Bonding
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Ionic bond
Electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
Covalent bond
A shared pair of electrons
Dative covalent bond
The shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond come from only one of the bonding atoms
Direction of arrow when drawing dative covalent bond
From atom that provides lone pair to atom that is deficient
Metallic bond
Electrostatic force of attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons
3 factors affecting strength of metallic bond
Nuclear charge, number of delocalised electrons per atom, size of ion
Shape formed by ionic bonding
Giant ionic lattice
Shapes formed by covalent bonding
Simple molecular and giant covalent
Shape formed by metallic bond
Giant metallic lattice
Ionic boiling and melting points
High (because of giant lattice of ions with strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions)
Ionic solubility in water
good
Ionic conductivity when solid
Poor (ions can’t move/in fixed lattice)
Ionic conductivity when molten
Good (ions can move)
Simple molecular boiling and melting points
Low (weak intermolecular forces)
Simple molecular solubility in water
Generally poor
Simple molecular conductivity when solid
Poor (no ions)
Simple molecular conductivity when molten
Poor (no ions)
Macromolecular boiling and melting points
High (strong covalent bonds)
Macromolecular solubility in water
Insoluble
Macromolecular conductivity when solid
Diamond and sand poor, graphite good
Macromolecular conductivity when molten
Poor
Metallic boiling and melting points
High (strong electrostatic forces)
Metallic solubility in water
Insoluble
Metallic conductivity when solid
Good (delocalised electrons can move through structure)
Metallic conductivity when molten
Good
Metallic - malleable description
Planes of ions can slide over each other easily as ions are identical
Linear (b + l pairs, bond angle, example)
2, 0, 180, CO2
Trigonal planar (b + l pairs, bond angle, example)
3, 0, 120, AlCl3
Tetrahedral (b + l pairs, bond angle, example)
4, 0, 109.5, NH4+
Trigonal pyramidal (b + l pairs, bond angle, example)
3, 1, 107, PF3
Bent (b + l pairs, bond angle, example)
2, 2, 104.5, H2O
Trigonal bipyramidal (b + l pairs, bond angles, example)
5, 0, 120 and 90, PCl5
Octahedral (b + l pairs, bond angle, example)
6, 0, 90, SF6
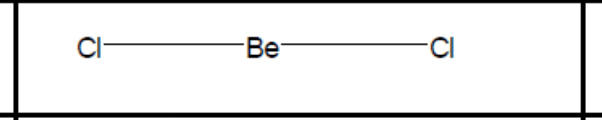
What shape of molecule?
Linear
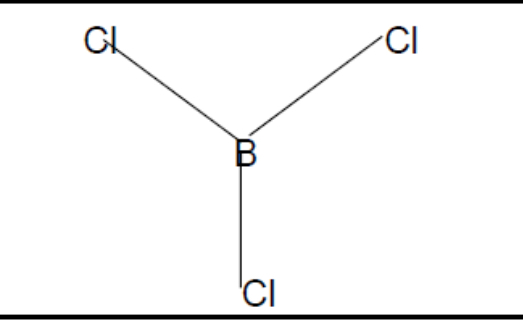
What shape of molecule?
Trigonal planar
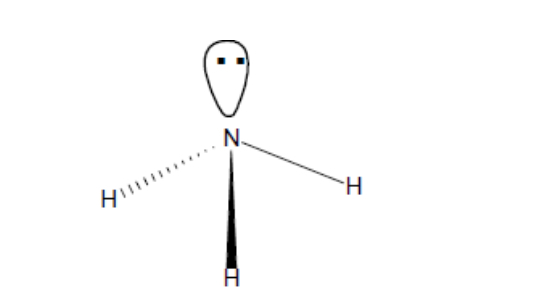
What shape of molecule?
trigonal pyramidal
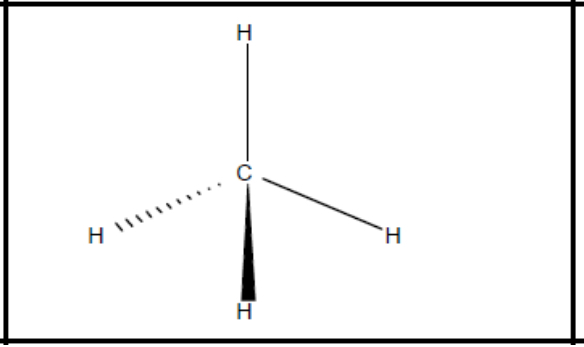
What shape of molecule?
Tetrahedral
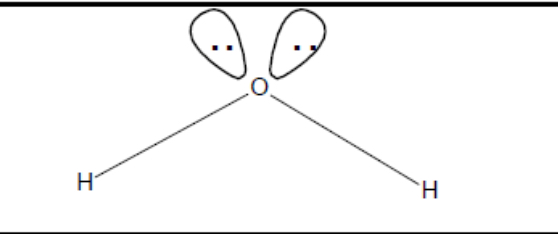
What shape of molecule?
Bent
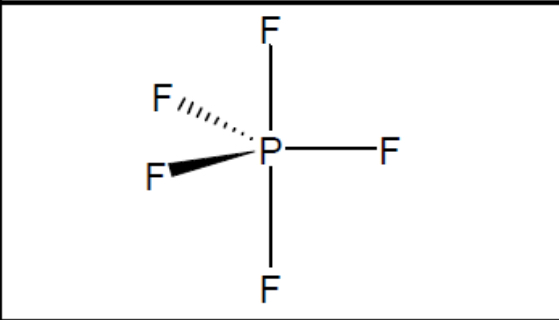
What shape of molecule?
Trigonal bipyramidal
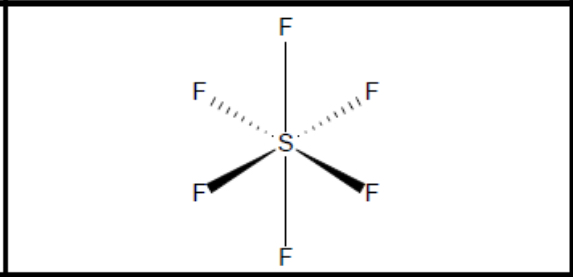
What shape of molecule?
Octahedral
Electron pair repulsion hierarchy
lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bond pair > bond pair-bond pair
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom in a covalent bond to attract electrons in the covalent bond to itself
Scale that measure electronegativity
Pauling Scale (0 to 4)
4 most electronegative atoms
F, O, N, Cl
Why does electronegativity increase across a period
The number of protons increases and the atomic radius decreases because electrons in the same shell are pulled in more
Why does electronegativity decrease down a group
The distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons increases and the shielding of the inner shell electrons increases
how large does difference in electronegativity have to be to form an ionic compound
More than 1.7
When does a polar covalent bond form
When atoms in the bond have different electronegativity (from 0.3 to 1.7)
How is a charge separation in a polar covalent bond produced
Unequal distribution of electrons (forming dipole ends)
Why symmetrical molecules can never be polar
If polar bonds are present, the individual dipoles ‘cancel out’ so there is no net dipole moment
how induced dipoles are formed
In any molecule electrons move about randomly which can form areas of high/low electron density so parts of molecule become more/less negative. This can cause dipoles to form in neighbouring molecules
Main factor affecting Van der waals forces
The number of electrons (the more electrons, the higher the chance that temporary dipoles will form, making VdW stronger between molecules)
What types of molecules do permanent dipole-dipole forces occur between
Polar molecules
Where do hydrogen bonds form
In compounds that have a hydrogen atom attached to on of the 3 most electronegative atoms (N, O and F - which must have an available lone pair of electrons)
Hierarchy of intermolecular forces
Hydrogen > permanent dipole-dipole > Van der Waals
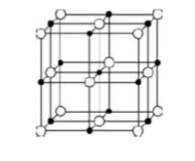
What type of bonding structure is shown?
Giant ionic lattice (alternate positive and negative ions)
What type of bonding structure is shown?
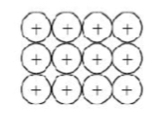
Giant metallic lattice (close packing metal ions)
What type of bonding structure is shown?
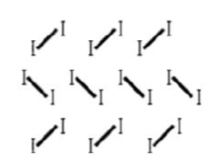
Simple molecular structure (regular arrangement held together by weak vdw forces)
What type of bonding structure is shown?
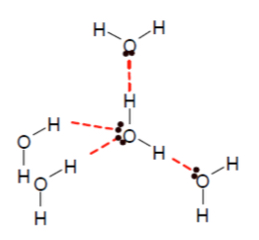
Simple molecular - ice (central water molecule with 2 ordinary covalent bonds and 2 hydrogen bonds in a tetrahedral arrangement)
What type of bonding structure is shown?
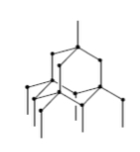
Macromolecular - diamond
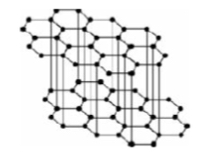
What type of bonding structure is shown?
Macromolecular - graphite (planar arrangement of carbon atoms in layers, 3 covalent bonds per atom in each layer, 4th outer electron is delocalised and is between layers)