AP Biology Final
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
A researcher proposes a model of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in which a reactant is converted to a product. The model is based on the idea that the reactant passes through a transition state within the cozyme-substrate complex before the reactant is converted to the product. Which of the following statements best helps explain how the enzyme speeds up the reaction?
(A) The enzyme's active site binds to and stabilizes the reactant, which decreases the free-energy change of the reaction.
(B) The enzyme's active site binds to and stabilizes the transition state, which decreases the activation energy of the reaction.
(C) The enzyme's active site binds to and stabilizes the product, which increases the amount of energy released by the reaction.
(D) The enzyme's active site binds to and stabilizes both the reactant and the product at the same time, which increases the reaction's equilibrium constant.
The enzyme's active site binds to and stabilizes the transition state, which decreases the activation energy of the reaction.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is an enzyme that aids in the decomposition of ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) into nontoxic substances. Methyl alcohol acts as a competitive inhibitor of ethyl alcohol by competing for the same active site on ADH. When attached to ADH, methyl alcohol is converted to formaldehyde, which is toxic in the body.
Which of the following statements best prediets the effect of increasing the concentration of substrate (ethyl alcohol), while keeping the concentration of the inhibitor (methyl alcohol) constant?
(A) There will be an increase in formaldehyde because ADH activity increases.
(B) Competitive inhibition will be terminated because ethyl alcohol will bind to methyl alcohol and decrease ADH activity.
(C) The peptide bonds in the active site of the enzyme will be denatured, inhibiting the enzyme.
(D) Competitive inhibition will decrease because the proportion of the active sites occupied by substrate will increase.
Competitive inhibition will decrease because the proportion of the active sites occupied by substrate will increase.
A mutation in the gene coding for a single-polypeptide enzyme results in the substitution of the amino acid serine, which has a polar R group, by the amino acid phenylalanine, which has a nonpolar R group. When researchers test the catalysis of the normal enzyme and the mutated enzyme, they find that the mutated enzyme has much lower activity than the normal enzyme does.
Which of the following most likely explains how the amino acid substitution has resulted in decreased catalytic activity by the mutated enzyme?
(A) The substitution decreased the mass of the enzyme so that the mutated enzyme binds more weakly to the substrate than the normal enzyme does.
(B) The substitution altered the secondary and tertiary structure of the enzyme so that the mutated enzyme folds into a different shape than the normal enzyme does.
(C) The substitution caused many copies of the mutated enzyme to cluster together and compete for substrate to bind.
(D) The substitution caused the directionality of the enzyme to change such that the amino terminus of the normal enzyme has become the carboxy terminus of the mutated enzyme.
The substitution altered the secondary and tertiary structure of the enzyme so that the mutated enzyme folds into a different shape than the normal enzyme does.

Which of the following best explains the reaction represented in Figure 1 ?
(A) It is a dehydration synthesis reaction involved in the formation of a lipid.
(B) The reaction is the hydrolysis of a nucleic acid and results in the formation of a nucleotide.
(C) The reaction is the hydrolysis of a nucleic acid and results in the formation of a phospholipid.
(D) It is a dehydration synthesis reaction involved in the formation of a polypeptide.
It is a dehydration synthesis reaction involved in the formation of a polypeptide.
Which of the following statements about glucose, galactose, and fructose is most likely true?
(A) The carbohydrates have the same properties because they have the same number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
(B) The carbohydrates have the same properties because they each have a single carbon-oxygen double bond.
(C) The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different arrangements of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
(D) The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different numbers of carbon-carbon bonds.
The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different arrangements of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
A researcher designs an experiment to investigate the effect of environmental temperature on the function of an enzyme. For each trial included in the experiment, the researcher will add the enzyme and its substrate to an aqueous buffer solution and then measure the amount of product formed over 20 minutes.
Which of the following must remain the same for all trials of this experiment?
(A) The initial concentration of the substrate
(B) The final concentration of the product
(C) The three-dimensional structure of the enzyme
(D)The temperature of the aqueous buffer solution
The initial concentration of the substrate.
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of an enzyme?
(A) The free energy of the reactants is greater than the free energy of the products.
(B) The equilibrium constant of the reaction is much greater than 1.
(C) The shape and charge of the substrates are compatible with the active site of the enzyme.
(D) The concentration of the enzyme inside living cells is greater than the concentration of substrate.
The shape and charge of the substrates are compatible with the active site of the enzyme.
Which of the following best describes the hydrolysis of carbohydrates?
(A) The removal of a water molecule breaks a covalent bond between sugar monomers.
(B) The removal of a water molecule forms a covalent bond between sugar monomers.
(C) The addition of a water molecule breaks a covalent bond between sugar monomers.
(D) The addition of a water molecule forms a covalent bond between sugar monomers.
The addition of a water molecule breaks a covalent bond between sugar monomers.
Trypsin and pepsin are enzymes that function in different areas of the digestive tract. One functions in the stomach, where the pH is between 1.5 and 3.5, while the other functions in the small intestines, where the pH is between 6 and 8.
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best describes where each enzyme functions?
(A) Pepsin works in the intestines because the optimal pH for pepsin is basic.
(B) Trypsin works in the stomach because the optimal pH for trypsin is basic.
(C) Pepsin works in the stomach because the optimal pH for pepsin is acidic.
(D) Trypsin works in the stomach because the optimal pH for trypsin is acidic.
Pepsin works in the stomach because the optimal pH for pepsin is acidic.
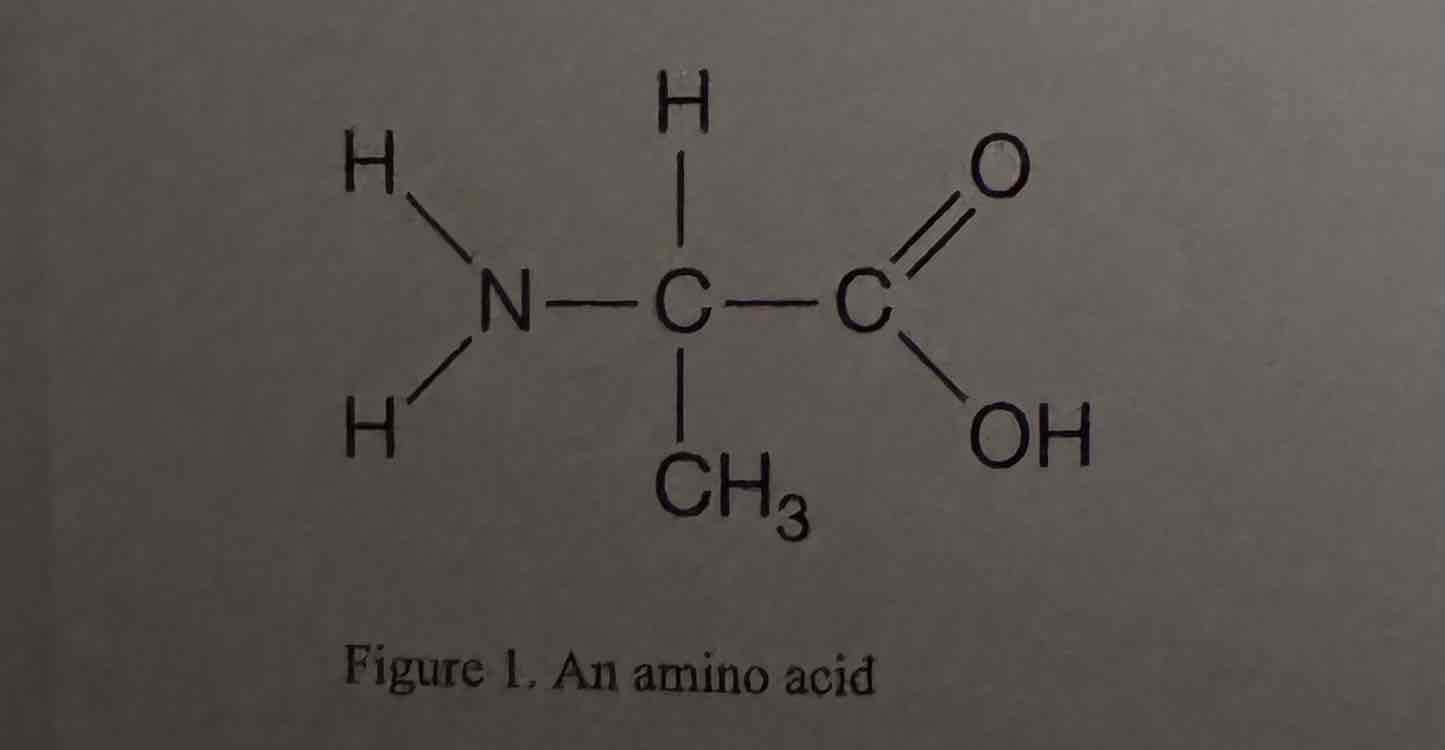
The amino acid in Figure 1 is found in a region of a polypeptide that folds away from water. Which part of the amino acid most likely contributes to the hydrophobic behavior of this region of the polypeptide?
(A) Amine (NH2) group
(B) Carboxyl (COOH) group
(C) Methyl (CH3) group
(D) Hydrogen (H) atom
Methyl (CH3) group
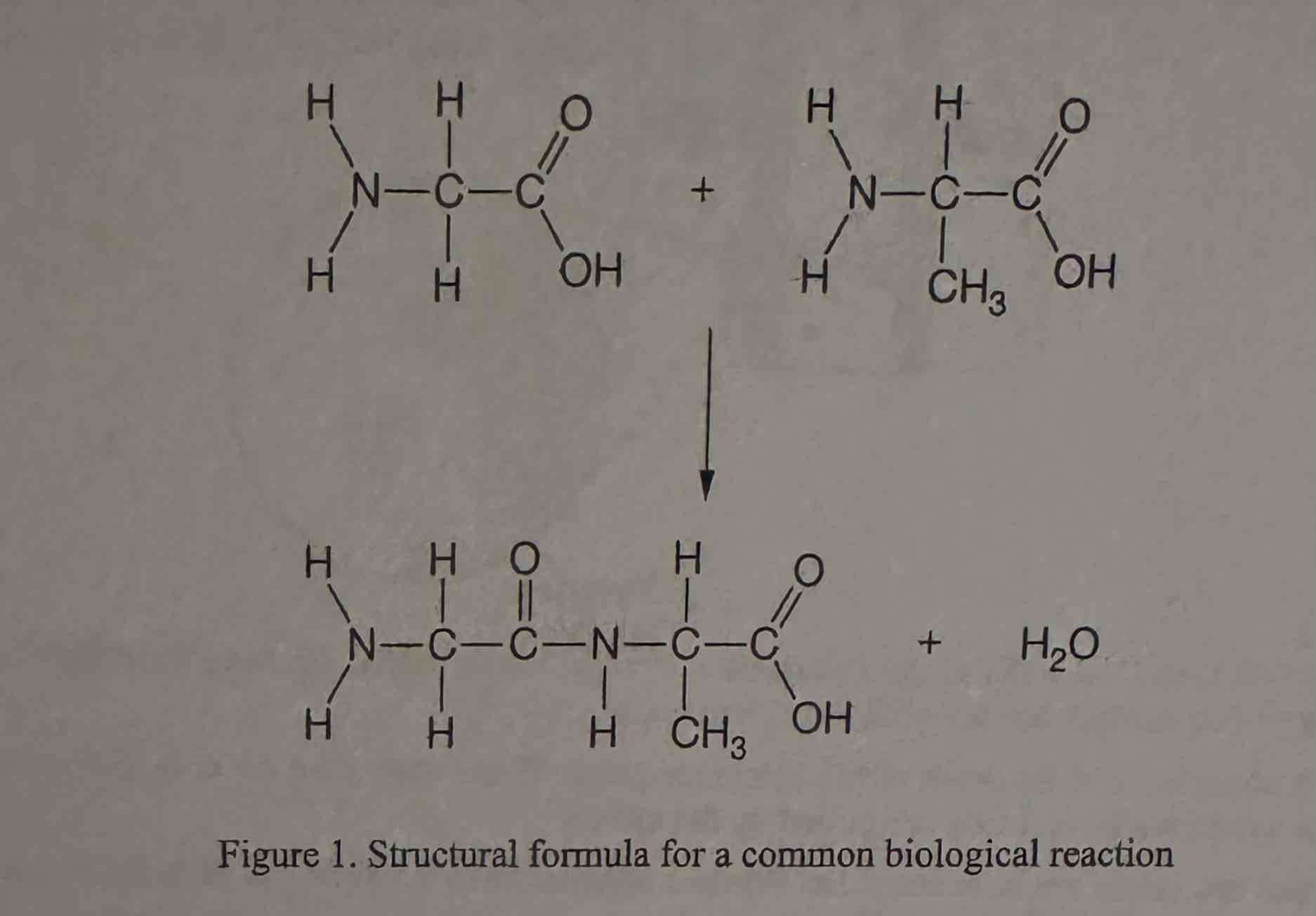
Which of the following is an accurate description of the process shown in Figure 1 ?
(A) The linking of amino acids with an ionic bond as an initial step in the protein synthesis process
(B) The formation of a more complex carbohydrate with the covalent bonding of two simple sugars
(C) The hydrolysis of amino acids with the breaking of covalent bonds with the release of water
(D) The formation of a covalent peptide bond in a dehydration synthesis reaction
The formation of a covalent peptide bond in a dehydration synthesis reaction.
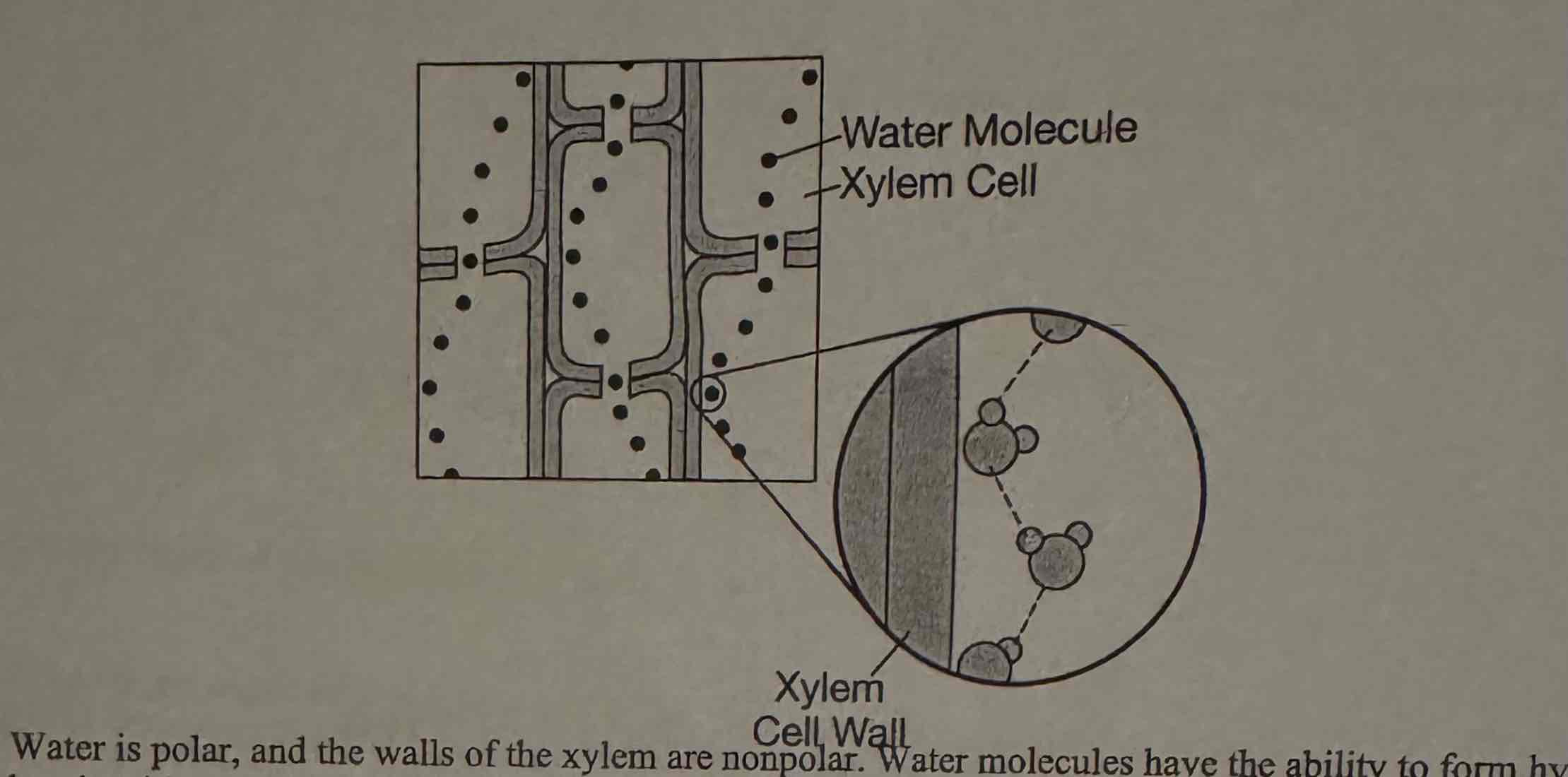
The diagram shows how water can adhere to the xylem in the stems of plants, which contributes to water move. in the plant. Which of the following best explains how water is able to move upward from the roots of a plant, through its xylem in the stem, and out to the leaves?
(A) Water is polar, and the walls of the xylem are nonpolar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with one another but not with the xylem walls.
(B) Water is nonpolar, and the walls of the xylem are polar. Water molecules are able to form hydrogen bonds with the xylem walls, and they are pulled up the xylem.
(C) Water and the xylem are both nopolar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with one another but not with the xylem walls.
(D) Water and the xylem are both polar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with the walls of the xylem.
Water and the xylem are both polar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with the walls of the xylem.
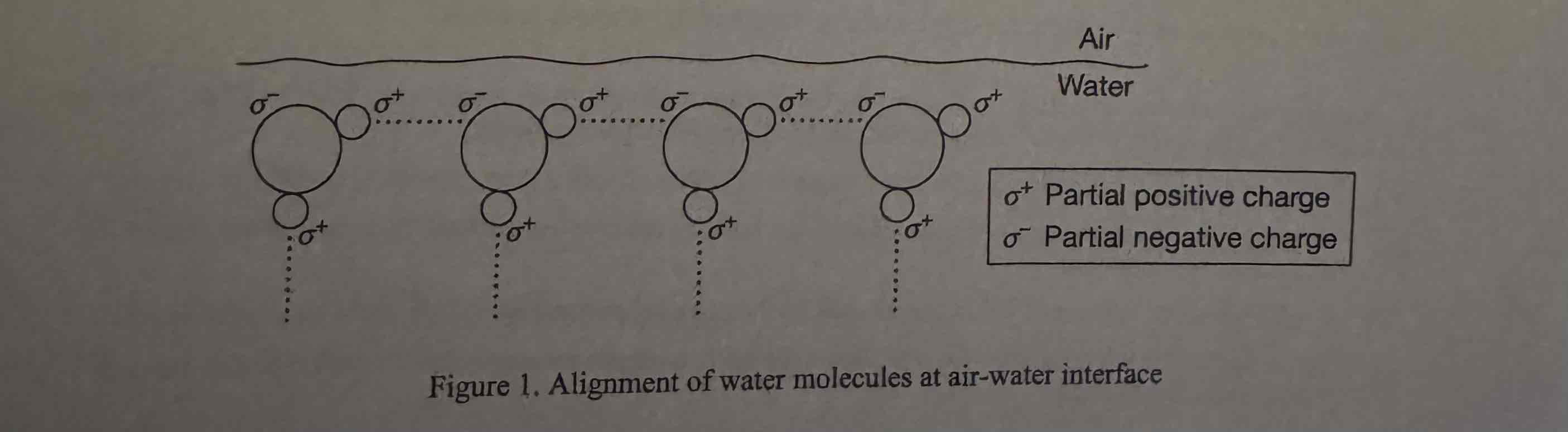
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best describes how the properties of water at an air-water interface enable an insect to walk on the water's surface?
(A) Covalent bonds between water molecules and the air above provide cohesion, which causes tiny bubbles to form under the feet of the insect.
(B) Ionic bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide an electric charge, which attracts the feet of the insect, keeping it on the surface.
(C) Polar covalent bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide adhesion, which supports the weight of the insect.
(D) Hydrogen bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide surface tension, which allows the water surface to deform but not break under the insect.
Hydrogen bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide surface tension, which allows the water surface to deform but not break under the insect.
Researchers claimed that a particular organelle originated from a free-living prokaryotic cell that was engulfed by a larger cell, as shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following provides evidence to best support the researchers' claim?
(A) The organelle has a phospholipid membrane.
(B) The organelle has protein in the membrane.
(C) The organelle has a double membrane.
(D) The organelle has an internal aqueous environment that is similar to the cytosol of the larger cell.
The organelle has a double membrane.
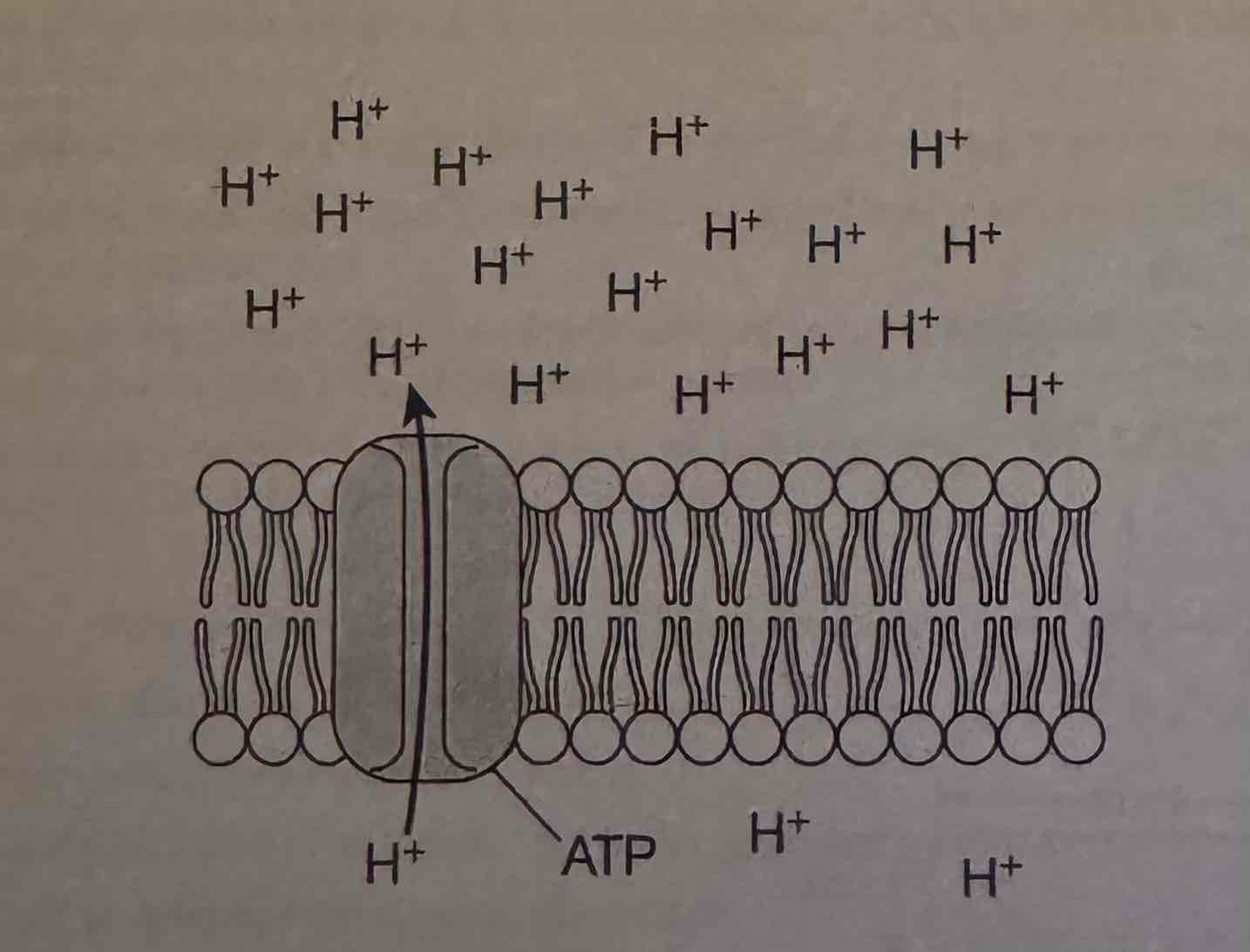
The illustration shows the active transport of hydrogen ions through a membrane protein. Which of the following best predicts the effect of not having ATP available to supply energy to this process?
(A) H* ions will stop moving through the protein.
(B) H ions will move in the other direction through the protein.
(C) Ht ions will continue to move through the protein in the original direction but at a slower rate,
(D) Ht ions will begin to move through the phospholipid portion of the membrane in the original direction.
H* ions will stop moving through the protein.
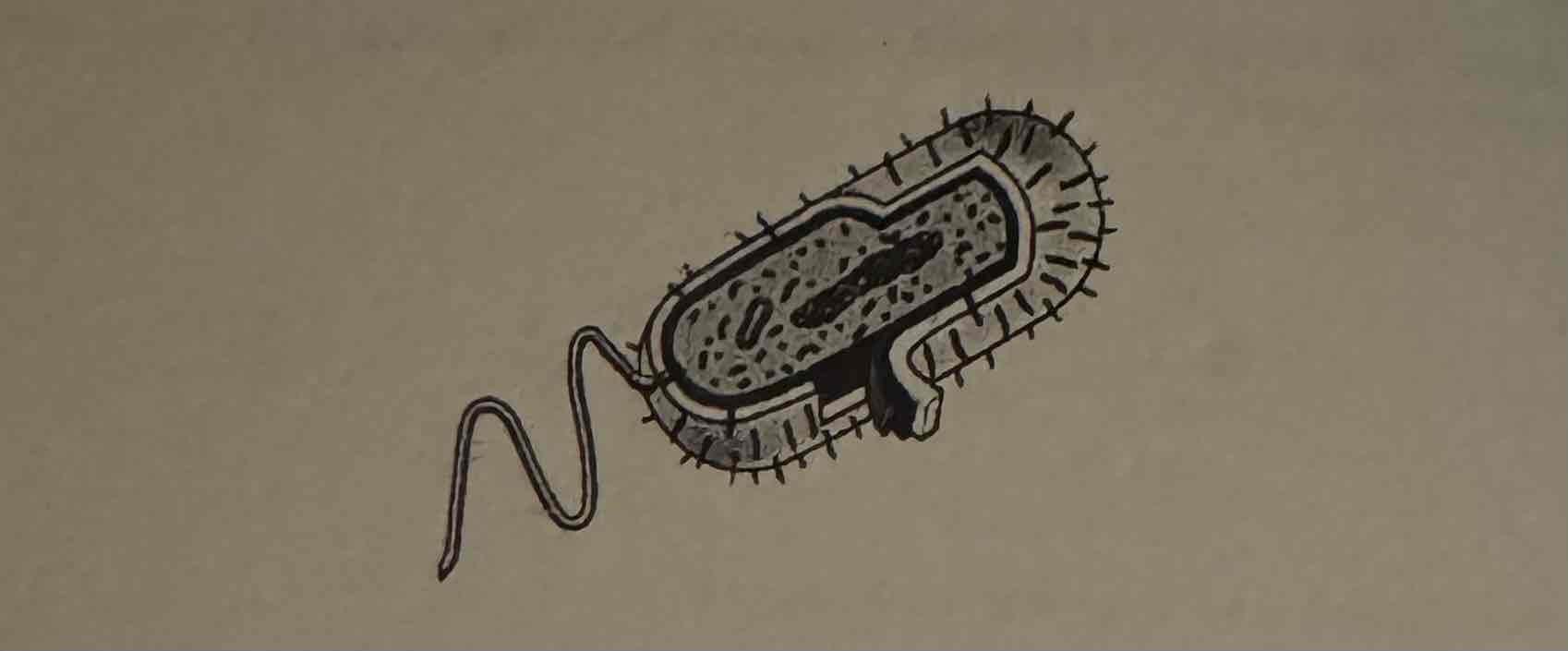
The diagram above represents a typical rod-shaped bacterium. Which of the following best describes a feature shown in the diagram that is unique to archaea and bacteria?
(A) The organism is surrounded by a cell wall.
(B) The organism contains ribosomes.
(C) The organism does not have a nuclear membrane surrounding its genetic material.
(D) The organism is not capable of making or providing itself with ATP.
The organism does not have a nuclear membrane surrounding its genetic material.
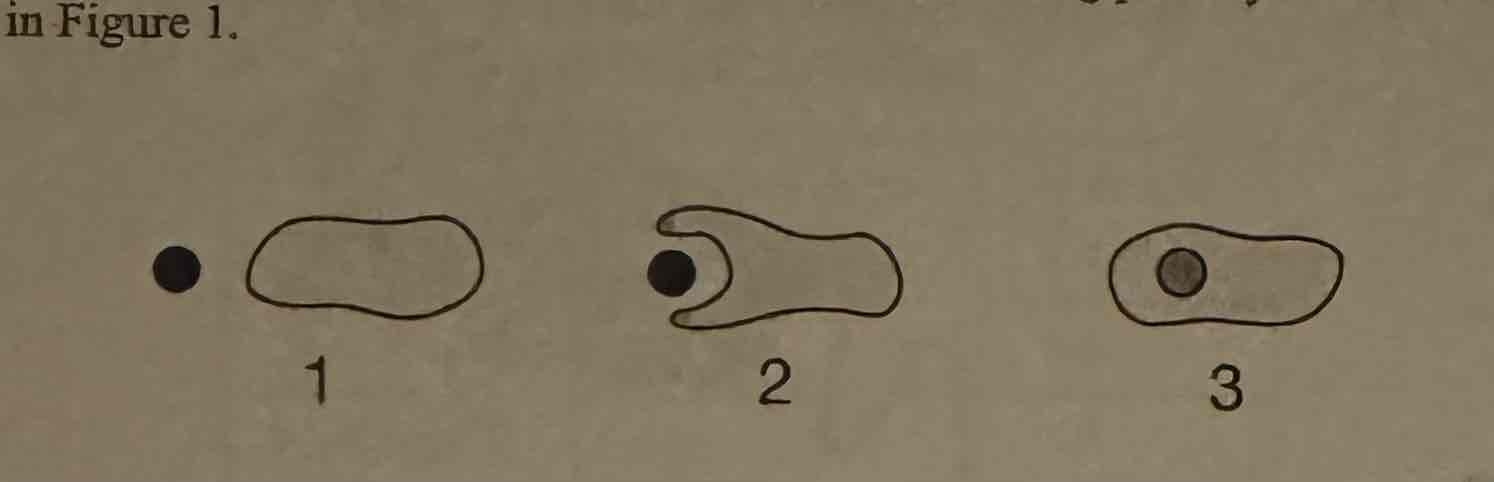
Which one of the following cells is likely to be the most efficient at eliminating waste by diffusion?
A. (The smallest one)
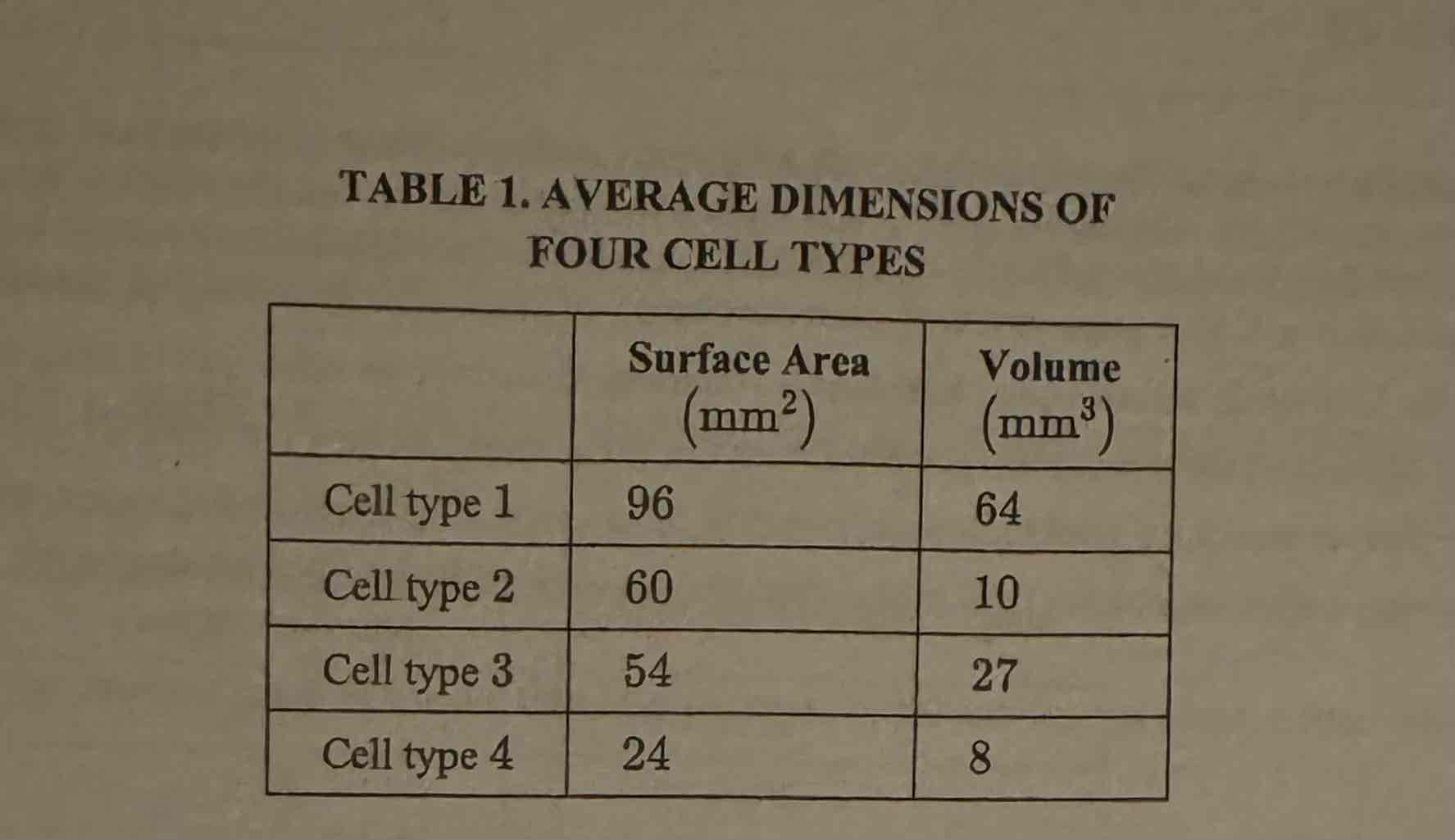
Which of the cell types represented in Table 1 is most efficient at acquiring nutrients by diffusion?
(A) Cell type 1
(B) Cell type 2
(C) Cell type 3
(D) Cell type 4
Cell Type 2.
Which of the following statements best supports the claim that certain organelles within eukaryotic cells evolved from free-living prokaryotic cells?
(A) The cytoplasm of both eukaryotes and prokaryotes is surrounded by a plasma membrane.
(B) Eukaryotes and prokaryotes both contain ribosomes, but the ribosomes of eukaryotes are more complex in structure than those of prokaryotes.
(C) Eukaryotes exchange segments of internal membranes between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, but prokaryotes have no such internal membranes.
(D) Some organelles contain their own DNA that is more similar to prokaryotic DNA in structure and function than to the eukaryotic DNA found in the cell's nucleus.
Some organelles contain their own DNA that is more similar to prokaryotic DNA in structure and function than to the eukaryotic DNA found in the cell's nucleus.
Which of the following is evidence that eukaryotes and prokaryotes share a common ancestor?
(A) All eukaryotes and prokaryotes contain linear DNA.
(B) All eukaryotes and prokaryotes contain ribosomes.
(C) All eukaryotes and prokaryotes use organic molecules as an energy source.
(D) All eukaryotes and prokaryotes are capable of mitosis.
All eukaryotes and prokaryotes contain ribosomes.
Which of the following is the strongest evidence supporting the endosymbiont hypothesis?
(A) Mitochondria have their own DNA and divide independently of the cell.
(B) Mitochondria can carry out hydrolytic reactions on organic molecules.
(C) Mitochondria have a highly folded membrane.
(D) Mitochondria are found in both plants and animals.
Mitochondria have their own DNA and divide independently of the cell.
Over 100 different types of G-protein-linked receptors have been observed in eukaryotes, including scent receptor in animals, mating-signal receptors in yeasts, and light-sensing proteins in vertebrates. The proton pumps of bacteria: have protein structures similar to G-protein-linked receptors. Based on this information, which of the following scientific questions will best guide research on the evolution of G-protein-linked signal transduction?
(A) Did the G-protein-linked signal transduction pathway in eukaryotes arise from a precursor in prokaryotes?
(B) Are G-protein-linked receptors acquired from the environment as they are needed?
(C) Do eukaryotes require symbiotic prokaryotes in order to use G-protein-linked receptors?
(D) Do single-celled organisms have more efficient cell communication than do multicellular organisms?
Did the G-protein-linked signal transduction pathway in eukaryotes arise from a precursor in prokaryotes?
All eukaryotic cells contain at least one Golgi complex, typically located in the cytoplasm and near the endoplasmic reticulum.
Which of the following best describes a process that occurs within the Golgi complex?
(A) Enzymatic modification of newly synthesized integral membrane proteins
(B) Synthesis of cytosolic proteins based on the nucleotide sequences of mRNAs
(C) Degradation of proteins by hydrolytic enzymes contained within the complex
(D) Synthesis of various types of lipids
Enzymatic modification of newly synthesized integral membrane proteins.
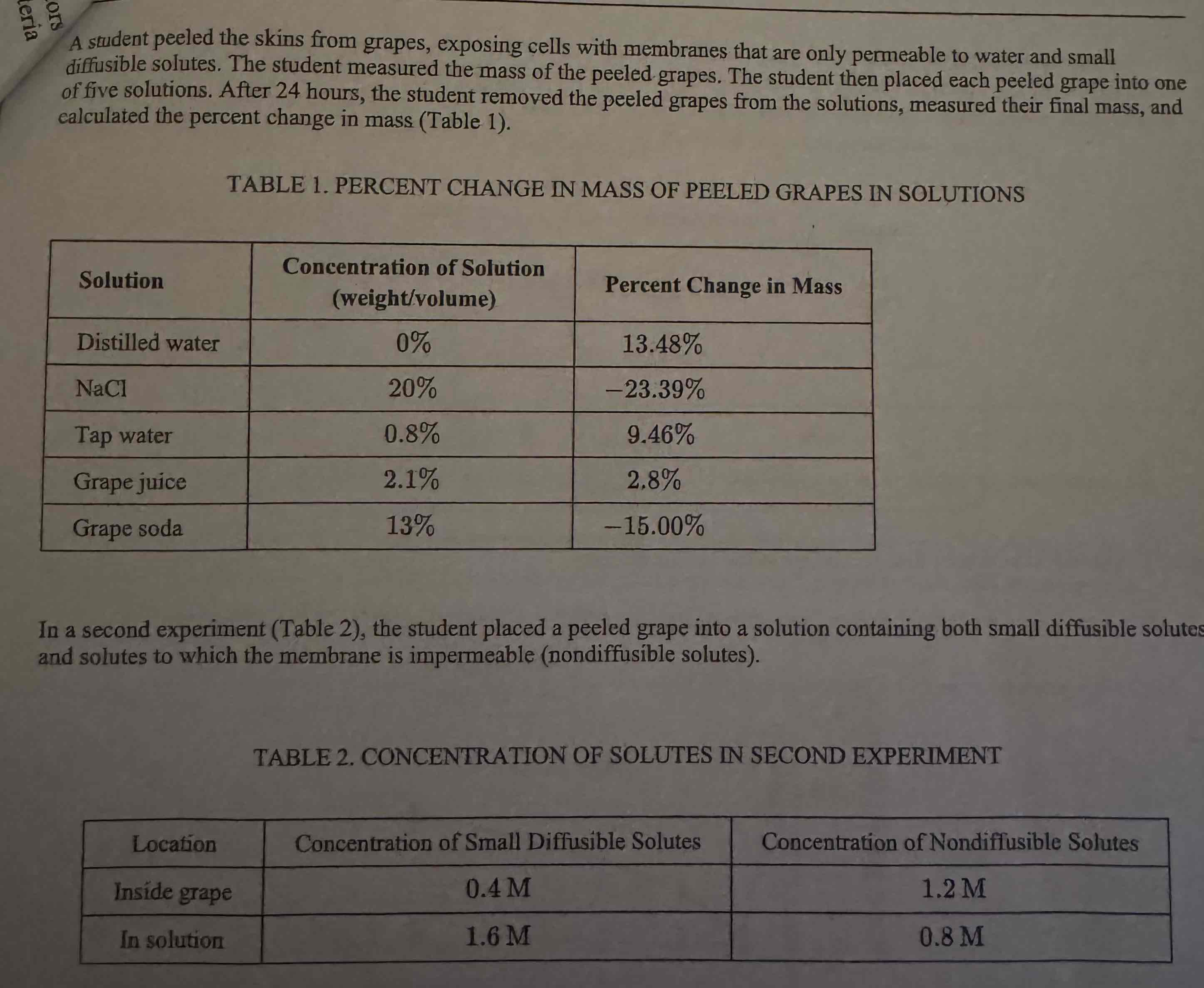
Based on Table 1, which of the following best explains the difference in water potential between certain solutions and the grapes?
(A) NaCl and tap water have a lower water potential because these two solutions caused the grape to gain water.
(B) Grape soda and NaCl have a lower water potential because these two solutions caused the grape to lose water.
(C) Tap water and grape juice have a lower water potential because these two solutions caused the grape to lose water.
(D) Grape soda and grape juice have a lower water potential because these two solutions caused the grape to gain water.
Grape soda and NaCl have a lower water potential because these two solutions caused the grape to lose water.
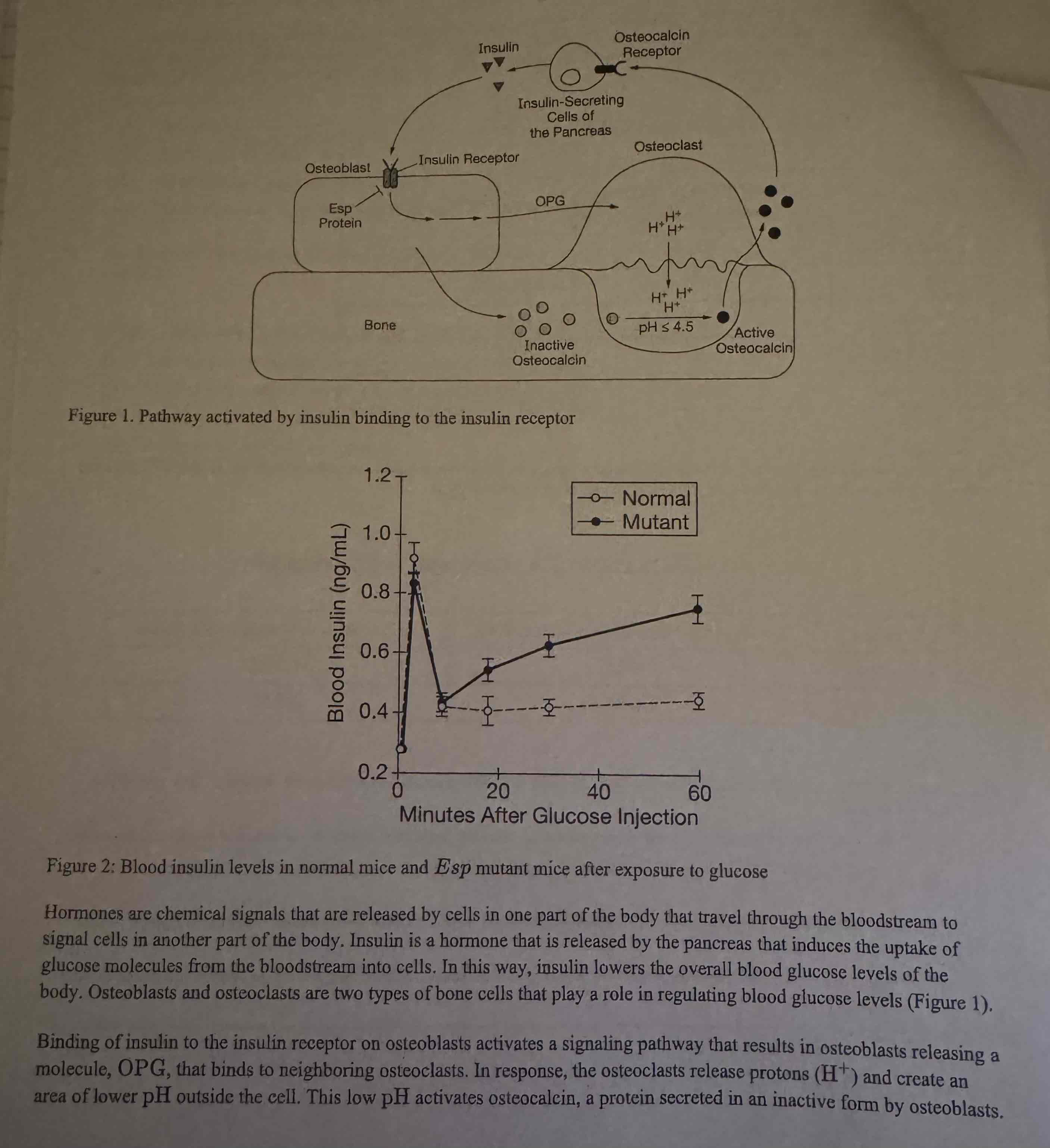
The Esp gene encodes a protein that alters the structure of the insulin receptor on osteoblasts and interferes with the binding of insulin to the receptor. A researcher created a group of osteoblasts with an Esp mutation that prevented the production of a functional Esp product (mutant). The researcher then exposed the mutant strain and a normal strain that expresses Esp to glucose and compared the levels of insulin in the blood near the osteoblasts (Figure 2).
Which of the following was a positive control in the experiment?
(A) Minutes after glucose injection
(B) Blood insulin
(C) Mutant strain
(D) Normal strain
Normal strain.
Which of the following best explains how molecules such as O2 and COz can move across the membrane of a cell?
(A) The majority of the cell membrane contains protein channels that allow this type of molecule into the cell.
(B) The majority of the cell membrane is nonpolar, which allows small, nonpolar molecules to freely cross.
(C) The phospholipids of the membrane are tightly packed, so only small molecules and ions can fit between phospholipids.
(D) ATP is hydrolyzed to provide energy to help O2 and CO2 move against their concentration gradient and across the membrane.
The majority of the cell membrane is nonpolar, which allows small, nonpolar molecules to freely cross.

(A) At higher osmolarity, lower rates of contraction are required because more salt diffuses into the paramecia.
(B) The contraction rate increases as the osmolarity decreases because the amount of water entering the paramecia by osmosis increases.
(C) The contractile vacuole is less efficient in solutions of high osmolarity because of the reduced amount of ATP produced from cellular respiration.
(D) In an isosmotic salt solution, there is no diffusion of water into or out of the paramecia, so the contraction rate is zero.
The contraction rate increases as the osmolarity decreases because the amount of water entering the paramecia by osmosis increases.
Which of the following groups of cellular components are found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells?
(A) Ribosomes, a nucleus, and chloroplasts
(B) Circular chromosomes, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum
(C) A nucleus, ribosomes, and cell walls
(D) An endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and a nucleus
An endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and a nucleus.
In flowering plants, plasmodesmata are narrow channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells. An explanation of how plant cells communicate across cell walls will most likely refer to the diffusion through plasmodesmata of which of the following?
(A) Membrane-bound organelles
(B) Condensed, duplicated chromosomes
(C) Branched polysaccharides
(D) Small, water-soluble molecules
Small, water-soluble molecules.
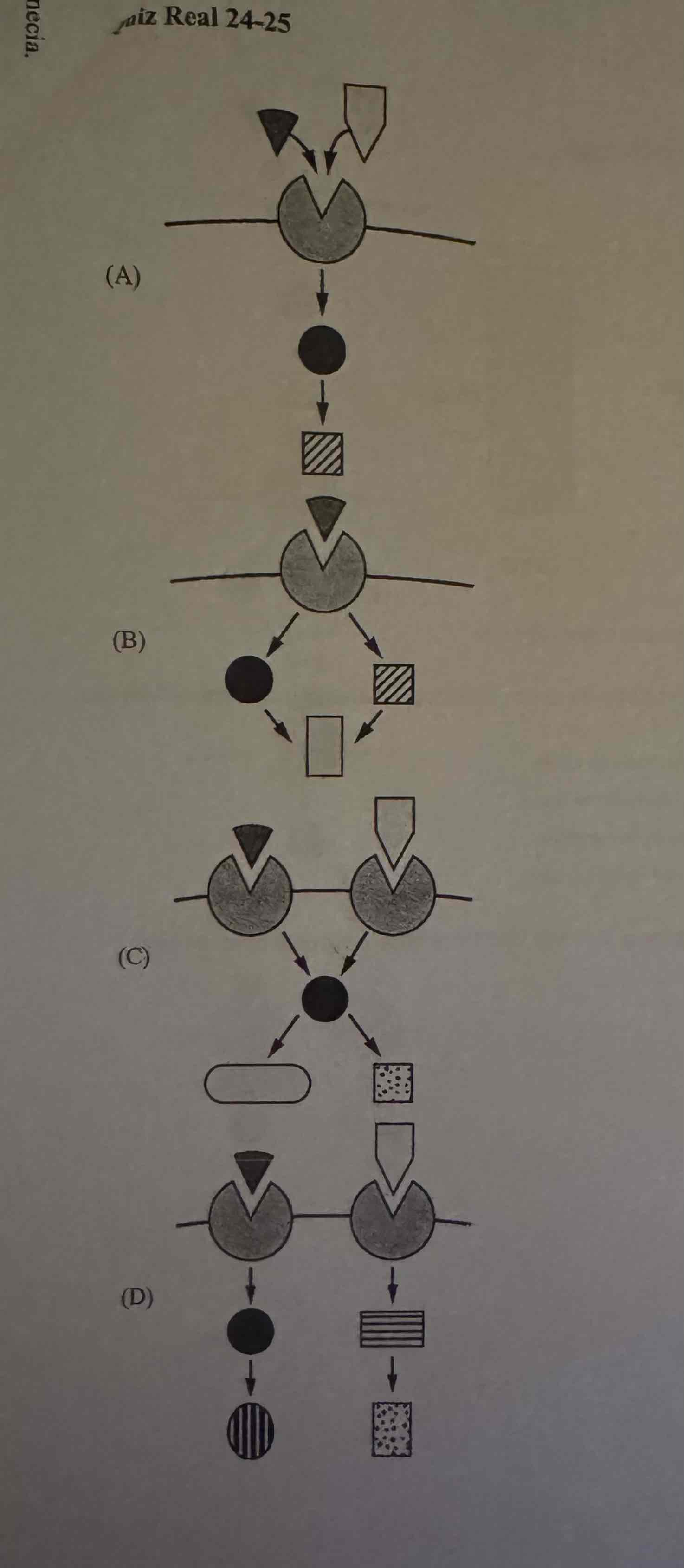
Which of the following best represents two different signaling pathways that share a second messenger?
C.
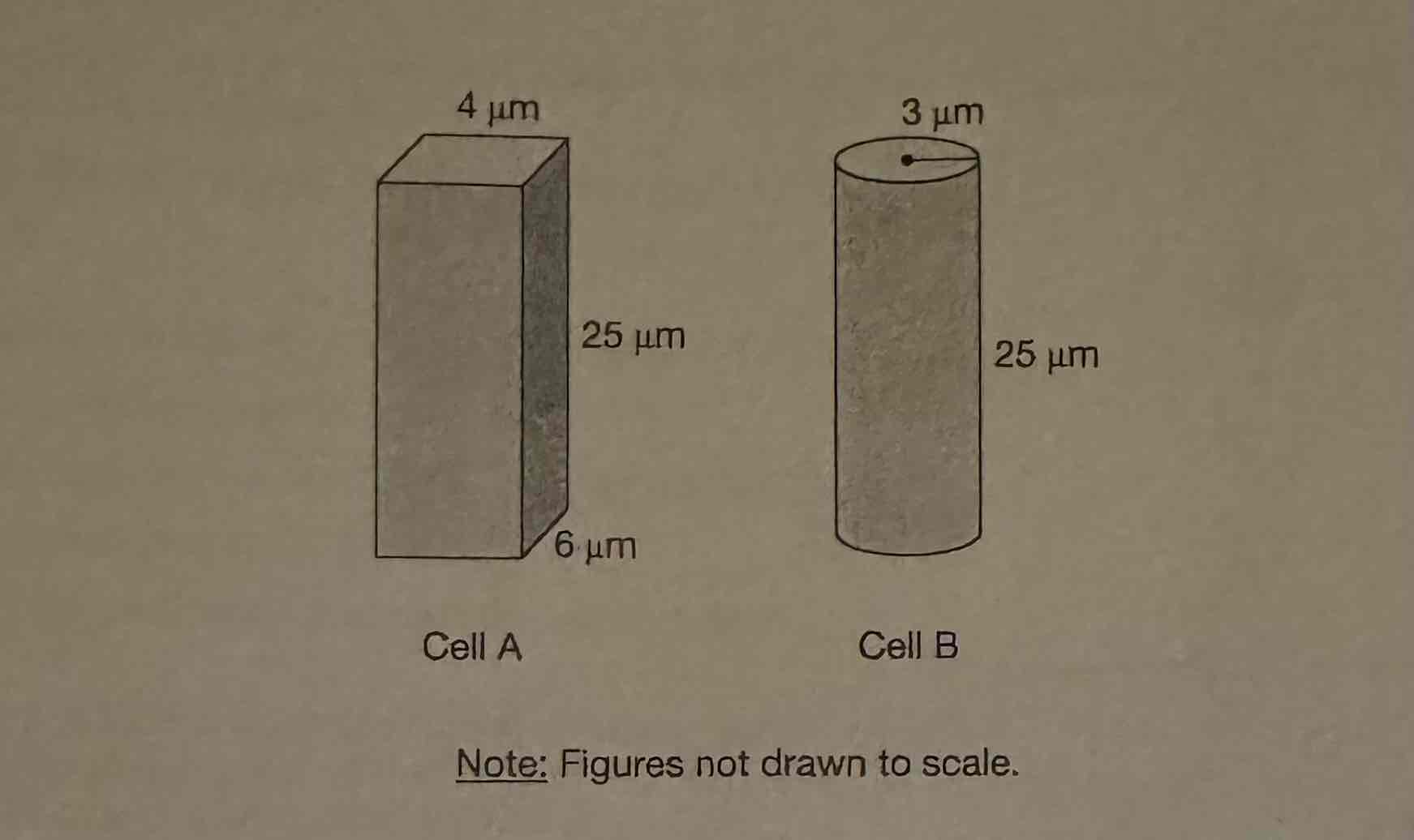
Of the two cells represented in the figure, which would likely be more efficient at exchanging substances with the surrounding environment?
(A) Cell A, because it has the larger surface-area-to-volume ratio.
(B) Cell A, because it has the smaller surface-area-to-volume ratio.
(C) Cell B, because it has the larger surface-area-to-volume ratio.
(D) Cell B, because it has the smaller surface-area-to-volume ratio.
Cell A, because it has the larger surface-area-to-volume ratio.
Which of the following best represents a signaling pathway that will lead to multiple responses from the same signaling molecule?
C.
Intact cells of two unknown cell types were placed into solutions with different concentrations of NaCl. Type I cells swelled and burst in the solution with the lowest concentration of NaCI. Type II cells swelled but did not burst in the solution with the lowest concentration of NaCl.
Which of the following descriptions of cell type I and cell type II are most consistent with the data?
A.
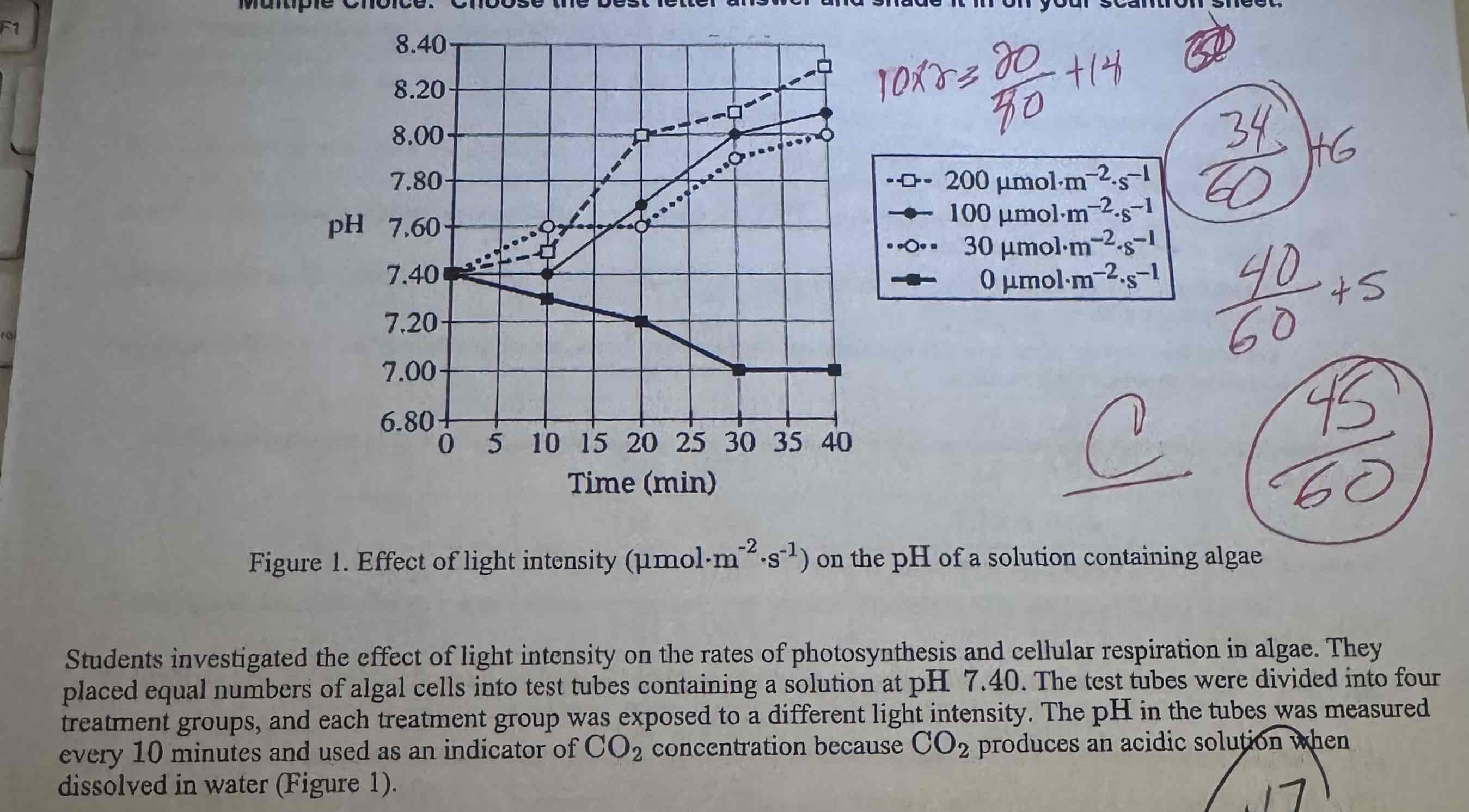
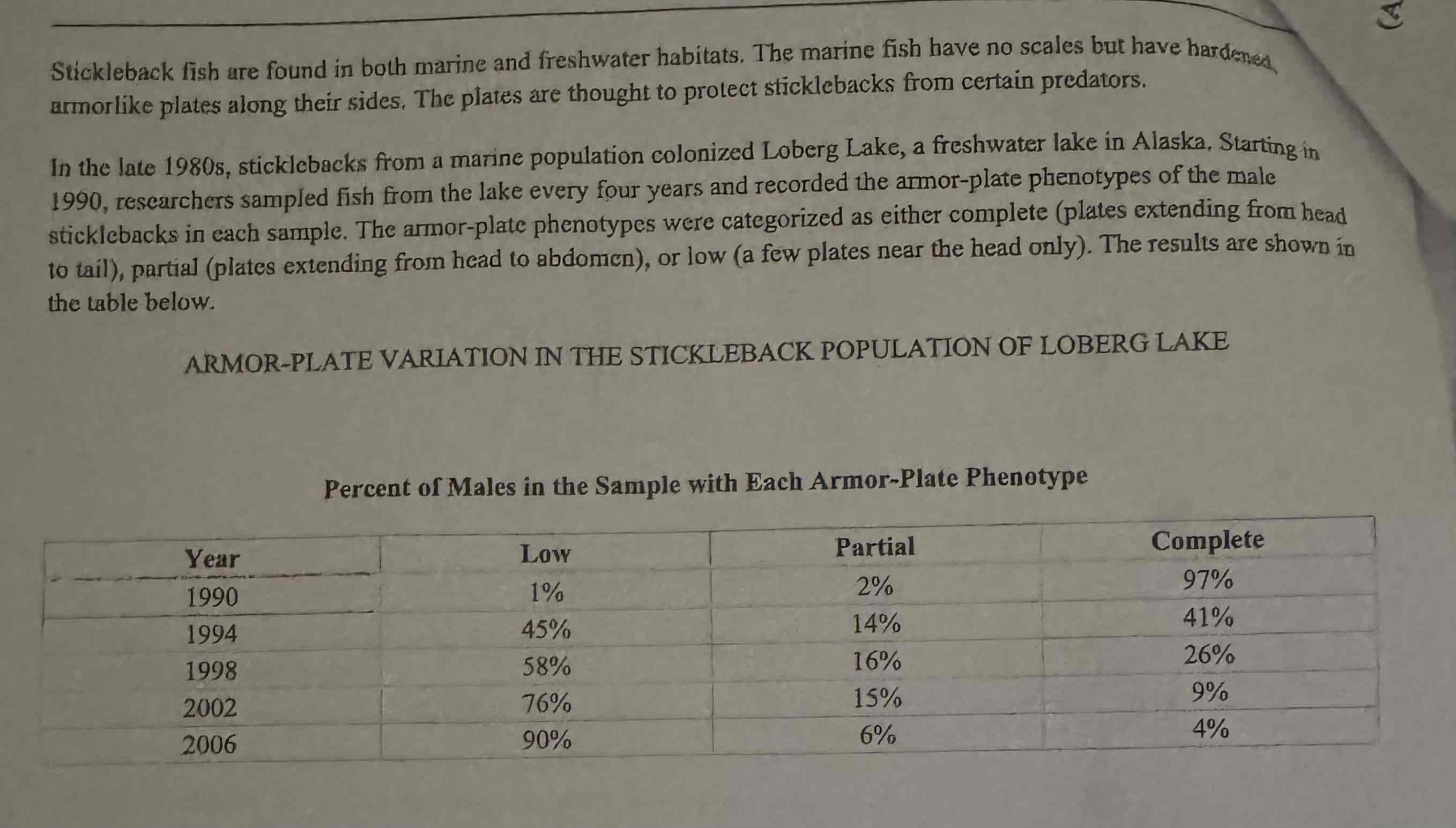
Scientists claim that changes in the rate of photosynthesis will be reflected by changes in pH.
Which of the following best supports their claim?
(A) Algae performing photosynthesis remove CO2 from the solution, increasing p.H.
(B) Algae performing photosynthesis release CO2 into the solution, decreasing pH
(C) Algae performing photosynthesis remove O2 from the solution, decreasing pH
D) Algae performing photosynthesis release O2 into the solution, increasing pH.
Algae performing photosynthesis remove CO2 from the solution, increasing p.H.
Based on Figure 1, which of the following was used as a control in the experiment?
(A) A test tube placed directly in front of a light source
(B) The 0 umol-m-2. light-intensity treatment
(C) The 200 pmol-m -2,' light-intensity treatment
(D) A test tube containing no algal cells
The 0 umol-m-2. light-intensity treatment.
A researcher claims that increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels cause increased growth rates in plants.
Which of the following statements best supports the researcher's claim?
(A) Atmospheric carbon dioxide is produced by the burning of fossil fuels, which are formed from the remains of living organisms such as plants.
(B) Atmospheric carbon dioxide is a byproduct of cellular respiration, which is a metabolic process that occurs in plants and other living organisms.
(C) Atmospheric carbon dioxide typically enters plant leaves through stomata, which plants rely on for regulating gas exchange with the atmosphere.
(D) Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis, which plants rely on for producing sugars and other organic compounds.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis, which plants rely on for producing sugars and other organic compounds.
A researcher claims that the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) is essential to cellular function.
Which of the following statements best helps justify the researcher's claim?
(A) ADP is a small molecule that some cells release into their environment as a way of communicating with other cells.
(B) ATP hydrolysis is an energy-releasing reaction that is often coupled with reactions that require an input of energy.
(C) Inorganic phosphate (Pi) is a substance that cells typically acquire from their environment.
(D) ATP synthase is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of ADP and P; to ATP.
ATP hydrolysis is an energy-releasing reaction that is often coupled with reactions that require an input of energy.
A researcher claims that different metabolic pathways allow bacteria to use different molecules as sources of matter and energy.
Which of the following statements best helps justify the researcher's claim by providing a relevant example?
(A) Rhizobía bacteria form close associations with the roots of bean plants.
(B) E. coli bacteria reproduce in liquid media containing either glucose or galactose.
(C) The antibiotic rifampicin inhibits the growth of some bacterial strains but not of others.
(D) Some viruses that infect bacteria reproduce by either the lysogenic cycle or the lytic cycle.
E. coli bacteria reproduce in liquid media containing either glucose or galactose.
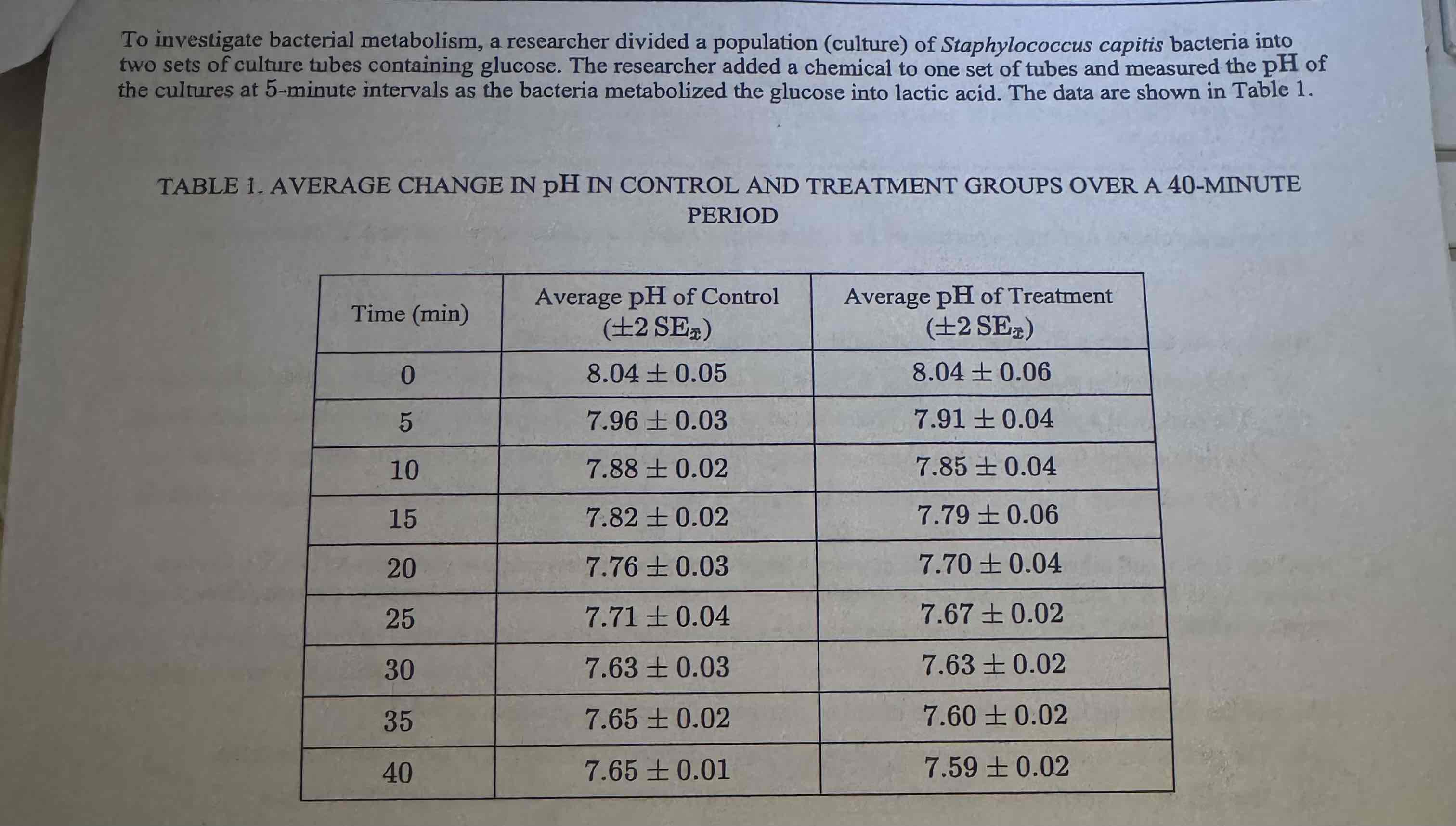
Which of the following best describes the process by which the bacteria are breaking down the glucose to produce lactic acid?
(A) The bacteria are breaking down sugars in the absence of oxygen.
(B) The bacteria are creating a H* gradient to synthesize more ATP.
(C) The bacteria are using their mitochondria to break down glucose in the presence of oxygen.
(D) The bacteria are producing CO2 in the Krebs cycle that is then converted into lactic acid.
The bacteria are breaking down sugars in the absence of oxygen.
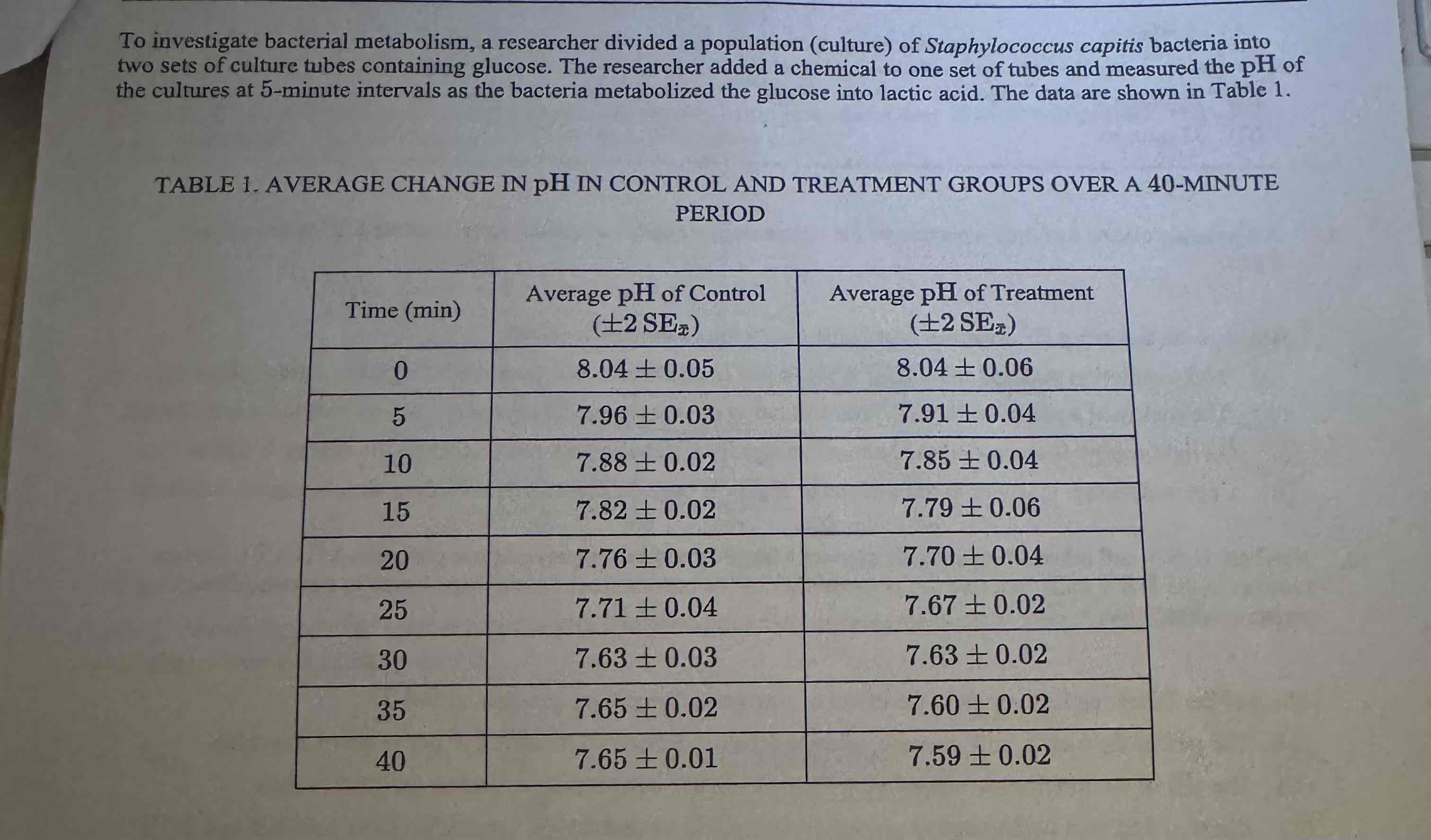
Which of the following was the dependent variable in the researcher's experiment?
(A) Time
(B) pH
(C) Glucose concentration
(D) Lactic acid concentration
Time.
Newborn babies and hibernating animals contain a large amount of brown adipose (fat) tissue (BAT). Certain proteins in the BAT cells increase the permeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane to protons, disrupting the proton gradient.
Which of the following best predicts the effect of disrupting the proton gradient in BAT?
(A)The pH of the matrix will increase, allowing the production of more ATP per gram of substrate.
(B) The pH of the inter-membrane space will decrease, allowing a steeper proton gradient to form.
(C) Electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation will be decoupled, generating more heat but less ATP.
(D) The number of protons available to pass through ATP synthase will increase, resulting in more ATP.
Electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation will be decoupled, generating more heat but less ATP.
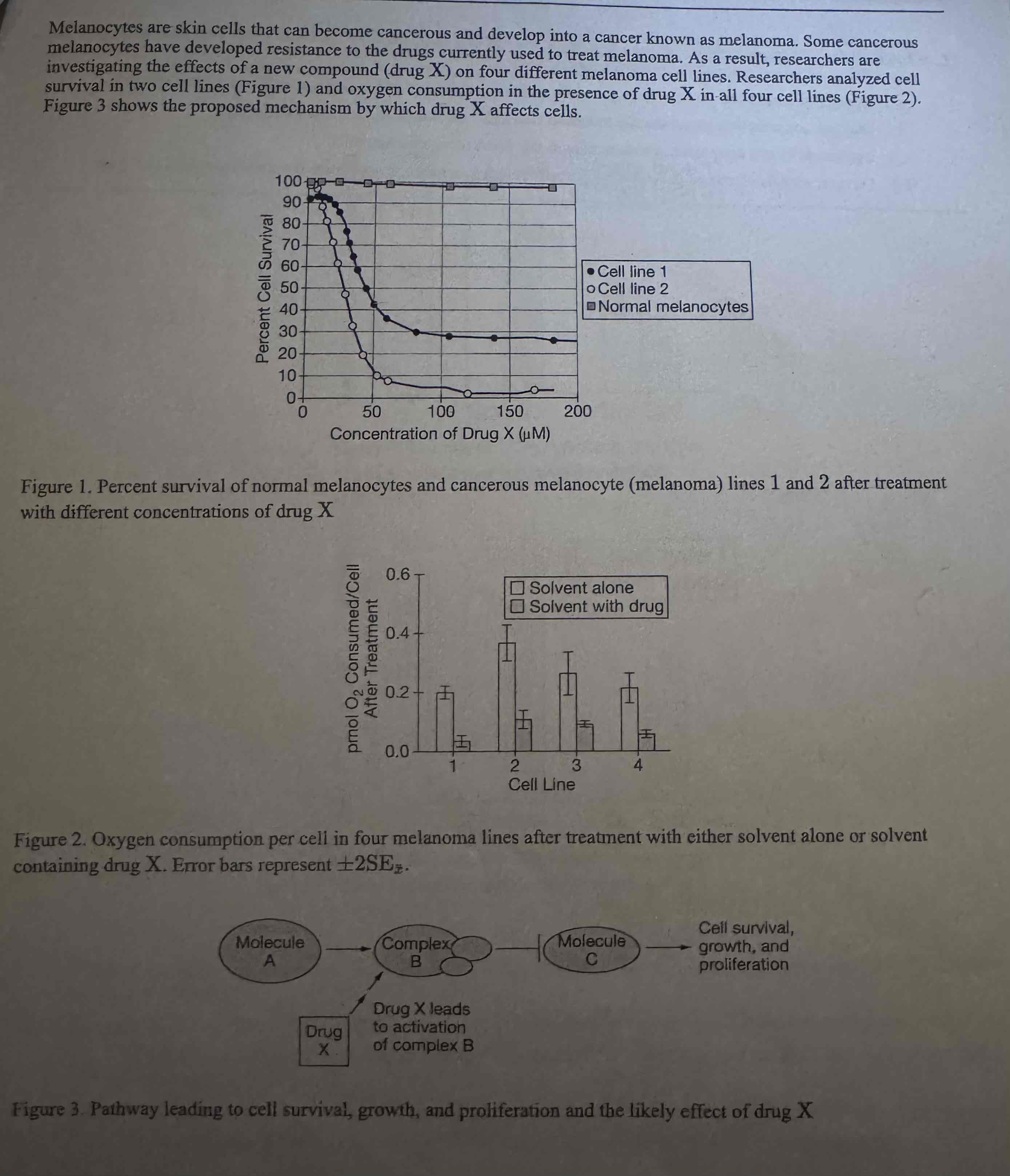
Based on the information presented, which of the following best explains why the researchers measured oxygen consumption as an indicator of the effectiveness of drug X?
(A) Oxygen provides the source of electrons for cellular respiration and is necessary for energy production.
(B) Oxygen consumption increases the mutation rate and causes cells to become cancerous.
(C) Oxygen activates apoptosis, which results in the death of melanoma cells.
(D) Oxygen accepts electrons in oxidative phosphorylation, a process necessary for melanoma cell survival.
Oxygen accepts electrons in oxidative phosphorylation, a process necessary for melanoma cell survival.
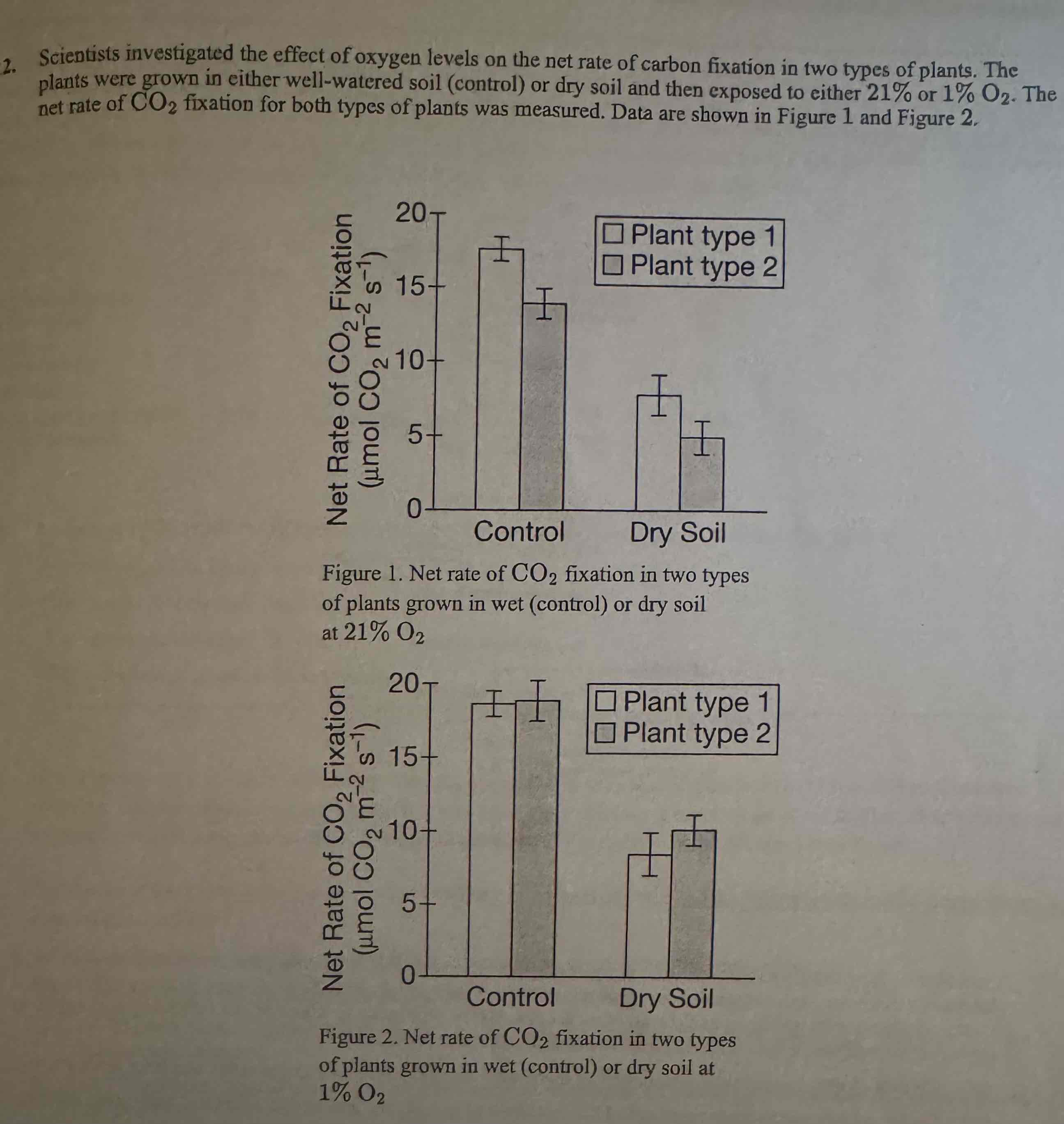
Which of the following statements about the rate of CO, fixation in the two types of plants is supported by the data shown in the figures?
(A) At 21% Oz, plant type 2 has a lower rate of COz fixation than plant type I does in both types of soTt.
(B) At 1% O2: plant type 2 has a higher rate of CO, fixation than plant type 1 does in the dry soil but not in the control soil.
(C) Plant types 1 and 2 have a statistically different rate of COz fixation in both soil types at both oxygen levels.
(D) The rate of CO2 fixation is the same in both types of plants in the control soil at both oxygen levels.
At 21% Oz, plant type 2 has a lower rate of COz fixation than plant type I does in both types of soTt.
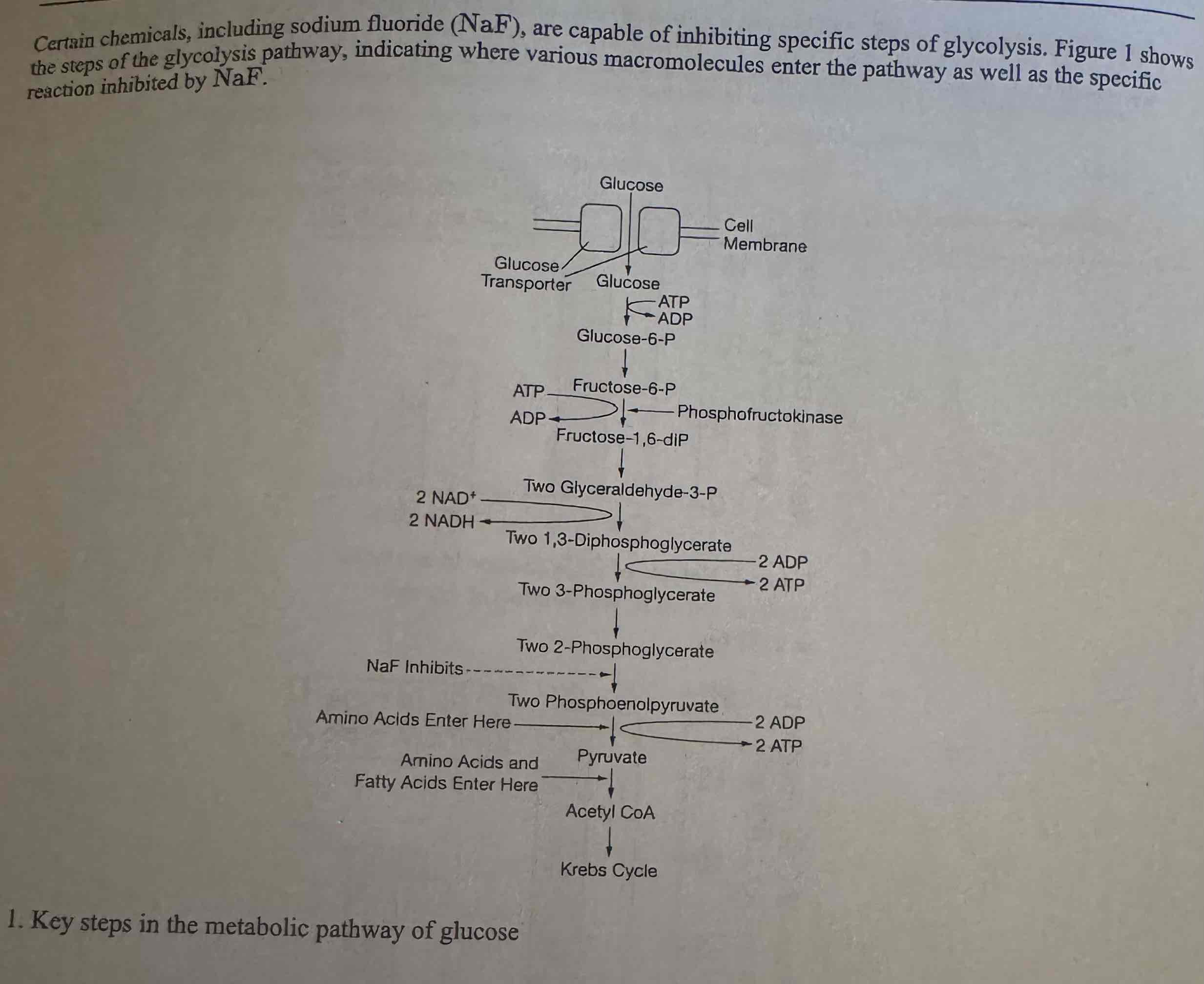
Tarui disease is an inherited disorder that is caused by mutations in PF KM, the gene that encodes a subunit of phosphoructokinase, an enzyme in the glycolysis pathway. Individuals with Tarui disease produce little or no functional phosphofructokinase in skeletal muscle cells. Based on Figure 1, which of the following best explains why a low carbohydrate diet is recommended for those with Tarui disease?
(A) Carbohydrates are capable of undergoing lactic acid fermentation, and amino acids and fatty acids are not.
(B) Carbohydrate metabolism requires all the reactions of glycolysis, and amino acids and fatty acids do not.
(C) Carbohydrates cannot be used to synthesize important metabolic enzymes like amino acids and fatty acids can be.
(D) Carbohydrates cannot be stored, while amino acids and fatty acids can be.
Carbohydrate metabolism requires all the reactions of glycolysis, and amino acids and fatty acids do not.
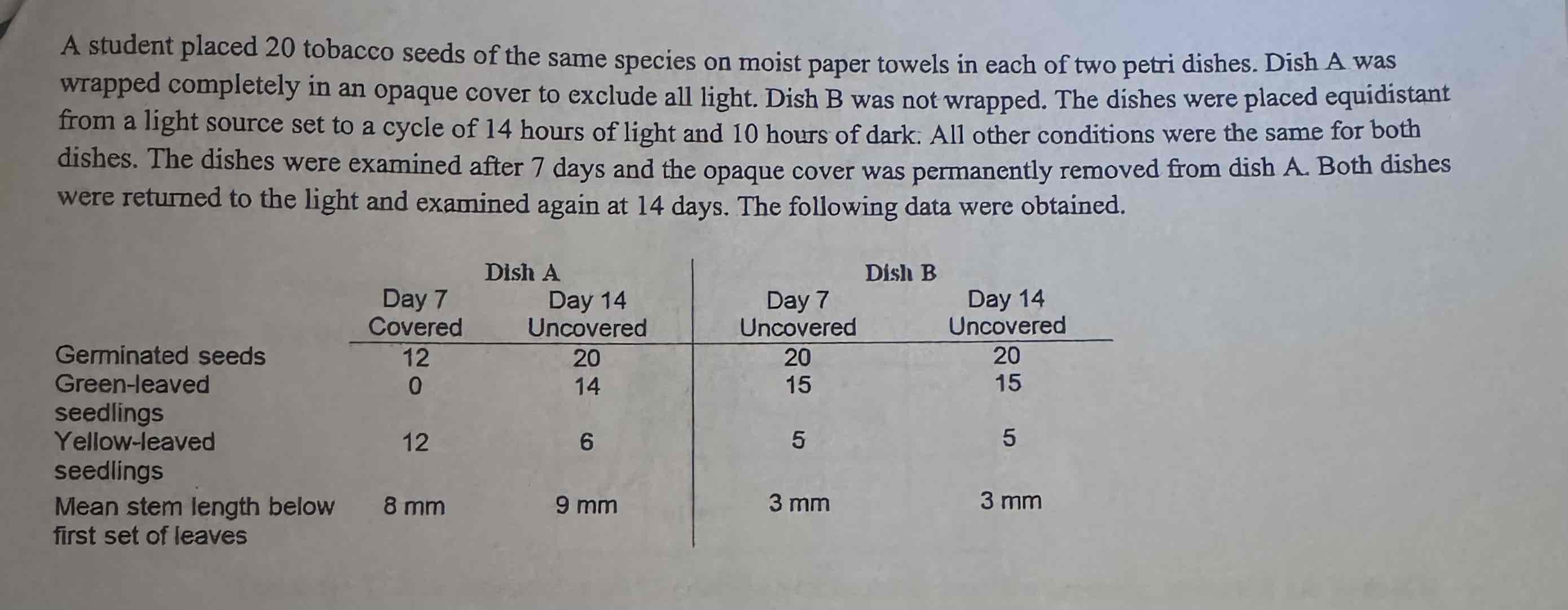
According to the results of this experiment, germination of tobacco seeds during the first week is
(A) increased by exposure to light
(B) unaffected by light intensity
(C) prevented by paper towels
(D) accelerated in green-leaved seedlings
increased by exposure to light.
In an experiment, a scientist isolates mitochondria from living cells and suspends them in two different buffered solutions. One solution is maintained at pH 4, while the other solution is maintained at pH 9. The scientist finds that mitochondria in the solution at pH 4 continue to produce ATP but those in the pH 9 solution do not.
The results of the experiment can be used as evidence in support of which of the following scientific claims about mitochondrial activity?
(A) Mitochondria in a cell-free environment are unable to convert thermal energy into ATP.
(B)The electron transport chain pumps electrons from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix.
(C) ATP production in mitochondria requires a hydrogen ion gradient that favors movement of protons into the mitochondrial matrix.
(D) ATP synthase molecules change their orientation in relation to the proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane.
ATP production in mitochondria requires a hydrogen ion gradient that favors movement of protons into the mitochondrial matrix.
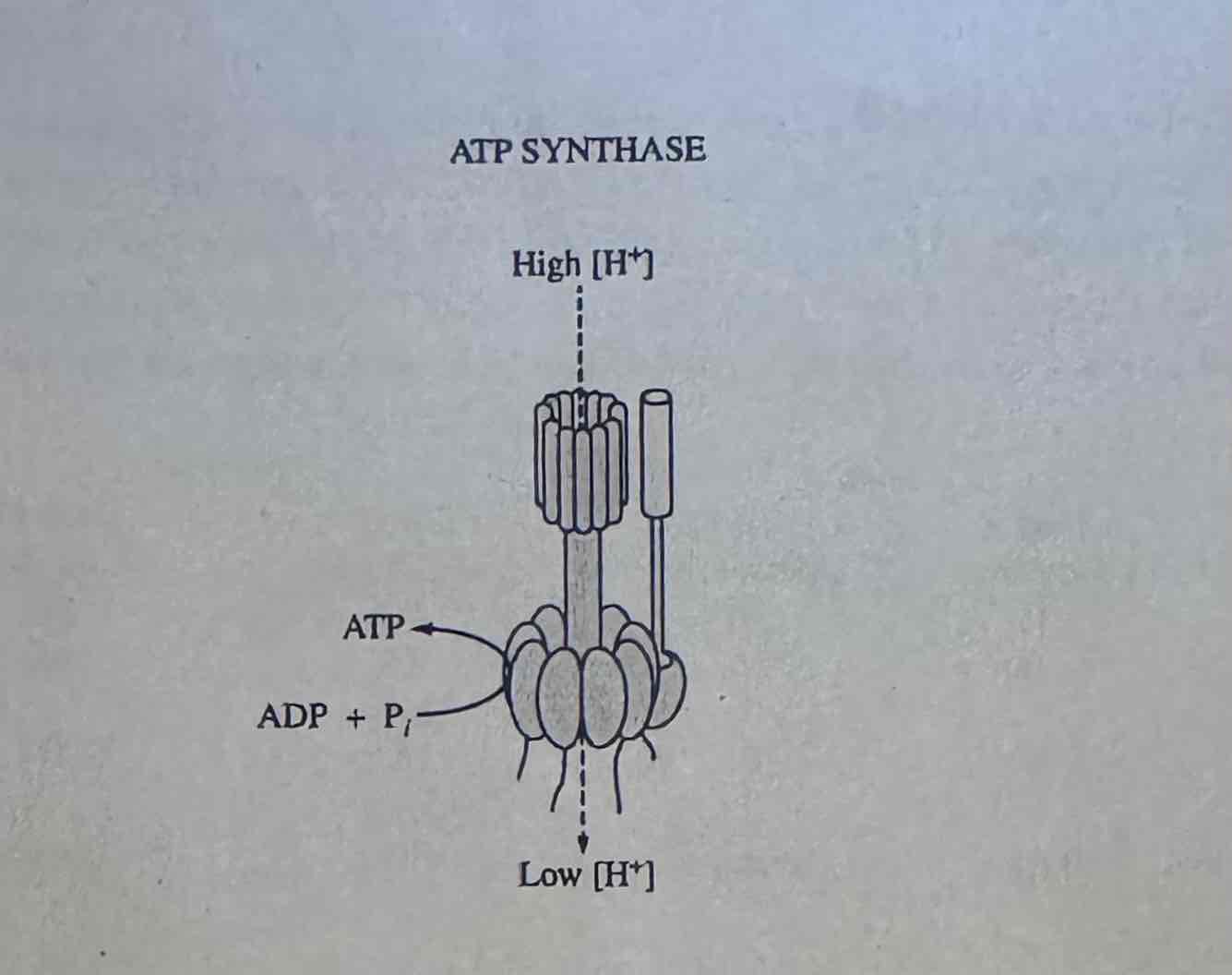
Which of the following questions will best direct an investigation of the mechanism of ATP synthase?
(A) What is the source of the inorganic phosphate that is used to generate ATP from ADP?
(B) Is the phosphorylation of ADP by ATP synthase dependent on the formation of a proton gradient?
(C) Can ATP synthase use the energy released by phosphorylation of ADP to pump protons against a concentration gradient?
D) Can oxidative phosphorylation be uncoupled from the electron transport chain?
Is the phosphorylation of ADP by ATP synthase dependent on the formation of a proton gradient?
In addition to the pigments commonly associated with photosynthesis, a certain photosynthetic species contains two additional pigment types.
Which of the following best supports the claim that this species is better adapted to environmental changes than other photosynthetic species are?
(A) The increased pigment concentration better facilitates energy production within the cells of the species.
(B) The pigment combination allows the organism to absorb heat as well as light, making better use of available
(C). The additional pigments allow the species to outcompete other species for the wavelengths of light commonly used in photosynthesis.
(D) The additional pigments allow the species containing them to harvest energy from wavelengths of light that the other photosynthetic species cannot use.
The additional pigments allow the species containing them to harvest energy from wavelengths of light that the other photosynthetic species cannot use.
A researcher is investigating the effects of a chemical that makes thylakoid membranes permeable to hydrogen ions (H*).
Which of the following is the most likely direct effect of adding the chemical to plant cells?
(A) The plant cells will produce less NADPH
(B) The chloroplasts will generate less ATP.
(C) Chlorophyll will require less light energy to excite its electrons.
(D) The plant cells will split fewer water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen,
The chloroplasts will generate less ATP.
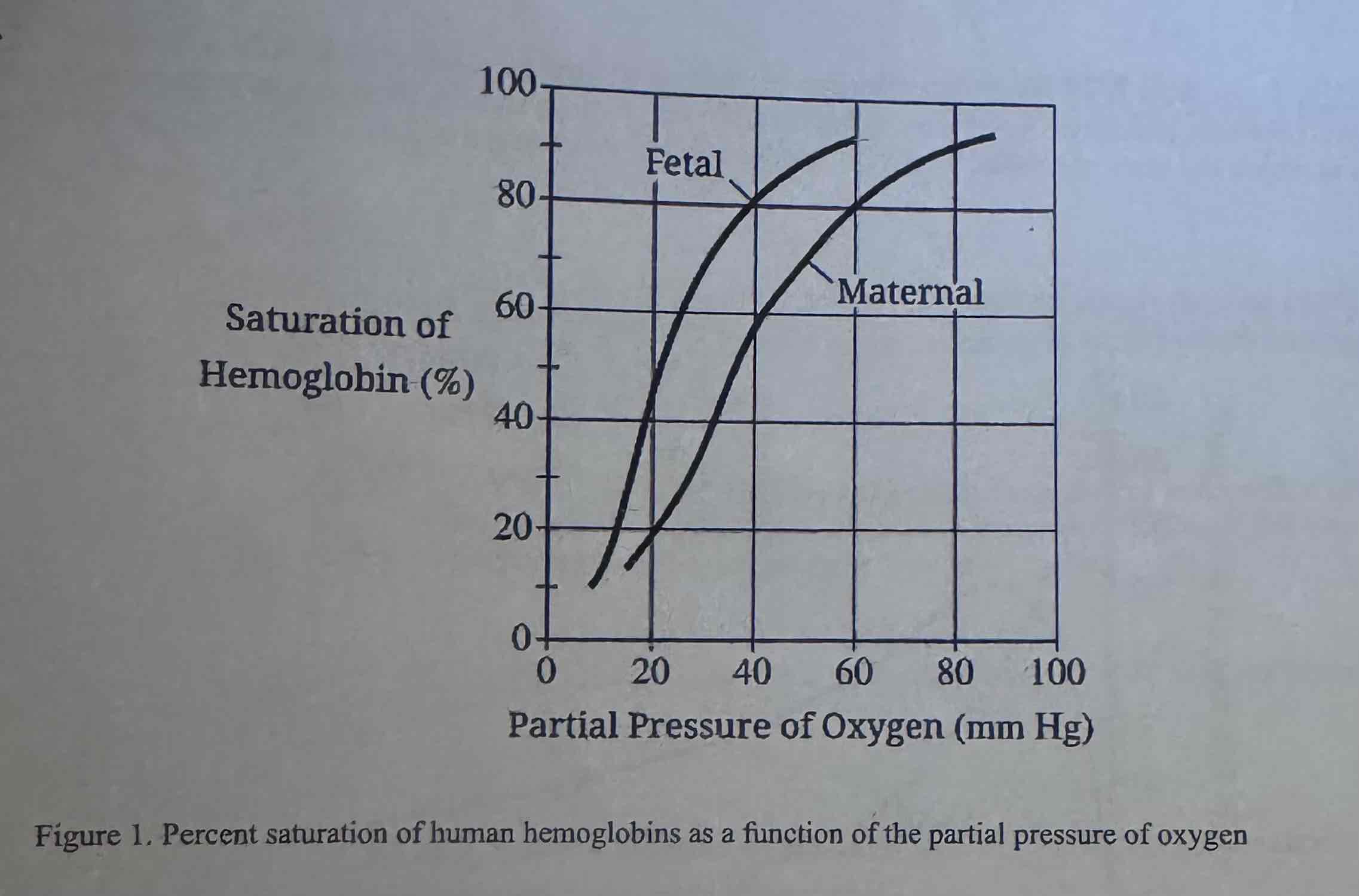
The graph in Figure 1 shows the percent saturation of fetal hemoglobin and maternal hemoglobin in humans as a function of the partial pressure of oxygen. Based on the data, which of the following values is closest to the predicted difference in the percent saturation of fetal hemoglobin and maternal hemoglobin at 40 mm Hg?
(A) 10
(B) 12
(C) 20
D) 40
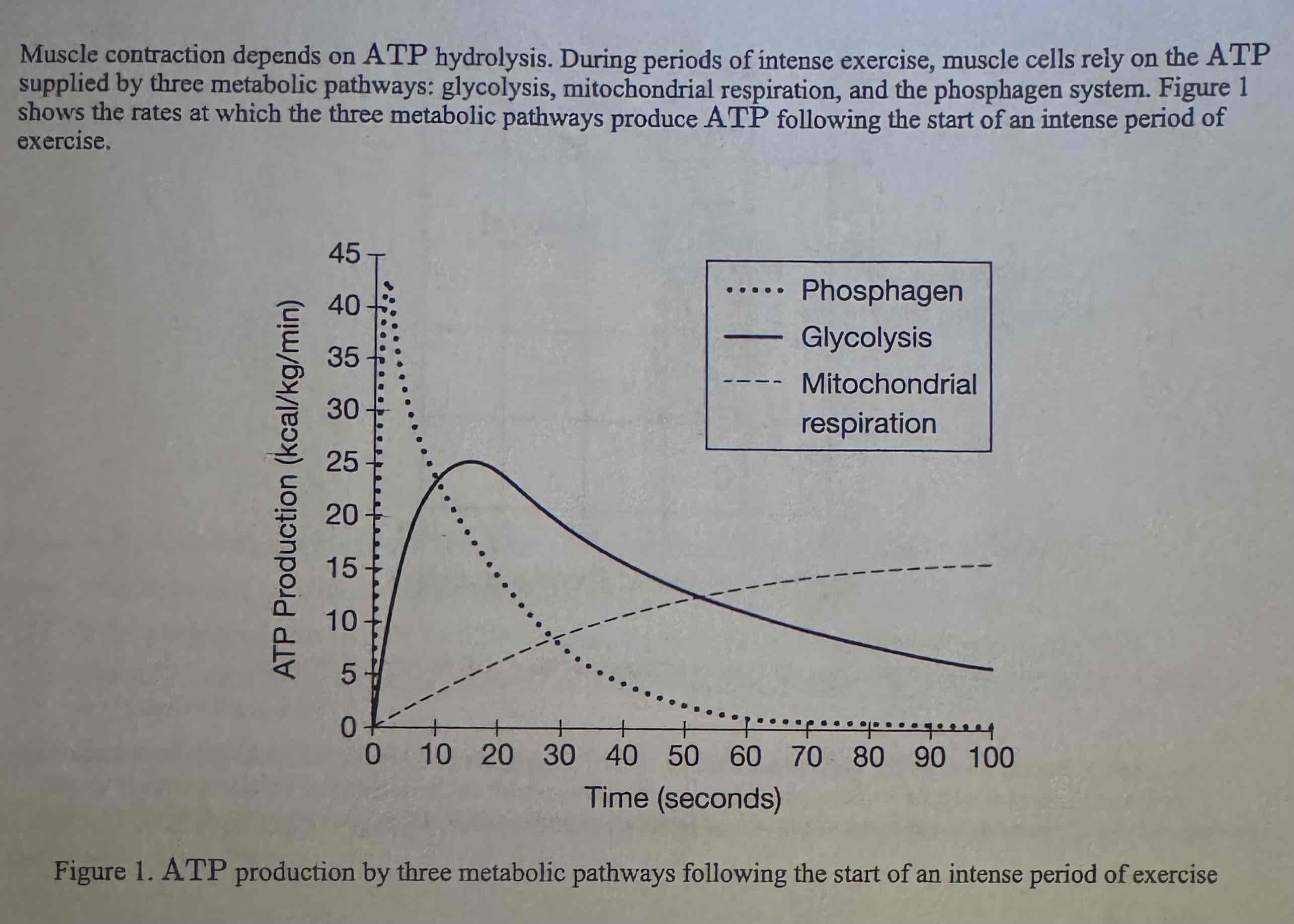
Which of the following correctly uses the data to justify the claim that the phosphagen system is an immediate, short-term source of ATP for muscle cells?
(A) ATP production by the phosphagen system increases and decreases rapidly following the start of the exercise period.
(B) ATP production by the phosphagen system increases gradually and continuously throughout the entire exercise period.
(C) The ATP produced by the phosphagen system contains more energy per molecule than does the ATP produced by the other pathways.
(D) ATP hydrolysis in muscle cells occurs immediately after the start of the exercise period but stops before the end of the exercise period.
ATP production by the phosphagen system increases and decreases rapidly following the start of the exercise period.
Which of the following best describes the cellular process illustrated in Figure 1 ?
(A) Sister chromatids separating during anaphase of mitosis
(B) Chromosomes lining up along the midline of the cell during mitosis
(C) Reducing the chromosome number during anaphase I of meiosis
(D) Chromatids failing to separate during meiosis
Reducing the chromosome number during anaphase I of meiosis
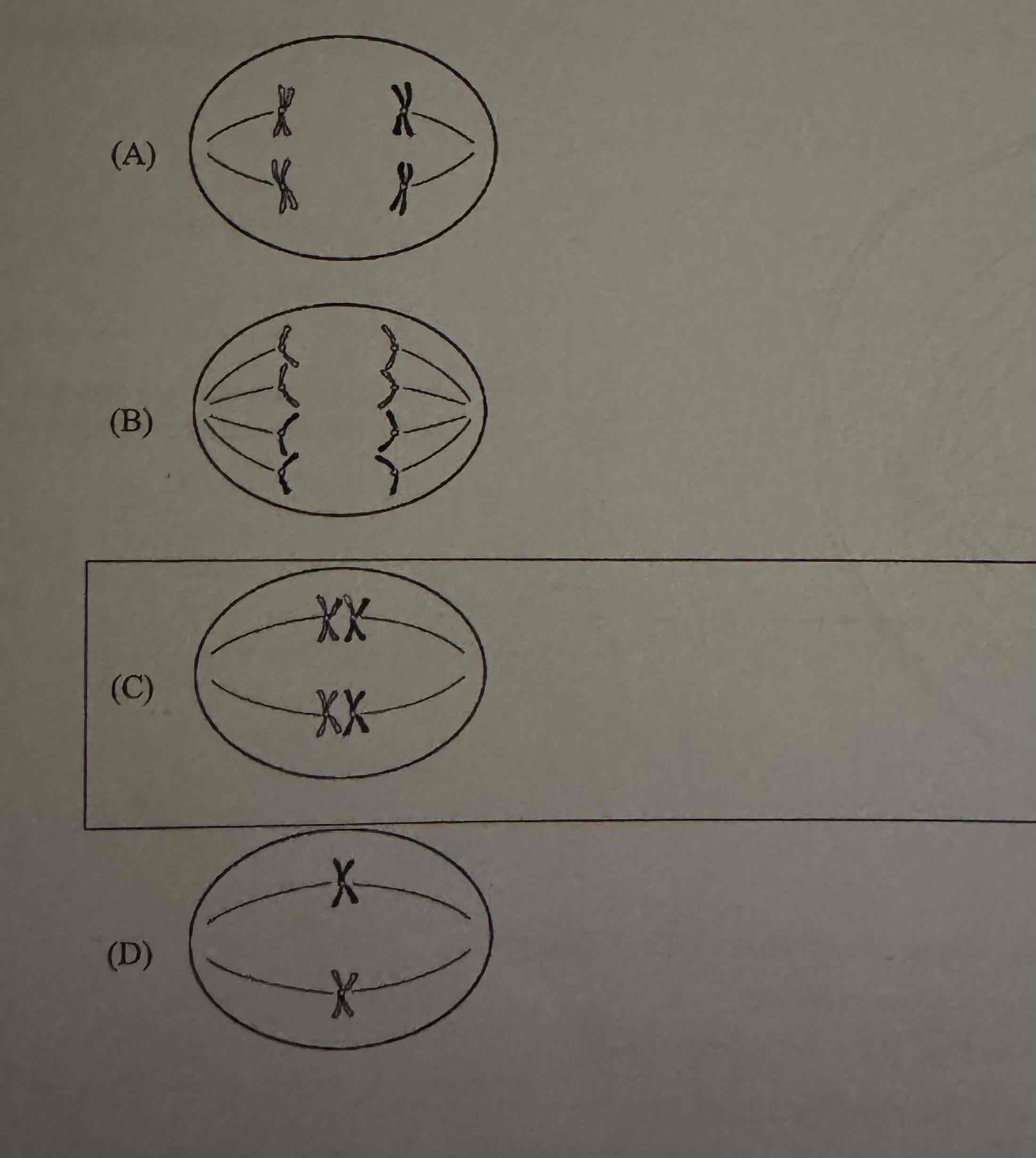
Within a forest ecosystem, there is a large amount of diversity among members of a warbler species. Of the following stages of meiosis illustrated for a typical cell, which contributes most to diversity among the warblers?
C.
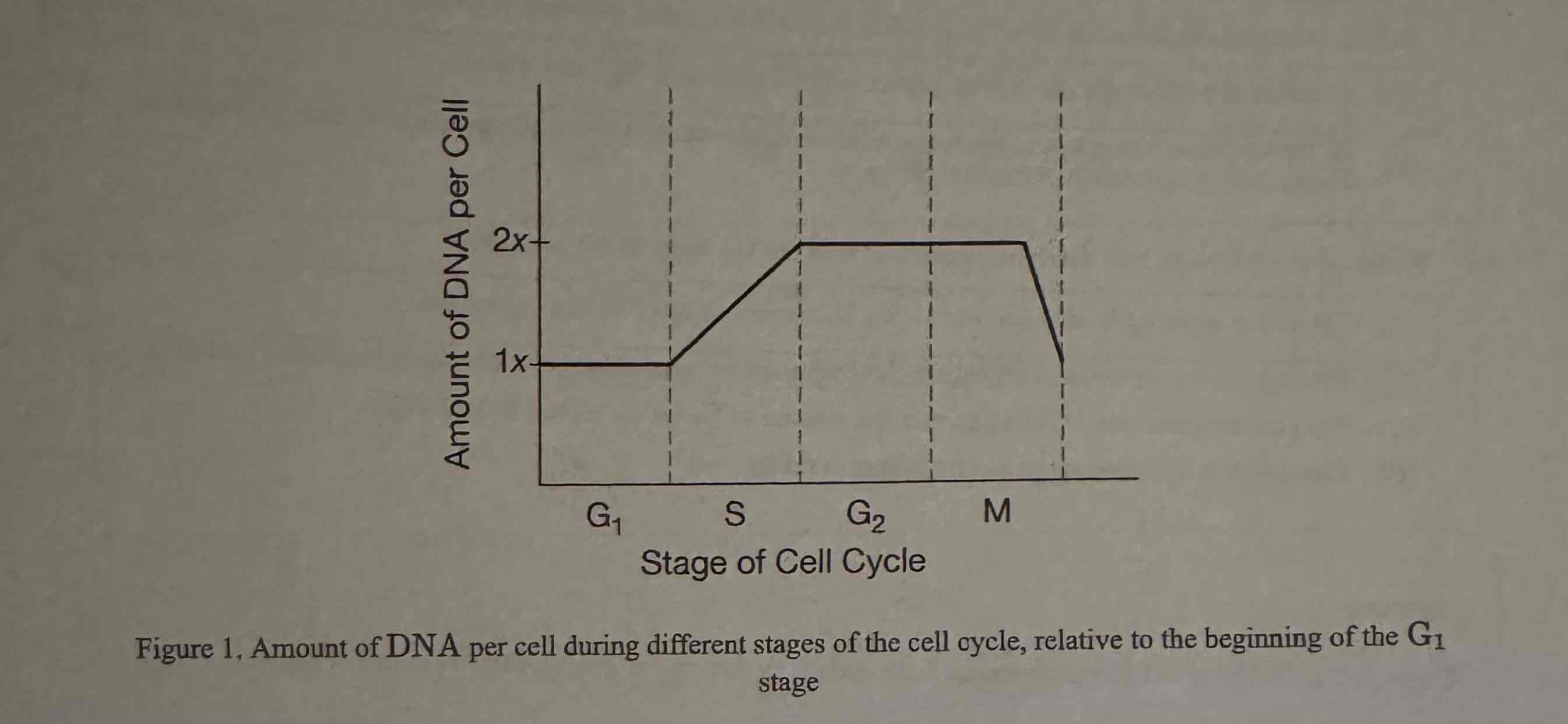
Which of the following best describes how the amount of DNA in the cell changes during M phase?
(A) The amount of DNA doubles as the DNA is replicated.
(B) The amount of DNA slightly increases as a result of new organelle synthesis.
(C) The amount of DNA does not change while the cell grows.
(D) The amount of DNA is halved as the cell divides into two daughter cells.
The amount of DNA is halved as the cell divides into two daughter cells.
Cancer can result from a variety of different mutational events. Which of the following is LEAST likely to result in the initiation of a cancerous tumor?
(A) A receptor mutation results in activation of a cell-division pathway in the absence of the appropriate ligand.
(B) A mutation results in the loss of the ability to produce a tumor-suppressor protein.
(C) A defect in a cell-cycle checkpoint prevents a cell from entering the S phase.
(D) At the anaphase checkpoint, separation of chromatids occurs without all centromeres being attached to kinetochore microtubules from both poles.
A defect in a cell-cycle checkpoint prevents a cell from entering the S phase.
Which of the following best describes a cell that is in the G1 stage of the cell cycle?
(A) The cell is growing in size and increasing its number of proteins and organelles.
(B) The chromosomes within the cell are checked to make certain that they have been replicated correctly.
(C) The chromosomes are replicating, and the amount of DNA in the cell is doubling.
(D) The cell is in a resting stage and no longer dividing.
The cell is growing in size and increasing its number of proteins and organelles.
What is the expected percent change in the DNA content of a typical eukaryotic cell as it progresses through the cell cycle from the start of the G1 phase to the end of the G2 phase?
(A) -100%
(B) -50%
(C) +50%
(D) +100%
+ 100%
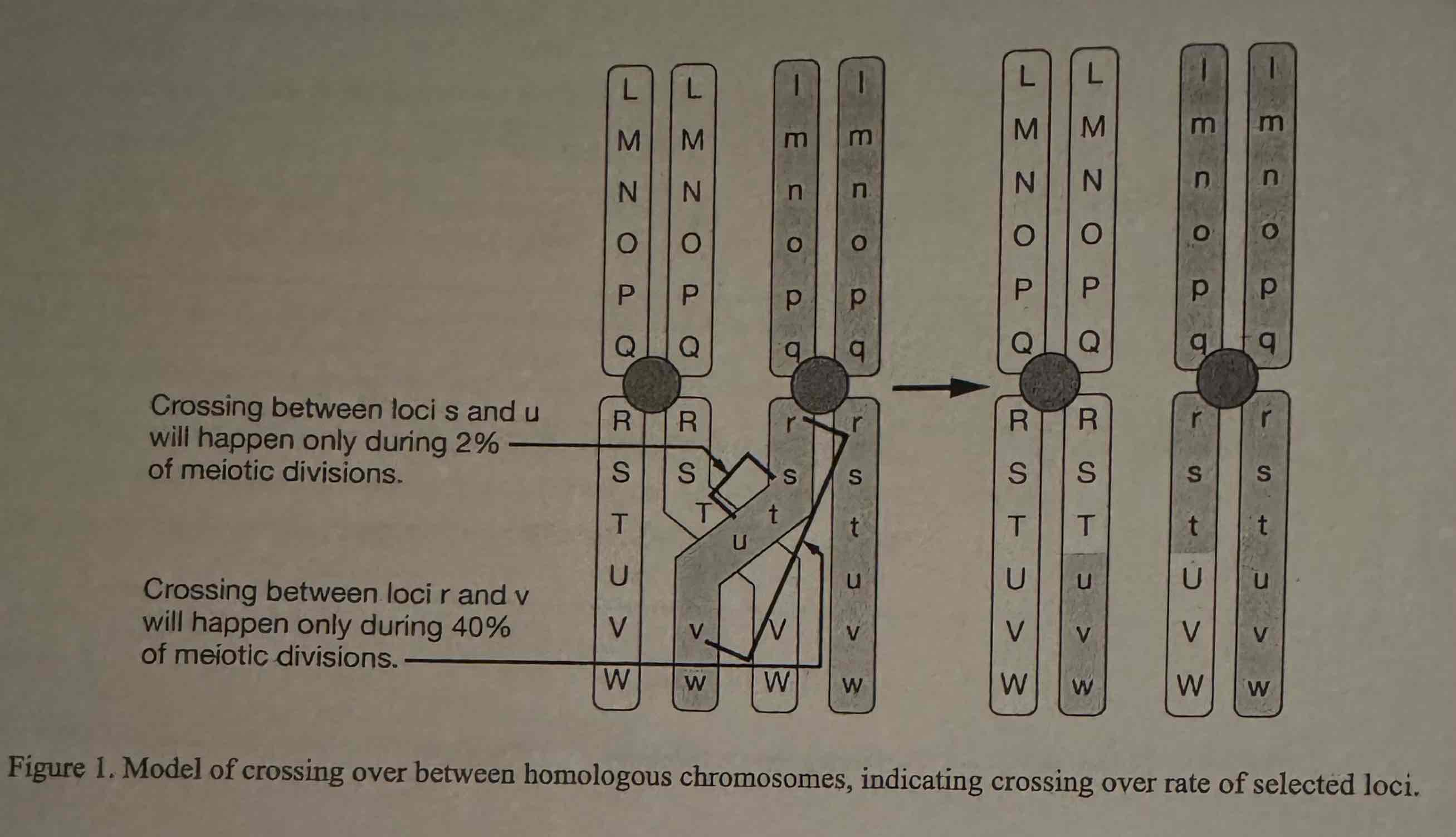
During prophase I replicated homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo synapsis. What testable question is generated regarding synapsis and genetic variability by Figure 1 ?
(A) Is the distance between two gene loci related to crossover rate?
(B) Does crossing over occur more often in some chromosomes than in others?
(C) Is crossing over inhibited by methylation?
(D) Is crossing over promoted by methylation?
Is the distance between two gene loci related to crossover rate?
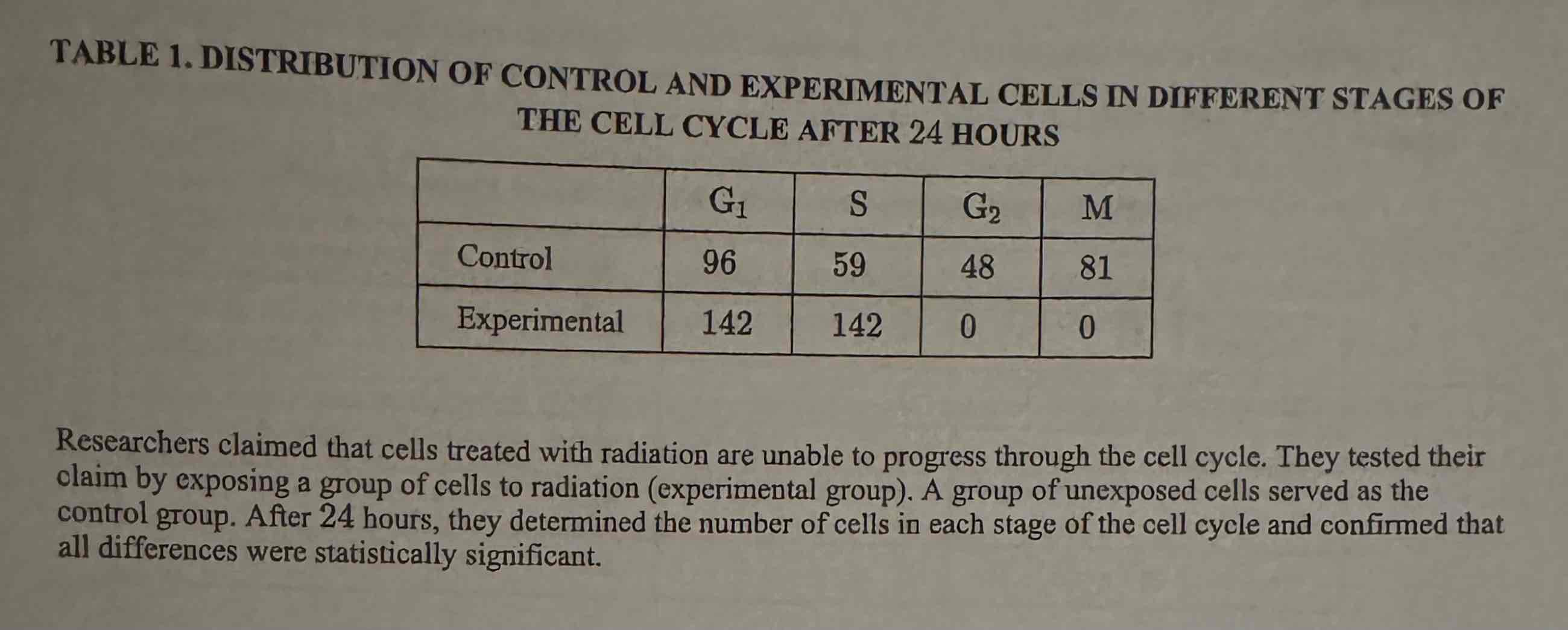
Based on Table 1, which of the following best supports the researchers' claim?
(A) In the experimental group, no cells were able to enter G2.
(B) In the control group, the number of cells in G2 was less than the number of cells in M.
(C) In the control group, the number of cells in each stage decreased as the cell cycle continued.
(D) In the experimental group, the number of cells in Gi was the same as the number of cells in S.
In the experimental group, no cells were able to enter G2.

Which of the following statements correctly describes the chromosomes in each daughter cell at the end of meiosis I ?
(A) Each daughter cell contains 12 chromatids, Each chromatid is one of two from a single chromosome with the other one of the pair found in the other daughter cell.
(B) Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Since the chromosomes were randomly divided, one daughter cell may contain both of a pair of homologous chromosomes, while the other cell contains both of another pair of homologous chromosomes.
(C) Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Each chromosome is one of a pair of homologous chromosomes from the parent cell, with the other homologue found in the other daughter cell.
(D) Each daughter cell contains 24 separate chromatids. Since every two chromatids were originally joined, forming one homologous chromosome, the number of chromatids is divided by two to determine the number of chromosomes.
Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Each chromosome is one of a pair of homologous chromosomes from the parent cell, with the other homologue found in the other daughter cell.
Both mitosis and meiosis begin with a parent cell that is diploid. Which of the following best describes how mitosis and meiosis result in daughter cells with different numbers of chromosomes?
(A) In mitosis, the chromosomes consist of a single chromatid, which is passed to two haploid daughter cells. In meiosis, the chromosomes consist of two chromatids during the first round of division and one chromatid during the second round of division, resulting in two haploid daughter cells.
(B) In mitosis, synapsis of homologous chromosomes results in four haploid daughter cells after one division. In meiosis, synapsis of homologous chromosomes occurs during the second division and results in four diploid daughter cells.
(C) Mitosis produces one identical daughter cell after one round of division. Meiosis has two rounds of division and doubles the number of chromosomes in the second round of division, producing four diploid cells.
(D) Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells after one round of division. Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells after two rounds of division.
Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells after one round of division. Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells after two rounds of division.
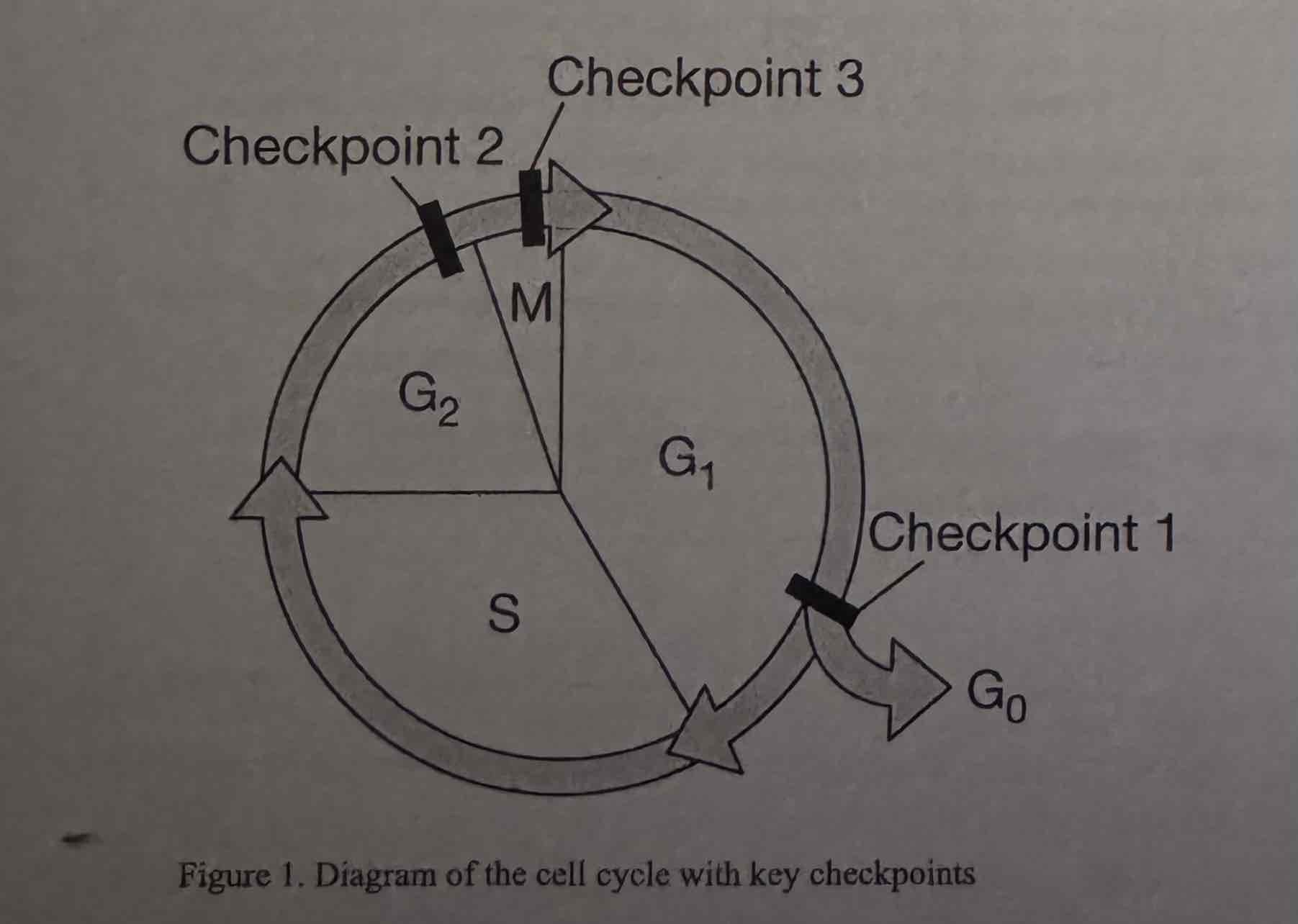
Which of the following describes a mutation that would lead to an increase in the frequency of nondisjunction?
(A) A mutation affecting checkpoint I proteins that forces cells to enter Go
(B) A mutation affecting checkpoint 2 proteins that allows cells to divide with DINA damage
(C) A mutation affecting checkpoint 3 proteins that prevents attachment of spindle fibers
(D) A mutation affecting checkpoint 2 proteins that prevents duplication of the chromosomes
A mutation affecting checkpoint 3 proteins that prevents attachment of spindle fibers.

Based on Figure 1, what percent of the time required to complete a full cycle do the cells typically spend in interphase?
(A) 5%
(B) 35%
(C) 50%
(D) 95%
95%
Researchers studying cell cycle regulation in budding yeast have observed that a mutation in the CDC15 gene causes cell cycle arrest in telophase when the yeast cells are incubated at an elevated temperature. Which of the following statements best predicts the effect of the cell cycle arrest on proliferating yeast cells?
(A) The yeast cells will transition out of Go but will fail to complete the G1 phase.
(B) The yeast cells will initiate mitosis but will fail to complete the G2 phase.
(C) The yeast cells will replicate their chromosomes but will fail to complete cytokinesis.
(D) The yeast cells will replicate their organelles but will fail to complete the S phase.
The yeast cells will replicate their chromosomes but will fail to complete cytokinesis.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a diploid yeast species that can reproduce either sexually or asexually. An experiment was performed to induce mitotically dividing S. cerevisiae cells in G2 to undergo meiosis. Which of the following best describes the steps these cells will follow to form gametes?
(A) The first division will result in crossing over between homologous chromosomes, and the second division will reduce the original number of chromosomes by half in the daughter cells.
(B) The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell, and the second division will result in each daughter cell having one-fourth of the original number of chromosomes.
(C) The first division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell, and the second division will double the number of chromosomes in each daughter cell.
(D) The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell, and the second division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell.
The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell, and the second division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell.
Which of the following patterns is shown by the data?
(A) Mutant 1 cells are more similar to mutant 3 cells than to wild-type cells.
(B) In wild-type cells, the percent of cells in anaphase is twice the amount of those in telophase (C)
(C) In mutant 3 cells, more time is spent in prophase/prometaphase than in the later stages of mitosis.
(D) The percent of mutant 2 cells in anaphase is higher than that of mutant 1 cells.
In mutant 3 cells, more time is spent in prophase/prometaphase than in the later stages of mitosis.

Which of the following presents a correct interpretation of the changes in chromosome number depicted in Figure 1?
(A) DNA replication occurs between metaphase and anaphase, doubling the number of chromosomes. Between telophase and cytokinesis, the cell divides in two, with each cell receiving half of the replicated chromosomes.
(B) New chromosomes formed during prophase are doubled during anaphase and are recombined before cytokinesis.
(C) Chromosomes enter metaphase containing two chromatids attached by a centromere. During anaphase, the chromatids are separated, each becoming a chromosome. Cytokinesis distributes the chromosomes into two separate cells.
(D) At anaphase a cell contains two identical copies of each chromosome, but following telophase, one of the copies is broken down into nucleotides.
Chromosomes enter metaphase containing two chromatids attached by a centromere. During anaphase, the chromatids are separated, each becoming a chromosome. Cytokinesis distributes the chromosomes into two separate cells.
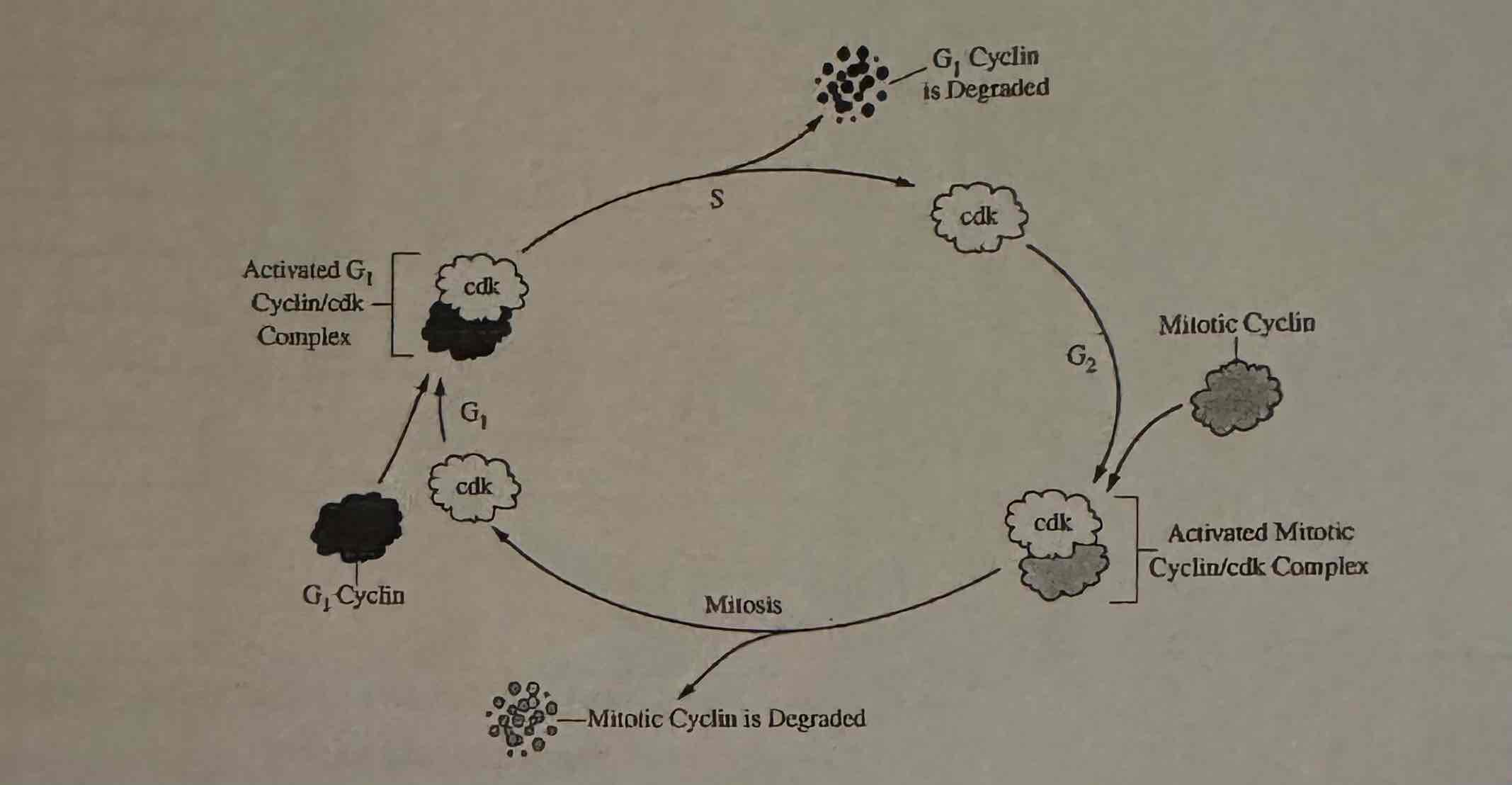
Based on the model of eukaryotic cell cycle regulation shown in the figure, which of the following best describes the effect of a drug that blocks the production of the mitotic cyclin?
(A) The cell cycle would proceed uncontrollably, and the cell would become cancerous.
(B) The G1 cyelin would functionally replace mitotic cyclin, and the cell would continue dividing normally.
(C) DNA synthesis would be prevented, and the cell would stop dividing.
(D) The cell would be prevented from entering mitosis, and the cell would stop dividing.
The cell would be prevented from entering mitosis, and the cell would stop dividing.
Cancer cells behave differently than normal body cells. For example, they ignore signals that tell them to stop dividing.
Which of the following conditions will most likely cause a normal body cell to become a cancer cell?
(A) The environment already contains cancer cells.
(B) The environment has an abundance of nutrients.
(C) The environment lacks signals that would otherwise tell the cell to stop dividing.
(D) The environment contains mutagens that induce mutations that affect cell-cycle regulator proteins.
The environment contains mutagens that induce mutations that affect cell-cycle regulator proteins.
Which of the following best explains why triploid bananas do not produce seeds?
(A) The cells of the banana plant are unable to replicate DNA, thus preventing cell division and limiting growth.
(B) The banana plants lack enough genetic diversity to properly hybridize.
(C) The production of gametes is disrupted because of unequal pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
(D) The production of seeds is not required because triploid plants produce gametes without fertilization.
The production of gametes is disrupted because of unequal pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.