Exam 1, Mass Flashcards (The Last Two Lectures)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Mendel’s Law of Dominance
when an individual, ONLY the dominant allele will be expressed
Dominance Relationship in ducks is an example of ____ dominance
Cascading
True or false:It is not possible for there to be more than 2 alleles at a given locus and each allele has its own dominance relationship
False
what does “Mr > M> md “ mean in ducks genes
Mr is dominant to M, which is dominant to md
White Morphs Are Abundant in Nature Because
Loss of function mutations are more popular than gain of function mutations
There a discrete biochemical pathways for color & one perturbance in the pathway disallows color
Incomplete Dominance (define)
an intermediate phenotype where one allele is not expressed more than the other (neither is dominant to the other)
mixed
Red x White = Pink
Incomplete Dominance ___ to the number of possible phenotypes
adds, so if you have two initially, the incomplete phenotype counts as one
*****In incomplete dominance the genotypic ratio and phenotypic ration are __
equal to one another
Codominance (define)
Both of the alleles of a gene pair are FULLY expressed (just in different areas)
vitiligo
calicos
Mechanism of Cystic Fibrosis
having faulty CTFR membrane proteins, causing lack of regulation of Cl- in lung cells, impairing lung function
Cystic Fibrosis is ___ but ___
recessive
co-dominant
True or False: Cystic Fibrosis severity varies due to the co-dominance of faulty CFTR & proper CTFR
True
Penetrance (define)
the percentage of individuals having a particular genotype that express the expected phenotype
Are Incomplete dominance & codominance fully or incompletely penetrant
incompletely
Penetrance Equation
p = # of people with phenotype/ # of people with genotype
Expressivity (define)
the degree to which a trait is expressed
An Example Of Incomplete Penetrance
polydactyly, because it is dominant but most humans have exactly 5 digits on each limb
Draw increasing polydactyl expressivity
ok
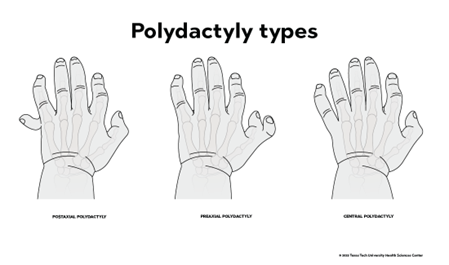
Epistasis (define)
interaction among genes in which the phenotype of a gene is dependent on the presence of one or more modifier genes
Genetic Background
modifier genes that influence epistasis and in turn, phenotype
Epistasis breaks which of Mendel’s Laws?
Law of independent assortment
law of segregation
Epistatic Genes
when a gene or locus suppressed or masks the phenotypic expression of another gene
Hypostatic Genes
the gene or locus that is suppressed by the epistatic gene, messing up phenotypic expression
Epistasis Event
when an epistatic gene suppresses the hypostatic gene, thereby effecting phenotypic expression
The Two Types of Epistasis (main)
dominant & recessive
Dominant Epistasis
when only a single copy of the heterozygous allele is required to inhibit phenotypic expression of the hypostatic gene
need BB or Bb to have an effect
Recessive Epistasis
when the presence of two recessive alleles inhibits the expression of an allele at a different locus
must be bb
ee with the labrador puppies
Cascading Epistasis Pathways
When a single epistatic gene interacts with multiple hypo- or epistatic genes, resulting in one final hypostatic gene
In a heterozygous dihybrid cross, there is a ___ ratio
9:3:4 ratio
Two Types of Duplicate Epistasis
recessive & dominant
Recessive Duplicate epistasis (define)
Two recessive alleles at either of two different loci can suppress a genotype
Duplicate Epistasis
when two sets of alleles are needed for epistasis
Dominant Duplicate Epistasis
A single dominant allele at either of two loci is capable of suppressing a genotype
Is gender a biological or social phenomenon & do other species outside of humans exhibit it ?
Social phenomenon
Only humans have gender
How Biological Sex is Defined
Only by the gametes the individual produces
Defntitons of gametes
sex cells, either sperm or eggs
Characteristics of Male Gametes
Smaller & Mobile
Characteristics of Female Gametes
Bigger and non-mobile
Chromosomal Sex Determination Systems (definition)
Sex is determined by specific chromosomes (non-autosomes) that result in different se4xes having different chromosomes.
Autosomes Definition
any chromosome pair that is not differentiated between sexes
Heteregamtekic
a sex chromosome pair that is different (XY, ZW)
Homogametic
a sex chromosome air that is the same in a given sex (XX, ZZ)
XX-XO system
XX is female
XOw (where O is nothing at all, no Y)
seen in grasshoppers and insects
ZZ-ZW system (Missy Elliot system)
ZZ is male
ZW is female
In birds, snakes, butterflies, & some amphibians & fishes
XX-XY system
XX is female
XY is male
homogametic sex is female
seen in mammals
Definition of Haplodiploidy Sex Determination System
Sex determination system that results in one sex being haploidy(1n) and the other sex being diploidy (2n)
bees, wasps & ants
Haplodoploidy Sex Determination System
Haploids are male, Diploids are females, when males are created they are unfertilized, when females are create they are fertilized
Genic Sex Determination System
Sex is determined by sex determining genes in autosomes only
The genes matter
Found in some plants, fungi, & fish
Environmental Sex Determination System
system that determine ssex base don the environment
ex is the crocodiles, males are at the bottom of the divot while females are at the top of the divot
Hermaphroditism
both sexes are in the same organism
both eggs and sperm are in the same exact flowers in the same tree
Monoecious
both male and female reproductive systems in the same organism
egg and sperm on different flowers in the same tree
Dioecious (us)
either male or female reproductive structures sin one organism, not both.
All Sex Determination Systems
Genic
Environmental
Chromosomal
Haplodiploidy
Human Sex Determination
Humans are diploid (2n)
Chromosomes 1-22 are autosomes
Chromosome 23 is an allososme
Allosome
non homologous chromsomes
Which Sex Chromosome is more important and why?
The X chromosome is much more important because
it contains information pertaining to both sexes,
-has more genes than Y,
is required while Y is not
SRY gene
gene only found in the Y chromosome that makes males males,
once it is there, the male phenotype is created, without it the female genotype is created.
DSDs (abv meaning )
disorder of sexual development
Definition of DSDs
congenital conditions that effect reproductive development
Swyer Syndrome
a DSD that o caused by a mutation in the SRY gene that causes XY indiuvudals to develop as female (because SRY is not working correctly) but they lack estrogen making them infertile
Nondisjunction
An error during meiosis or mitosis in which sister chromatids fail to separate, resulting in daughter cells with an abnormal number of chromosomes.
The cause fo aneuploidy
True or False: aneuploidy can be n+-1
True
XXX
Triple X Syndrome
XOw
Turnery Syndrome (O means that they only have an X chromosome)
XXY, XXXY, XXXXXY, XXYY
Klienfelter’s Syndrome
OY
nonviable, no X means no life
Sex Linked Genes
genes linked to sex chromosomes
includes sex determination and developmental genes
Reciprocal Cross
a breeding experiment designed to ties the role of parental sex on a given inheritance pattern
Requirement for Reciprocal Cross
In the P generation, both parents must be true breeding
Dosage Compensation
The process by which an organism equalizes gene expression from the sex chromosome between individuals of different biological sexes
MAIN way Dosage Compensation is seen in humans
in females, one of the X chromosomes is inactive at random so only one of them is actually being expressed
X-Inacvitaiton
process by which one of the copies of X in a cell is randomly inactivated, creating a barr body
Barr Body
the inactive X chromosome in a female somatic cell
Sex Influenced Traits
autosomal traits that are expressed differently in different sexes, one phenotype has higher penetrance than the other
sometime resulting in a flipped dom-recessive relationship
Sex Limited Traits
autosomal trait that results in a phenotype ONLY BEING SEEN in one sex, zero penetrance in the other
Cytoplasmic Inheritance
inheritance that doesn’t abide by the medelian rules of genetics
applies to organelle genes (mitochondria comes from mom only)
usually uniparental and zero combination