3.7.1 Inheritance
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
genotype
the genetic constitution of an organism
phenotype
the expression of an organism’s genetic constitution combined with its interactions with the environment
dominant allele
an allele whose characteristic will always appear in phenotype
recessive allele
an allele whose characteristic will only appear in phenotype if there are 2 present + no dominant allele is present
homozygous + heterozygous
-homo = 2 identical alleles
-hetero = 2 different alleles
monohybrid inheritance
where one phenotype characteristic is controlled by a single gene
diagrams to display inheritance
1) genetic diagrams
2) punnet squares
codominant alleles
2 dominant alleles that are both expressed in phenotype
sex linkage
where an allele is located on one of the sex chromosomes meaning its expression depends on the sex of the individual
X and Y chromosomes
-males = XY, females = XX
-the Y chromosome is shorter than the X chromosome and carries fewer genes so most genes are carried on X chromosome
why are males more likely to get recessive phenotype
-as males have one X chromosome, they only get 1 copy of the allele so will express it even if recessive
-females have two X chromosomes, they get 2 copies of the allele
-so males are more likely to express recessive phenotype
inheritance of sex-linked characteristics
-males inherit these from the mother as father has Y chromosome so mother is carrier
autosome
any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
autosomal linkage
when 2 or more genes are located on the same autosome
linked genes
-the closer together 2 genes are on the autosome the more closely they are linked - crossing over is less likely to split them so they stay together during independent segregation in meiosis and are more likely to be inherited together
why the observed ratio differs from phenotypic ratio
linked = if the alleles are linked, that means they mostly produced the more common alleles so there are lots of them but have still made the uncommon alleles due to crossing over (does not happen often so there is few)
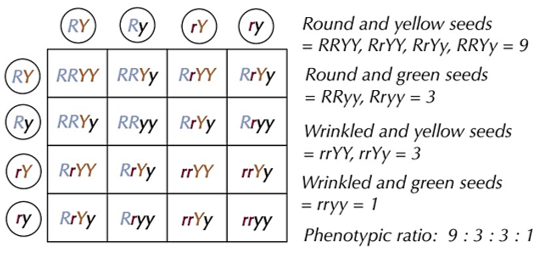
dihybrid inheritance
where 2 phenotypic characteristics are controlled by 2 different genes
-if both heterozygous parents = 9:3:3:1
epistasis
where 2 non-linked genes interact to form phenotype with one gene masking the other gene
recessive epistasis
where 2 homozygous recessive alleles mask expression of another allele
-if homozygous recessive + dominant parents = 9:3:4
-example: yy = epistatic gene
dominant epistasis
where 1 dominant allele masks expression of multiple other alleles
-if homozygous recessive + dominant parents = 12:3:1
-example: W = epistatic gene
chi-squared test
used to compare observed and expected results in genetics to see if any difference between them is significant or not
criteria for chi-squared test
-data is in discrete categories
-large sample size
-no data values equal 0
-need to know degrees of freedom/classes and significance level
chi-squared formula
sum of (observed no. - expected no.)2 / expected no.
chi-squared value
-if less than critical value, accept null hypothesis and any difference is due to chance + is not significant
-if greater than critical value, reject null hypothesis and accept experimental/alternative hypothesis so difference is significant