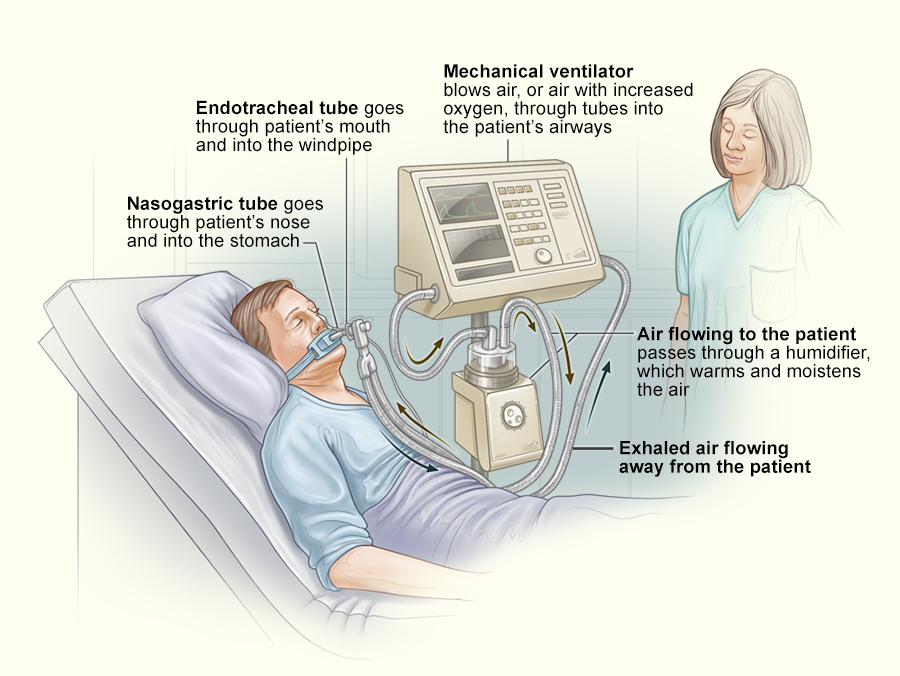
how does mechanical ventilation work?
* ventilator pushes mixture of air & O2 into pt’s lungs. can hold a constant amt of low pressure (positive end-expiratory pressure, PEEP) to keep alveoli from collapsing
* can support or replace spontaneous ventilation
* can support or replace spontaneous ventilation
63
New cards
what are the benefits of mechanical ventilation?
1. provides positive pressure to inflate lungs
2. decreases work of breathing & muscle fatigue
3. provides access for pulmonary hygiene (suctioning)
4. supports gas exchange
5. reverses hypoxemia & acute respiratory acidosis (by removing CO2)
64
New cards
mechanical ventilation
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. avoid placing ==extensive tension on or movement of tube==, which reduces optimal ventilation
1. make sure tube doesn’t slide too far down & out; note where markings are at mouth or teeth
2. monitor vitals & other pulmonary function signs
3. elevate HOB b/t 30-45° at all times if pt condition allows
4. %%no absolute contraindications%%; can use stationary devices for bedside PT like peddlers, free weights, therabands, etc
65
New cards
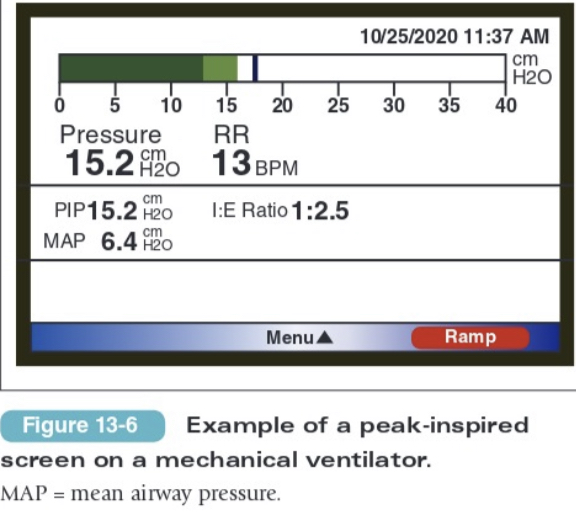
what can peak inspired pressure (PIP) > 30 cm H2O indicate?
1. kinked tube
2. need for suctioning
3. bronchospasm
66
New cards
what does a ==red== alarm on a mechanical ventilator indicate?
apnea or disconnected circuit
67
New cards
what does a yellow alarm on a mechanical ventilator indicate?
low TV, high RR, or high pressure (PP)
68
New cards
what are signs that a pt weaning off mechanical ventilation needs to rest?
1. RR increases,
2. TV decreases, OR
3. increase in accessory muscle use
69
New cards
what are the indications & pt populations associated w/ supplemental O2 (O2 delivery systems)?
1. __indications:__ SaO2
70
New cards
oxygen delivery systems
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. ensure that order for PT stipulates SaO2 (eg, maintain SaO2 > 90%) so you can titrate O2 flow during activity
2. nasal cannula —> venturi mask —> manual resuscitator bag / non-rebreather mask
3. assess vitals, heart rhythm, & other signs of distress
4. return flow rate to original setting after treatment
5. include breathing exercises, other activities & rest intervals
71
New cards
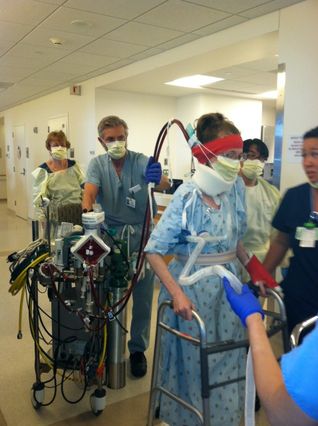
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
72
New cards
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
* oxygenates blood & removes CO2 (filters blood; does the work of the heart & lungs for you)
* %%indications%%: cardiac or respiratory failure that isn't responding to medical therapy
* most severe form of life support you can be on
* may be on ventilator to prevent atelectasis
* %%indications%%: cardiac or respiratory failure that isn't responding to medical therapy
* most severe form of life support you can be on
* may be on ventilator to prevent atelectasis
73
New cards
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
1. ambulation depends on type of ECMO
1. venous-venous (V-V): used for respiratory issues, often need to ambulate a certain distance prior to surgery
2. venous-arterial (V-A): not standard practice
2. watch for @@skin discoloration@@ (embolism, LE ischemia)
3. @@neuro screen@@: post-pump chorea
74
New cards
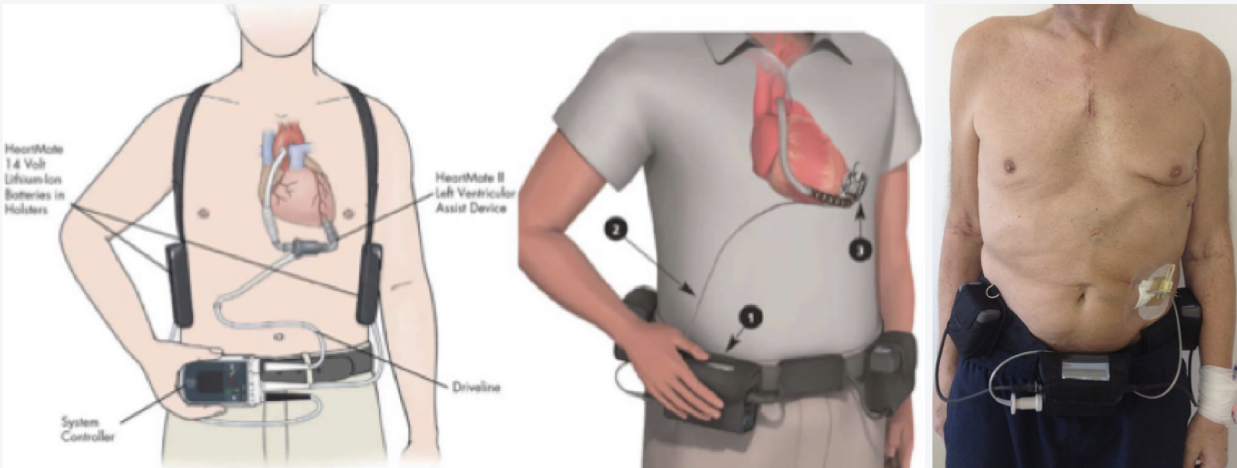
\
ventricular assist device
75
New cards
ventricular assist device
* provides prolonged circulatory assistance in pts who have acute or chronic ventricular failure
* helps pump blood through the body
* NYHA class III & IV, cardiac index (CI) < 1.8 LPM
* can be used as a bridge to transplant or "destination therapy"
* helps pump blood through the body
* NYHA class III & IV, cardiac index (CI) < 1.8 LPM
* can be used as a bridge to transplant or "destination therapy"
76
New cards
pacemaker
* small device that is placed in the chest (upper L) or abdomen to help control abnormal heart rhythms
* typically set at about 60 bpm
* typically set at about 60 bpm
77
New cards
what intervention(s) are contraindicated for pts w/ pacemakers?
e-stim
78
New cards
automatic internal cardiac defibrillator (AICD)
* placed in chest under skin like a pacemaker (may have both)
* can deliver shocks to a pt in an arrhythmia
* if someone goes into an irregular rhythm, this shocks them back into a normal rhythm
* life vest does the same thing but externally
* can deliver shocks to a pt in an arrhythmia
* if someone goes into an irregular rhythm, this shocks them back into a normal rhythm
* life vest does the same thing but externally
79
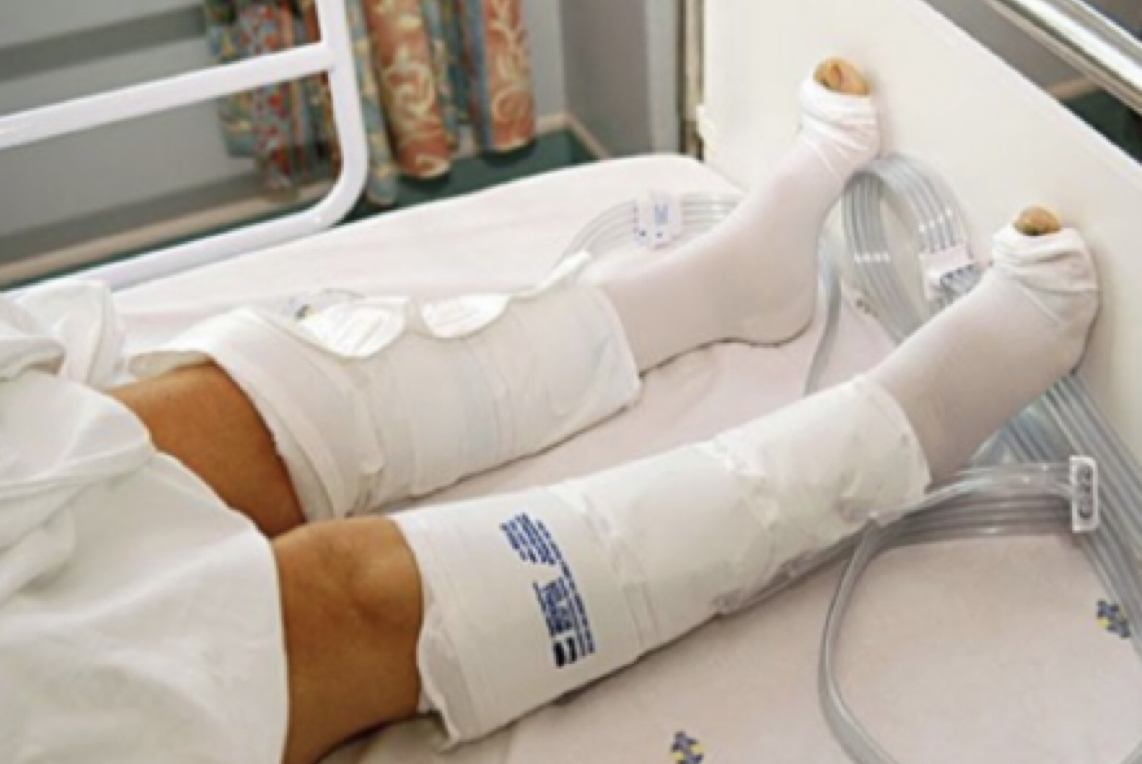
New cards
sequential compression devices (SCD)
80
New cards
sequential compression devices (SCD)
* provides intermittent pressure (squeezing) to the LEs to promote venous return & prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
* best way to prevent DVT is early ambulation + TED hose (the compression stocking underneath SCD that applies continuous pressure)
* best way to prevent DVT is early ambulation + TED hose (the compression stocking underneath SCD that applies continuous pressure)
81
New cards
sequential compression devices (SCD)
(PT implications)
(PT implications)
* reapply when pt returns to bed or chair
* discontinue when pt is ambulating on regular basis
* do not use directly over a ==fx, open wound, or cellulitis==
* discontinue when pt is ambulating on regular basis
* do not use directly over a ==fx, open wound, or cellulitis==