3.02. IPSec VPN Fundamentals
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is IPSec?
A suite of protocols that create secure, encrypted tunnels between networks across insecure networks such as the public internet.
What are common use cases for IPSec?
Site-to-site VPNs between geographically separated business locations or hybrid cloud connections like AWS to on-premises data centers.
What does IPSec provide?
Authentication of peers and encryption of traffic to ensure confidentiality and integrity.
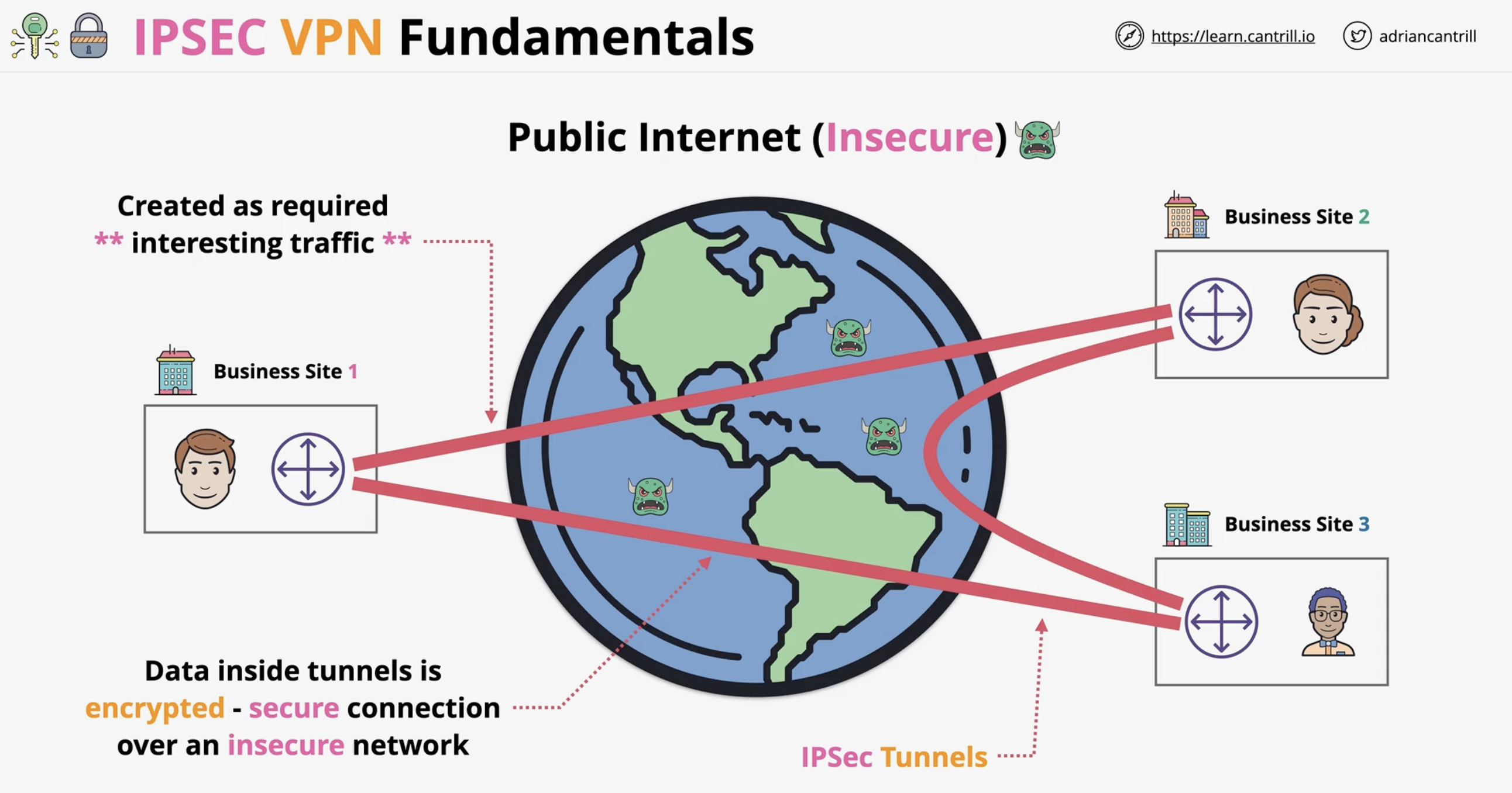
What is "interesting traffic" in IPSec?
Traffic that matches configured rules (e.g. IP ranges or port-based rules) and triggers the creation of an IPSec VPN tunnel.
When does an IPSec tunnel get torn down?
When no interesting traffic is detected for a period of time.
Why is symmetric encryption used for data transfer in IPSec?
It is faster and more efficient than asymmetric encryption for large volumes of data.
Why is asymmetric encryption used in IPSec setup?
It allows secure key exchange without transmitting the symmetric key, thus enabling both sides to independently derive it.
What are the two main phases of an IPSec VPN?
IKE Phase 1 and IKE Phase 2.
What does IKE stand for?
Internet Key Exchange.
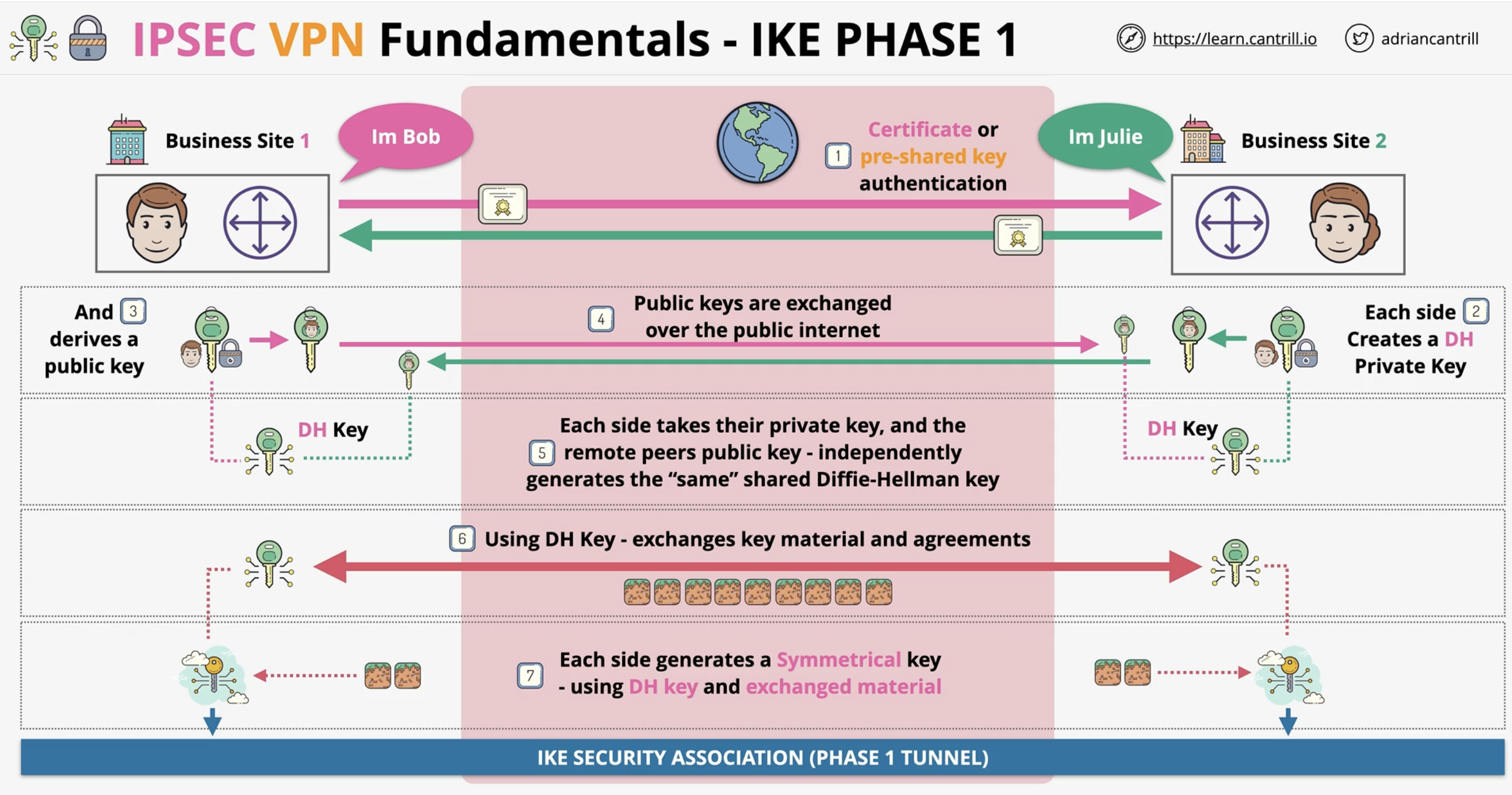
What is the purpose of IKE Phase 1?
To authenticate peers and establish a secure encrypted tunnel (Security Association) using asymmetric encryption and key exchange.
What are common authentication methods in IKE Phase 1?
Pre-shared keys or digital certificates.
What is a Security Association (SA)?
A logical construct in IPSec representing a one-way secure communication path. Two SAs are used for bidirectional communication.
What protocol handles the key exchange in IKE Phase 1?
Diffie-Hellman (DH) key exchange.
What is exchanged during the Diffie-Hellman process?
Public keys. Each side uses its private key and the other side’s public key to derive a shared secret key.
What is the outcome of IKE Phase 1?
A Phase 1 Security Association and a symmetric key used for Phase 2 negotiations.
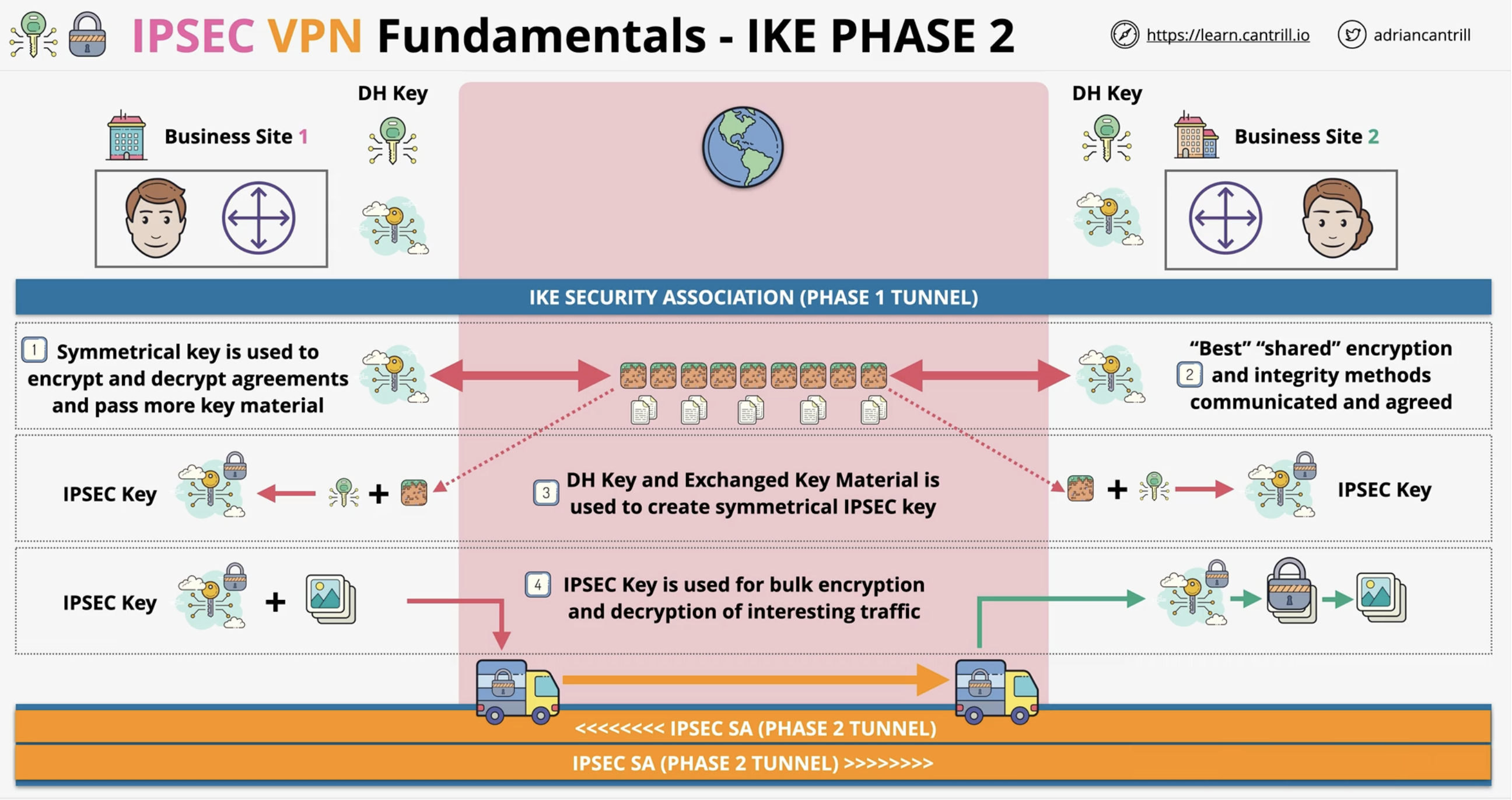
What is the purpose of IKE Phase 2?
To negotiate encryption methods and establish the keys used to protect data traffic in the IPSec tunnel.
What is derived in IKE Phase 2?
A Phase 2 (IPSec) Security Association and a new symmetric encryption key for data transfer.
Is Phase 2 slower or faster than Phase 1?
Faster – Phase 1 does the heavy cryptographic lifting.
Can the Phase 1 tunnel persist even after Phase 2 is torn down?
Yes. Phase 1 can persist, enabling rapid re-establishment of Phase 2 as needed.
How many SAs are required for communication between two peers?
Two – one for each direction of traffic.
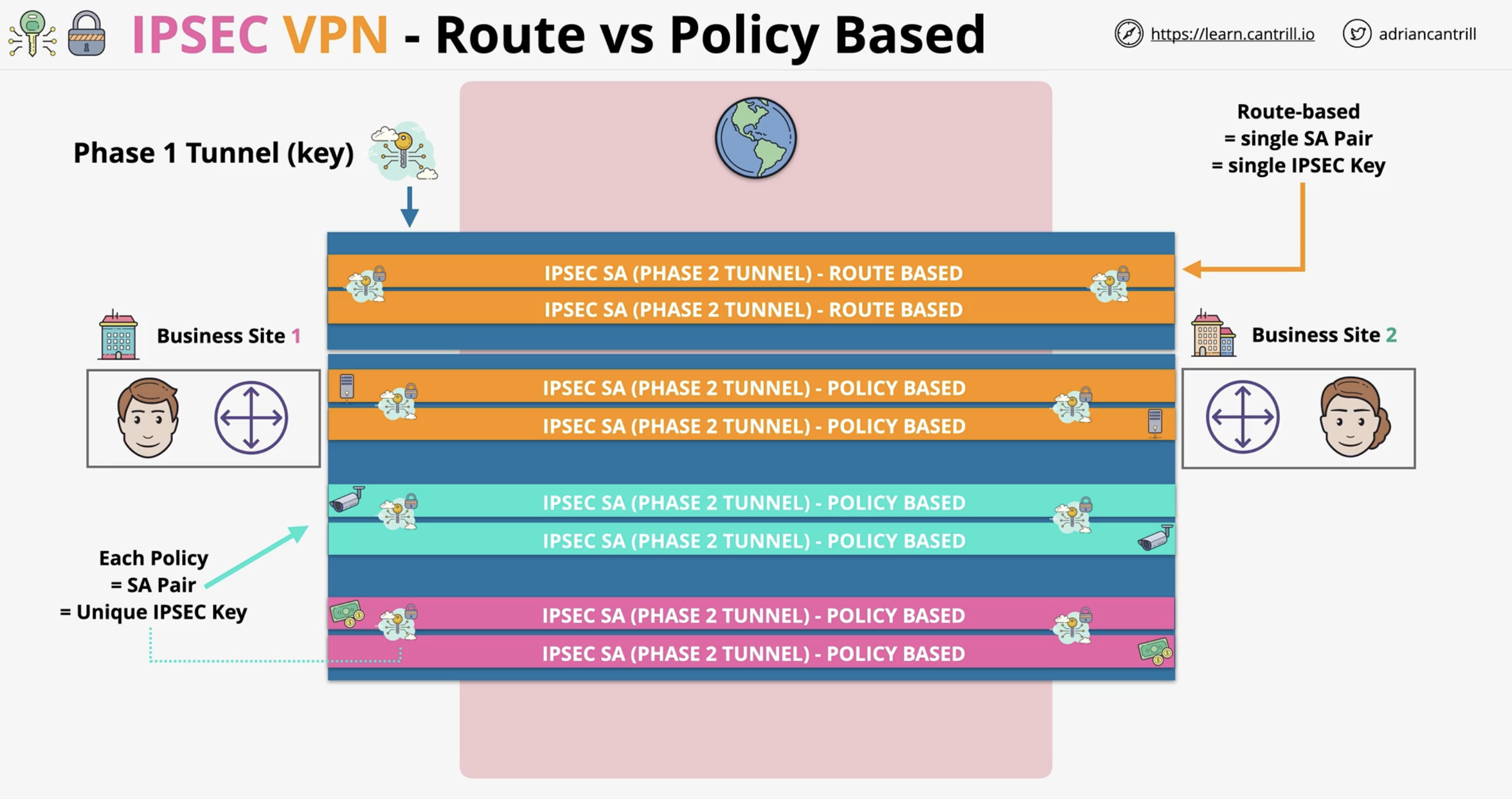
What are the two types of IPSec VPNs?
Policy-based VPNs and Route-based VPNs.
What is a Policy-based VPN?
A VPN where specific policies define which traffic is considered interesting and which SA to use. Each policy creates a distinct SA pair.
What is a Route-based VPN?
A VPN where routes (IP prefixes) define interesting traffic. One SA pair is used for all traffic between two networks.
Which VPN type allows for more granular traffic control?
Policy-based VPNs.
Which VPN type is easier to set up?
Route-based VPNs.
In a route-based VPN, how is traffic matched?
By destination prefix (e.g. 192.168.0.0/24).
In a policy-based VPN, how is traffic matched?
By detailed policies, possibly including port numbers, protocols, or specific subnets.
What does a Phase 2 tunnel rely on from Phase 1?
The symmetric key derived during Phase 1 and the security association established.
What is the benefit of the DH-derived key mechanism?
It allows secure key agreement without ever transmitting the actual symmetric key over the network.
Can multiple Phase 2 tunnels exist over a single Phase 1 tunnel?
Yes, especially with policy-based VPNs where each policy creates its own SA.
What protocol enables the mathematical basis for securely exchanging keys in IPSec?
Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
In IPSec terminology, what is a “tunnel”?
A secure logical path for encrypted traffic between two peers over an insecure network.
Why is IPSec considered secure even over the public internet?
Because it encrypts all payload traffic, uses authenticated peers, and resists tampering and eavesdropping.
Which AWS services make use of IPSec-based VPNs?
AWS Site-to-Site VPN, Transit Gateway VPNs, and sometimes custom VPNs built on EC2 instances.
How are cipher suites chosen in Phase 2?
One peer presents supported options, the other selects the strongest mutual suite, and this is used for encrypting IPSec traffic.
What does “SA pair” mean in the context of IPSec?
A bidirectional tunnel formed by two unidirectional Security Associations (one in each direction).
What happens if no interesting traffic is detected for a time?
The Phase 2 tunnel (IPSec SA) may be torn down.
Can IPSec support different encryption settings for different traffic types?
Yes, with policy-based VPNs.
Why is the Phase 1 and Phase 2 split considered elegant?
It separates heavy cryptographic operations (Phase 1) from efficient data tunneling (Phase 2), improving performance and reusability.
What is IPSEC?

What does IPSEC architecture look like over public network? What is interesting traffic?
Traffic that match certain rules. If no interesting traffic, IPSEC tunnels are torn down.
What is symmetric and asymmetric encryption in the context of IPSEC?

What are the two phases of IPSEC?

What does Phase 1 of IPSEC look like?
What does Phase 2 of IPSEC look like?
What are the two types of VPNs?

What are the two types of VPNs architecturally?