microbiota
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
halobiont
assemblages of different species that form ecological units - provides survival benefit for the different species involved
humans are holobionts
symbiosis
interaction between two different organisms living in close physical association, typically to the advantage of both e.g. nutritional benefits, transport benefits, protection
facts and figures
our gut microbiota contains tens of trillions of bacteria
ten times more than human cells in our body
microbiota, in total can weigh up to 2kg
can be considered as a endocrine organ on its own
our microbiota has co-evolved with us over millions of years
changes in the microbiota mirror species divergence
the composition of gut microbiota in unique to each individual, just like our fingerprints
more than 1000 different known bacterial species can be found in human gut microbiota, with about 150 and 170 predominating in any given subject
microbiota and our health
important in digestion (metabolizes fiber to SCFAs)
also important in many other aspects of intestinal physiology
barrier function - mucus secretion, epithelial proliferation and death, defensin production, tight junction permeability
transport function - nutrient, electrolytes ad fluid
hormone secretion from neuroendocrine cells
also important in many aspects of extra-intestinal physiology
fat and sugar metabolism
immune function
cardiovascular function
cognition
mood
enhances: metabolism, immunity, cognition, socialization, coping with stress, physical fitness
normal composition of the microbiota
can be determined by 16S DNA sequencing
estimated to be > 1000 bacterial species in the human gut
belong to 9 phyla
firmicutes
bacteriodetes
actinbacteria
fusobacteria
proteobacteria
verrucomicrobia
cyanobacteria
spirochetes
vadinBE97
bacteriodetes
communities determined by diet e.g. bacteriodes and prevotella
firmicutes
more dependent on genetic makeup e.g. clostridia and lactobacillus
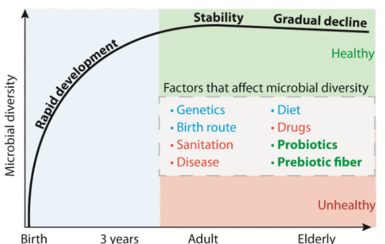
the microbiota and age
baby: fetus is sterile. becomes inoculated with vaginal and skin microbes at birth - diversity increases through interacting with the environment
adult: microbiota has fully diversified (100 spp.) and stabilized
elderly: microbiota stability and diversity decreases
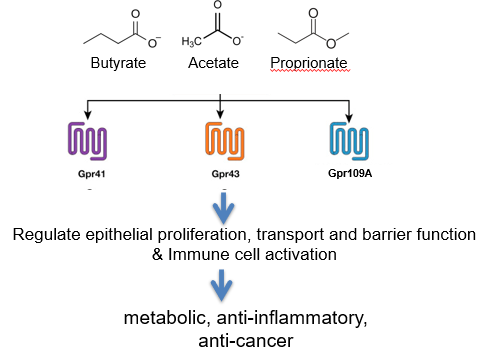
communication - the microbiota and SCFAs
colonic microbes are important in digestion of fiber to SCFAs - provides an important energy source for epithelial cells
SCFAs also have important roles in regulating our physiology
communication - the microbiota and bile acids
bile acids are produced by the liver to facilitate lipid digestion and absorption
90-95% are reabsorbed by the terminal ileum and recycled by the liver by the EHC
5-10% enter the colon and undergo bacterial metabolism
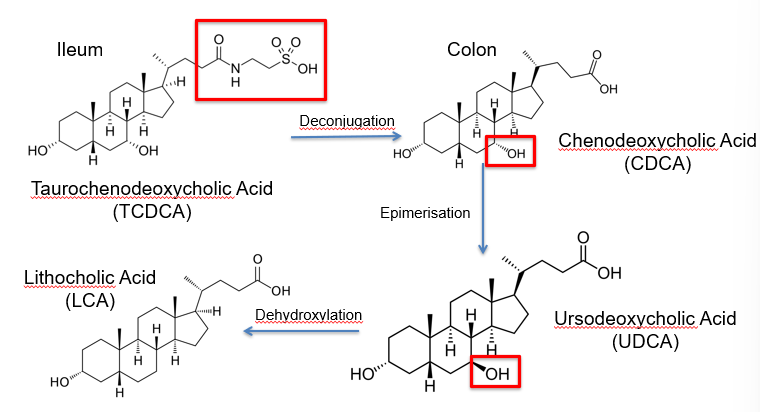
communication - the microbiota and bile acids
the colon expresses 2 receptors for bile acids
TGR5 - cell surface G protein-coupled receptor. activated by conjugated bile acids
farnesoid X receptor - nuclear receptor. activated by deconjugated bile acids. antagonized by UDCA
extent of FXR vs TGR5 activation is dependent on the makeup of the colonic microbiome
both FXR and TGR5 play critical roles in regulating
intestinal function - motility, fluid transport, barrier function
metabolic function - fat metabolism, glucose metabolism, energy expenditure
dysbiosis - alteration in the microbiota
imbalance in the normal levels of bacteria within the gut - usually associated with poor health or disease
the ratio of firmicutes to Bacteroidetes in the stool is a gauge of overall gut microbiota balance
antibiotic-associated diarrhea, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis are associated with decreased firmicutes and increased Bacteroidetes and a reduced gut biodiversity
Dysbiosis has been suggested to play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Patients with T2D have a lower F/B ratio than nondiabetic control
A higher ratio (i.e.. increased firmicutes and decreased Bacteroidetes) is associated with obesity
other disease associated with dysbiosis include: infectious diseases, IBS, cancer, atherosclerosis, autism, depression etc.)
fecal microbial transplantation
FMT is defined as the transfer of fecal material containing bacteria from a healthy donor into a diseases recipient
stool is collects from a donor (200-300g), mixed with saline and strained and placed into a patient by enema
>90% cure rate is C difficile-associated diarrhea