Amorphous solid dispersions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
From a delivery perspective drugs for oral delivery need to display:
adequate solubility and dissolution properties
adequate absorption through the gut (eg. permeability)
The bioavailability of a drug: class 1
is determined only by delivery of the drug solution to the intestine
Formulation independent
Rate Limiting Step: Gastric Emptying
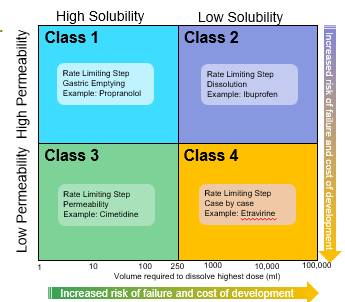
The bioavailability of a drug: class 2
Rate limiting step: drug solubility/dissolution
Formulation dependent
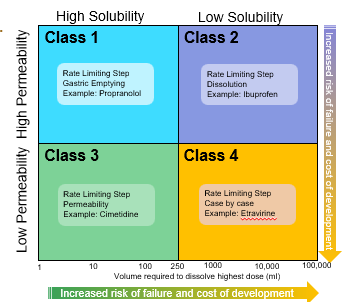
The bioavailability of a drug: class 3
Rete limiting step: intestinal permeability
Dependent on barrier properties
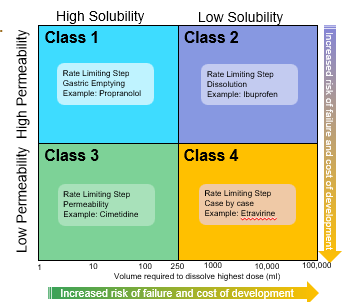
The bioavailability of a drug: class 4
Rate limiting step: solubility /dissolution and intestinal permeability
Formulation and barrier properties dependent
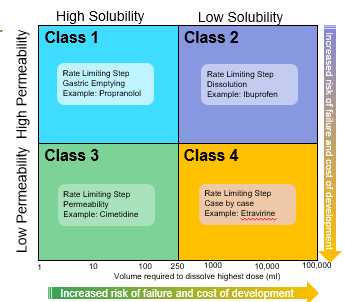
Oral Formulation approaches for poorly water soluble compounds → rank: Conventional → Non-Conventional : Risk and complexity
Salt formulation/ particle size reduction
Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS)/ Complexes
Nanoparticles/ Crystalline solid dispersions
Amorphous drug and Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Particle size reduction
Increases dissolution because for a given solute mass there is more surface area exposed to the solvent. Can work well for BCS Class 2 (low sol, high permeability)
SEDDS (Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems)
Stable mixtures of oil, surfactant, co-surfactant and drug that spontaneously form fine oil in water emulsions (down to 50nm in size) on exposure to water. Formulated in capsule form
Complexes
Entrapping poorly soluble drug within a soluble structure can be used to increase bioavailability
Nanoparticles
increased surface to volume ratio dissolves more quickly
Specialised nano-milling using surfactants to stabilise the nanoparticles can increase bioavailability.
Crystalline Solid Dispersions
Small ordered particles of drug are stabilised in a solid water-soluble polymer matrix
Amorphous drug and Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Disrupt ordered crystalline state to form a disordered amorphous state.
Solid now dissolutes much more rapidly.
Drug can also be molecularly dispersed and stabilised in a solid water-soluble polymer matrix. Often known as a Solid Solution.
What influences physical stability of amorphous materials and solid dispersions?
Glass transition temperature (Tg)
What is the Glass transition temperature (Tg)?
is a physical transition that takes place in amorphous materials, from a brittle to a rubbery state.
The lower the Tg…
the less stable the amorphous material may be
Main manufacturing methods for solid dispersions
Solvent based methods
Heat based methods
Solvent based methods:
Spray drying
Rapid solvent evaporation.
Needs acceptable solubility of drug in low boiling solvent required.
Heat based methods
Hot melt extrusion
Temp. and shear can cause degradation
No solvent required
Melting point < 200 °C required
Why the amorphous form of a poorly soluble drug is an important formulation strategy to bring such drugs to market.
Curial for poorly soluble drugs
Micro and Nanoscale analysis of spray dried solid
Small piece cut using an ion beam in the microscope
high-powered transmission electron microscope (TEM)
TEM of slice shows no structure, so drug is well dispersed in the polymer (no crystals)
At high temperatures drug starts to separate out and crystalize. Spectral amylases confirms that the dark spots are drug (contain Bromine)