AP Environmental Science-Unit 1
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Biogeochemical Cycles
The movement of abiotic factors between the living and nonliving components within ecosystems; also known as nutrient cycles (i.e., water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle).
The Water Cycle
Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, run off, transpiration, infiltration. Humans impact this by storing water in reservoirs, irrigation, deforestation, and putting chemicals in it
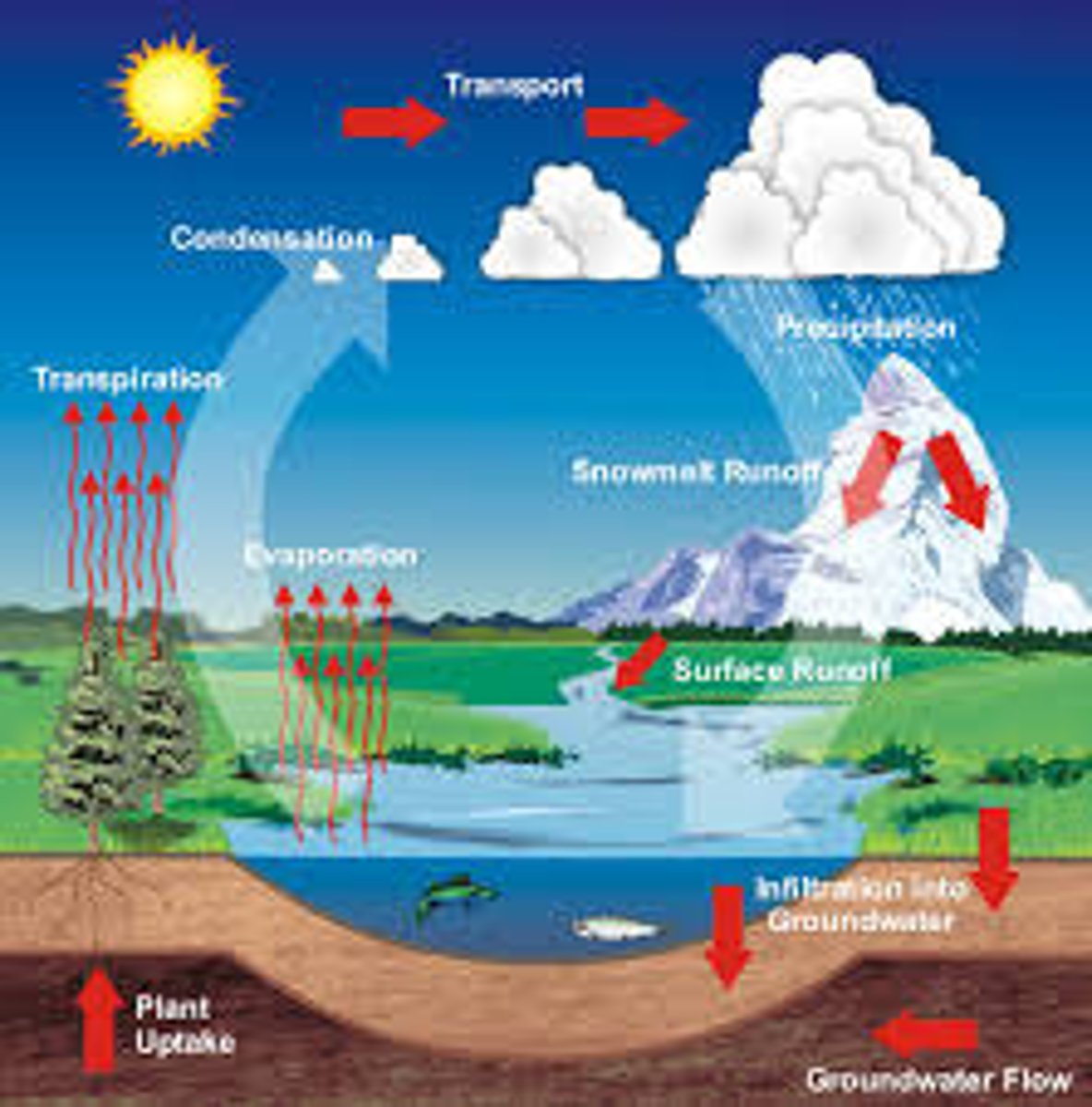
Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
Run off
The draining away of water (or substances carried in it) from the surface of an area of land, a building or structure, etc.
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
Infiltration
Flow of water from the land surface into the subsurface
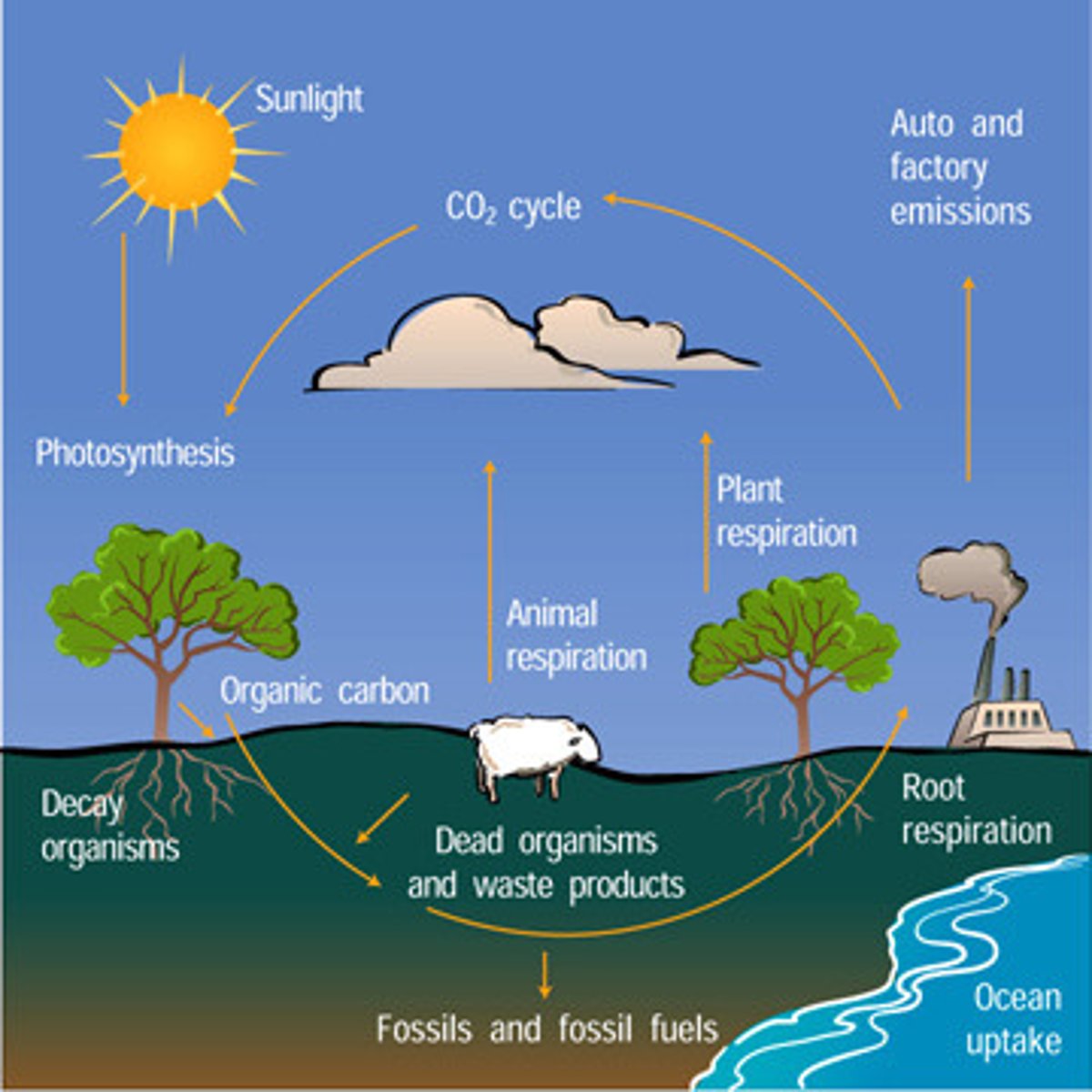
The Carbon Cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again. Humans impact this by burning fossil fuels and cutting down trees,
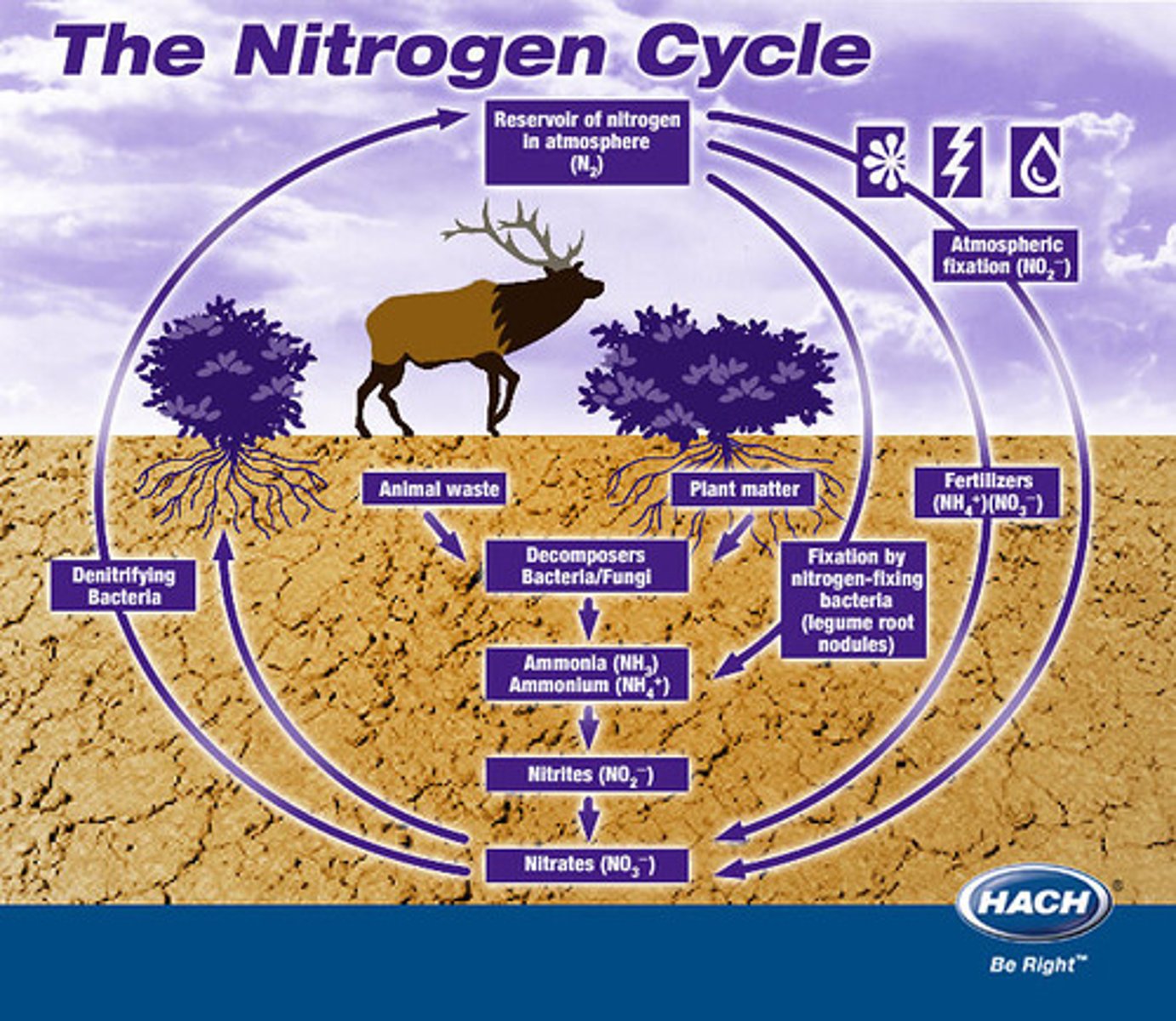
The Nitrogen Cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere. Humans impact this by altering the amount of nitrogen that is stored in the biosphere.
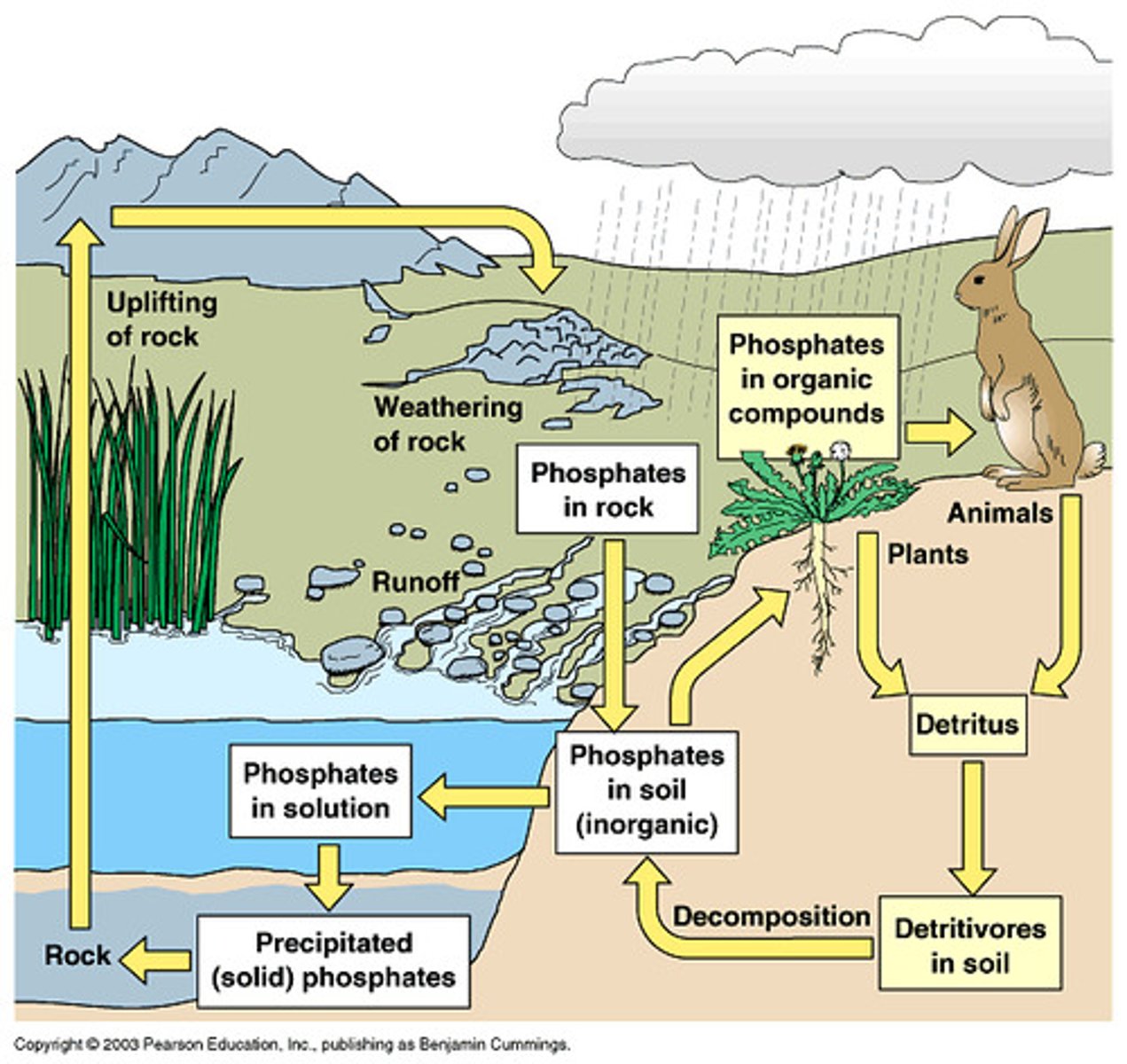
The Phosphorus Cycle
The movement of phosphorus atoms from rocks through the biosphere and hydrosphere and back to rocks.
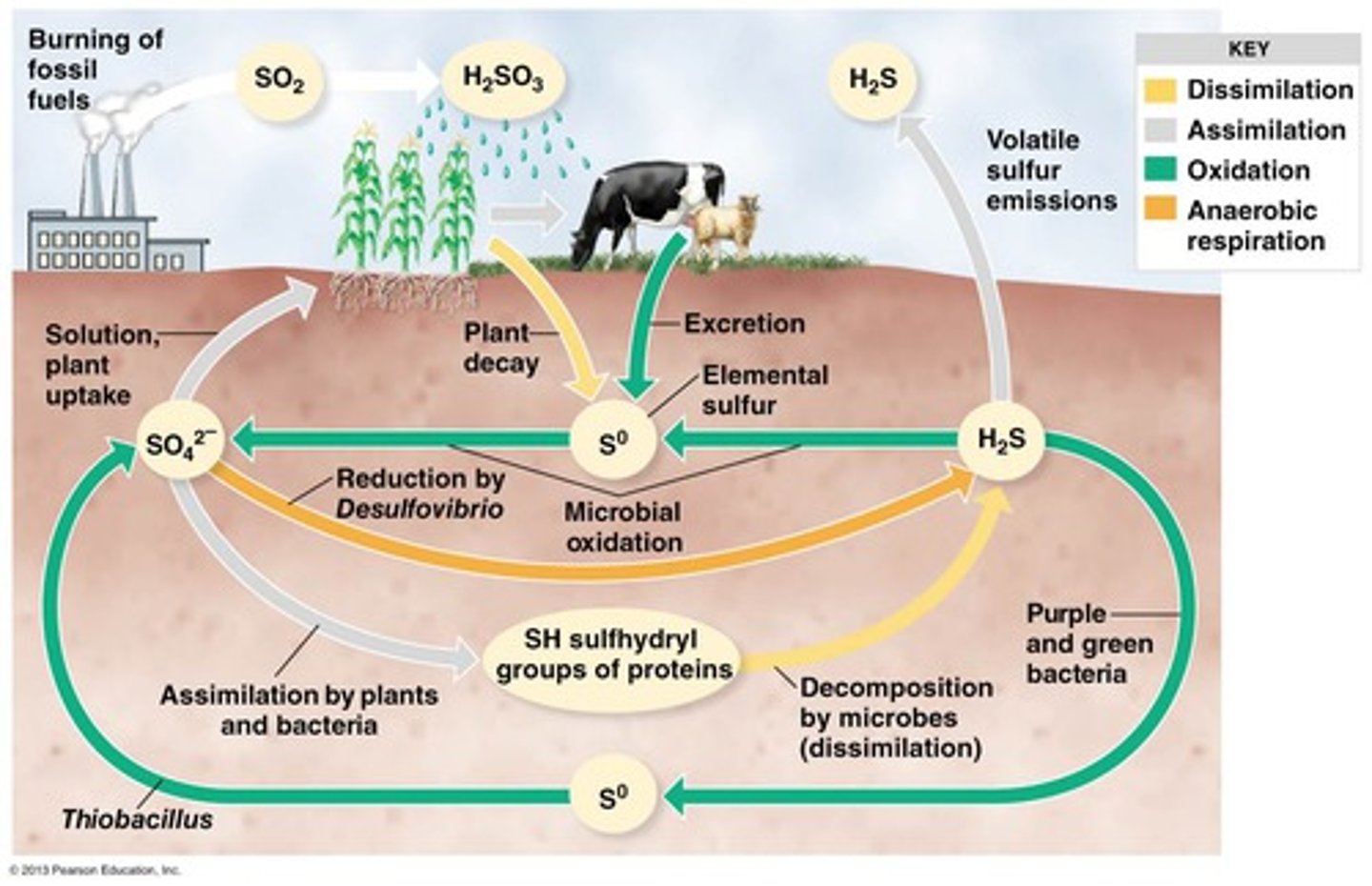
The Sulfur Cycle
Cyclic movement of sulfur in various chemical forms from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment. Humans impact this by burning coal, natural gas, and other fossil fuels which greatly increases the amount of sulfur in the atmosphere and ocean and depleted the sedimentary rock sink
Where are the four major areas of water storage on Earth?
Atmosphere, surface water, ground water, and living things
Abiotic Factors
Nonliving components of environment.
Biotic Factors
All the living organisms that inhabit an environment
Habitat
Where an organism lives and any aspect of the location
Niche
Full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions
Organism
Any form of life. Belongs to any of the 6 kingdoms
Species
Group of organisms of same type that can reproduce to have fertile offspring
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment. All abiotic and biotic factors.
Producers/Autotrophs
Organisms that make their own food from compounds and energy obtained from the environment
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy
Salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid
Plankton
Small, weakly-swimming, free floating organisms
Decomposers
Organisms that break down the dead remains of other organisms
Phytoplankton
Photosynthetic algae found near the surface of the ocean
Euphotic Zone
Surface layer where photosynthesis is usually confined to
Where are nutrients found in abundance?
In shallow and cold waters
Coral Reef
The most diverse marine biome on Earth, found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline. Only in waters 18-30 degrees celsius
Cultural Eutrophication
When human inputs of nutrients from the atmosphere and nearby urban areas accelerate the eutrophication of lakes
Watershed
The area of land that is drained by a water system
Human Impact on Freshwater Ecosystems
1. Dams, diversions, and canals fragment about 40% of our world's largest rivers
2. Flood control levees destroy aquatic habitats
3. Cities and farmlands add pollutants and excess plant nutrients to streams and rivers causing eutrophication
4. Many inland wetlands have been drained or filled to grow crops or have been covered with concrete, asphalt, and buildings
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
Climatograms
Chart that is used to better understand climate by looking at the average temperature and precipitation
Desert
An area where evaporation exceeds precipitation and usually has little vegitation. Plants are well adapted to prevent water loss.
Grasslands
Usually occur in the interiors of continents in areas too moist for deserts and too dry for forests. Seasonal drought
Savanna
Has warm temperatures year round with alternating wet and long dry seasons. Plants have deep root systems, grasses and shrubs. Grazing animals
Tundra
Treeless arctic or alpine biome characterized by cold, harsh winters, a short growing season, and potential for frost any month of the year; vegetation includes low-growing perennial plants, mosses and lichens
Tropical Rainforest
Found around the equator and has a wet and warm climate year round allowing for the growth of a dense canopy of tall trees. Have shallow root systems. Soil is low in nutrients. 40% have been destroyed
Temperate Deciduous Forest
Forest in a temperate region, characterized by trees that drop their leaves annually
Taiga(Boreal Forest)
Subarctic climate with long, cold, dry winters, and short , mild summers. Dominated by coniferous evergreen trees. Plant diversity is low
Chemosynthesis
When organisms use geothermal energy to convert inorganic compounds into carbohydrates
Consumers
An organism that obtains energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms or their remains
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Intraspecific competition
Competition among members of the same species
Interspecific Competition
Competition between members of different species
Resource Partitioning
When species competing for similar scarce resources evolve specialized traits that allow them to share resources by using parts of them, using them at different times, or using them in different ways
How does the phosphorus cycle differentiate from other biogeochemical cycles?
It does not include a gas phase
Predator Adaptations
Camouflage, speed, packs, poisons, acute senses, claws, teeth, fangs, stingers, etc.
Prey Adaptations
retreat, camouflage, warning coloration, poison, mimicry, spines, thorns, etc.
What two factors are most important in determining the type of biome that exists in an area?
Temperature and precipitation
Coral bleaching
A phenomenon in which algae inside corals die, causing the corals to turn white. When this happens, the habitat for the animals are destroyed
What are some major threats to coral reefs?
Overfishing, fishing using cyanide and dynamite, pollution from sewage and agriculture, massive outbreaks of predatory starfish, invasive species, and sedimentation from poor land use practices
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The amount of energy lost through respiration by producers sublated from the gross primary productivity of an ecosystem.
Food Chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
Food web
A community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains
What limits the number of trophic levels in an ecological pyramid?
Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels limits this. When the number of links keep increasing, the amount of energy available decreases, as only 10% of energy gets transferred from one trophic level to the next
Ecological Efficiency
Percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to another in a food chain or web
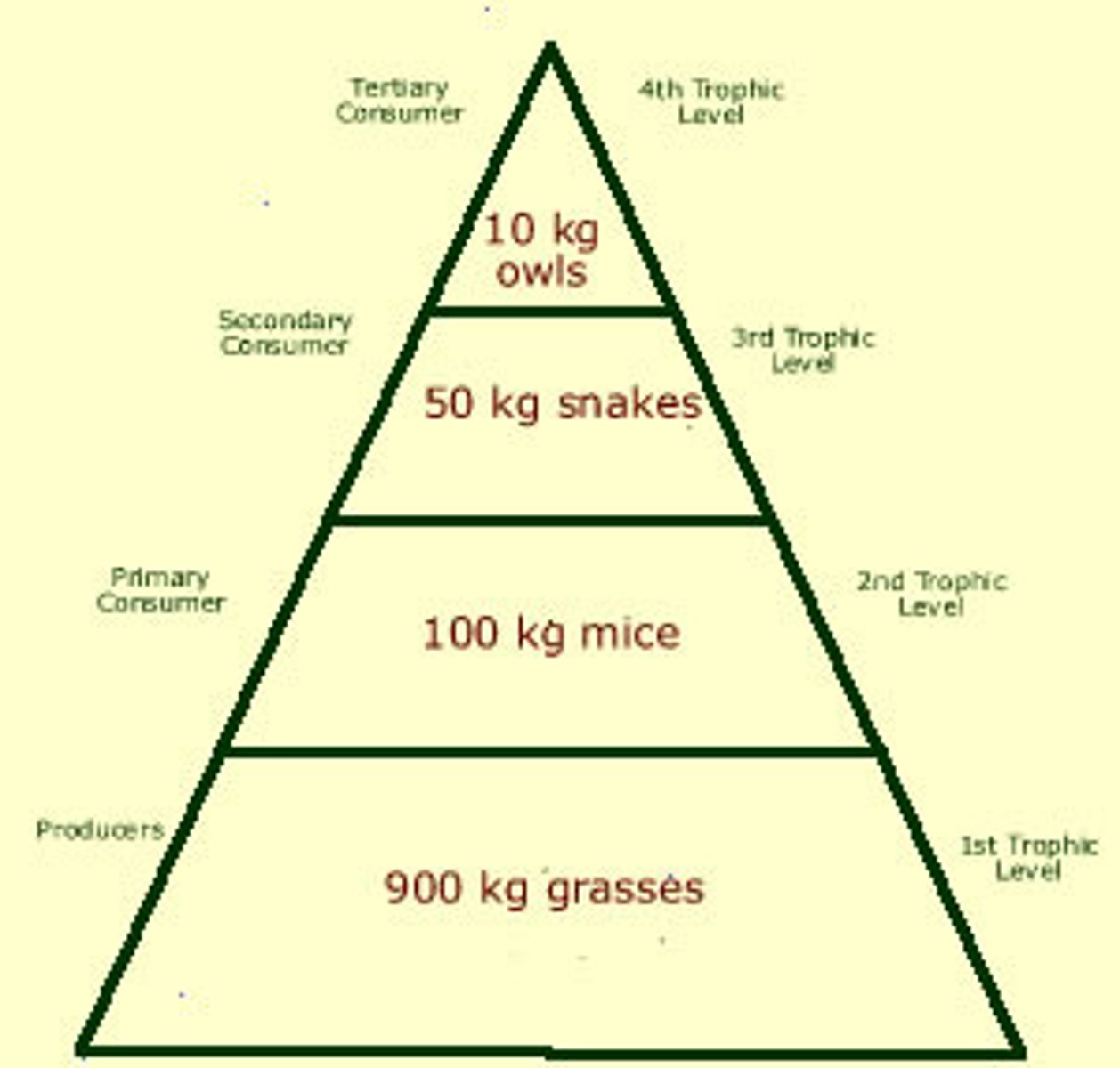
Biomass
A measure of the total dry mass of organisms within a particular region
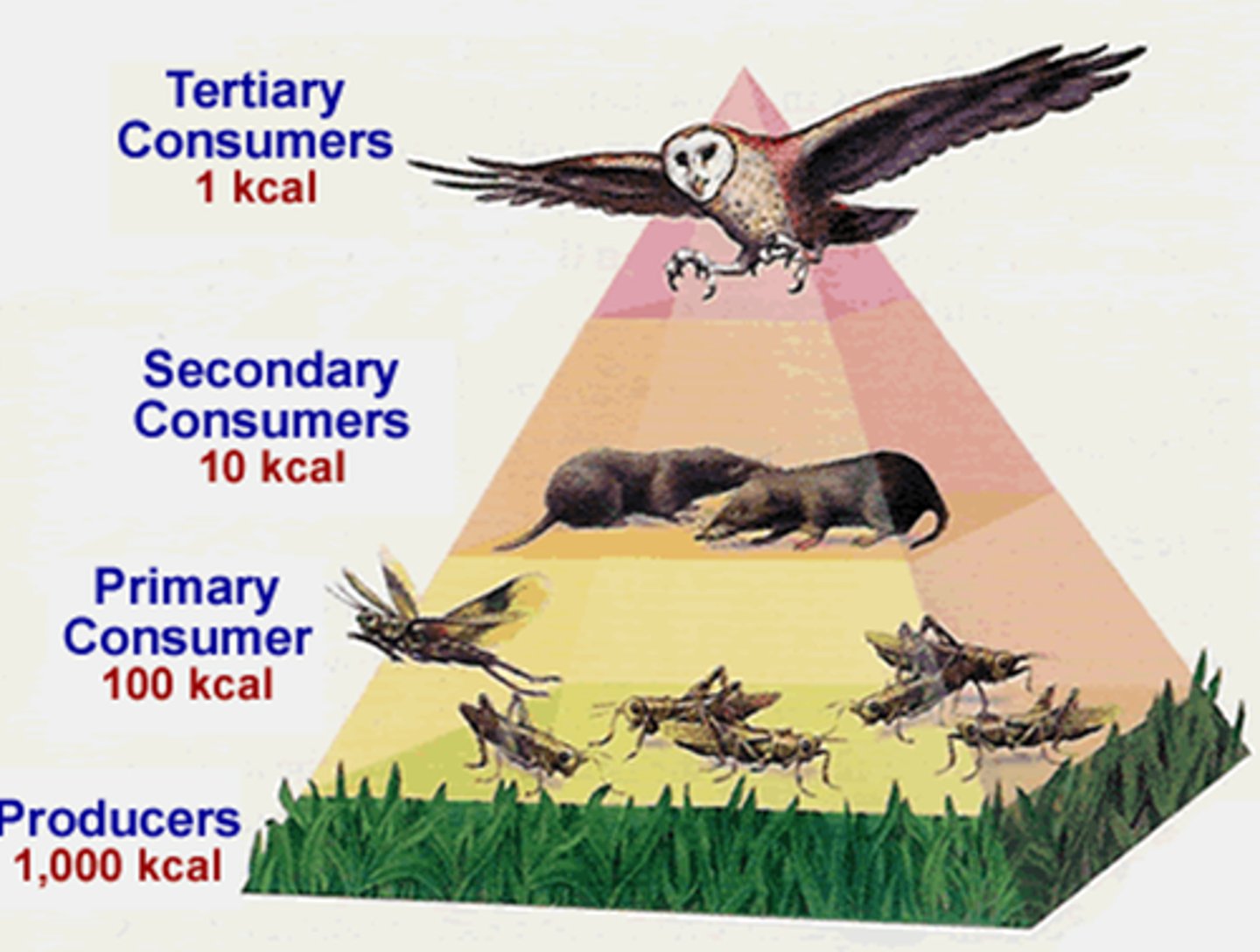
Pyramid of energy
A pyramid that shows the total amount of energy available at each trophic level
Biomass Pyramid
Diagram representing the biomass in each trophic level of an ecosystem
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
Fresh Water Biomes
ponds, lakes, streams, rivers. **Vital source of drinking water**
The Ocean
a major storage reservoir of carbon
For a primary producer, the main function of photosynthesis is to manufacture
glucose
In a typical forest ecosystem, dead trees and fallen trees are most important because of their role in
providing habitats for wildlife
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the food pyramid reduces as you go up.
Nitrogen
Most abundant gas in the atmosphere
phosphorus reservoirs
sedimentary rocks from ancient oceans (sediments)
soil
dissolved in oceans
biomass
The two major processes involved in the carbon cycle are
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
The ultimate source of energy for terrestrial ecosystems is the
sun
Tropical rain forest soil
is quickly depleted of nutrients when the forest is removed
competitive exclusion
Strong competition can lead to local elimination of one of the species.
Brazil and Indonesia
Contain the greatest area of rain forests
Bacteria in soil
Responsible for "fixing" atmospheric nitrogen so it can be used for amino acids, DNA, etc.
The approximate efficiency of the conversion of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis
1%
resource partitioning
The division of environmental resources by coexisting species such that the niche of each species differs by one or more significant factors from the niches of all coexisting species. Example: Birds and seed size