APWH FINAL REVIEW
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
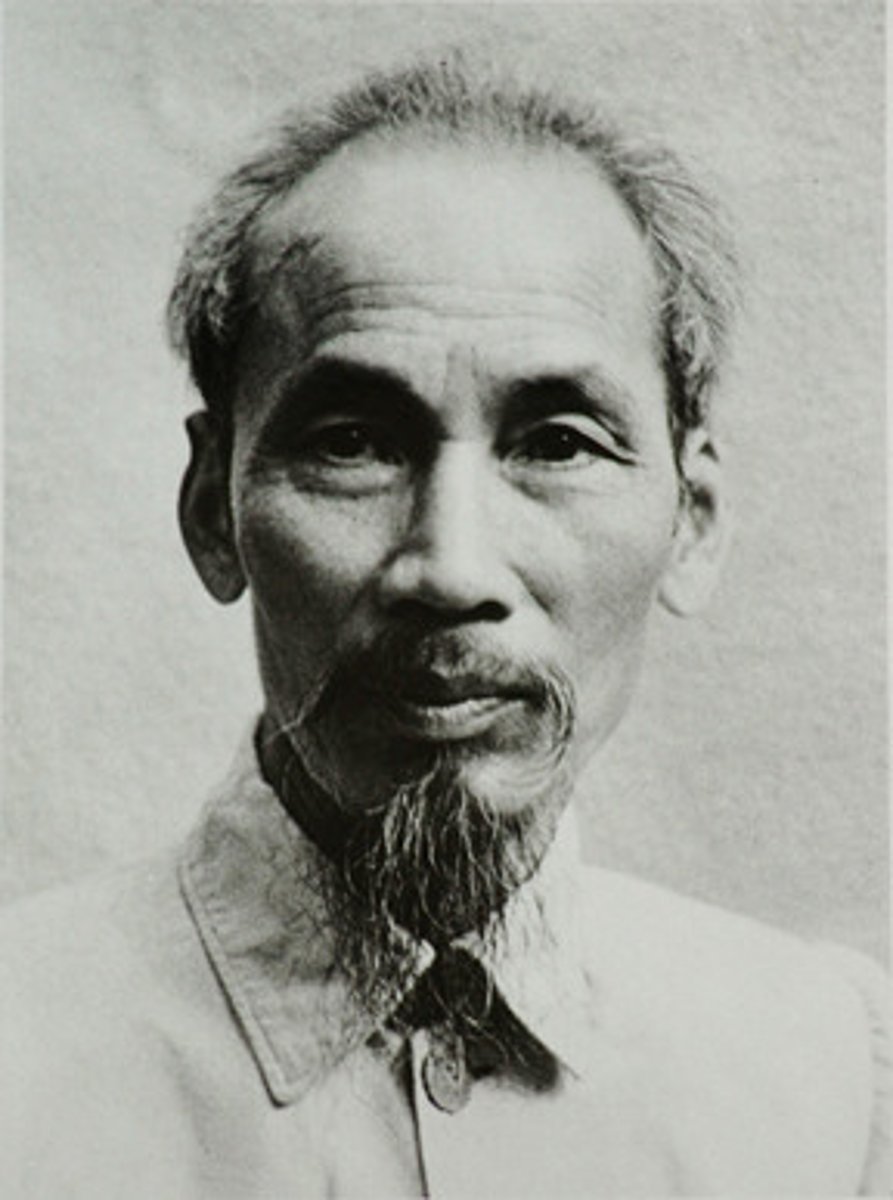
Ho Chi Minh
Vietnamese nationalist and communist leader who led the fight for independence from France and later fought the U.S. in the Vietnam War.

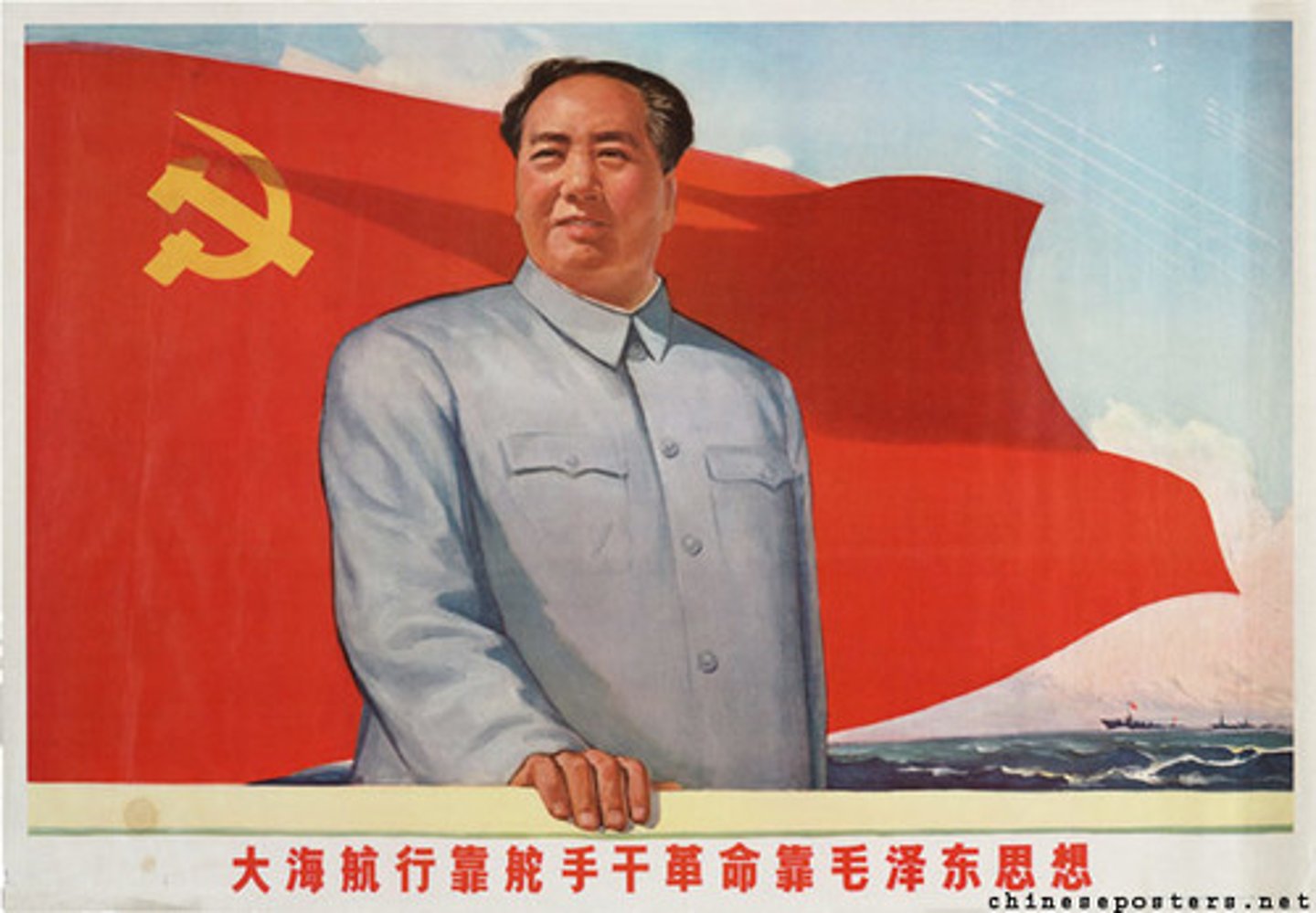
Mao Zedong
Chinese communist revolutionary; led the Communist Party to victory in the Chinese Civil War, launched the Great Leap Forward and Cultural Revolution.

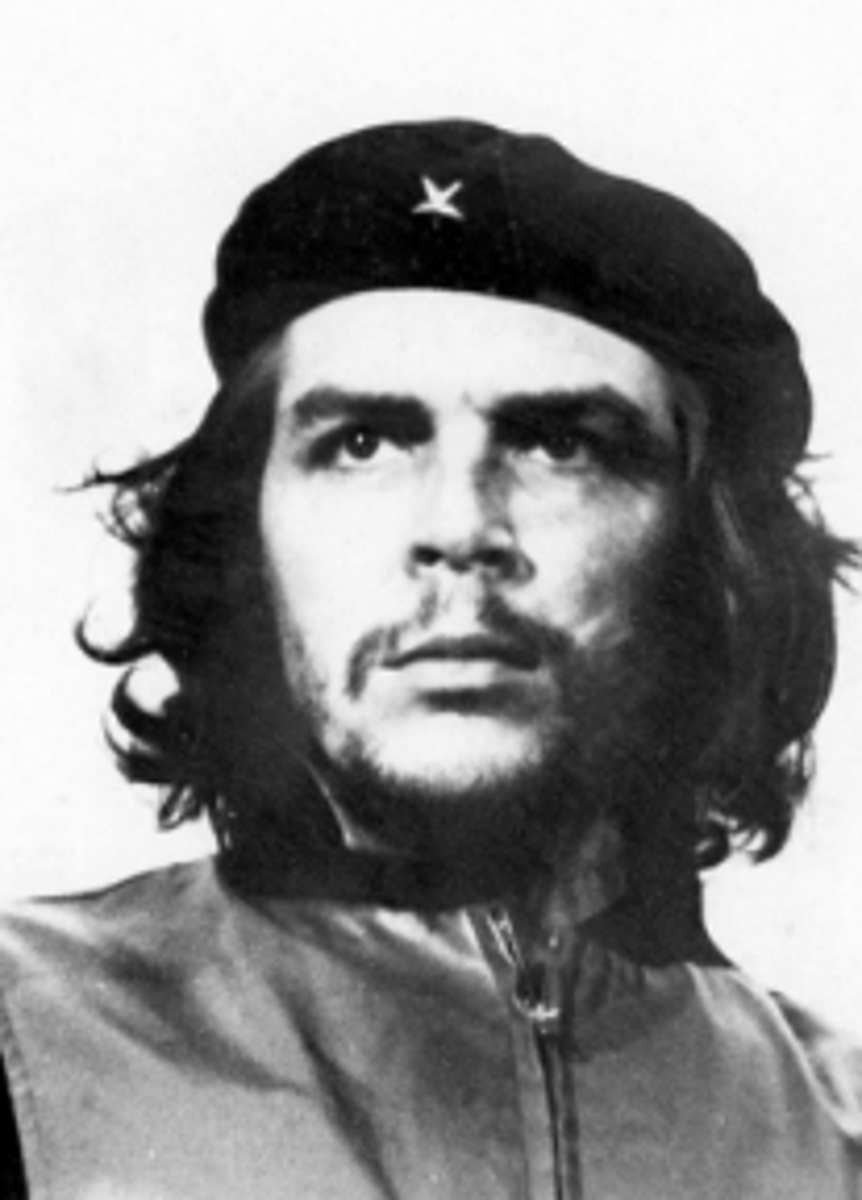
Che Guevara
Marxist revolutionary who helped Fidel Castro in the Cuban Revolution; symbol of global anti-imperialism.

Young Turks
Reform group in the Ottoman Empire that promoted modernization and nationalism; contributed to the fall of the Ottoman Empire.

Congress Party (India)
Main political party during British rule; led by Gandhi and Nehru; central to India's independence movement.

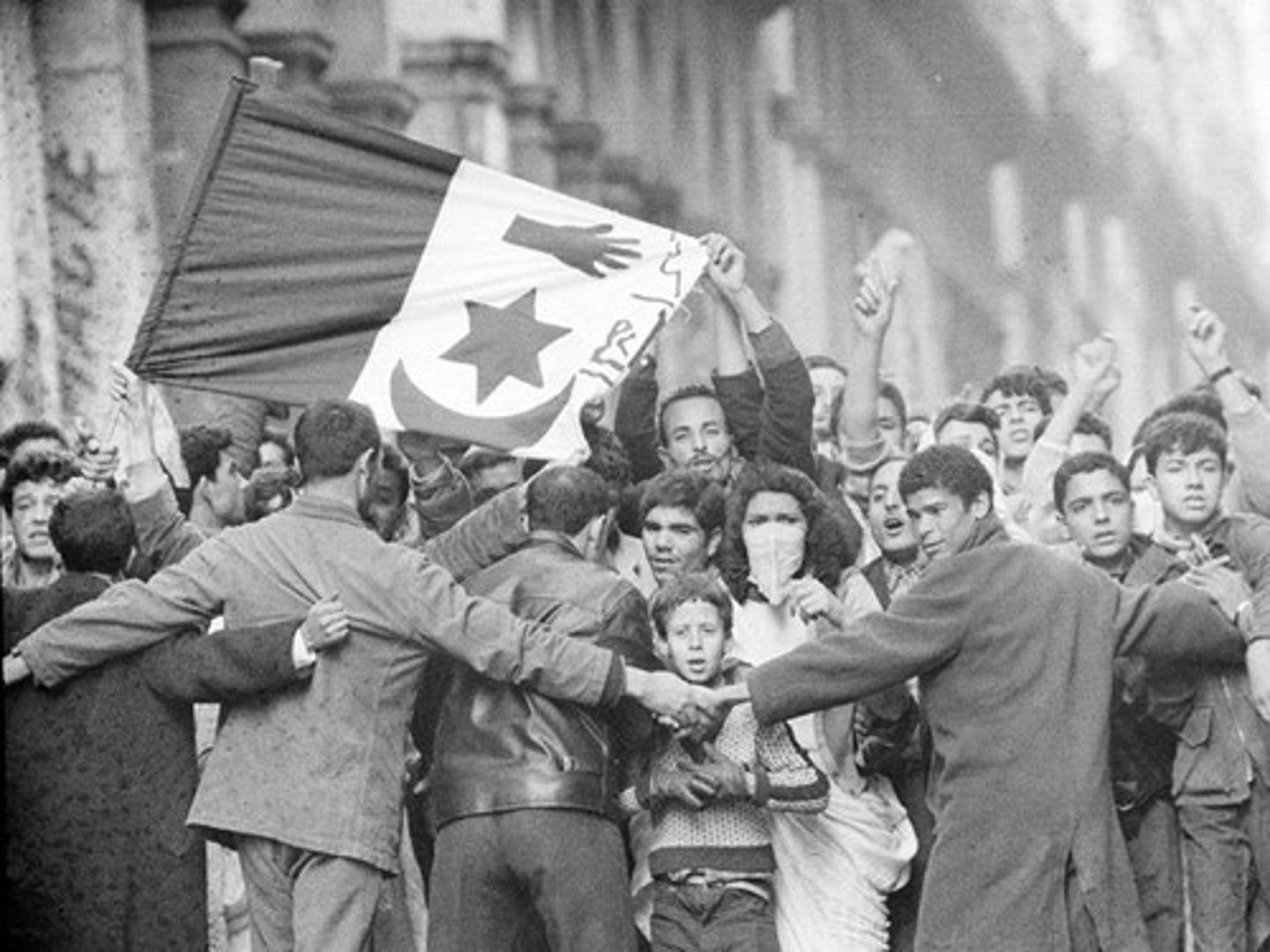
Pan-Africanism
Movement aimed at strengthening bonds between people of African descent; promoted unity and resistance to colonial rule.

Nationalism
Belief in loyalty to one's nation; fueled decolonization, unification movements (Italy/Germany), and conflicts (Balkans, WWII).

NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization):
Military alliance of Western democracies formed in 1949 to oppose Soviet expansion during the Cold War.

Liberation Theology
A Christian movement (mostly in Latin America) that used religion to advocate for social justice and fight poverty.

The World Bank
International financial institution created post-WWII to aid reconstruction and development, often tied to neoliberal policies.

Metropoles
Colonial powers' core cities; post-colonial migration led many from former colonies to settle in these cities (e.g., London, Paris).
Total War
Conflict in which nations devote all resources to the war effort (e.g., WWI, WWII), including civilian and economic participation.

Arms Race:
Competition between the U.S. and USSR during the Cold War to build up nuclear weapons and military capabilities.

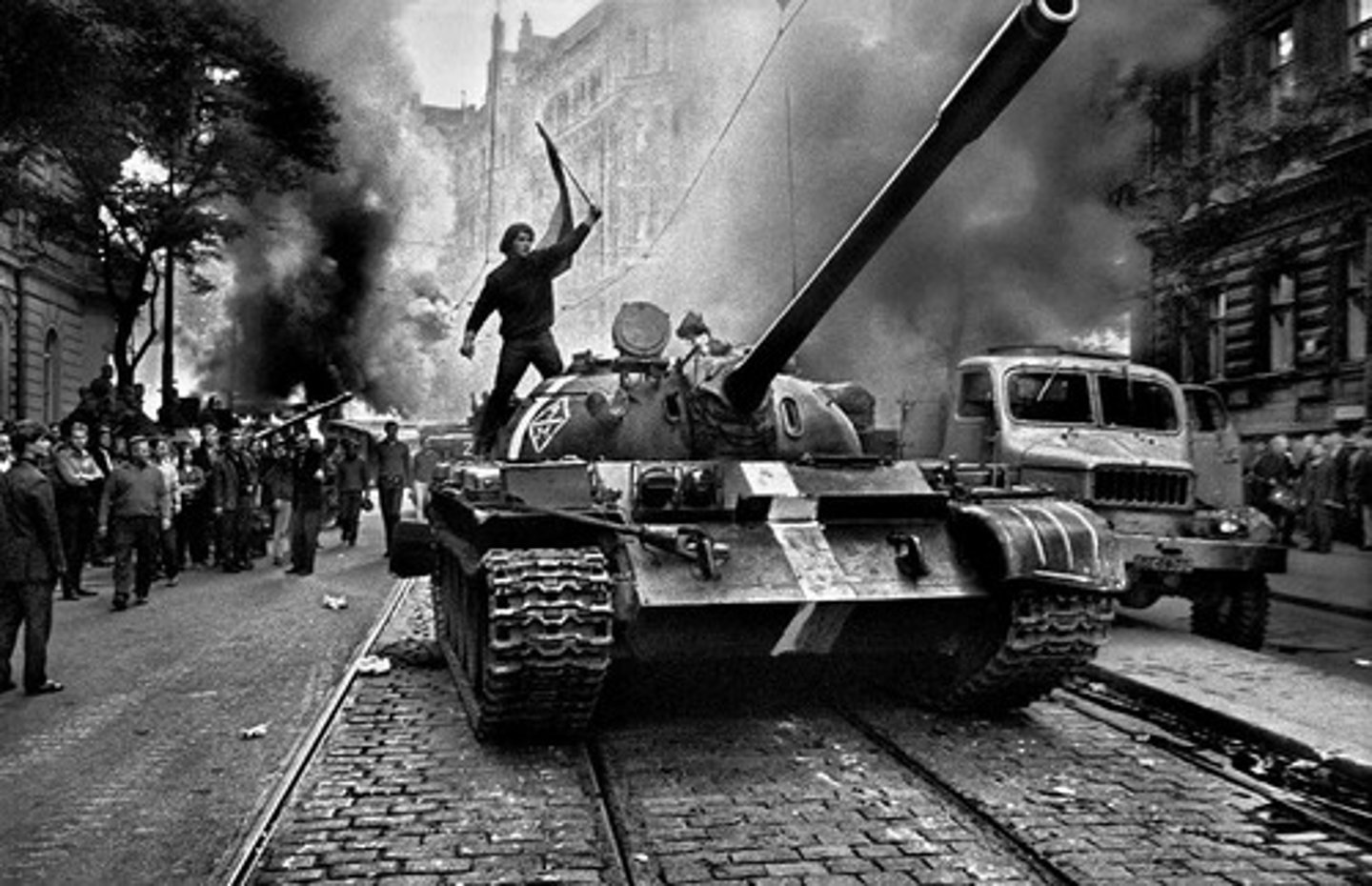
Prague Spring (1968)
Reform movement in Czechoslovakia crushed by Soviet forces; highlighted limits of liberalization in the Eastern Bloc.

Civil Disobedience:
Nonviolent resistance to unjust laws, famously used by Gandhi to challenge British rule in India.

Social Darwinism
Misapplication of Darwin's ideas to human societies; used to justify imperialism, racism, and inequality.

Neoliberalism in Latin America
Economic policy shift toward free markets, privatization, and reduced state intervention in the 1980s-90s, often promoted by the IMF and World Bank.

Green Revolution
Spread of high-yield crops and chemical fertilizers to developing countries; increased food production but led to environmental damage and social inequality.

Globalization
Increasing interconnectedness of economies, cultures, and people; accelerated by technology, trade, and international institutions.

Triple Alliance
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy (pre-war).
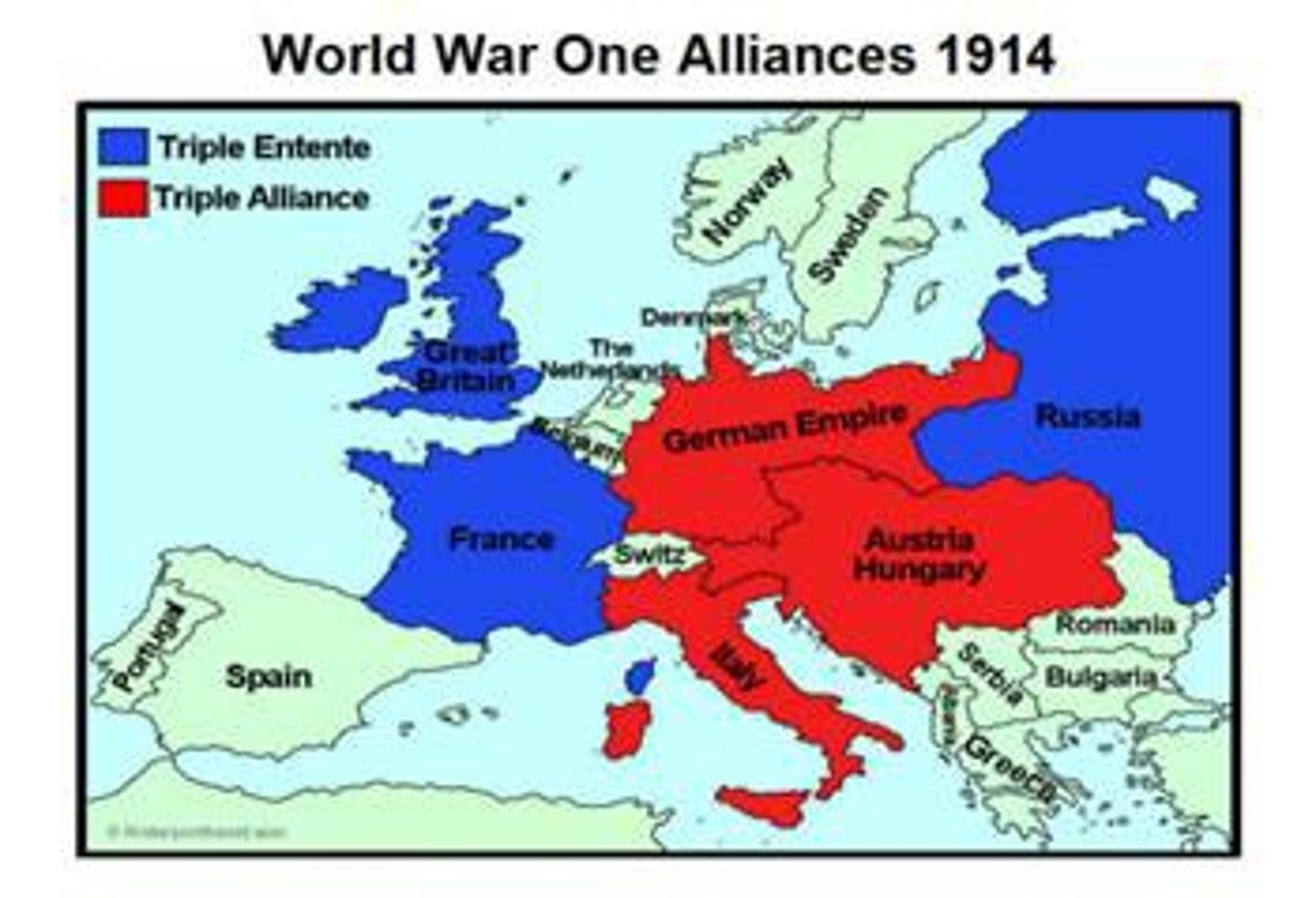
Triple Entente
Britain, France, Russia.

Alliances
Alliances created a web of obligations, making a localized conflict (assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand) escalate into a world war.

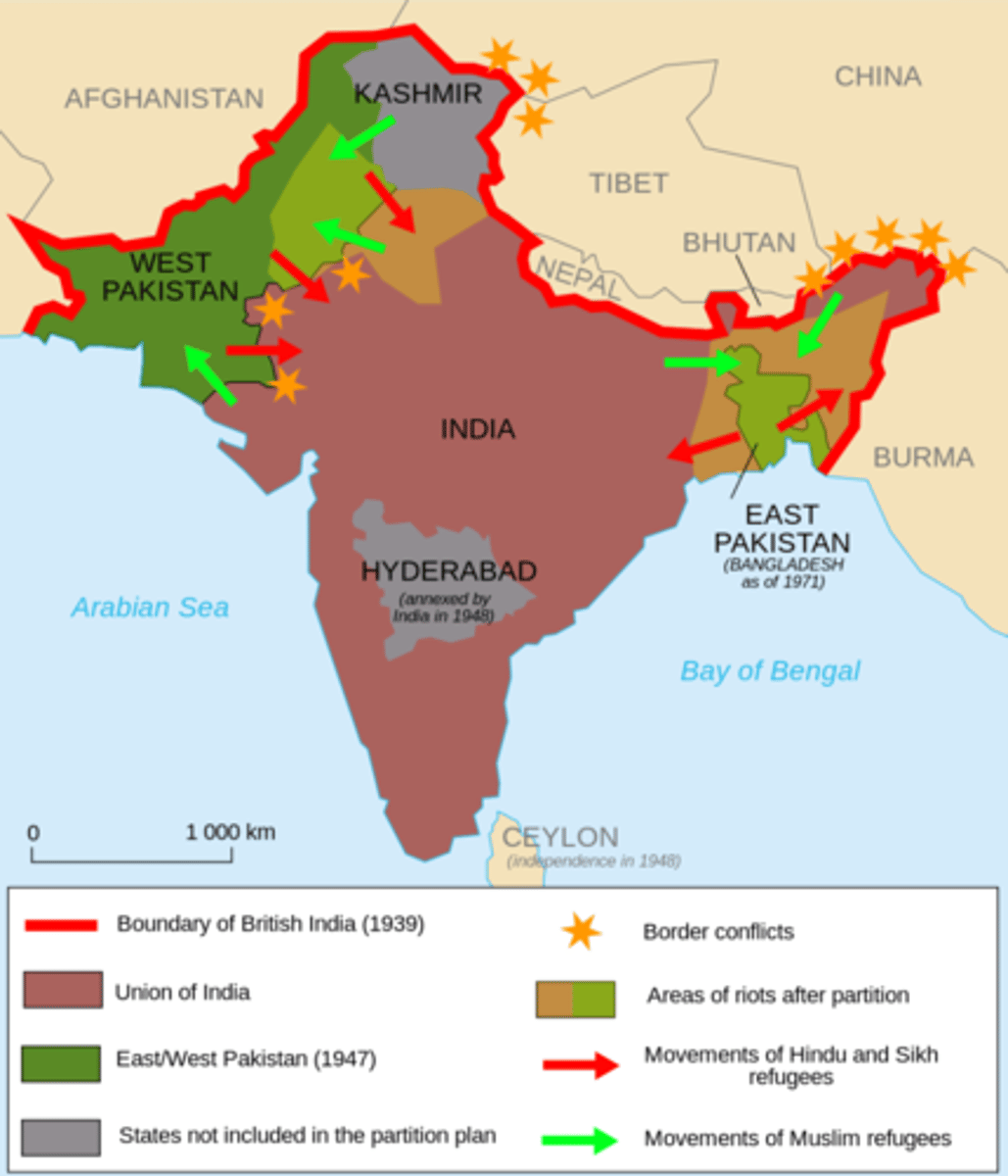
What Caused the Partition of India (1947)
Religious tensions between Hindus and Muslims; British colonial divide-and-rule; demands by the Muslim League for a separate nation (Pakistan).

What Effects Occurred Due to the Partition of India (1947)
Mass migrations (~15 million), violent riots, ~1 million deaths, creation of India and Pakistan, ongoing conflict over Kashmir.
What did Soviet Propaganda essentially do?
It Promoted Communist ideology and Soviet superiority.

What Did Soviet Propaganda come as?
It came as media, art (socialist realism), education, and censorship to control public opinion and suppress dissent.

What were the causes of Soviet Collapse (1991)
economic stagnation
Costly arms race with the U.S.
Nationalist movements within republics
Gorbachev's reforms (Glasnost and Perestroika) backfired
Loss of Eastern Bloc control (e.g., fall of Berlin Wall)
What were some examples of Nazi Ideology?
Extreme nationalism
Racial purity and antisemitism
Reaction to Treaty of Versailles (blame and humiliation)
Fear of communism and desire for strong leadership
Inspired by Social Darwinism and mythic German past

How did agricultural changes form into the Industrial Revolution?
Enclosure movement, crop rotation, and new tech increased food supply → population growth → available labor force → urbanization → industrial workforces.

What was the impact of Industrialization on Society
Positive: Tech innovation, urban growth, increased production.
Negative: Harsh working conditions, child labor, pollution, rise of class divisions → later reforms and socialism.