Sexual Reproduction v. Asexual Reproduction
Telomeres- Protective caps on chromosomes
consists of DNA associated with proteins in chromatins
might be involved in both aging and cancer
the same sequences of bases repeated over & over
Telomere sequence in humans: TTAGGG
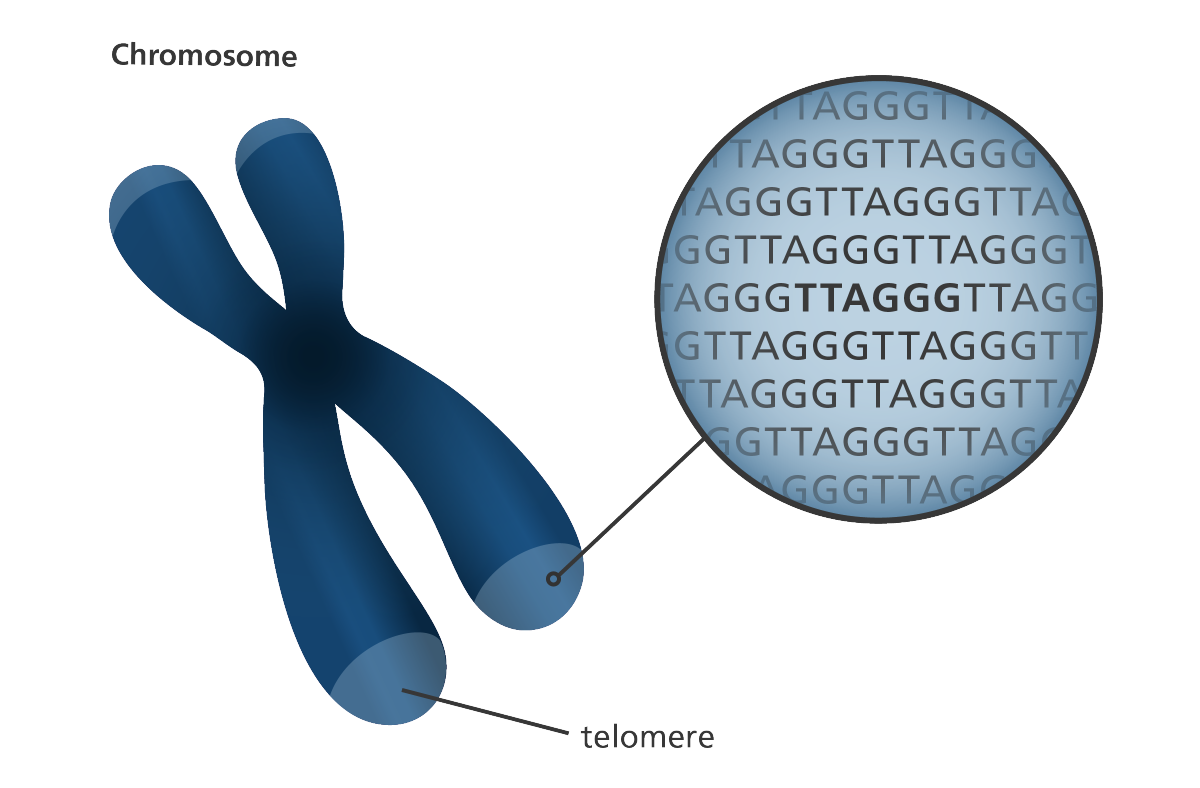
Function of telomere
help organize 46 chromosome in the nucleus
DNA is left undamaged in the chromosome during DNA replication
Important DNA would be lost everytime a cell divides without a telomere
Leads to the loss of entire genes
Karyotypes and Nondisjunction
Karyotypes: individual’s complete set of choromosomes
Nondisjunction: cell division during which sister chromatids fail to separate properly
occurs in any organism in which gametes are produced through meiosis
associated with serious human disorders
Outcomes of nondisjunction:
it leads to daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes, known as aneuploidy
Two types of nondisjunction:
Mitotic nondisjunction
occurs in anaphase when sister chromatids fail to separate
Meiotic nondisjunction
homologous chromosomes fail to segregate at anaphase I and lead to haploid cells with abnormal number of chromosomes(meiosis I)
sister chromatids fail to separate and leads to half of the haploid cells with abnormal chromosomes(meiosis II)
loss or gain of one or more chromosomes
Having a set of three chromosmes of one kind - Trisomy (2n+1)
Having only one of particular type of chromosome - Monosomy(2n-1)
The loss of both pairs of homologous chromsomes Nullisomy (2n-2)
Chromosomes are inherited from one parent only Disomy (n+1)
Cause of Nondisjunction
Cellular Differentiation and Stem Cells
Cellular differentiation
all cells in the body strts at fertilized egg with unique genetic expression
It needs to manipulate genes that will be expressed and developed
This is done through transcription factors: one of a class of proteins that bind to specific genes on the DNA molecule promoting or inhibiting transcription.
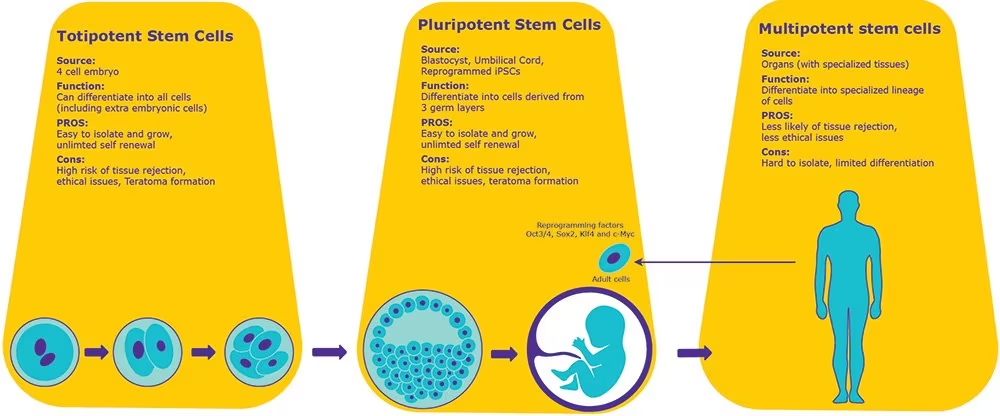
Stem Cells
type of cell that can be directed to become a specialized cell.
can divide without limit as needed under specific conditions
Two types of stem cells
Embryonic stem cells
Adult stem cells