Lecture 4 NURS 116 - Toxicity
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
toxicity
when a drug reaches outside the therapeutic range (that's why we look at the TI)
factors influencing patient response.
1. Clinical factors
2. Administration
3. Pharmacokinetics
4. Pharmacodynamics
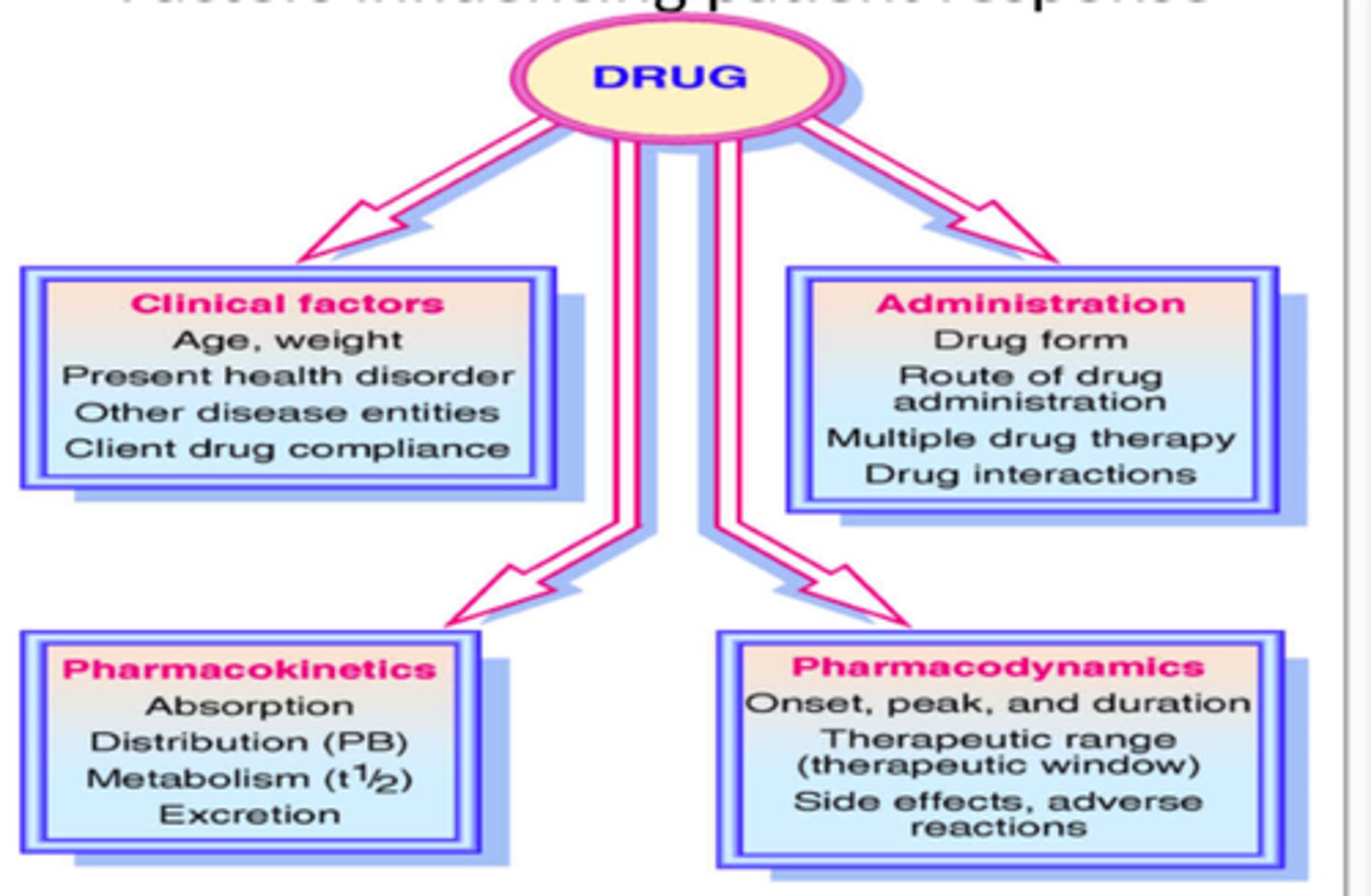
clinical factors
Age and weight, Present health disorder, other disease entities, Client drug compliance
administration
drug form, route of drug administration (bioavailability), multiple drug therapy, drug interactions
pharmacokinetics
Absorptions
Distribution (PB)
Metabolism (t1/2)
Excretion
Pharmacodynamics
onset, peak, and duration, therapeutic range (therapeutic window), side effects, adverse reactions
drug side effects
are not toxicity (may look like toxicity), what are the associated symptoms?
ex nausea and vomiting - due to noxious substance present
genetic differences affecting ADME
genetic polymorphism, metabolism - enzymatic presence and their activity with substances
ex. decreased CYP2D6 enzyme = reduced metabolism of specific drugs, risk of toxicity + reduced metabolism of prodrugs (codeine) risk of low efficacy
special safety considerations across the lifespan (pregnancy)
A = 100% safe - maternal vitamins
X = never going to use
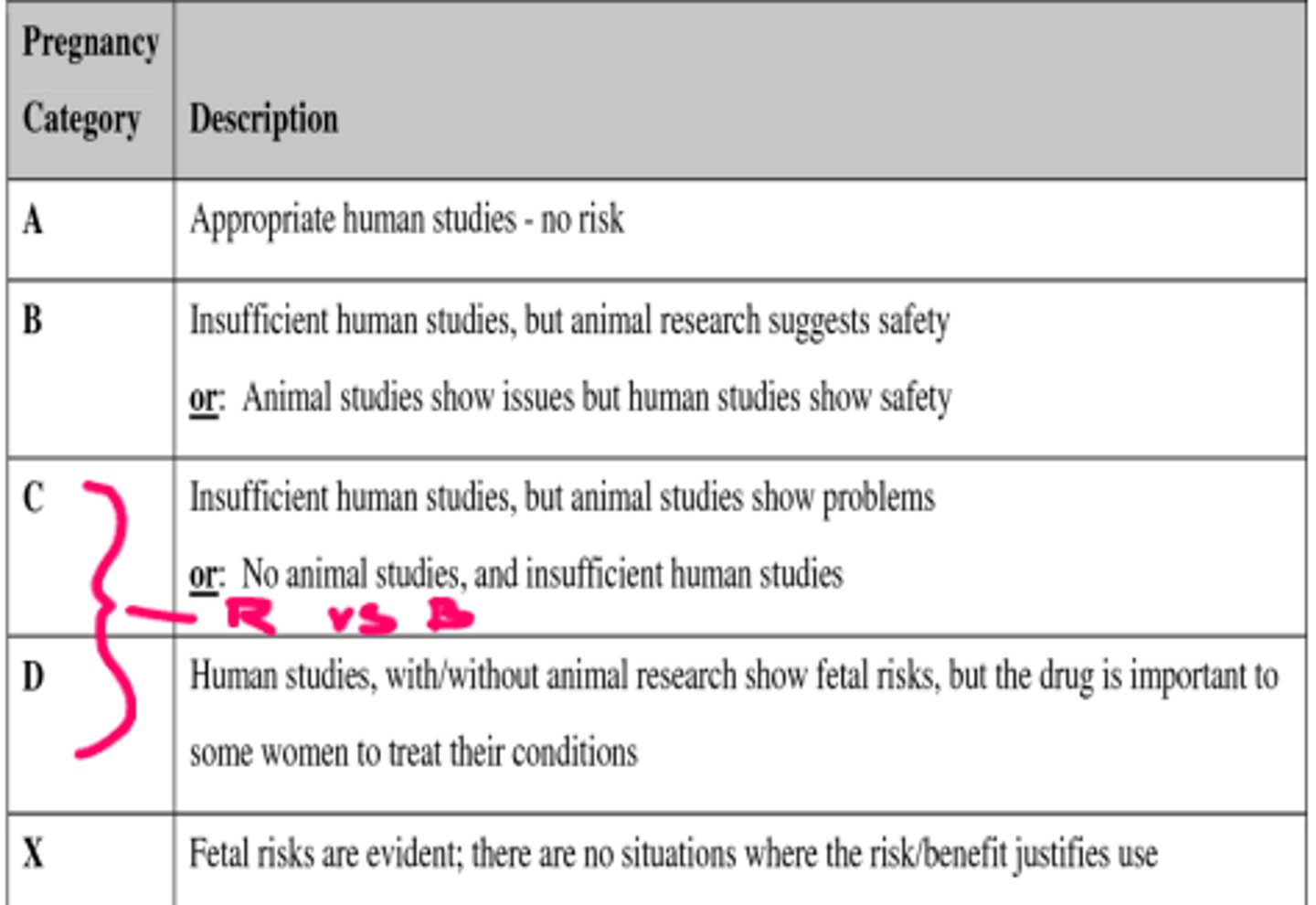
R vs B
risk vs benefit
is the risk to the baby higher than the benefit to the mother (different from patient to patient), is there any other drug in the class that will not have the risks?
How does pregnancy affect gastrointestinal function?
Pregnancy causes delayed GI emptying, leading to longer drug absorption times.
What happens to gastric acidity during pregnancy?
There is decreased acidity in the gastrointestinal tract during pregnancy.
By how much can blood volume increase during pregnancy?
Blood volume can increase by up to 50% during pregnancy.
What physiological changes occur in blood flow during pregnancy?
Increased blood flow to placenta,
higher HR
Decreased protein binding
Higher glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
Increased rate of elimination of drugs
Do most drugs cross the placenta and enter breast milk?
Yes, most drugs can cross into the placenta and into breast milk, especially those that are lipophilic with high volume of distribution (Vd).
Which medications are contraindicated during breastfeeding
Ibuprofen and opioids
How is pediatric pharmacotherapy calculated?
By body mass (per kg of body weight)
What is the pediatric blood volume per kg of body weight?
80 ml/kg of body weight
What is a key consideration for caregiver involvement in pediatric pharmacotherapy?
Education and protection from poisoning
What are common treatment focuses for teens in pediatric pharmacotherapy?
Menstrual cramps, sports injuries, and skin problems
What educational topics should be discussed with teens regarding health?
STIs and recreational drug use
How does organ function differ in neonates and young infants?
They have lower liver, renal, and lung function
What should be checked to assess organ function in pediatric patients?
Creatinine clearance, liver enzyme levels, and urine volume per hour
What happens to organ function in older adults?
Everything is decreased.
How does gastrointestinal function change in older adults?
Decreased peristalsis, acidity, and elimination.
What is the rate of decline in GFR for elders?
1% per year.
How does lung function change in older adults?
Shallower respirations.
What happens to albumin levels in older adults?
Albumin levels are lower.
How does lower albumin affect pharmacokinetics?
It affects protein binding and ADME.
What happens to cardiac output in older adults?
Cardiac output is decreased.
How does decreased cardiac output affect drug distribution?
It affects distribution of drugs.
What is the effect of lower total body water in older adults?
Increased risk of dehydration.
How does lower muscle mass affect body water in older adults?
It leads to lower total body water.
What communication issues can affect medication adherence in older adults?
Understanding and cognitive ability to remember.
What is polypharmacy?
The concurrent use of multiple medications.
- adding on to maintain a state of wellness
when they have side affects and you treat them = mountain of drugs (some cancel each other out)
Most common drug toxicities
1. ASA (aspirin)
2. Tylenol (acetaminophen)
3. opioids (oxycodone, fentanyl)
4. Benzodiazepines (xanax - alprazolam, valium - diazepam)
5. Alcohol (ETOH)
6. THC
7. Cocaine
medication errors
common nursing errors, dose errors, crushing of enteric-coated tablets or sustained-release tablets, late charting, rushing (not checking all the rights, every time)
clinical procedure in toxicity (overdose)
A = airway
B = breathing
C = circulation
D = disability
E = exposure
A &B
assess patency, effort, rate, colour
- ET tube insertion?
- O2?
C
assess perfusion quality
ex. LOC, pulses, skin, BP
- IV fluids?
- Sympathomimetics (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
D
assess for dysfunctions & treat as needed
ex. apnea, seizures, cardia arrhythmias, hyperthermia
E
identify the drug/substance & initiate treatment
Identify drug/substance
patient's health history
lab toxicology (urine, serum)
physical assessment of S&S, using a clinical tool: toxidromes
toxidromes
The SxS related to a certain group of chemicals. - hard to rely on with mixed drugs
ASA = Aspirin toxidrome
- confusion
- tachycardia
- tachypnea
- hyperthermia
- diaphoresis
- vomiting
Acetominophen (Tylenol) toxidromes
- Abdominal pain
- loss of appetite
- nausea/vomiting
- diaphoresis
- somnolence
opioids (fentanyl, codeine, morphine, oxycodone, heroin) toxidromes
everything slows down
- bradypnea/apnea
- bradycardia
- somnolence/coma
- pupils constricted
cocaine toxidromes
sodium channel blockers = numbing
- agitation, tremors
- tachycardia
- tachypnea
- hyperthermia
- diaphoresis
- pupils dilated
What are the neurocognitive effects of cannabis toxicity?
Variable presentation including agitation and coma.
What are the vital sign changes associated with cannabis toxicity?
Tachycardia and hypertension.
What are the gastrointestinal symptoms of cannabis toxicity?
Nausea and vomiting.
What severe neurological symptom can occur with cannabis toxicity?
Seizures.
What is the onset time and bioavailability of cannabis when administered via inhalation?
15-30 min onset, bioavailability 50%.
What is the onset time and bioavailability of cannabis when administered orally?
1-2 hr onset (variable), bioavailability 20%.
What effect does THC have on the central nervous system?
Causes CNS and vital sign instability, dose dependent.
What role does CBD play in relation to THC?
CBD modulates the effect of THC at receptors.
cannabis toxicity treatment
only supportive - no direct way of treating cannabis overdose
What is a clinical tool used in treatment?
Algorithms
What does ADME stand for in treatment utilization?
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion
What is the first step in stabilizing a patient?
Supportive treatment
What is the treatment for seizures?
Benzodiazepines - are inhibitory for the brain - calm brain
What is the treatment for hypertension?
Antihypertensives
What is the treatment for respiratory distress?
Intubation
What is the treatment for psychosis?
Antipsychotics
adsorption
binding of drug, to decrease its absorption - bind drug before it enters systemic circulation (very reliable if toxin can be bound)
ex. Tylenol, ASA, benzodiazepines
What is the name of the drug used in adsorption treatment?
Activated charcoal
How does activated charcoal work in adsorption treatment?
It binds the drug to the surface of carbons.
What is the route of administration for activated charcoal?
Enteral route (the drug must be in the GI tract).
How is activated charcoal eliminated from the body?
Via stool.
What are the two main ways to induce metabolism?
1. Give a substance that will induce metabolism
2. Give an enzyme that will metabolize the drug
What happens in Tylenol toxicity?
It depletes the liver enzyme glutathione.
What is NAC and its role in Tylenol toxicity?
NAC (n-acetylcysteine) is a glutathione enzyme precursor that enhances phase 2 metabolism.
alcohol toxidromes
Becomes a sedative = inhibitory to the brain
- slow or irregular breathing
- low body temperature
- vomiting
- seizures
- unconsciousness and can't be woken up
What enzyme metabolizes alcohol in the liver and gastrointestinal tract?
Alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme (ADH)
What is the role of acetaldehyde in alcohol metabolism?
Metabolized by ALDH; lack of ALDH leads to flushing and sweating.
What effect does acetaldehyde have on alcohol dehydrogenase?
Acetaldehyde shuts off ADH, inhibiting phase 1 metabolism.
What are the central nervous system effects of alcohol?
Alcohol has drug-dose dependent effects, binding to GABA receptors and inhibiting glutamate.
How does alcohol affect antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Alcohol inhibits ADH, leading to diuresis.
What are the consequences of alcohol-induced diuresis?
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
What vitamin is depleted during chronic alcohol use?
Vitamin B.
What is the effect of chronic alcohol use on GABA receptors?
Chronic use down-regulates GABA receptors.
What is a treatment drug for alcohol metabolism?
Metadoxine.
What is the function of metadoxine in alcohol treatment?
It induces alcohol dehydrogenase metabolism.
What supportive treatment is often given alongside metadoxine?
IV fluids.
How can activated charcoal increase drug elimination?
It increases GI elimination of charcoal-bound drugs.
What is a method to induce acidic drug excretion via the kidneys?
Alkalization, such as using sodium bicarbonate for ASA toxicity.
What is hemodialysis used for?
It is used for the active removal of substances from the blood.
What is antagonism in pharmacology?
Antagonism of a specific receptor leads to cessation of drug action.
What is the opioid receptor antagonist used in the treatment of opioid toxicity?
Narcan
What is the route of administration for Narcan?
IV
What is the GABA receptor antagonist used in the treatment of benzodiazepine toxicity?
Flumazenil
What is the route of administration for flumazenil?
IV