A2 Unit 3.1 & 3.3: ATP & Respiration
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Energy Transfer
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. Food contains chemical energy.
Glucose & Fatty Acids are energy rich respiratory substances that are broken down during respiration.
C-C, C-H & C-OH bonds are the high energy bonds broken during respiration.
Lower energy bonds are formed and the difference is released. Energy from respiration is transferred to ATP & released as heat.
Define Endergonic & Exergonic
Endergonic - A reaction in which energy is absorbed and stored in the products.
Exergonic - A reaction in which energy is released from the products.
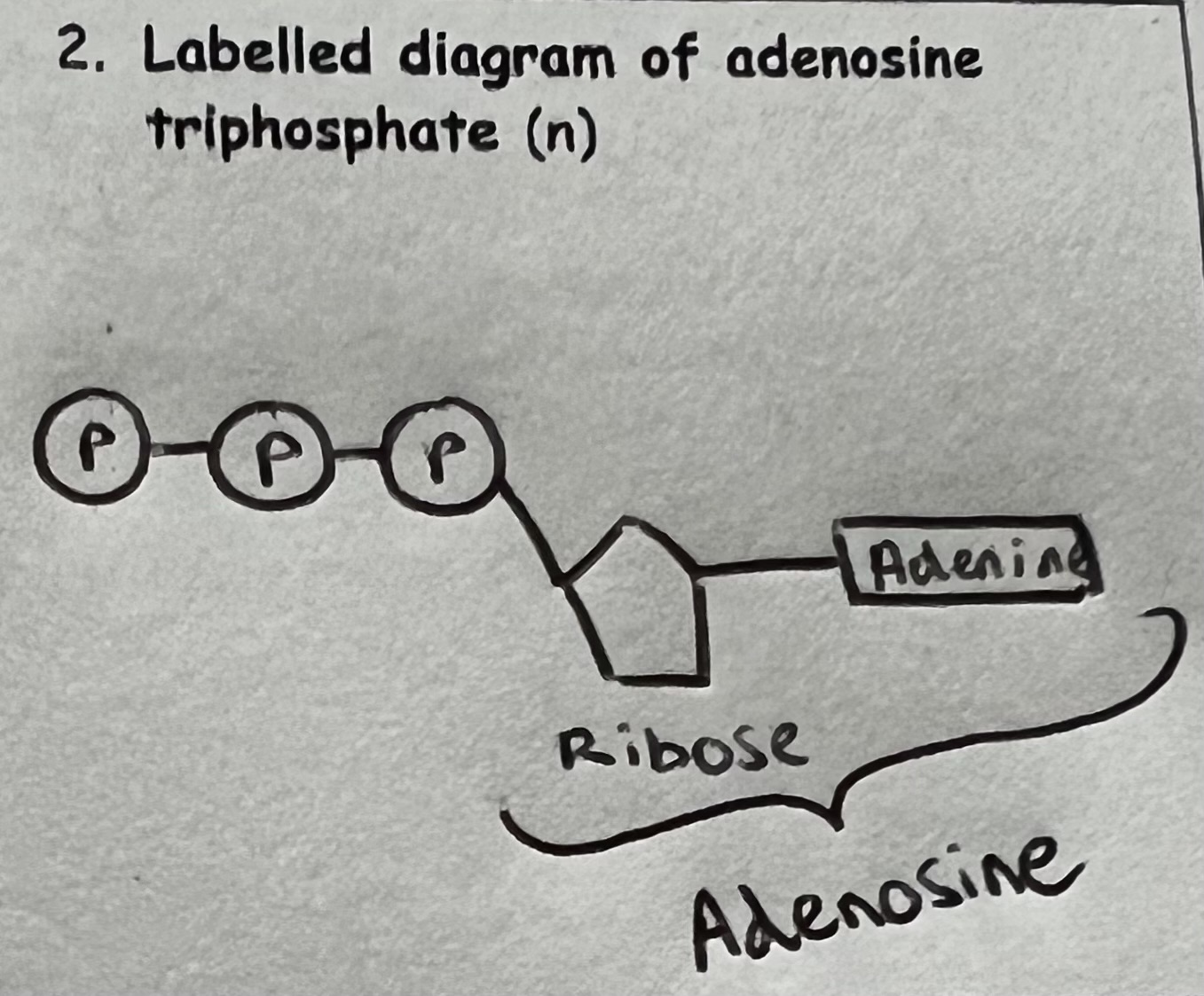
What is ATP & Synthesis of ATP?
ATP is referred to as the ‘Universal Energy Currency’ as ATP is present in all living organisms and used to provide energy for all cell reactions.
ATP Synthesis - Condensation reaction forms a bond between phosphate groups (Phosphorylation) when ADP reacts with inorganic phosphate during respiration - ADP + Pi (inorganic phosphate) —> ATP (Endergonic)
How is energy released from ATP?
ATP Breakdown - Hydrolysis reaction that breaks a bond between phosphate groups (Dephosphorylation) of ATP - ATP —> ADP + Pi + 30.6kJmol-1 (Exergonic - happens when energy is used, e.g during active transport)
High energy bond broken between (terminal/ last two) 2nd & 3rd Phosphate group by enzyme ATPase to release energy from ATP to provide energy for different chemical reactions.
Define Anabolism & Catabolism
Anabolism - Smaller molecules built up to form larger molecules.
Catabolism - Complex molecules broken down to form smaller molecules.
Advantages of ATP as an energy carrier
1 enzyme needed to break down ATP (ATPase)
Single step reaction (only 1 bond broken)
Releases small amounts of energy when and where needed
Less energy wasted and energy release controlled
Respiration
Aerobic Respiration: Glucose + Oxygen —> Carbon Dioxide + Water & 38 ATP Molecules
Anaerobic Respiration: Glucose —> Lactic Acid
Enzymes such as ATPase catalyse the series of reactions in respiration.
Respiration is Catabolic.
What is the purpose of sweating? + cause of death
More sweat to lower body temperature.
Overheating can cause rapid death of a person.
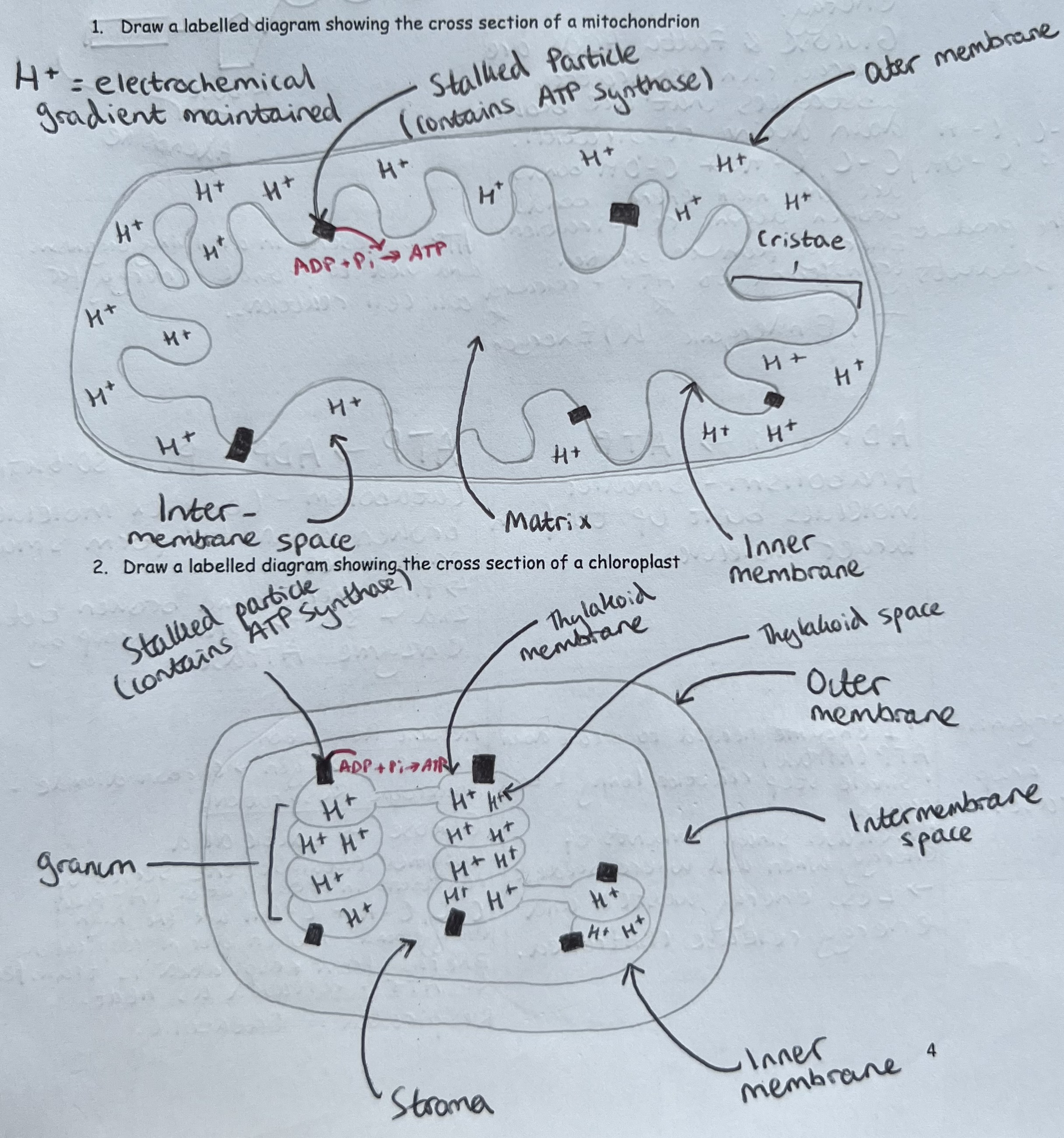
ATP production in mitochondria & chloroplasts
ATP is produced during:
Respiration (chemical energy from glucose is transduced to chemical energy in ATP)
Photosynthesis (light energy is transduced to chemical energy in ATP)
Why would a lack of ATP cause the death of a living organism?
Less ATP for protein synthesis/ active transport
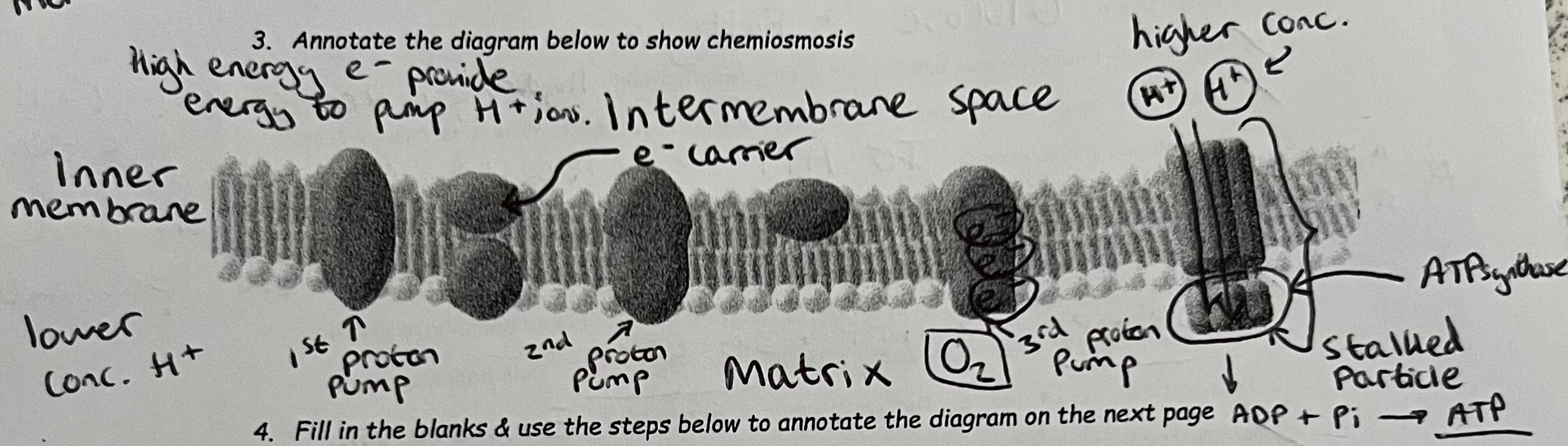
What is Chemiosmosis?
Chemiosmosis: Flow of protons down an electrochemical gradient across membranes through a stalked particle with ATP synthase (which catalyses phosphorylation of ADP into ATP)
ATP is synthesised by the enzyme ATP synthase
ATP synthetase is located in stalked particles
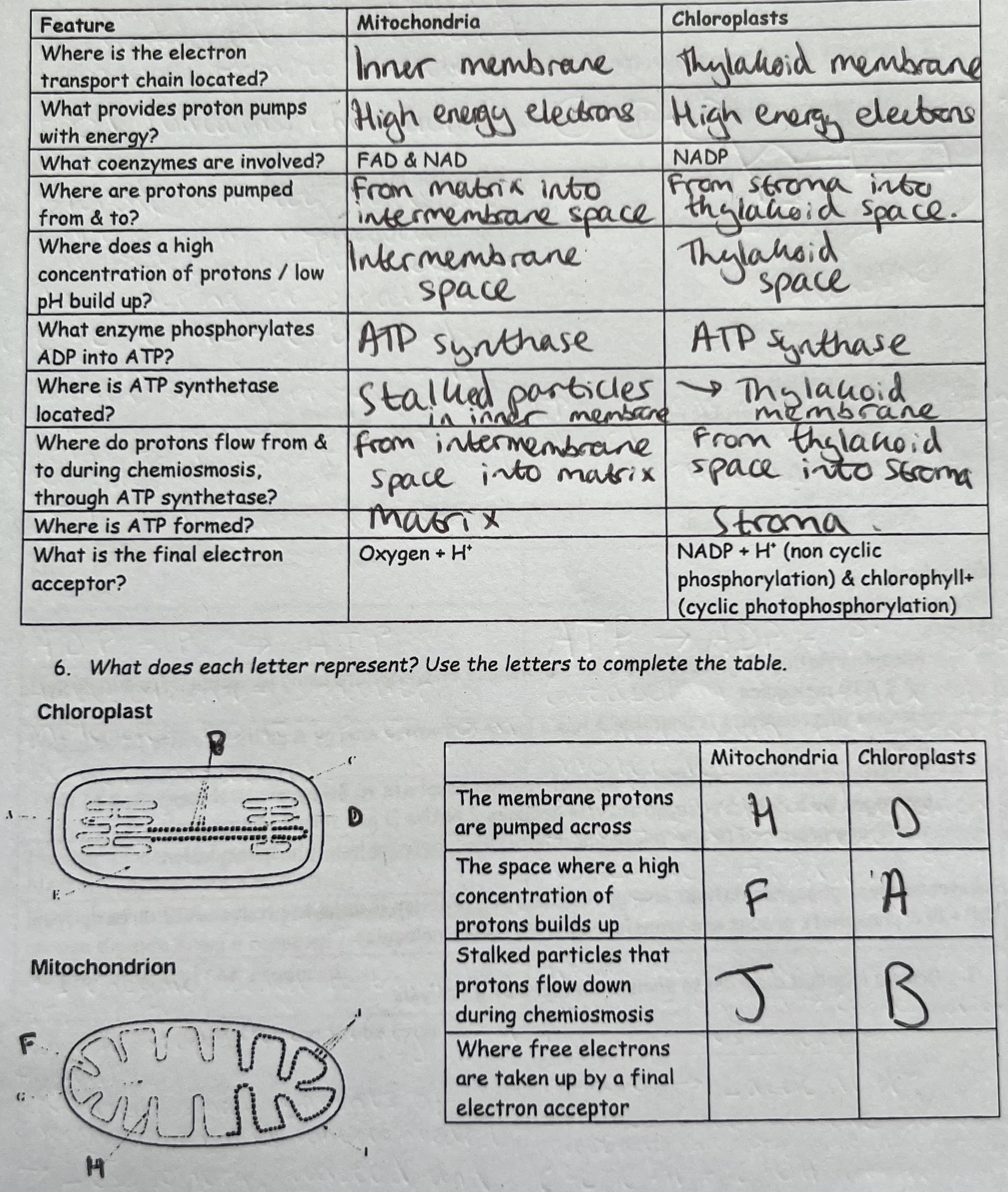
Stalked particles are present in the inner membranes (cristae) of mitochondria & thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Proton pumps are driven by potential energy from excited electrons in an electron transport chain (an alternate arrangement of proton pumps and electron carriers)

Chemiosmosis Labelled Diagram
How does the Electron Transport Chain establish an electrochemical gradient?
Reduced NAD leads to the reduction of 3 proton pumps (forming 3 ATP).
Reduced FAD leads to the reduction of 2 proton pumps (forming 2 ATP).

Describe Chemiosmosis

Chemiosmosis Labelled Diagram & How is a low concentration of H+ ions maintained in the Matrix?
In the matrix, a lower conc. of H+ ions is maintained by combining H+ (and e-) with Oxygen, to form water.
½ O2 + 2e- + 2H+ —> H2O
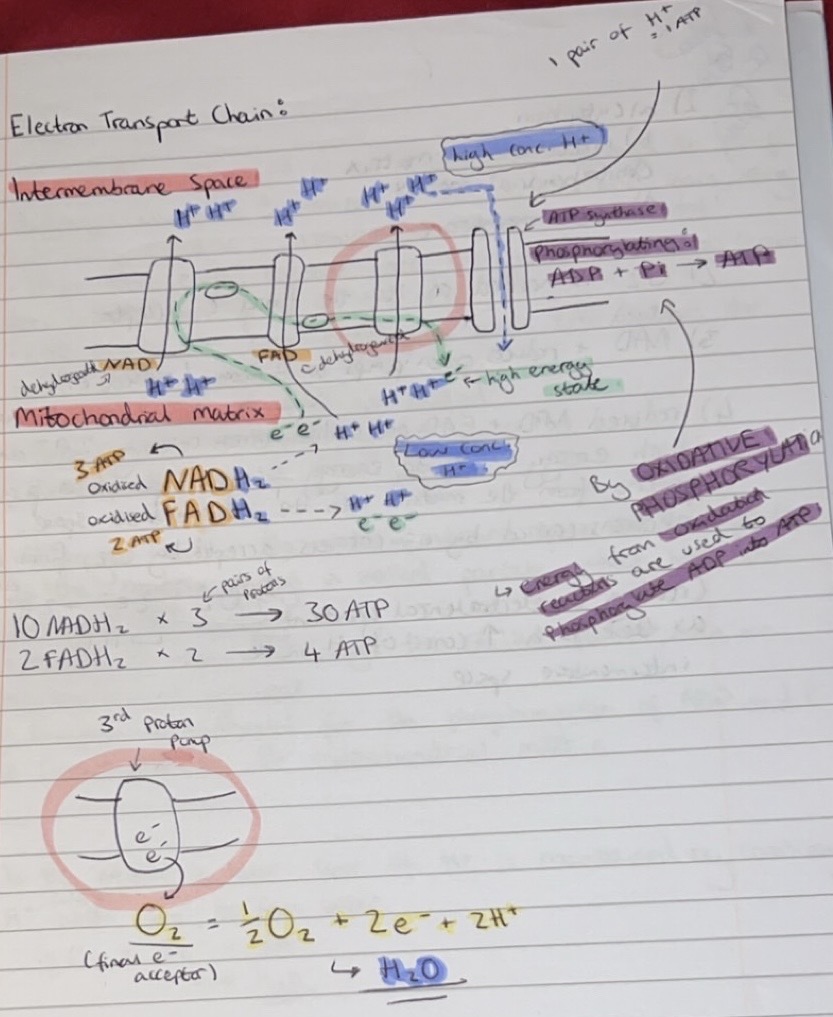
Describe Chemiosmosis
A molecule in a reduced form (has extra hydrogens attached) becomes oxidised.
The hydrogen atom passes through a proton pump. As it is passed through, an electron is removed, and the remaining proton (H+) is pumped to the other side of the membrane.
The electrons are passed from one proton pump/ electron carrier to another. The energy released in this process is used by the proton pumps to pump more protons across the membrane.
A higher concentration of protons builds up on one side of the membrane - they cannot diffuse across the membrane as the membrane is impermeable to H+. The difference in H+ concentration creates a difference in the pH. (more H+ = more acidic) and a big difference in charge across the membrane.
Embedded in the membrane are numerous stalked particles which contain the enzyme ATP synthetase.
Chemiosmosis
The protons can pass down an electrochemical gradient through a channel in the enzyme.
The protons have high energy. This energy is used by the ATP synthetase to combine ADP with organic phosphate to form ATP.
Some Hydrogen ions are pumped back across the membrane to maintain the electrochemical gradient across the membrane.
The electrons passed through the electron carrier proteins are picked up by a final electron acceptor - it also picks up some protons and is reduced in the process.
Labelled Diagrams - Electron Transport Chain, Mitochondria & Chloroplast
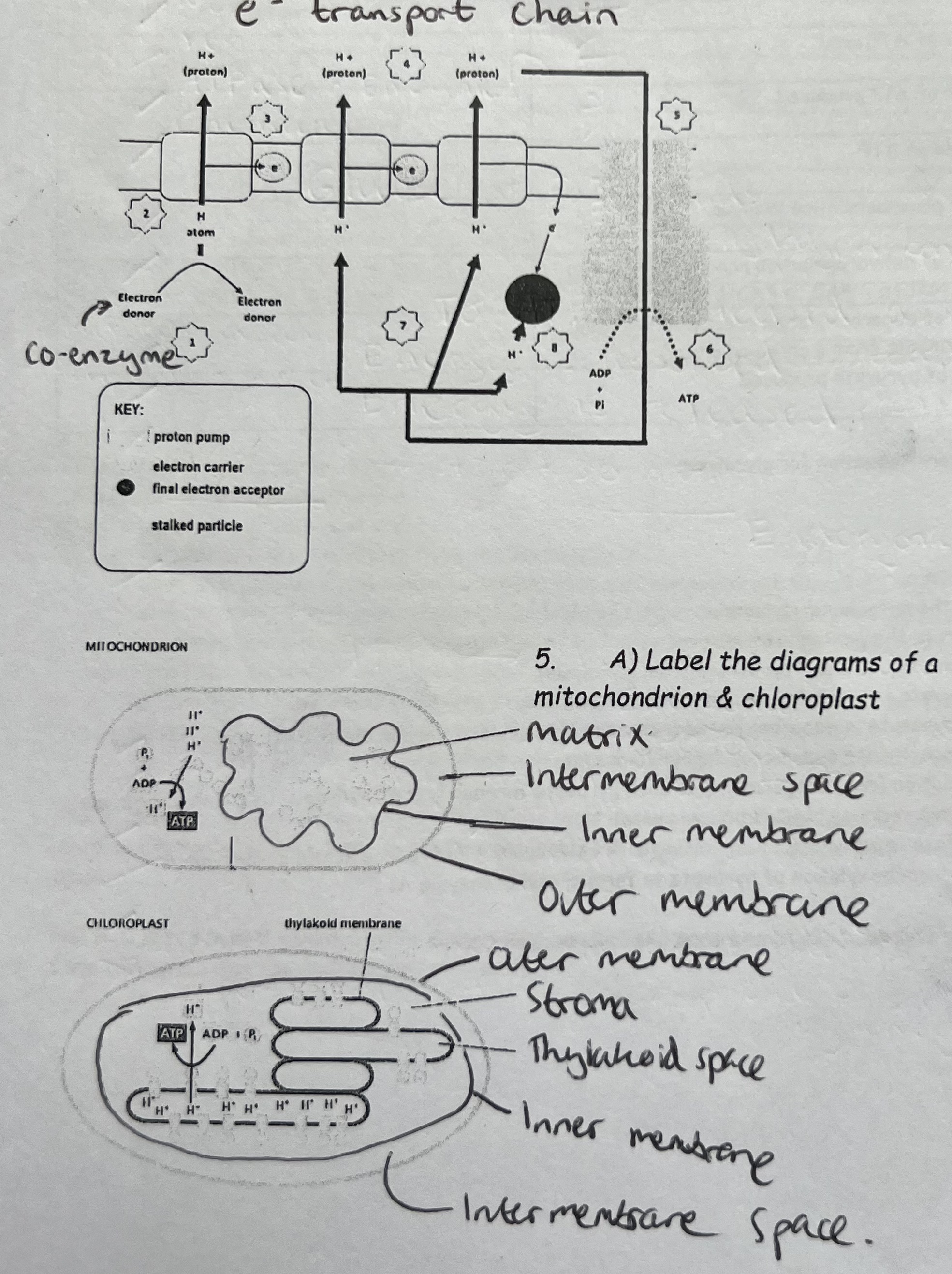
Features of Mitochondria & Chloroplasts
Respiration

What are the 4 Stages of Aerobic Respiration?
Glycolysis
Link reaction
Krebs cycle
Electron transport chain
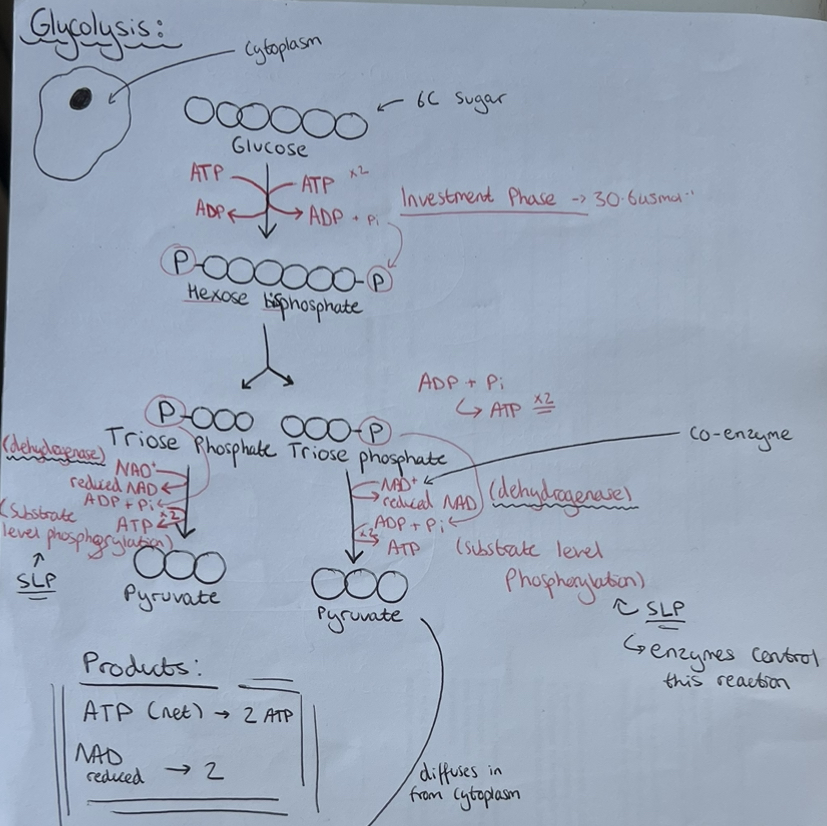
Glycolysis
Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol (cytoplasm)
Stages:
Phosphorylation of glucose into 6 carbon hexose bisphosphate using phosphate from hydrolysis of 2 ATP molecules
Hexose bisphosphate is unstable & has a lower activation energy & splits into two 3C triose phosphate molecules
Oxidation (dehydrogenation) of each of triose phosphate to 3C pyruvate through loss of hydrogen by a dehydrogenase enzyme reduces 2 NADs (1 per triose phosphate).
4 ATP are produced (2 per triose phosphate) by substrate level phosphorylation.
Substrate level phosphorylation: energy released in a reaction is used to produce ATP directly from ADP + Pi & phosphate groups are transferred from donor molecules
Glycolysis Labelled Diagram
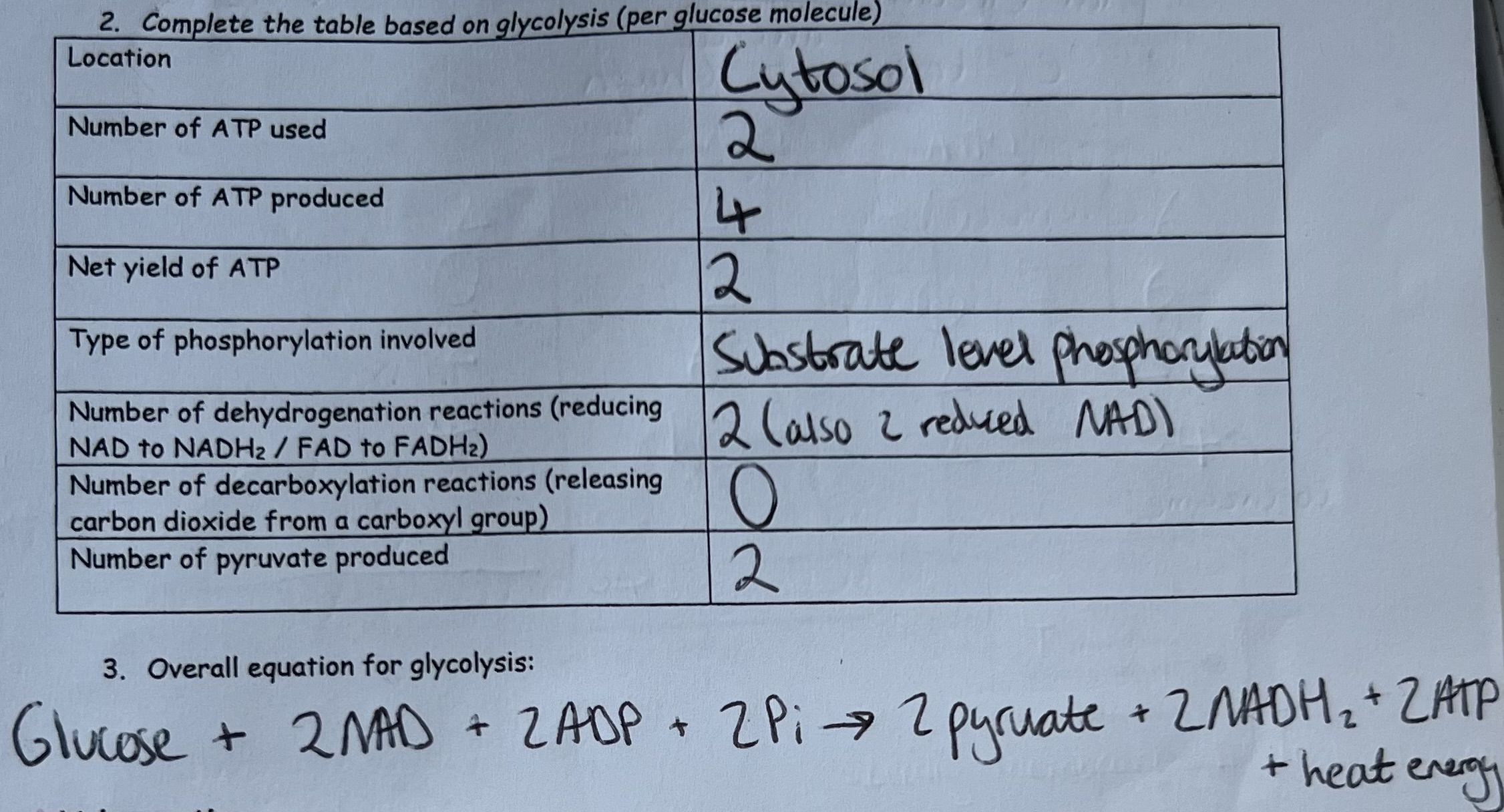
Glycolysis - Products & Reactions per Glucose
Suggest why Substrate Level Phosphorylation is referred to as the 'simplest and oldest way to make ATP'.
Does not involve the ETC/complex series of carriers and pumps;
Does not need stalked particles/ATP synthetase;
Does not need an electrochemical gradient/eq;
Does not require oxygen;
Link Reaction
The Link reaction occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Only occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Stages (for each of the 2 pyruvates from glycolysis):
Pyruvate transported into mitochondrial matrix
3C pyruvate is decarboxylated (releasing 1 molecule of carbon dioxide per pyruvate) by a decarboxylase enzyme producing 2C acetate
Oxidation (dehydrogenation) of each pyruvate through loss of hydrogen by a dehydrogenase enzyme reduces NAD (1 per pyruvate)
Acetate is activated by combining with co-enzyme A to produce acetyl co-enzyme A
(Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to form acetyl coenzyme A)
Link reaction labelled diagram
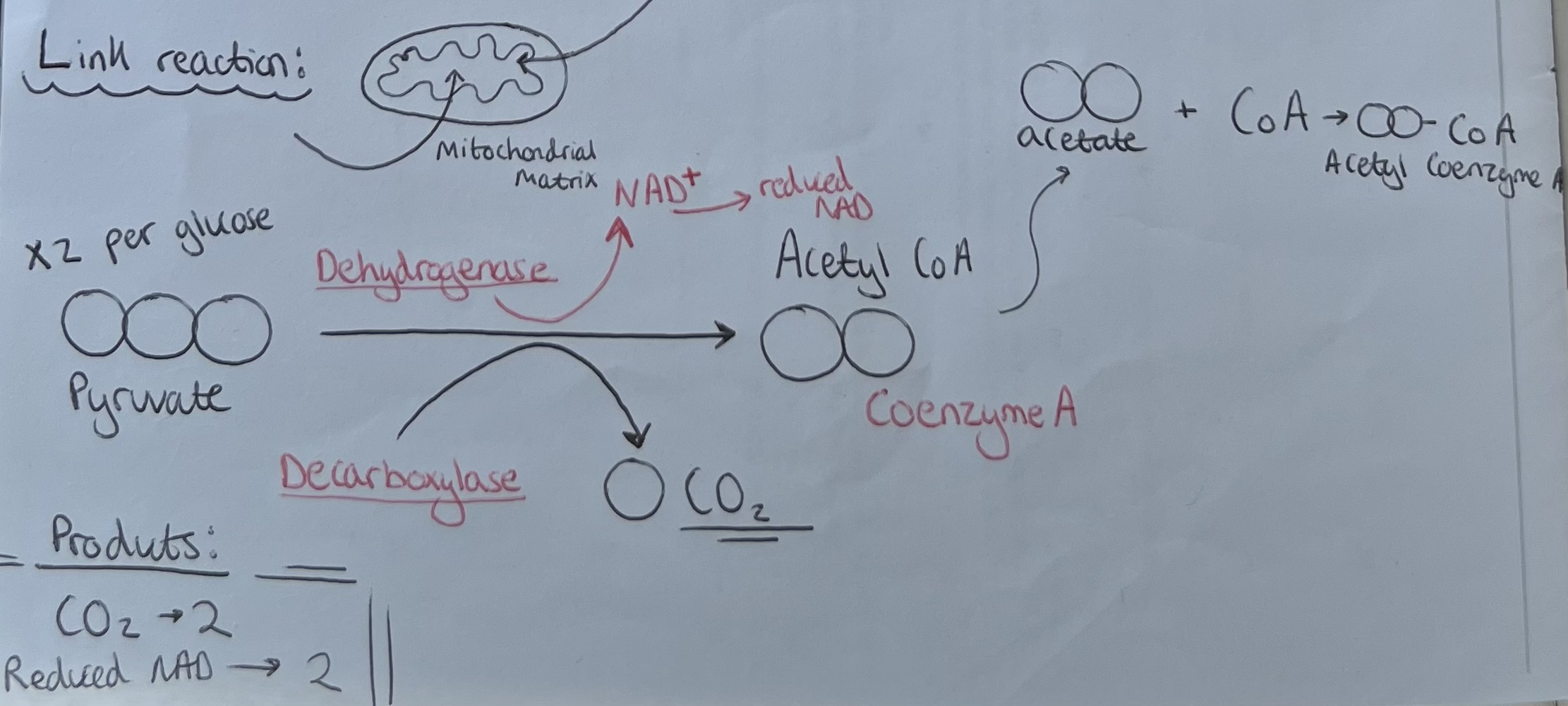
Link Reaction - Products & Reactions per Glucose

Krebs Cycle (citric acid cycle)
Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Only occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Stages (for each of the 2 acetates from the link reaction):
Acetate from acetyl coenzyme A combines with a 4C compound the form a 6C acid
6C acid is decarboxylated (releasing 1 molecule of carbon dioxide) by a decarboxylase enzyme & oxidised (degydrogenated) through loss of hydrogen by a dehydrogenase enzyme, reducing NAD (1 per 6C acid) producing a 5C acid
5C acid is decarboxylated (releasing 1 molecule of carbon dioxide) by a decarboxylase enzyme & oxidised (dehydrogenated) through loss of hydrogen by a dehydrogenase enzyme, reducing 2 NAD & 1 FAD (per 5C acid) to produce a 4C acid. 1 ATP is produced by substrate level phosphorylation.
The 2C acetate fragment that entered the Krebs cycle is completely broken down by the oxidative decarboxylation reactions & the 4C acid is regenerated & combines with acetyle CoA to repeat the cycle.
NB: H2O is fed in at 3 reactions. The oxygen that combines with carbon (from decarboxylation) to form carbon dioxide comes from water molecules.
Krebs Cycle Labelled Diagram
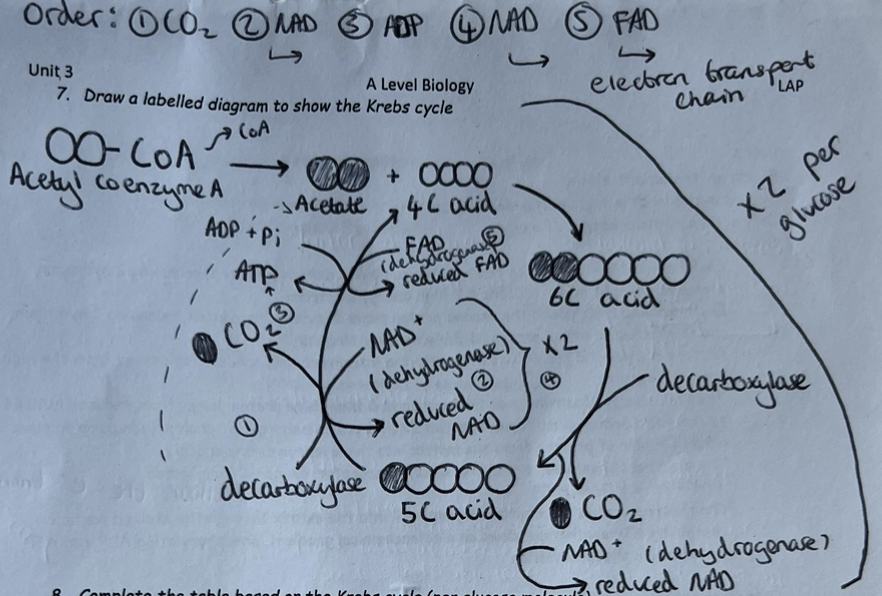
Krebs Cycle - Products & Reactions per Glucose
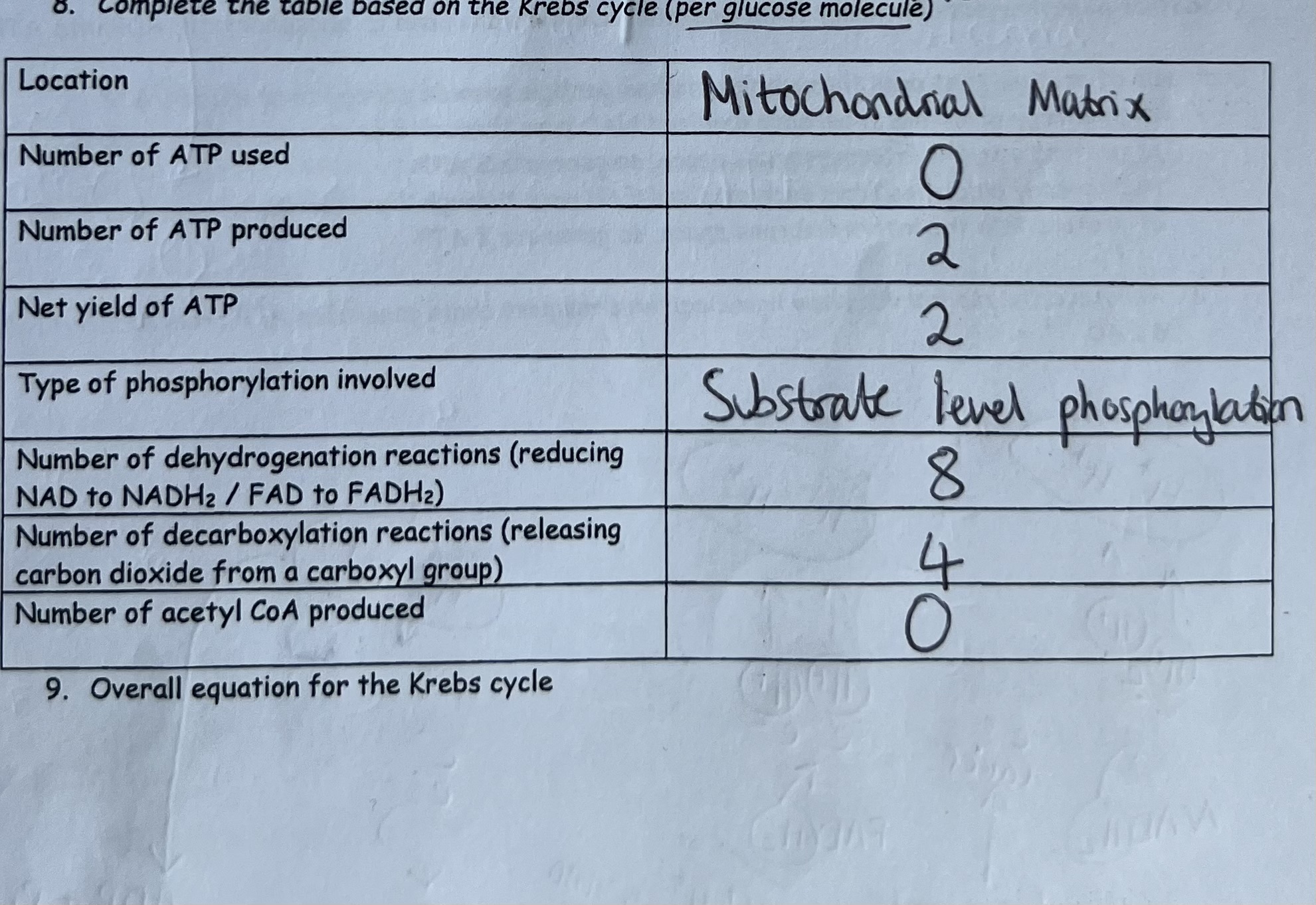
Respiration Practical Limitations & Solutions
What is the effect of respiration on PH at 30oC?
Carbon dioxide dissolves in water to form carbonic acid —> more acidic pH
How does a higher number of capillaries benefit a living organism?
Higher number of capillaries supply tissue with more oxygen/ nutrients or remove CO2 / distribute heat.
Suitable tissue to examine mitochondria
(Skeletal) muscle tissue, as high numbers of mitochondria and easy to access.
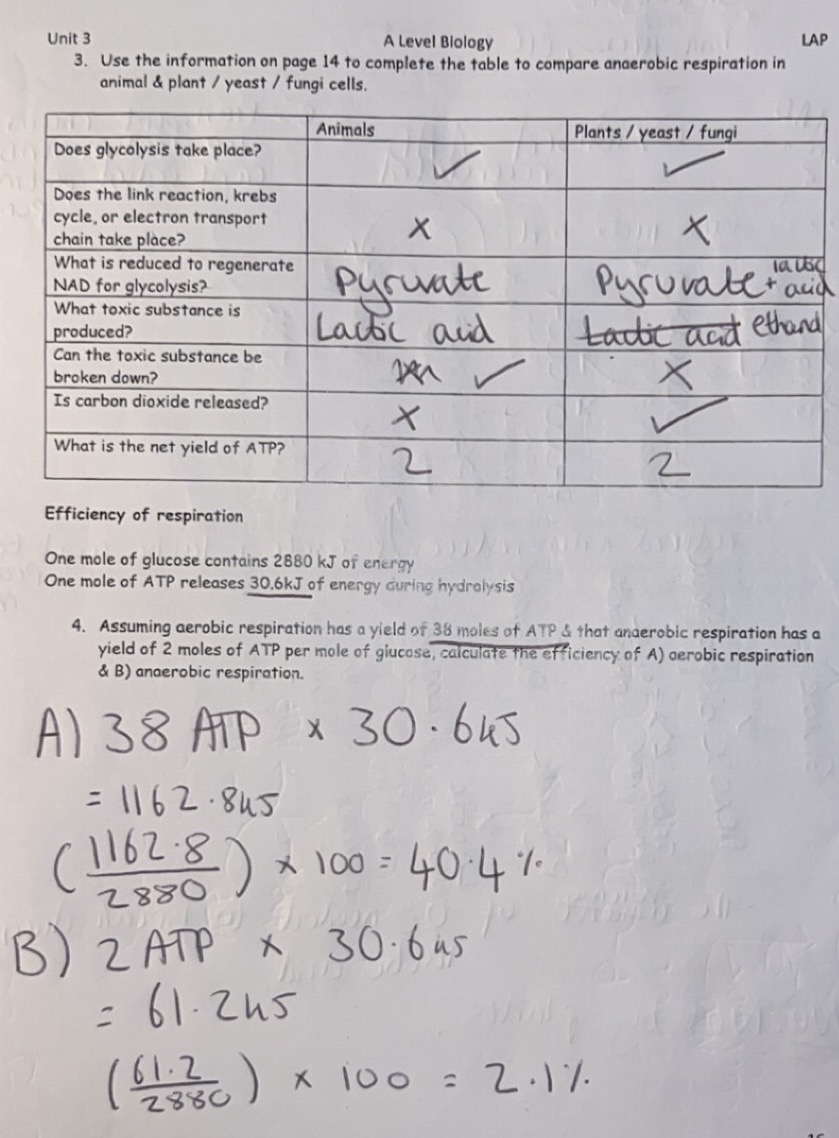
Yield from the complete oxidation of one glucose molecule
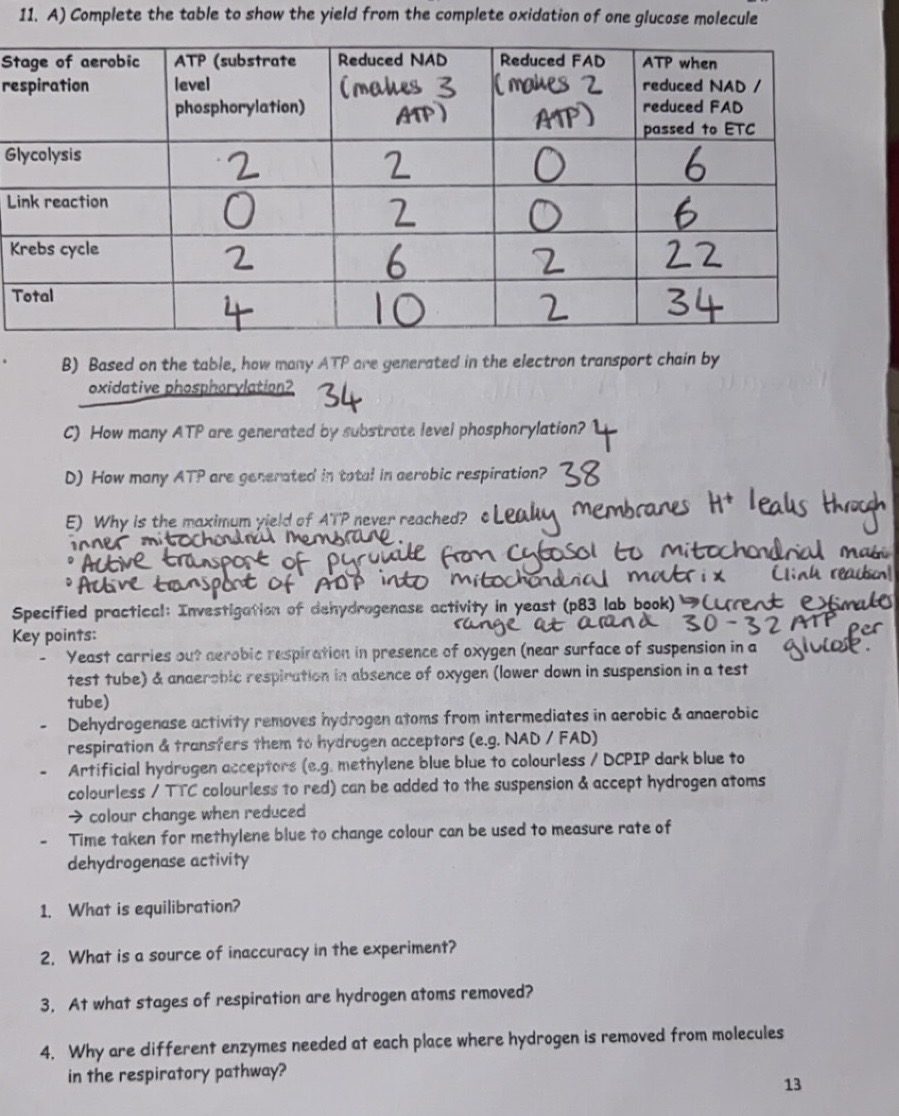
Specified Prac

Anaerobic Respiration
Equation: Glucose —> Lactic acid
Anaerobic respiration takes place when oxygen is not available. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain and without oxygen, reduced NAD & reduced FAD cannot be oxidised, as the ETC chain stops.
This means that NAD & FAD are not regenerated to pick up more hydrogen during glycolysis, the link reaction or the Krebs cycle.
What happens during glycolysis in anaerobic respiration?
During glycolysis, dehydrogenation (reducing NAD) occurs before the production of ATP, so the lack of NAD would stop ATP production.
To overcome this and allow glycolysis to still take place in animals, reduced NAD formed in glycolysis transfers the hydrogen to pyruvate to form lactic acid.
To allow glycolysis to still take place in plants, yeast & fungi, reduced NAD formed in glycolysis transfers the hydrogen to pyruvate to form lactic acid which is then reduced to ethanol & carbon dioxide.
NAD is therefore regenerated so that glycolysis can continue. Glycolysis has a net yield of 2 ATP.
The link reaction or the Krebs cycle cannot take place as NAD & FAD cannot be oxidised or regenerated.
Lactic acid & Oxygen debt
Lactic acid that builds up in animals is toxic, but its formation is reversible. Anaerobic respiration in animals leads to oxygen debt, which is the amount of oxygen needed to break down lactic acid.
Oxygen debt requires breathing more deeply to supply more oxygen to oxidise lactic acid (& release more energy).
Ethanol that builds up in plants, yeast & fungi is toxic but it cannot be broken down, so is not reversible.
Example Questions & Labelled Diagrams
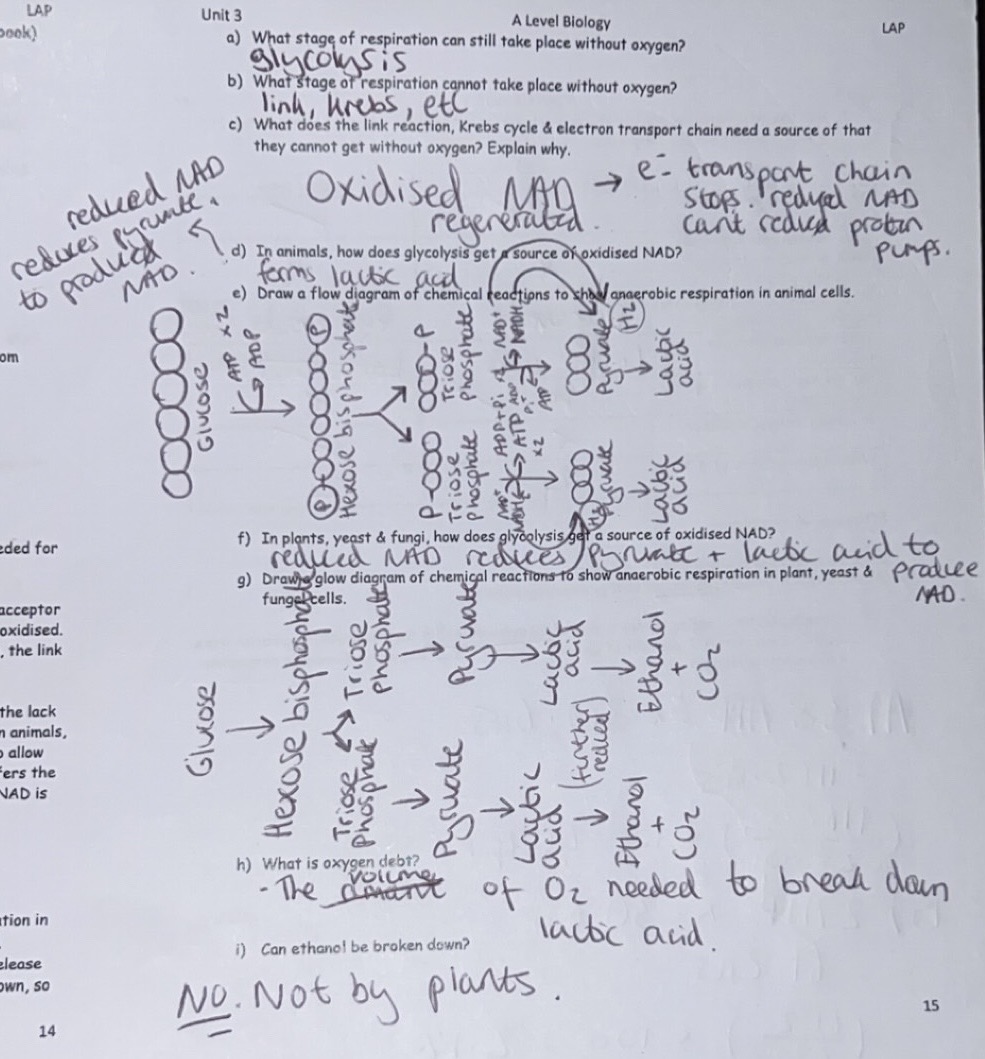
Comparing anaerobic respiration in animals, plants, yeast and fungi + ATP Efficiency
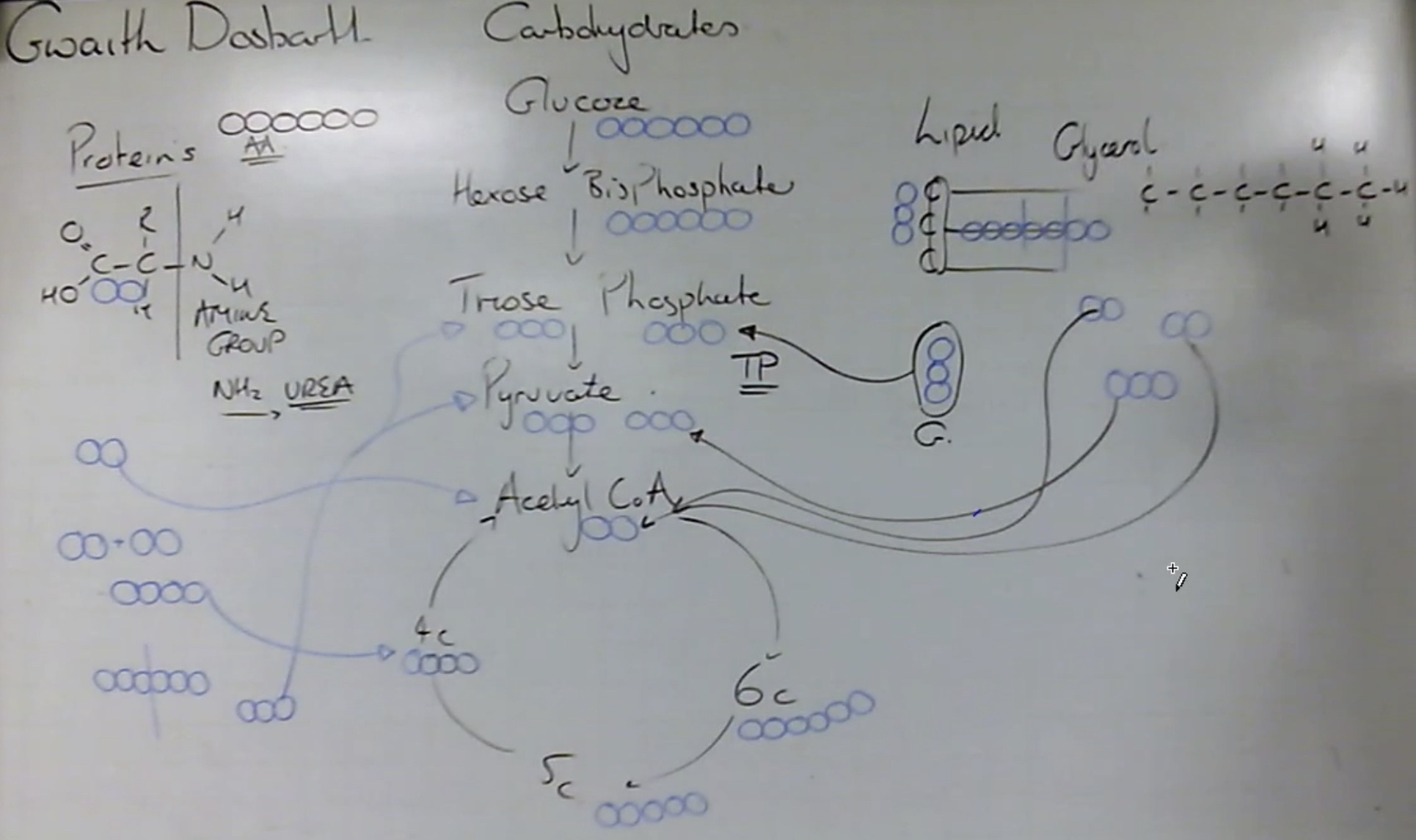
Alternative Respiratory Pathways - Other carbohydrates, fats and proteins

Alternative Respiratory Pathways Diagram


How is CO2 removed from a human?

How is reduced NAD produced in the Krebs Cycle?

Why must lactate be produced in anaerobic conditions?

Advantages of anaerobic respiration to produce ATP
