Midterm Review
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms

what is impossible with acceleration?
d, because an object cannot have a stagnant velocity if there is acceleration

Suppose a car traveling to the west begins to slow down as it approaches a traffic light. which of the following statements is correct?
d, because if a car is slowing down, that means the acceleration is in the opposite direction

When two objects are dropped 1 second apart when air resistance is negligible, what is the length of their separation and why?
e, because acceleration is -9.8 m/s2, the velocity of both objects constantly increases. Since the first object got a one-second headstart, its velocity would increase more rapidly compared to the second object which was at zero after one second
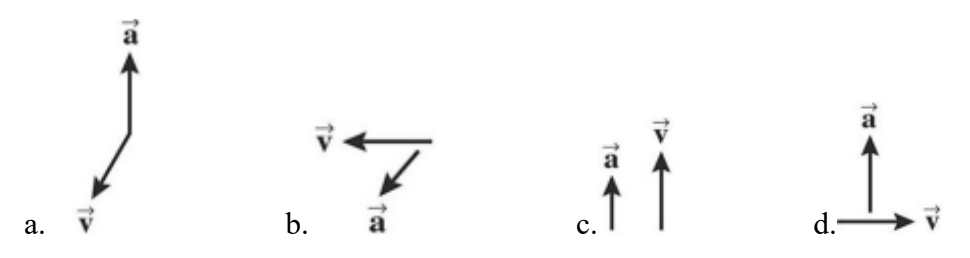
Below are the velocity and acceleration vectors for an object in several different types of motion. In which case is the object’s velocity changing while its speed is not changing?
d, because the acceleration is pointing towards a center while the velocity is tangent with the edge of the circle, controlling its direction but not its magnitude

if a satellite moves with constant speed in a perfectly circular orbit around the earth, what is the direction of the acceleration of the satellite?
c, because of the force of gravity
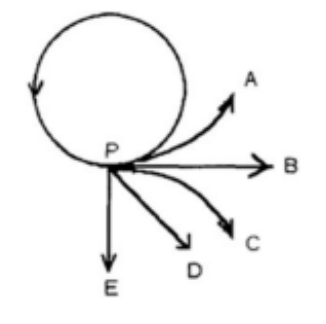
A girl attaches a rock to a string, which she then swings counter-clockwise in a horizontal circle. The string breaks at point P in the figure, which shows a bird's-eye view (as seen from above). Which path (A-E) will the rock follow?
B, because it will just start following the path of its velocity without the pull of acceleration

You are in a train traveling on a horizontal track and notice that a piece of luggage starts to slide directly toward the front of the train. From this observation, you can conclude that this train is
b, because the applied force of the train is negative so the acceleration has become negative, causing everything in the train to move backwards

An object is moving with constant non-zero velocity. Which of the following statements about it must be true?
d, because the velocity is not changing at all, there is no force present that could make it change

An object of mass m rests on a flat table. The earth pulls on this object with a force of magnitude mg. What is the reaction force to this pull?
e, and not from the table because it is only the object and the earth interacting, not including the table

When a 45-kg person steps on a scale in an elevator, the scale reads a steady 480 N. Which of the following statements must be true? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
c, because it’s more than what they would weigh as the force of gravity is stronger than usually in order to counteract the increasing upward pulling force
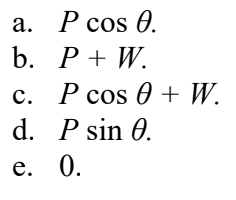
The figure shows that a push of magnitude P acts on a box of weight W. The push is directed at an angle θ below the horizontal, and the box remains at rest. The box rests on a horizontal surface that has some friction with the box. The friction force on the box due to the floor is equal to
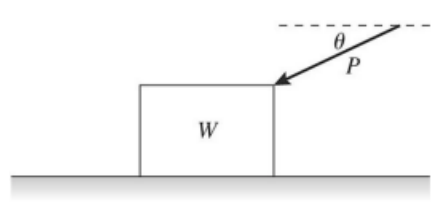
a, because the force of friction is opposite to the push but the same magnitude of the x-axis
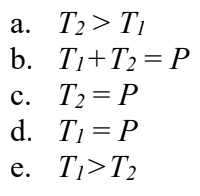
Three boxes are pulled along a horizontal frictionless floor by a constant horizontal pull P. The boxes are connected by very light horizontal strings having tensions T1 and T2 as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements about the tensions is correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
e, because t1 has to pull 120 newtons while t2 only has to pull 100 newtons
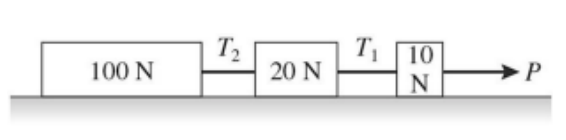
As shown in the figure, two boxes are connected to each other by a string. The 10-N box slides without friction on the horizontal table surface. The pulley is ideal and the string has negligible mass. What is true about the tension T in the string?

a
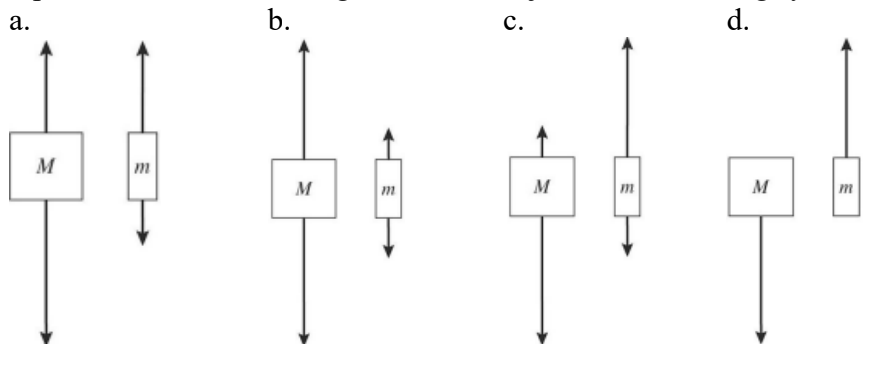
Two objects of unequal masses, M and m (M > m), are connected by a very light cord passing over an ideal pulley of negligible mass. When released, the system accelerates, and friction is negligible. Which one of the following free-body diagrams most realistically represents the forces acting on the two objects in the moving system?
a, because there is the tension of the string acting on both objects as well as the force of gravity. the tension force is equal on both objects, while the force of gravity is much stronger on the heavier object

Two objects have masses m and 5m, respectively. They both are placed side by side on a frictionless inclined ramp and allowed to slide down from rest without any air resistance. Which one of the following statements about these objects is correct?
e, since they aren’t affected by friction, they aren’t slowed down in any way by a force opposing the push of gravity
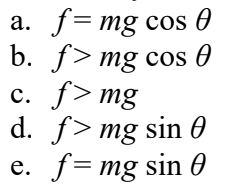
A block of mass m sits at rest on a rough inclined ramp that makes an angle θ with the horizontal. What must be true about the force of static friction f on the block?
e, because it is the opposite and equal force to the force of gravity along the x-axis
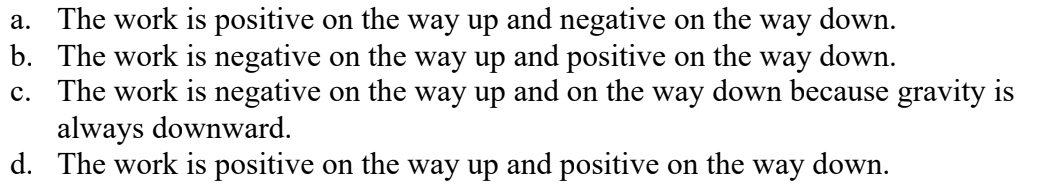
You throw a baseball straight up. Compare the sign of the work done by gravity while the ball goes up with the sign of the work done by gravity while it goes down.
b, because its positivity or negativity depends on the acceleration of the system, which changes with the direction of the object
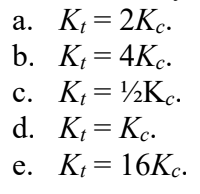
A truck has four times the mass of a car and is moving at twice the speed of the car. If Kt and Kc refer to the kinetic energies of truck and car, respectively, it is correct to say that
e, because of mv2/2

A 4.0 kg object is moving with speed 2.0 m/s. A 1.0 kg object is moving with speed 4.0 m/s. Both objects encounter the same constant braking force, and are brought to rest. Which object travels the greater distance before stopping?
c, because of the work-energy theorem mvf2/2 - mvi2/2

Two frisky otters slide down frictionless hillsides of the same height but on different slopes. The slope of the hill of otter 1 is 30°, while the slope of the hill of otter 2 is 60°. If both start from rest, which otter is moving faster when she reaches the bottom of her hill?
c, because both of the hills are at the same height, they both have the same amount of potential energy, so they have the same final velocity because of energy conservation, which states Einitial=Efinal
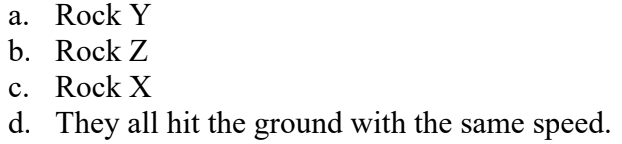
A person stands on the edge of a cliff. She throws three identical rocks at the same speed. Rock X is thrown vertically upward, rock Y is thrown horizontally, and rock Z is thrown vertically downward. If the ground at the base of the cliff is level, which rock hits the ground with the greatest speed if there is no air resistance?
d, because they are all dropped from the same height, they all have the same final velocity because of energy conservation, which states Einitial=Efinal

Two identical grasshoppers jump into the air with the same initial speed and experience no air resistance. Grasshopper A goes straight up, but grasshopper B goes up at a 66° angle above the horizontal. Which of the following statements about these grasshoppers are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
a, because they have the same initial velocity so the mechanical energy is also the same
b, because although they have the same mechanical energy, grasshopper A is higher up so it leans more on potential energy
d, because grasshopper A has more potential energy, grasshopper b has more kinetic energy

A heavy sled and a light sled, both moving horizontally with the same speed, suddenly slide onto a rough patch of snow and eventually come to a stop. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sleds and the rough snow is the same for both of them. Which of the following statements about these sleds are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
a, because the heavier slide takes more friction to slide down because it has more mass
d, because the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same for both sleds
if 2 objects fall from the same height along a vertical path and a parabolic path, which will land first?
they will both land at the same time since vertical and horizontal motion act independently of one another, so they both have the same vertical motion
how is time determined for an object thrown along a parabolic path?
according to only the y component since it only depends on the vertical movement
traits of horizontal velocity
is constant throughout the entire parabolic path if there is no air resistance
traits of vertical velocity
it is completely symmetrical, and it decreases until it reaches maximum height and is at 0, then increases it until the object lands because of the force of gravity
equations for movement along the x direction when an object is pushed off a cliff
x = vit
vx = vi
ax = 0
Equations for movement along the y direction when an object is pushed off a cliff
y = yi - 4.9t2
vy = -9.8t
ay = -9.8
how to find the final velocity when an object is pushed off a cliff
first, find the velocity along the x and y axes and then use the Pythagorean theorem, and if needed, find the angle with tanϴ
how much work is done when there is no displacement
none because work is dependent on displacement and the magnitude of the applied force
does all force acting upon an object contribute to the work done?
only the component of force parallel to the displacement counts toward the work
how can work be positive and negative?
because it is a scaler, meaning it’s only magnitude and not the direction. it’s positive when the applied force is in the same direction as the displacement and negative when the applied force is in the opposite direction.
why is it important whether or not work is positive or negative?
because it shows if the speed of an object will increase or decrease as the result of applied force
what is the unit of measurement for energy?
joules
Newton’s First Law
An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external net force
what must happen for an object to continue moving?
there must be a force acting upon it, such as friction or gravity
inertia
the capacity of an object to resist changes in motion that is proportional to its mass. more mass means more force is required to start or stop moving.
a collision can stop a car, but why do you continue moving?
because of inertia, the external force is acting upon the car and not you so you still take a moment to stop
the law of inertia
an object will preserve its state of motion unless acted upon by some external net force
Newton’s Second Law
the force acting upon an object is equal to the object’s mass times its acceleration
1 Newton
1 kg x 1 m/s2
the acceleration an object experiences is proportional to what and inversely proportional to what else?
the acceleration an object experiences is directly proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to its mass
Newton’s Third Law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
What are the action and reaction forces if a car crashes into a wall?
If a car crashes into a wall, there is the force the car imparts on the wall and an equal force from the wall onto the car
what forces contribute to the motion of an object?
only the forces acting directly upon an object
when a nail is driven into wood by a hammer, why does only the nail move?
when looking at the nail, we only consider the force of the hammer acting on the nail to influence motion because the hammer and nail are two different systems, and the hammer has a greater mass so it is more resistant to forces
the acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to what?
the mass of an object, so the lighter an object the larger the acceleration
if a bowling ball and bowling pin impart equal forces onto each other, why does only the bowling pin move?
because it has a lighter mass, so it has a greater acceleration
the law of the conservation of energy
the total mechanical energy of a closed system is conserved to that system and can not grow or shrink
if a pendulum is swinging, at what point does it have the highest potential energy and at what point does it have the most kinetic energy?
it has the highest potential energy when it is at its highest point and highest kinetic energy when it is at its lowest because potential energy is dependent on the y position and kinetic on the velocity
what is the formula for kinetic energy?
mv2/2
what is the formula for potential energy based on position?
mgh
what is the formula for elastic potential energy?
kx2/2
what is the formula for the conservation of energy?
E = K + U
what causes acceleration in circular motion
the velocity of the object around the center is tangent to the path the object takes; the magnitude is constant, but the direction changes, so velocity changes, causing acceleration
centripetal acceleration
acceleration that always points towards a center which produces a circular motion, generated by centripetal force
formula for centripetal acceleration
ac = vt2/r
formula for centripetal force
Fc = mac or Fc = mvt2/r
if Fc suddenly vanished, which path would the object take?
the path tangent to the curved path
centripetal force
the force that pulls objects towards the axis of rotation during circular motion. it could be tension from a string, gravitational pull, friction, etc.
centrifugal force
the reaction force to the centripetal force that is not an actual force, but a sensation your inertia produces to your tangential velocity