Chapter 12: Developing New Products MKTG-300 Exam #3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Why do firms produce new products?
because of changing customer needs ex: chat assist on Samsung phone
if the products are one-time purchase/consumption per customer ex: pixar movies
to become a market pioneer
new products as a growth strategy (Product Development)
as a product portfolio strategy (?: Invest/Improve/Divest)
How does marketing support new product development?
marketing should take an active (or leading) role in new product development
marketing should help in finding directions of new product development. It is about defining a dynamic benefit dimension
are sales curves of one-time purchased goods different from repeat purchased goods and services?
so much different from one another
3 advantages of market pioneers?
greater market share
reputation
more funding and resources
ex: apple

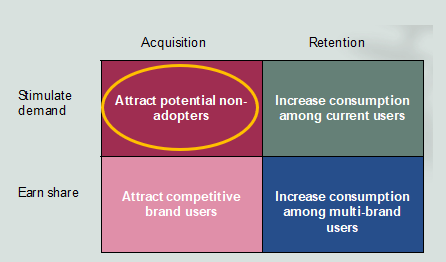
Marketing innovation diffusion starts from….
customer acquisition/stimulate demand
Diffusion of innovation is an _____________ __________.
adoption process
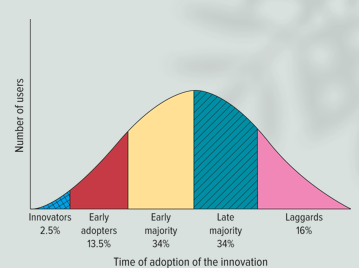
Adoption Process graph
from 0% to 100% of adoption rates
people have different levels of trying and adopting new products
in general, 2.5% always try new things. They are called innovators. They are adventuresome, curios and risk takers
Chasm between Early adopters and Early majority
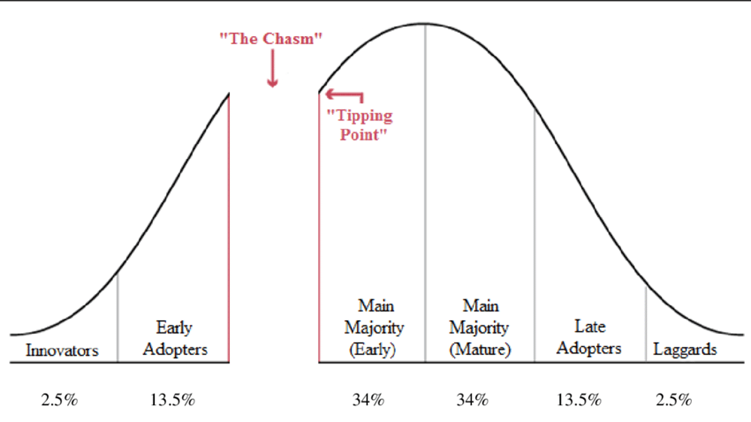
13.5% are early adopters. If marketers can not take early adopters, the innovation diffusion often breaks. It is called the chasm
Early Adopters
don’t take as much risk as innovators do but wait and purchase the product after careful review
thus this market waits for the first reviews
tend to enjoy novelty and often are regarded as the opinion leaders for particular product categories
early majority
they are numerous (34%)
influenced by early adopters and innovators
will not buy if it is not visibility accepted (the chasm)
different types of adopters
innovators
late majority
early adopters
laggards
early majority
Some Innovations Diffuse Faster bc of perceived attributes of innovations such as
relative advantage
compatibility
observability
complexity and trialability
Relative Advantage
degree to which an innovation is perceived better than the idea it supersedes
either greater benefits or lower price
Compatibility
the degree to which an innovation is perceived as consistent with the existing values, past experiences, and needs of potential adopters

Observability
the degree to which the results of an innovation are visible to others

Trialability
the degree to which an innovation may be experimented with on a limited basis

How to Develop a new product steps
Idea generation
concept testing
product development
market testing
product launch
evaluation of results
Idea Generation
R&D
Brainstorming
Customer input
Competitor’s product
Concept Testing
You should refine the new product idea and develop a concept statement of the new product
concept statement should include verbal or visual presentation of:
product features and benefits
price
where to purchase
brand name and logo
You need to ask potential customers to rate their purchase intent
Product development
product development costs money, time and effort a lot!
make sure to do concept tests before your commitment
during the product development, you should consider getting feedback again (prototype tests- alpha and beta testing)
Alpha testing
firm attempts to determine whether the product will perform according to its design and as it intended
Beta testing
uses potential consumers who examine the product prototype in a real-use setting to determine its functionality, performance, potential problems, and other issues specific to its use
Marketing testing
after completed the new product development, do market testing with the completed product if needed
in general, market testing is trial sales attempt with different marketing mix variables
different pricing
different advertising and promotion
different distribution
be aware that your competitors can see your product’s presence when you do a market testing
Competitive imitation
a situation where one company fully copies or adopts strategies, products, processes, or other elements of another firm’s business with the goal of gaining a competitive advantage or improving its own performance
ex: General Food’s Toast Em’s —> Kellogg pop tarts
General Goods Maxim freeze-dried coffee —> Nestle Nescafe freeze-dried coffee
Product Launch
this step requires tremendous financial resources and extensive coordination of all aspects of the marketing mix
the firm confirms its target market(s) and positioning, and finalized the remaining marketing mix variables, and determines the marketing budget
timing of the launch may be critical
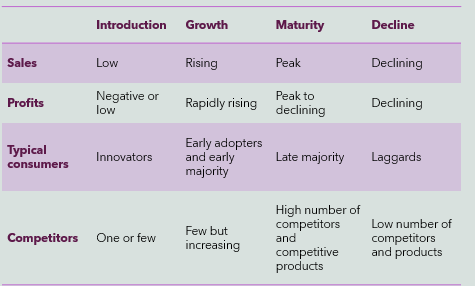
Product Life Cycles & Graph
Development
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
The product life cycle graph helps understand the traditional evolution of products, particularly technology products or others subject to fads in consumer preferences
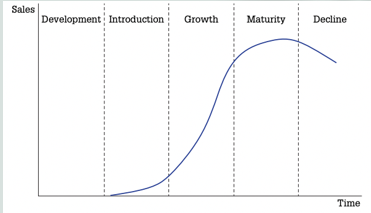
Points of Inflection of Life Cycle Curve
in the life stages of products at which sales accelerate, flatten, or decline
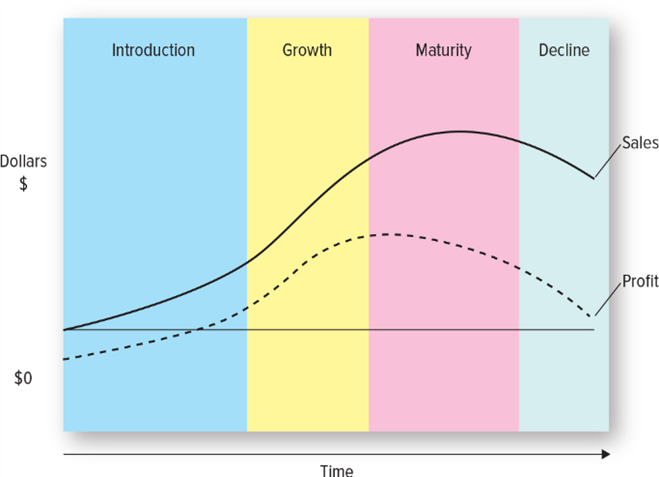
Are all products subject to the life cycle?
No, some products and some brands like Coca-Cola and baking soda are not subject to the life cycle at all

Characteristics of each stage in product life cycle