Unit 5: The Integumentary System
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
membranes
these cover surfaces, line body cavities, and form protective sheets around organs
epithelial
this group of membranes contains cutaneous, mucous, and serous
connective
this group of membranes includes synovial
cutaneous membrane
outermost membrane, protects all underlying organs
mucous membrane
membrane that makes mucus, lines cavities and tubes that open to the outside of the body, and prevents membranes from drying out
mucous membrane
this membrane is found in the mouth, nose, digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
serous membrane
membrane that covers body cavities that do not open to the outside
serous fluid
what type of fluid allows organs to slide by each other without friction?
parietal
outer
visceral
inner
pleura
serous fluid around the lungs
pericardium
serous fluid around the heart
peritoneum
serous fluid around other internal organs
synovial
membrane that lines the joints
synovial fluid
what type of fluid is in the joint cavity?
skin
what is the largest organ in the body?
protective covering, aids in the regulation of body temp, slows down water loss from underlying tissues, excretes waste
what are the functions of the skin?
epidermis
the outer layer of the skin
stratified squamous epithelium
what kind of tissue is the epidermis made of?
avascular
is the epidermis vascular or avascular?
epidermis
what layer of skin is capable of keratinizing?
dermis
the inner, thicker layer of skin
connective tissue
what type of tissue is the dermis mostly made of?
subcutaneous layer/hypodermis
the additional layer beneath the dermis
adipose tissue
what type of tissue is the hypodermis made of?
anchor skin to underlying organs, shock absorber & insulator
what are the main functions of the hypodermis?
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
what are the 5 zones of the epidermis?
keratinocytes
keratin cells
stratum basale
layer of the epidermis where cells are alive and nourished by blood vessels in the dermis and are dividing
stratum spinosum
2nd layer up where daughter cells land
granulosum
middle layer of the epidermis that is the first layer of completely dead cells, keratin accumulating
stratum lucidum
layer of epidermis that is on the palms and soles of feet only
stratum corneum
outermost layer, full of keratin, 20-30 layers of dead cells
every 25-45 days
how often do we have a “new” epidermis?
melanin
type of pigmented protein made in the stratum basale by specialized cells
melanocytes
cells that make melanin
epidermis
What is A?
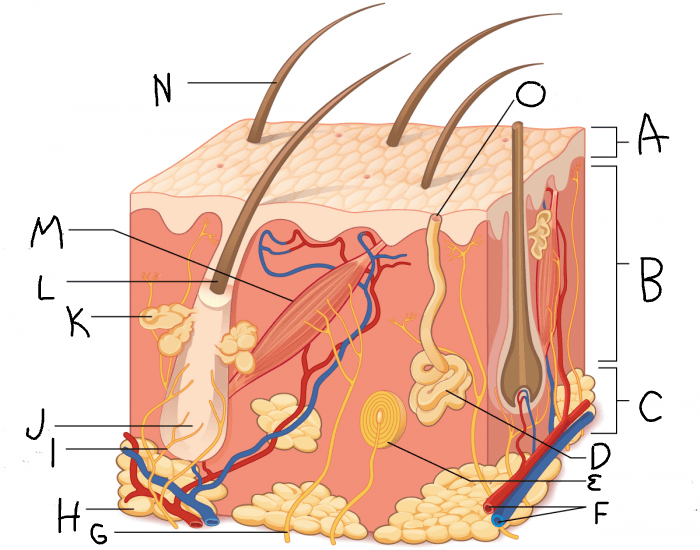
dermis
What is B?
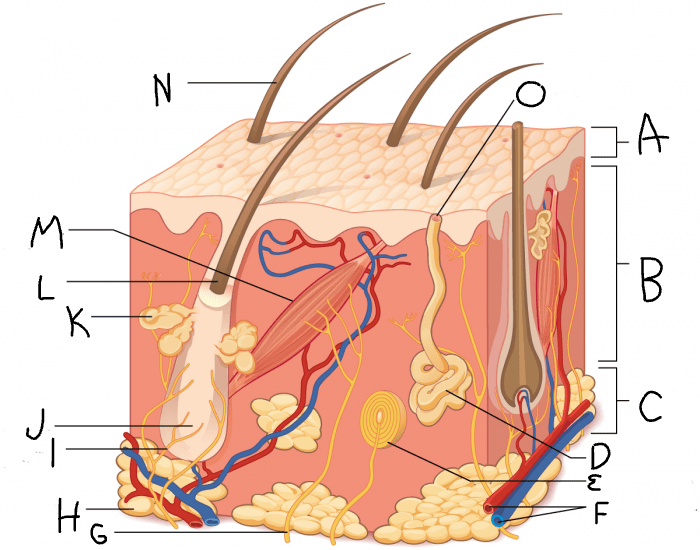
hypodermis/subcutaneous layer
What is C?
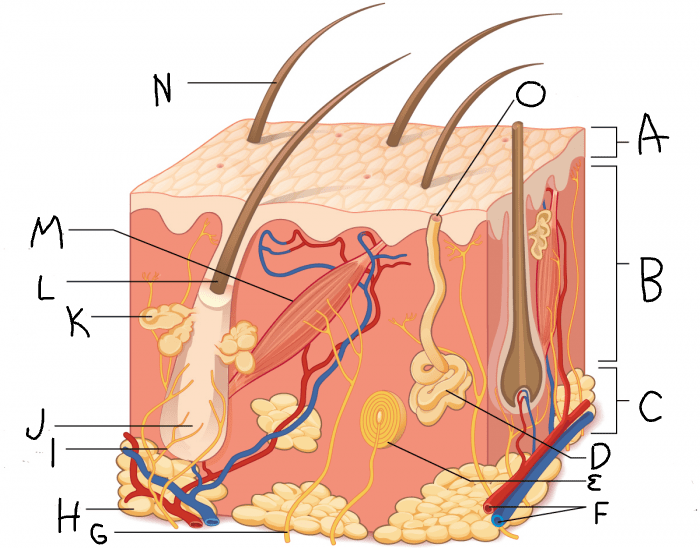
eccrine sweat gland
What is D?
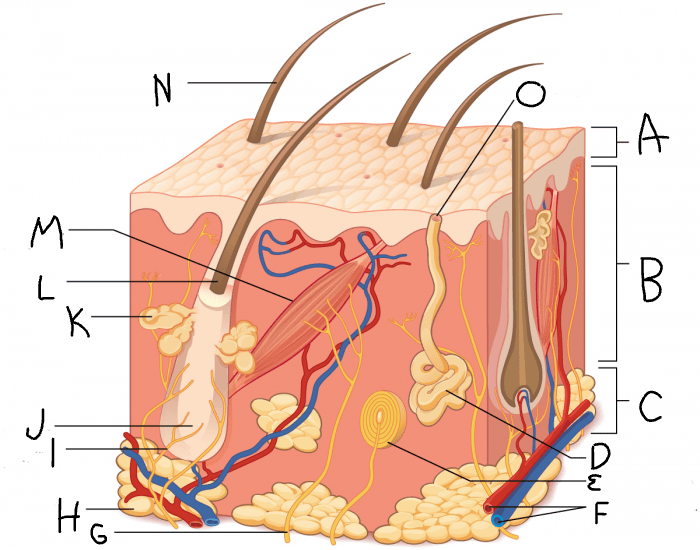
hair follicle
What is J?
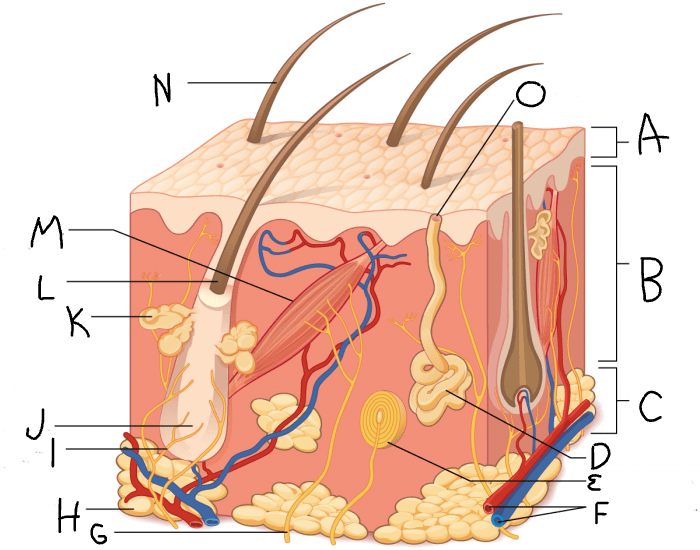
sebaceous gland
What is K?
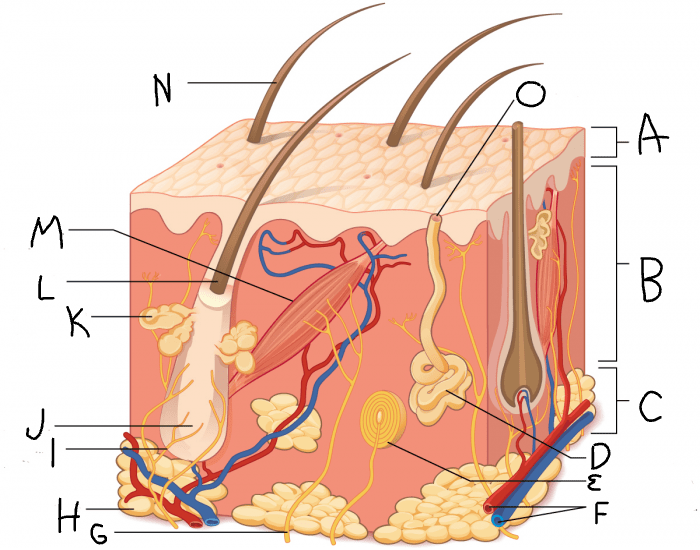
arrector pili muscle
What is M?
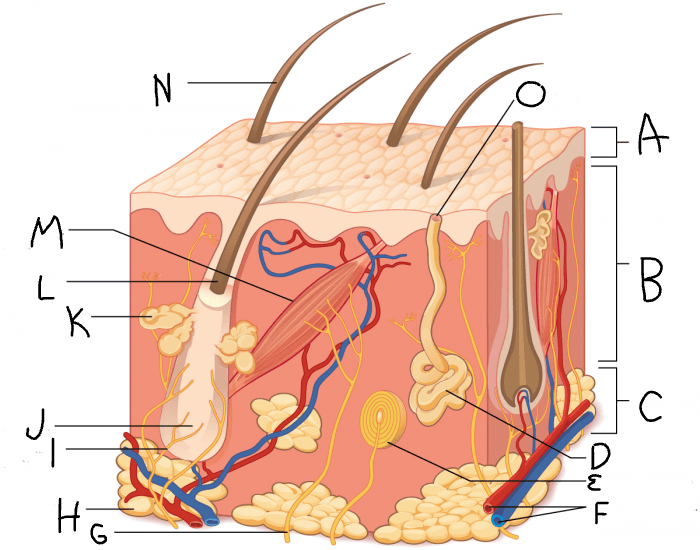
hair
What is N?
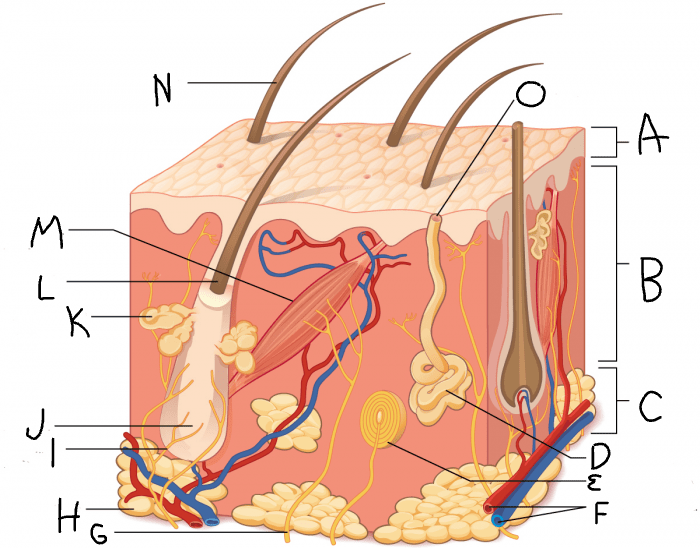
eccrine sweat pore
What is O?
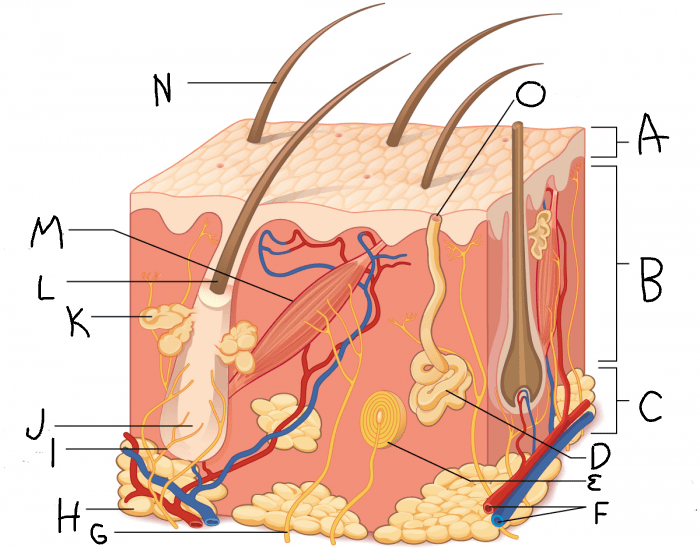
papillary layer
the layer of the dermis that contains dermal papillae
fingerprints
dermal papillae that are arranged in a pattern, genetically determined, and indent the epidermis
oil
what do fingerprints leave behind due to lots of sweat pores?
reticular layer
what is the deepest skin layer that contains blood vessels, sweat glands, oil glands, hair follicles, and muscles?
collagen
what makes the dermis tough?
wrinkles
as collagen and elastin decrease with age, this causes…
blood vessels
These play an important role in maintaining body temperature…
swell
when the body temp increases the blood vessels do what?
constrict
when the body temp decreases, the blood vessels do what?
melanin, carotene, hemoglobin
what 3 factors determine skin color all the time?
erythma
blushing/red color
pallor/blanching
ill, anemic, scared/white color
jaundice
yellowing
hematoma
bruise
sebaceous gland
glands whose ducts empty into hair follicles
sebum
what do sebaceous glands produce?
sweat
sudor means…
sweat glands
glands that look like a coiled ball
eccrine sweat glands
glands that are activated by elevated body temp
pores/directly out of the skin
where do eccrine sweat glands exit?
apocrine sweat glands
glands that are activated when a person is emotionally upset and at the onset of puberty, empty into hair follicle
armpits and groin
where are apocrine sweat glands located?
follicle
a pouch where hair grows from within the dermis
root
hair enclosed in the follicle
dead epidermal cells
what is hair?
hair shaft
older cells that have been pushed to the surface, become keratinized, and die, making the…
medulla
core of hair
cortex
middle layer of hair
cuticle
outer layer of hair
genes
what determines your personal hair color?
darker
if you produce more melanin, your hair will be…
lighter
if you produce less melanin, your hair will be…
white
if you produce no pigment, your hair will be…
arrector pili muscle
smooth muscle attached to each hair follicle
nails
these contain more keratin than your hair and skin and grow from the stratum basale
lunula
whitish, half moon region on your nail, most active grownng region
cyanotic
blue fingernails/toenails are…
athlete’s foot
fungal infection of the feet
boils and carbuncles
inflammation of a hair follicle (or follicles)
cold sores
blisters caused by herpes virus
contact dermatitis
redness, swelling, caused by exposure to chemicals
impetigo
lesions caused by staph infections
psoriasis
overproduction of skin cells results in red lesions covered by scales
burn
tissue damage and cell death caused by intense heat, electricity, UV radiation, chemicals
intense heat, electricity, UV radiation, chemicals
what are the 4 ways to get a burn?
1st degree burn
burn where only the epidermis is damaged: red, painful, dry (no blisters), generally heals in 2-3 days
2nd degree burn
burn where there is damage to the epidermis and upper regions of the dermis, red, painful, and blisters
3rd degree burn
burn that destroys the entire thickness of the skin, nerve endings are destroyed and regeneration is not possible
neoplasm
another word for tumor
benign
noncancerous
malignant
cancerous
skin cancer
what is the most common type of cancer?
skin cancer
overexposure to UV rays, chemicals, and physical trauma are the causes of what?
basal cell carcinoma
the type of cancer that is the least malignant, most common, occurs in the stratum basale, and appears as a shiny dome nodule
squamous cell carcinoma
cancer that arises from the stratum spinosum, is scaly and a reddened elevation, is common on the scalp, ears, back of hands, and lower lip