Melting Points
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the effects of impurities?
depresses (lower) and broadens the MP range.
How do you identify an unknown using mixed melting points?
Do a mixed melting point with known sample and unknown
Take MP values as normal
If the range is low and wide, then the sample is impure and there are two different compounds present in our melting point. If the range is within 1-2 C, then the compound is pure.
Decomposition
solid darkens to a black solid without liquefying; usually a sharp range is observed.
Polymorphs
different crystalline forms of a solid that have different mp ranges.
ex: diamond and graphite
Hydrates
anhydrous solid will have a different MP range compared to its hydrated form
Sublimation
sample will undergo phase change from solid directly to a gas
no real MP observed
eutectic point
the lowest temperature at which a mixture of two or more substances will completely melt, forming a eutectic mixture.
eutectic mixture
a specific combination of two or more substances that, when mixed together in certain proportions, forms a mixture with a lower melting point than any of the individual component’s original melting points.
the different regions of a melting point diagram
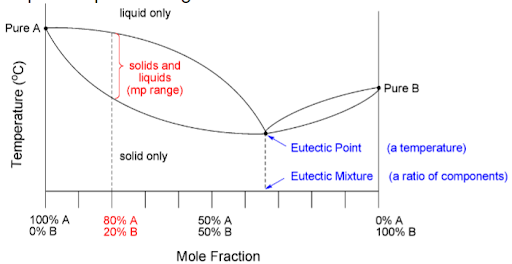
What is the heating rate for a proper melting point?
1-2 C per minute when near melting point
for quick melting point, 10 °C per minute
Describe the preparation of a melting point sample.
grind sample on spot plate
pack 1-2 mm of sample into capillary tube by dropping it down a glass tube
insert in mp apparatus and take melting point
For mixed MP, mix small, evenn amount of two different components to make a homogeneous mixture
Why take a melting point?
To aid in determining purity of a solid
To aid in determining identity of a solid