5.8,9,10- solids,liquids and gases
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
what are the two types of energy stores in a moelcule?
The molecules within a substance have 2 different stores of energy:
Kinetic energy (due to their random motion/vibration).
Chemical potential energy (due to the bonds between the
molecules).
Together, these two stores of energy make up the thermal (heat) energy
of the substance.
what happens when a substance is heated?
When a substance is heated, that heat will usually cause the kinetic energy of the molecules to increase.The kelvin temperature of the material is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules. When the substance reaches a certain temperature, the kinetic energy will stop increasing and the heat will go into the chemical potential energy, breaking the bonds between the molecules and changing the state of the material.
what happens when energy si transferred to molecules?
When energy is transferred to a substance, the energy can transfer to two different energy stores of the particles:
Temperature and kinetic energy are directly proportional.
The kinetic energy store=increase temp
The chemical potential energy store=change substance state
The energy can NEVER be transferred to these two stores at the same time. This means that when the temperature is changing, the substance CAN’T change state AND when the substance changes state, it CAN’T change its temperature.
Solids properties
-arrangement: moelcules tightly arranged close together in a regular pattern in a lattice by strong bonds/inter molecular forces of attraction -movement: vibrate but can't change position/move about,-cannot flow/not fluid, fixed shape and volume -can't be compressed,most dense,don't diffuse -low energy in particles
Liquid properties:
-arrangement: molecules close together/tightly packed (further then in solids) in random arrangement
-forces: weaker intermolecular forces of attraction then solids but still held close togehter
-Movement: molecules move around each other more freely-can slide past eachother -can flow to fill any shape-fluid (no definite shape? -Has fixed volume -Can't be compressed,less dense,can diffuse -greater energy
Gases properties:
-Arrangement: molecules very far apart in random arrangement -Forces: negligible/very weak intermoelcular forces. Particles have overcome intermolecular forces -movement: mvoe very quickly, random movement in all directions colliding with each other and the walls of their container -Can fill nay space/container completely. No fixed shape or volume,flow easily -Compressible,least dense and can diffuse -highest energy
why can gases be compressed?
because the gas molecules are very spread out. When a gas is squashed into a smaller container it presses on the walls of the container with a greater pressure.
hwo does forces between particles affect the state of matter?
because the magnitude of the forces affects the relative distances and motion of the particles This affects the ability of the substance to
-Change shape
-Change volume
-Flow
why do solids have a hgih density?
some solids have a high density because the particles that they are made from are very closely packed togehter in a regualr arrangement. There are strong forces between the particles which give solid objects their definite shape and in some materials a great deal of strenght.
what is temperature
The temperature of the material, therefore, is related to the average kinetic energy of the molecules
how do gases exert pressure
As the gas particles move about randomly they collide with the walls of their containers.These collisions produce a net force at right angles to the wall of the gas container (or any surface).There is no set direction in which the forces will act, pressure is therefore a scalar property.A gas at high pressure has more frequent collisions with the container walls and a greater force hence the higher the pressure, the higher the force exerted per unit area.
what si net force of moelcules?
Each molecule may exert a different force that results in an average force exerted on each wall every second. There is therefore an average force acting on each metre squared of the walls, creating a fixed pressure.
what does the amount of pressure that a gas exerts on its container depend on?
-on the temperature of the gas
-volume of container for a gas at fixed mass and temp
-speed of movement of molecules (temp of air)
-energy of the moelcuels (temp of air)
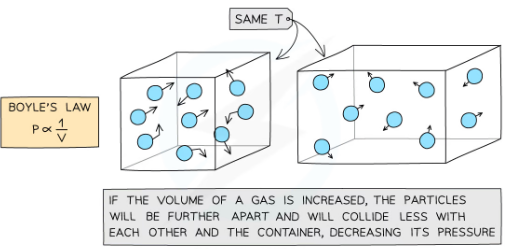
how does volume affect pressure?
If the temperature and mass (and numebr) of a gas/moelcules remains constant, the pressure of the gas changes when it is: Compressed - decreases the volume which increases the pressure.the same number of particles collide with the walls of a container but more frequently as there is less space.However, the particles still collide with the same amount of force meaning greater force per unit area (pressure).Expanded - increases the volume which decreases the pressure bcs the molecules collide less frequently wiht the walls.The molecules have a greater distance to travel between the inside surfaces of the container. This results in less collisions between the particles and the walls of the container decreasing the average force exerted on each metre squared of the walls of the container. As pressure and force are directly proportional, the air pressure will decrease as long as the temperature and mass of the molecules are fixed.
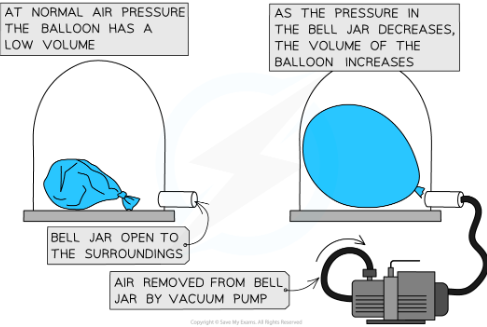
how does change in pressure cause a change in volume?
A vaccum pump can be sued to remove the air from a sealed container eg a balloon. At normal air pressure the ballon has low volume. As the pressure in the bell jar decreases the volume of the balloon increases.
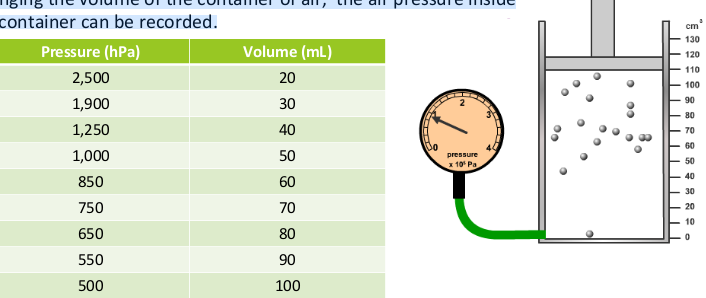
how to investigate affect of volume on pressure?
We can investigate how the volume of a container affects the pressure of a gas. By changing the volume of the container of air, the air pressure inside of the container can be recorded.
Graph of pressure an dchange in volume in a gas
P ∝ 1/V
P = kV
PV = constant
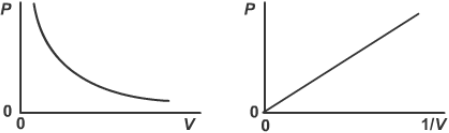
How does temperature of gas affect pressure
at constant volume and mass of molecules pressure increases with temperature. As temperature increases particles gain kinetic energy so average speed of molecules also increases so they collide more frequently with the walls so higher pressure. There is a greater change in momentum when they hit the sides so a greater force.
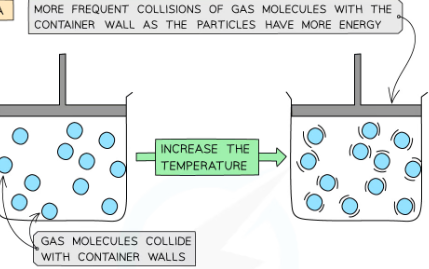
what can an increase in kinetic energy cause?
Cause the temperature of the system to increase
Or, produce a change of state
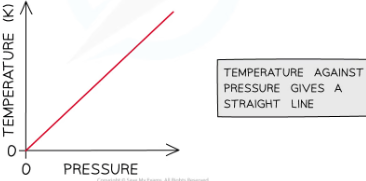
graph of temperature against pressure
since the temperature is proportional to the pressure, the graph against each is a straight line
what is the relationship between the pressure and volume for a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature equation? (boyles law)
P1V1=P2V2 P1 = initial pressure (Pa) P2 = final pressure (Pa) V1 = initial volume (m3) V2 = final volume (m3)
what is boyles law?
For a fixed mass of a gas held at a constant temperature:
pV = constant
Where:
p = pressure in pascals (Pa)
V = volume in metres cubed (m3)
This means that the pressure and volume are inversely proportional to each othe
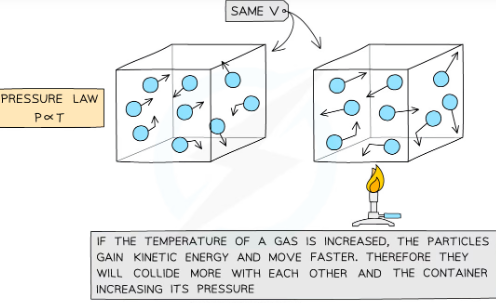
what is pressure law?
-If the volume V of an ideal gas is constant, the pressure law is given by:P ∝ T
-This means the pressure is proportional to the temperature
-P1/T1=constant P=KT
what is the formula for the relationship between pressure and (Kelvin) temperature for a fixed mass of gas at constant volume?
P1/T1 = P2/T2
P1 = initial pressure (Pa)
P2 = final pressure (Pa)
T1 = initial temperature (K)
T2 = final temperature (K)
Graph representing temperature directly proportional to volume
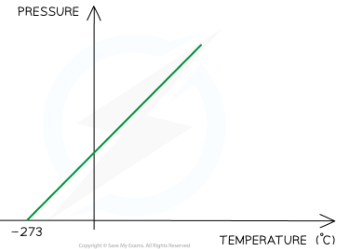
what is brownian motion?
It is the random jerky moevment of particles due to:
-slow,bigger particles colllide with other smoke particles
-smaller fast moving air molecules collide with the larger smoke particles causing them to change their speed and directions randomly, each time they are struck by a molecule
-smoke particles collide with the walls of the container
what does random motion of moelcules mean?
Random motion means that the molecules are travelling in no specific path and undergo sudden changes in their motion if they collide:
With the walls of its container
With other molecules
what is the internal energy of a molecule?
It is the total kinetic energy of all the molecule.The hotter a material is,faster its average speed of molecules and increased KE so the more internal energy it has.
relationship between temperature (in kelvin) and average KE of the molecules
The temperature (in Kelvin) is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules
T ∝ KE
How much the temperature of a system increases depends on
-The mass of the substance heated
-The type of material
-The amount of thermal energy transferred in to the system
what is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 °C
heat capacity equation
C=E/mΔt
ΔE = change in thermal energy, in joules(J)
m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
c = specific heat capacity, in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg °C)
Δt = change in temperature, in degrees Celsius (°C)
formula for power
power= energy/time
characteristic of a substance that has low and highspecific heat capacity:
-if it has low specific heat capacity it heats up and cools down quickly (takes less energy to change its temp)
-if it has high specific heat capacity it heats up and slows down slowly (takes more energy to change its substance)
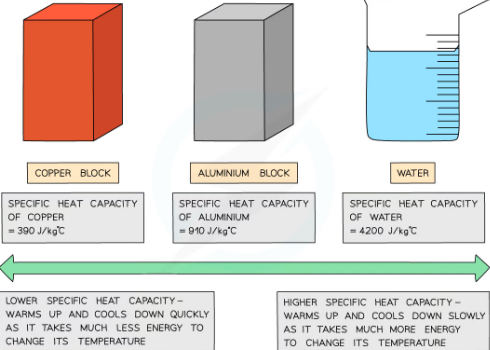
how to measure heat capacity of water: planning
-The aim of the experiment is to determine the specific heat capacity of a substance, by linking the decrease of one energy store (or work done) to the increase in temperature and subsequent increase in thermal energy stored -Variables: Independent variable = Time, t Dependent variable = Temperature, θ Control variables:Material of the blockCurrent supplied, IPotential difference supplied, V
Materials: 1 kg block of aluminium, a beaker contiang a known mass of volume thermometer immersion heater power supply stopwatch voltmeter ammeter
how to measure heat capacity of water: method and results
1) Ensure the power supply is switched off.
2) Place the immersion heater into the central hole at the top of the block.
3) Place the thermometer into the smaller hole and put a couple of drops of oil into the hole to make sure the thermometer is surrounded by a good conducting material.
4) Fully insulate the block by wrapping it loosely with cotton wool.
5)Record the temperature of the block.
6) Connect the heater to the power supply and turn it on for ten minutes. At apporximately 10V
7) Record the temperature of the metal block every minute.
8) After ten minutes the temperature will still rise even though the heater has been turned off and then it will begin to cool. Record the highest temperature that it reaches and calculate the temperature rise during the experiment.
9) Measure the voltage, V, current I and time, t to calculate the energy supplied every minute.
10) Repeat steps 2-9, replacing the beaker of water for the solid block of aluminium and starting with recording its mass using the digital balance
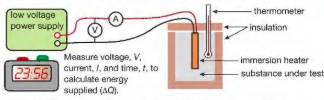
how to find SHC using this experiment
To find SHC:
The thermal energy supplied to the block can be calculated using the equation: E = IVt
E = thermal energy, in joules (J)
I = current, in amperes (A)
V = potential difference, in volts (V)
t = time, in seconds (s)
The change in thermal energy is defined by the equation:
ΔE = mcΔθ
Where:ΔE = change in thermal energy, in joules (J)m = mass, in kilograms (kg)c = specific heat capacity, in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg °C)Δθ = change in temperature, in degrees Celsius (°C)
Rearranging for the specific heat capacity, c:
To calculate Δθ:
Δθ = final temperature – initial temperature
To calculate ΔE:
ΔE = IVtf – IVti
Where:I = average current, in amperes (A)V = average potential difference (V)tf = final time, in seconds (s)ti = initial time, in seconds (s)
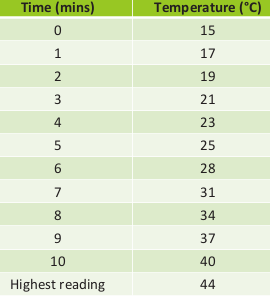
Analysis of Results
The readings on the voltmeter and ammeter are seen to significantly change in the first minute but changes insignificantly thereafter. The consistent readings for both were V = 10 V and I = 5 A.
Calculate the energy supplied every 60 seconds using the formula:
Electrical energy = voltage × current × time
Where:
Electrical energy is measured in Joules (J)
Voltage is measured in volts (V)
Current is measured in amps (A)
Time is measured in seconds (s)
Calculate the temperature change by subtracting the temperature at time 0 s from the temperature recorded each minute
The equation for specific heat capacity is:
ΔQ = m × c × ΔT
Where:
ΔQ = change in thermal energy, in joules (J)
m = mass of substance, in kilograms (kg)
c = specific heat capacity, in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg °C)
ΔT = change in temperature, in degrees Celsius (°C)
Plot a graph of the energy supplied (y-axis) against the temperature change multiplied by the average mass (x-axis)
Calculate the gradient of this graph in the straight line region in order to obtain the specific heat capacity of the water or solid block
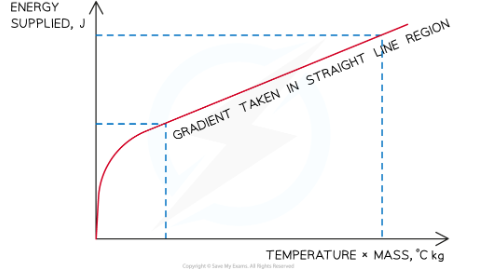
evaluating the experiment
Systematic Errors: Make sure the voltmeter and ammeter are initially set to zero, to avoid zero error.Some water may be lost to the surroundings by evaporation. Calculate an average mass of water (using the mass before the experiment and the mass after) to account for this.Remember to only take gradients on the straight-line region.Before this point the energy supplied is being used to heat the immersion heater itself
Random Errors: Not all the heat energy supplied from the heater will be transferred to the block, some will go into the surroundings or heat up the thermometer. This means the measured value of the specific heat capacity is likely to be higher than what it actually is.The greater the temperature difference between an object and the surroundings, the greater the rate of dissipation of energy. If effective insulation is used, however, the thermal energy dissipated to the surroundings is very small and can oftenbe neglected.Stir the water constantly whilst heating it to ensure the temperature measured is the temperature throughout the fluid.When the current or voltage values appear to be changing between two values next to one another then be consistent in choosing the higher value
Solution:A joulemeter could be used to calculate energy directlyThis would eliminate errors from the voltmeter, ammeter and the stopwatch.Make sure the temperature value is read at eye level from the thermometer, to avoid parallax error. The experiment can also be repeated with a beaker of water of equal mass, the water should heat up slower than the aluminium block.
Safety concerns: The beaker may become unstable with an immersion heater and thermometer resting in it
The immersion heater will get very hot
If you feel this is the case then use a clamp stand to hold both
Wear goggles while heating water
Make sure to stand up during the whole experiment, to react quickly to any spills
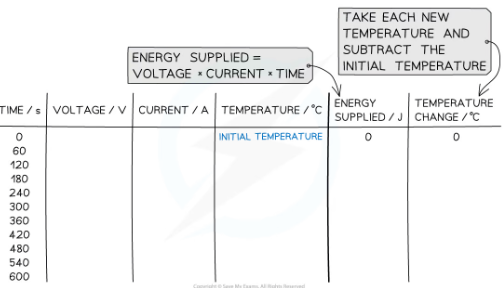
how could experiment be improved?
The experiment could have been improved by:
-Adding lagging (insulation) on the sides, top and underneath the block
-Repeating the experiment to take an averagewith a beaker of water of equal mass, the water should heat up slower than the aluminium block.
-A joulemeter could be used to calculate energy directlyThis would eliminate errors from the voltmeter, ammeter and the stopwatch.
-Make sure the temperature value is read at eye level from the thermometer, to avoid parallax error.
exampels of when high SHC is sueful
bcs water has high SHC its useful for carryign and storing thermal energy eg central heating systems, water carries thermal energy from boiler to radiators around house,in car system carries unwanted thermal energy from engien to raidator
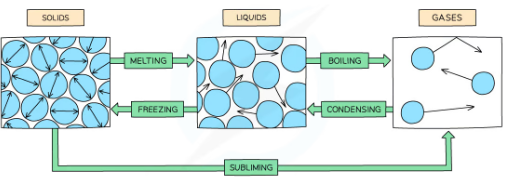
Core Practical: Investigating Changes of State
what happens while ice is melting?
while meltign ice goes on absorbing energy its temp doesn't change. It stays at 0 degrees celcius-the meltign point. The enrgy absorbed in called the latent heat fo fusion and is needed to separate the particles so that they can form the liquid. If the liquid changes back to a solid the energy is released again.At the melting point, even if more thermal energy is added, the solid water does not get warmer This means that the internal energy is not rising
what is sublimation?
When a solid turns into a gas
how to calcualte energy transferred?
energy transferred=mass x specific latent heat / E-ml where E is the energy needed in J,m is the mass in kg and I is the specific latent heat in Jkg-1
what happens during boiling?
energy absorbed at boiling point is called the latent heat fo vaporization. Most is needed to separate the particles so they can form a gas but some is required to push back the atmosphere as the gas forms. The temp rises until the water boils. Even id mroe thermla energy addedliquid doesnt get any hotter so itnernal energy doenst rise.
does temperature increase duirng melting,freezing,boiling and codnensing?
While a substance is changing state, either Melting or freezing,Boiling or condensing. The substance does not change temperature, even though energy is being transferred to or away from the thermal energy store of the substance.The additional thermal energy goes into overcoming or weakening the intermolecular forces between the molecules of water. When condensation occurs, the molecules slow down and the bonds are strengthened or formed. These bonds bring the molecules closer together and the substance becomes liquid. When solidification occurs, the temperature drops and fewer particles have enough kinetic energy to overcome neighbouring attractions. The molecules can only vibrate, the substance gains a shape of its own and becomes a solid.
what happens when a hot material is in contact with a cold one?
There is a transfer of thermal energy as the hot one cools down and loses internal energy (KE), while the cold one heats up and gains internal energy (KE). The energy transferred is known as heat-not same as temp. When both reach the same temp the transfer of energy stops bcs average KE per particle is the same in both-smae temp-same average KE per particle
what is thermal energy?
it is the term used for both internal energy and heat
what are heatign and cooling graphs used to show?
-How the temperature of a substance changes when energy is transferred to or away from it -Where changes of state occur
what si heating and cooling?
-Heating is when energy is transferred to the system and the kinetic energy of the molecules increases (red arrows to the right) -Cooling is when energy is transferred away from the system (or dissipated to the surroundings) and the kinetic energy of the molecules decreases (blue arrows to the left)
what happens durign condensation?
-when gas changes back into a liquid eg cold air can hold less water vapour then warm air so if cooled some of the water vapour may condense. -as a gas condenses into a liquid the gas has already lost heat energy (cooled down) -particle lose kinetic energy and move more slowly as they no longer have enough energy to overcome the intermoelcular forces of attraction btw molecules. The particle get closer together. They onyl have enough energy to flow over each otehr. The gas has condensed to a liquid with no change of temperature
what si solidification?
s a liquid solidifies into a solidThe liquid has already lost heat energy (cooled down)
The particles lose kinetic energy and move more slowlyThey no longer have enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules The particles get closer togetherThey only have enough energy to vibrate about their fixed position -the liquid has solidified into a solid wiht no change of temperature
what is temperature?
the temperature is related to the average kinetic energy of molecules. The higher the temp the greater the average kinetic energy so faster the average speed of molecules.
what is the kelvin temeprature scale?
kelvin scale is a thermodynamic scale based on the average KE of particles rather than on a property of a aprticular susbtance. Kelvin is the same size as degrees celcius eg a chnage in temperature of 1k is euqal to change in temp of 1C. But it uses absolute 0 as its 0 so never has a negative value. -237C=0K
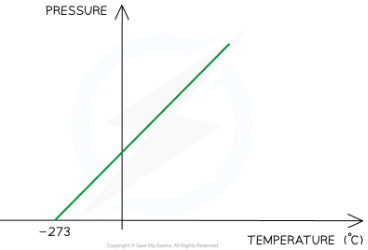
pressure of gas compared to kelvin scale
pressure is proportional to kelvin temperature
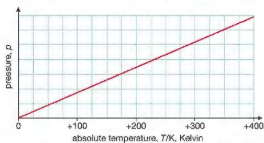
how to convert between temeprature of θ in the Celsius scale, and T in the Kelvin scale?
θ / °C = T / K − 273 or T / K = θ / °C + 273
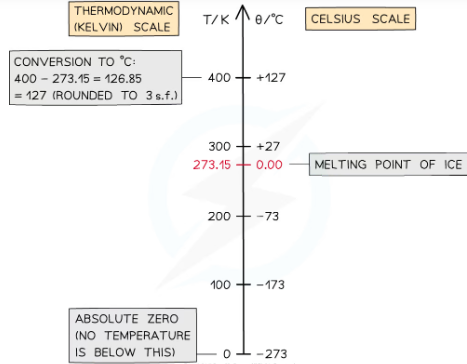
what is absolute zero?
the temperature (-237 decrees celcius) at which the particles in a gas have no kinetic energy/net movement and don't collide with their container so dont exert any pressure. Not posible to have a lower temp as not possibel to remove any mroe energy form it.
why do materials expand when heated?
when smt is heated its volume increases slightly and it expands because the vibration/molecules take up more space. The molecules start to move around or vibrate faster which causes them to knock into each other and push eachother apart. MOLECULES DONT EXPAND BUT THE SPACE BTW THEM DOES.
how do solids expand when heated?
when a solid is heated the molecules vibrate more but stay in place so the relative order of magnitude of the expansion is small bcs the low energy molecules can't overcome the intermolecular forces holding them together
how do liquids expand when heated?
when a liquid is heated it expands for the same reason as a solid but the inter molecular forces are less since the molecules have more energy to overcome them so it expands more
how do gases expand when heated?
when a gas is heated the molecules move faster and further apart so the relative order of magnitude of the expansion is the greatest because the high energy molecules have enough energy to completely overcome the inter molecular forces of attraction holding them together. Expand by convection
uses of thermal expansion:
-Thermometers rely on the expansion of liquids to measure temperature -Temperature-activated switches work when a bimetallic strip, whihc is a thin strip of 2 different metals bonded together. When heated one expands more then the other making it bend by a predictable amount at a given temperature. Used in some thermostate devices for keeping a steady temp
consequences of expansion:
The expansion of solid materials can cause them to buckle if they get too hot -railway tracks having small gaps so that they don't buckle when they expand -steel rods used to reinforce concrete because both materials expand equally. If expansion different the steel might crack the concreate on a hot day -gaps left at the ends of bridges to allow for expansion -overhead cables suspended from poles are left slack to allow for contraction
what happens when water expands? And how does thsi happen?
when water freezes it expands as it turns into ice. In liquid water the particles are very close together but in ice the molecules link up in a very open structure that takes up more space. Ice has lower density then liquid so floats. Molecules start formign into an open structure of ice as 9 degrees. So water expands slightly aas cooled form 40-0 degrees celcius.
what happens when a gas is heated?
it doesnt expand but depensind on circumstances a change in temp can produce a change in pressure,volume or both.
experiment to show expansion
place a coloured liquid in a flask and heat gas at constant pressure-atmospheric pressure bcs hte short length of liquid spearates the air from the atmosphere outside. as temp rises voluem of gas increases and the gas expands
what happens durign a change of state?
When a substance changes state, the number of molecules in that substance doesn't change and so neither does its mass The only thing that changes is its energy Changes of state are physical changes and so they are reversible.
explain how and hwy gases exert pressure on a container?
gases exert pressure on a container due to collisions between gas molecules and the wall which produce a net force at 90 degrees. When the molecules rebound off the walls,they change direction so their velocity and therefore momentum changes. This means they exert a force because force is equal to the change in momentum over time. Higher the force higher the pressrue exerted on container
what is boiling?
-It is a very rapid form of evaporation. When water boils vapour bubbles form deep in thte liquid. They expand,rise,burst and release large amoutns of vapour. -boilign is a change of state from liquid to a gas. It happens at a specific temperature and has bubbles. It happens throughout the liquid -In it molecules gain eenrgy to break bonds and change state.At 100 degrees celcium the vapour pressure in the bubbles is strong enough to overcome atmospheric pressure so the bubbles start to expand and boiling occurs.
what happens during meltign/freezing?
-meltign occurs when a soldi turns into a liquid-heat given,molecules gain enough energy to break the bond and change state -freezing occurs when a liquid turns into a solid
how does evaporation cause cooling down affect?
-evaporation cools a body in contact with an evaporatign liquid eg skin with sweat bcs the liquid absrobs thermal energy fromt eh body so it can continue to evaporate elaving slower molecules so temp is less. -evaporation is the escape of moelcules with higher energy from the surfaces of liquids -after they escape the remaining molecules haev a lower average kientic energy which emans the temp is lower-evaporation coosl teh liquid -the faster moving molecules near the surface have neough energy to escape and form a gas
what si evaporation?
evaporation when a liquid below its boiling point changes to a gas-it can happen at any temp and has no bubbles. It changes state and casues cooling to happen at surface of liquids
what factors affect the rate of evaporation?
-increase temp of water or surroundings: more higher energy molecules so more likely to overcome the intermolecular forces holding them in the liquid state and escape the surface -increase surface area: more molecules at the surface -draught/air movement above water: air removes molecules befroe they cna return to the liquid. This dries air and allows mroe water molecules to escape -resuce humidiity: if air v humid ir already has a high water vapour content. Evaporation slower bcs molecules in the water vapour reutrn to the liquid almost as fast as they escape
uses of cooling affect of evaporation in regrigerator:
in pipes in the freezer compartment, a liquid called a refrigerent evaporates and takes thermal energy from food and air 2)the vapours are drawn away by the pump whihc compresses ti nd turns it into a liquid. This releases thermal energy so the liquid heats up
the hot liquid is cooled as it passes htrough the pipes at hte back, and the thermal energy is carried away by the air